Fever and diarrhea in an adult
What causes diarrhea and fever in an adult?
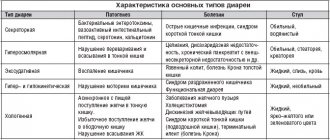
The reasons may vary. Most often, such symptoms appear during severe poisoning or infection. In this case, in addition to diarrhea, the person suffers from cramps, abdominal pain, and may experience nausea and vomiting. However, the state of the body is more accurately characterized by stool.
Let's look at the main diseases that are accompanied by high fever and diarrhea.
Food poisoning
Unfortunately, even seemingly normal food can be spoiled. The first unpleasant symptoms of poisoning usually appear after 2 hours (from 1 to 12). First, abdominal pain, nausea, and weakness occur. Then diarrhea, vomiting begins, and body temperature rises.
The stool may contain mucus, streaks of blood, be very watery, green, and smell bad. Sometimes there is a false urge to defecate. In total, the patient can run to the toilet up to 10 times. The most dangerous foods that cause severe intoxication: fish, meat, mushrooms, eggs, sour cream and milk.
What to do at the first signs of poisoning? If the overall condition is satisfactory, then you can be treated at home:
- Drink a large amount of boiled water to flush your stomach (about 1 liter).
- Take the sorbent according to the instructions. Popular drugs are “Activated Carbon”, “Polysorb”, “Atoxil”, “Smecta”.
- Avoid any food for 12 hours.
- Stay in bed and drink plenty of fluids.
Important. In case of poisoning, it is strictly forbidden to take antidiarrheals (Loperamide, Imodium). They stop diarrhea, and harmful substances remain in the body, intoxication continues to increase.
Viral infection
The disease is transmitted by airborne droplets or through water, less often through food. People call this disease “intestinal flu,” and doctors use the term “rotavirus infection.”
The first signs of infection are body aches, high fever, and chills. Then comes a runny nose, severe diarrhea, sometimes a cough, sore throat, and vomiting. The stool is usually yellow, and stools are repeated up to 20 times a day.
Rotavirus infection is treated as follows:
- Take any antiviral drug - Arbidol, Anaferon, Groprinosin.
- To remove harmful substances and toxins, use a sorbent - “Smecta”, “Polysorb” or another.
- Drink plenty of fluids and follow a gentle diet.
- As soon as the condition improves, undergo a course of treatment with probiotics - Linex, Acipol, Bifidumbacterin. They will help restore the intestinal microflora, which is often disrupted by rotavirus.
Important. Antibiotics are useless for viral infections.
Diarrhea and a temperature of 38 in an adult are often a sign of salmonellosis, colibacillosis, dysentery and other diseases caused by dangerous bacteria. There are about 30 species in total, but the most common is staphylococcus.
The bacterial infection is considered a disease of dirty hands, and is characterized by symptoms such as a high fever that is difficult to bring down, and watery, foul-smelling diarrhea. Feces are usually green, with bloody spots and mucus.
Effective treatment often requires hospitalization of the patient. For bacterial intestinal infections, the following drugs are usually prescribed:
- antibiotics “Enterofuril”, “Levomycetin”, “Stopdiar”;
- sorbents “Polysorb”, “Polyphepan”, “Activated Carbon”;
- pre- and probiotics “Enterol”, “Bifidumbacterin”, “Linex”, “Acipol” after the diarrhea stops.
Attention! Any intestinal infection requires isolation of the patient from healthy family members. To prevent infection, you need to thoroughly wash your hands, use separate dishes and towels, and also wear a cotton-gauze bandage (if diarrhea is caused by a virus).
As already mentioned, symptoms such as indigestion and fever can have many causes. This includes stress, climate change, changes in diet, etc.
But it is worth noting that in this case the malaise is short-term; after a day or two, the stool returns to normal.
What else can provoke diarrhea and fever in an adult? Pay attention to the following diseases:
- helminthiasis (worms);
- appendicitis;
- cholecystitis;
- pancreatitis;
- hepatitis;
- gastritis;
- dysbiosis.
Advice. If fever and diarrhea do not go away after 3 days or other complaints are present, then it is better not to self-medicate. Remember that timely consultation with a doctor will avoid possible complications and will also shorten the treatment time.
General recommendations
Any diarrhea is primarily dangerous due to dehydration. That is why a patient with indigestion needs to drink as much as possible - from 1.5 to 2 liters of fluid per day.
It is worth considering that if the frequency of stool reaches 20 times per day, ordinary water will not be enough.
In this case, you should take a special solution for rehydration - “Regidron”, “Gastrolit” or others.
What other measures should be taken?
- Fast for a little while at first. If you start eating right away, your stomach may rage even more.
- Avoid drinking coffee, alcoholic beverages, fresh fruits and vegetables, milk, heavy fatty and spicy foods.
- Give preference to black tea, rice water, wheat crackers, low-fat broth, baked apples.
- Do not lower the temperature to 38.5 degrees. Give your body a chance to fight.
- Call a doctor if you feel like you can't cope on your own.
Severe diarrhea is almost always accompanied by fever, so it is impossible to accurately determine the cause of the illness based on these two symptoms. The patient must analyze for himself what caused the stool disorder.
Did he eat something suspicious the day before? Are any other family members sick? Are there any other additional complaints or symptoms? If you cannot accurately determine the cause of diarrhea and fever, you should consult a doctor.
If a person has a high fever and diarrhea at the same time, doctors suggest a diagnosis of acute diarrhea. It can be caused by viral, parasitic or bacterial infections. The causes of acute diarrhea are a viral disease, traveler's diarrhea. The causative agents of the combination of diarrhea and fever are:
- E. coli – infects meat, fish, milk, vegetables, fruits, water. The infection is transmitted from person to person, symptoms are watery stools with blood, vomiting.
- Salmonella - contains raw milk and poorly fried eggs. An excited illness is accompanied by acute abdominal pain, fever, and a frequency of diarrhea 12-15 times a day;
- Shigella - found in food products, loose stools with blood, abdominal cramps are observed;
- Rotavirus (viral infection) - you can become infected from others, a person is bothered by vomiting, nausea, and diarrhea.
What diseases cause headache, fever and diarrhea?
If you are worried about diarrhea, headache, and at the same time the temperature rises, it is impossible to make a diagnosis yourself - the range of suspected diseases is very wide and specific treatment is required in each case.
You cannot hesitate, as the condition can rapidly deteriorate in the absence of adequate treatment. Only a doctor will determine the true cause of the ailment and select the necessary medications.
Causes that can cause headache, diarrhea and fever:
- Acute bacterial intestinal infections;
- Viral infections;
- Typhoid fever.
In some cases, it is impossible to determine the causative agent of the pathology, which is accompanied by diarrhea, headache and fever. In this case, general therapy is carried out to eliminate dangerous symptoms and normalize the patient’s condition.
In all other cases, treatment will depend on the causative agent of the disease.
Causes
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Intestinal infection (infection with viruses, bacteria, pathogenic fungi);
- Intoxication in diseases of internal organs;
- Poisoning with drugs and low-quality products;
- Radiation exposure;
- Pregnancy;
- Overdose of medications.
Diarrhea (or diarrhea) is a condition of the body that is accompanied by frequent loose stools (in some cases, like water), nausea, abdominal pain and sometimes fever.
Body temperature is an indicator of the thermal state of the human body, determining the relationship between the external environment and organs.
Types of body temperature are divided into: subfebrile - up to 38 degrees, febrile - up to 39 degrees, pyretic - up to 41 degrees, everything above 41 degrees is hyperpyretic.
Loose stools and fever in adults or children are more often associated with food poisoning. Other reasons are:
- eating a lot of food;
- allergic reactions;
- exceeding the dosage of medications;
- severe stress, emotional tension;
- sudden climate change;
- damage to the gastrointestinal tract by an infectious disease;
- stomach ulcer, gastritis;
- poisoning with heavy metals, poisons, chemical toxins;
- radiation damage.
Diarrhea with fever and nausea serves as a protective reaction to toxins entering the body. The reasons for the development of these symptoms together are:
- abuse of fatty foods with enzyme deficiency;
- cholera, hepatitis;
- gastritis, ulcer, inflammation of the pancreas, cholecystitis;
- poisoning with mercury vapor, nitrates, poisonous mushrooms.
When diarrhea and a temperature of 37 degrees appear, doctors may suspect gastroenteritis or intestinal flu due to viruses entering the intestines. Their toxins cause inflammation that affects the intestinal mucosa. A person becomes contagious to other people. Viruses can enter the body through food and drinks:
- with unwashed fruits, expired food;
- with unboiled water, when swimming in an infected body of water;
- airborne through sneezing or interacting with large numbers of people.
The incubation period lasts 16 hours, after which the intestinal mucosa is destroyed. Signs of a dangerous disease are:
- frequent liquid diarrhea – 10 times a day;
- nausea, vomiting, cough, sore throat;
- mucus in stool;
- gray-yellow clay-like stool color;
- pain in the stomach area.
With severe diarrhea and a temperature of 38 degrees, doctors diagnose “damage to the gastrointestinal tract due to the development of infection.” The causes may be an overdose of antibiotics, hormonal non-steroidal drugs, and digestive disorders. The latter can be caused by overeating or eating low-quality foods. If you feel worse, visit a gastroenterologist or therapist.
Symptoms of food poisoning include weakness, high fever and watery diarrhea in an adult or child. They appear suddenly after eating foods, without an incubation period. Two hours after ingestion, the pathogen (infection of microbes, viruses or ingestion of chemical toxins) acts on the body. Characteristic symptoms are:
- liquid stool that comes out spasmodically;
- decreased blood pressure;
- cold sweat;
- When poisoned by poisons, vision and brain function are impaired, and muscles lose tone.
Diarrhea page
Diarrhea and chills are signs of an inflammatory process in the human body. The condition appears against the background of the development of ARVI, the activity of viruses and other infectious agents. Vomiting attacks are designed to cleanse the digestive system of toxins and harmful elements. In such a situation, prompt and timely treatment will be required.
Modern medicine distinguishes between chronic and acute diarrhea. In the first case, the pathology is acquired (more than 4 weeks).
In acute forms of the disease, the main cause is the activity of intestinal and parasitic viruses.
Diarrhea can occur due to salmonellosis in chicken eggs. The disease is severe, accompanied by watery stools up to 10 times a day). In a short period of time, dehydration occurs. The skin becomes dry and blood pressure decreases. The bones begin to spin. Causes of the disease:
- poisoning with products of dubious quality;
- overeating fatty foods;
- activity of infectious agents;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and inflammation of the pancreas;
- manifestation of cholecystitis and IBS;
- intoxication with poisons and toxins.
Diarrhea with chills occurs in travelers. Digestive processes are affected by the quality of liquid, nutrition menu, and climate change. People experience stress disorder. This especially applies to children (up to one year and older).
Diarrhea is a sign of the development of abnormalities in human bodies. The disorder indicates dysfunction in the gastrointestinal tract. Chills and trembling are accompanied by a feeling of cold/hotness and muscle tremors.
Over time, a person’s well-being deteriorates. Diarrhea and chills without fever. Fever causes significant discomfort.
Acute forms of the pathological condition are caused by the consumption of low-quality products or the activity of toxins. Provoking factors:
- Malfunctions of the endocrine system. In diabetes mellitus, diarrhea can last more than 10 days. The disease disrupts blood flow. The treatment system must be immediate and effective. Malfunctions of the endocrine system occur in women over 45 years old due to hormones. Menopause occurs against the background of the production of a number of substances. Doctors prescribe replacement therapy.
- Severe intoxication. Poisoning occurs due to the ingestion of alcohol, arsenic, and mercury into the body. After a couple of hours, the victim experiences chills, weakness, and diarrhea. A headache often develops. For a child's body, the action of mushrooms is sufficient. Unwashed vegetables/fruits and meat products are a source of infection. The first signs of intoxication are visible after 90 minutes.
- Stomach flu. The disease indicates inflammation of the intestines and stomach. Pathology occurs due to the activity of viruses, bacteria, and non-infectious factors (medicines, food).
Enteritis is a disease that affects the small intestine. The mucous membrane of the organ becomes inflamed. The etiology of the disorder is associated with congenital anomalies.
Poor functioning of the valve between the intestines can be aggravated by toxins, medications, and infection. The course of treatment for the pathology is determined by a gastroenterologist. The patient follows a diet and adheres to drug therapy.
The rehabilitation period depends on the degree of the disease.
Diarrhea combined with chills is a serious symptom. In some cases, treatment must be started immediately. Diarrhea is not an independent disease, but one of the signs of deviation. Indicates a disturbance in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
With chills, the patient complains of feelings of cold and heat, as well as muscle tremors. The condition makes you feel worse. Chills and diarrhea together cause severe discomfort. In most cases, symptoms indicate the presence of poisoning. The violation occurs in an acute form.
Intoxication may be caused by the ingestion of low-quality products or toxic substances into the body.
The combination of chills and diarrhea is an alarming symptom
The approach to treatment depends on the factors that provoke the disorder. The causes of diarrhea with chills are described in the table.
| Endocrine system disorders | Endocrine abnormalities include:
|
| Intoxication of the body | Entry into the body:
All of these factors provoke the development of diarrhea and intense chills. |
| Stomach flu | Develops against the background of viral and bacterial infections. |
| Less common causes of chills and severe diarrhea | The violation may also be a consequence of:
|
If your condition worsens significantly, you may need to call an ambulance. If certain pathologies are present, the patient may be hospitalized in the infectious diseases department. It is important to pay attention to the accompanying symptoms. If you have such symptoms, you should not hesitate, you should call an ambulance
Often chills and diarrhea are a consequence of endocrine system disruption. In this case, diarrhea occurs over a long period of time. Often the signs indicate diabetes mellitus.
People with diabetes have poor circulation. Chills and diarrhea in this case are not accompanied by an increase in body temperature. Treatment should be started immediately.
Women aged 45-55 years experience hormonal changes due to menopause. This occurs due to stopping the production of a certain substance. In this case, it is necessary to resort to special replacement therapy.
Disturbances in the endocrine system can cause diarrhea and fever
Consumption of low-quality food products or those with an expired shelf life provokes intoxication.
Poisoning can result from exposure to chemicals such as alcohol, arsenic, mercury, etc.
Often this condition is accompanied by chills, weakness, diarrhea and headache. In children, intoxication can also be caused by any mushrooms. This product is not intended for children. Intoxication can be caused by:
- unwashed fruits and vegetables;
- poorly cooked meat and fish.
The first symptoms of poisoning appear after a few hours. The clinical picture of chills and intense diarrhea may indicate an individual intolerance to any food product. The disorder usually occurs without an increase in body temperature.
To avoid intestinal infections, you need to thoroughly wash vegetables and fruits.
Stomach flu
Diarrhea and fever along with chills may indicate intestinal flu. In this case, an inflammatory process occurs in the stomach and small intestine. Doctors identify the following reasons for this deviation:
- viral infection;
- bacterial infection;
- non-infectious inflammation.
Viral infection
Causes of the combination of chills and diarrhea
Modern medicine distinguishes between chronic and acute diarrhea. In the first case, the pathology is acquired (more than 4 weeks). In acute forms of the disease, the main cause is the activity of intestinal and parasitic viruses. In most cases, the disorder is accompanied by severe chills, lethargy, lack of appetite, and elevated body temperature (up to 39°C - take an antipyretic).
Diarrhea can occur due to salmonellosis in chicken eggs. The disease is severe, accompanied by watery stools up to 10 times a day). In a short period of time, dehydration occurs. The skin becomes dry and blood pressure decreases. The bones begin to spin. Causes of the disease:
- poisoning with products of dubious quality;
- overeating fatty foods;
- activity of infectious agents;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and inflammation of the pancreas;
- manifestation of cholecystitis and IBS;
- intoxication with poisons and toxins.
Diarrhea with chills occurs in travelers. Digestive processes are affected by the quality of liquid, nutrition menu, and climate change. People experience stress disorder. This especially applies to children (up to one year and older).
Symptoms for which you need to call an ambulance
In case of diarrhea and high temperature, treatment at home is unacceptable; an emergency visit to a medical facility is necessary.
Symptoms:
- The skin became dry and pale;
- Strong feeling of thirst;
- Dry mouth even after drinking large amounts of liquid;
- Cracks on the lips;
- Reduced amount of urine, the color of which becomes darker;
- Pain in the heart, arrhythmia, and increased heart rate (tachycardia) appear.
Before emergency medical services arrive, the patient should be given first aid:
- Prevent body dehydration by replenishing water loss. It is necessary to achieve abundant consumption of clean water, take a decoction of chamomile, saline solutions that maintain homeostasis of the body;
- You can relieve severe pain in the abdomen with antispasmodics (No-spa), but this is not recommended. The use of other medications that relieve or eliminate pain is unacceptable.
- If it is necessary to wait for medical help (up to several days), non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are used to prevent the occurrence of inflammatory processes.
A common cause of diarrhea and fever (above 37 degrees) in children and adults are infectious diseases of a viral and bacterial nature. Less commonly, acute intestinal infections are caused by infection with pathogenic fungi.
Escherichia coli
This disease refers to infectious diseases transmitted through water, food and airborne droplets. Most often, infection occurs through consumption of: vegetables, fruits, dairy products, fish and meat. And it manifests itself with similar symptoms:
- Temperature (37.5 – 39 degrees), chills;
- Vomiting, nausea;
- Abdominal pain;
- Diarrhea, sometimes with blood.
Acute intestinal infections such as dysentery and salmonellosis are accompanied by severe diarrhea, in which the following symptoms are observed:
- Feces become green;
- In the most severe cases, streaks of blood appear in the stool;
- The temperature rises (up to 40 degrees), and does not decrease when taking antipyretic drugs.
In such cases, hospital treatment in the infectious diseases department is required. Salmonellosis and dysentery are infections that pose a danger to others.
People with weak immune systems and children are mainly at risk of contracting rotavirus infections. Untimely medical care and poor hygiene of a sick family member can lead to infection of the entire family.
Symptoms:
- Fever and diarrhea (frequent, watery stools);
- Nausea and frequent vomiting (up to 6 times a day);
- Stomach ache;
- Lethargy, weakness, drowsiness.
Food poisoning
Food poisoning can be caused by eating dirty and stale foods, toxic and noxious substances. A food infection develops within 2-3 hours from the time of consumption of low-quality food products, sometimes within 10-20 minutes.
Symptoms:
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Weakness, apathy, body aches;
- Diarrhea and fever;
- Stomach upset;
- Headache.
It is necessary to thoroughly wash fruits and vegetables before eating, this will significantly reduce the risk of food poisoning.
Pancreatitis
Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract can also manifest themselves with fever and diarrhea. Inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis) is a very common cause of these symptoms. For complete restoration and normalization of stool and improvement of well-being, it is necessary to begin treatment of the disease in a timely manner and adhere to a strict diet.
To relieve signs of diarrhea, drinking plenty of fluids is recommended, you need to eat properly (broths, soups, cereals), in small portions, and also take enzymes that improve digestion (pancreatin, creon).
Acute appendicitis
The symptoms of the disease are varied, but are always accompanied by abdominal pain, high fever and abnormal bowel movements. An attack of pain begins in the epigastric region (between the costal line and the chest) and spreads to the lower abdomen. Acute appendicitis is a condition that requires mandatory medical intervention.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EQnRpcdJ6vc
The disease is characterized by chronic inflammation of the colon mucosa. Ulcerative colitis is manifested by loose stools, high fever, dizziness, general weakness, decreased performance, and abdominal pain.
The main goal of treating the disease is:
- Elimination of complications;
- Taking special nutritional supplements;
- Elimination of symptoms;
- Preventing seizures;
- Following a special diet.
Viral hepatitis
This is a very dangerous and common infectious disease, caused by viruses and primarily affects the human liver.
Viral hepatitis is manifested by the following symptoms:
- Diarrhea;
- Nausea, vomiting;
- Pain in the right hypochondrium;
- The skin takes on a yellow tint (jaundice);
- Weakness and apathy, body aches;
- Fever, headache;
- Discoloration of stool and dark urine;
- Skin itching.
When to see a doctor
For chronic forms of the disease, seek help from a doctor. The specialist will diagnose the patient and select a recovery plan. Self-medication at home can provoke additional disorders and complications. You should visit the hospital if the following symptoms appear:
- presence of intense vomiting;
- vomiting interspersed;
- frequent fainting;
- increased level of the patient’s body temperature (treat with antipyretics);
- a sharp decrease in body weight + begins to diarrhea severely;
- dysfunction of the organs of vision and hearing;
- manifestation of diarrhea for more than 48 hours;
- will freeze and feel sick in the evening;
- severe pain in the abdomen or intestines;
- dehydration + dry mouth.
Before the emergency ambulance team arrives, it is prohibited to take any medications. The exception is noshpa or activated carbon. Inform your doctor about the underlying causes of the disorder. The help of a gastroenterologist is needed for children who have problems with bowel movements for about a day.
Diarrhea and fever in childhood
In babies, the dangerous temperature for diarrhea is 37 degrees or more. The causes of these symptoms are:
- eating disorder, intoxication of the body - pale face, cold feet and hands, stomach pain;
- reaction to medications;
- acetonemic syndrome - lack of carbohydrates, past infectious diseases of the digestive system, stress, manifested by vomiting, unpleasant odor of acetone from the mouth;
- teething - gums may begin to swell;
- failure to comply with hygiene rules – signs of poisoning are visible;
- helminthic infestations - severe diarrhea;
- gastritis, colitis, dysbacteriosis - signs of toxins entering the body disappear with medication;
- enterovirus – bloody diarrhea (invasive bloody diarrhea);
- rubella, scarlet fever, measles - rashes on the skin;
- flu, sore throat, otitis media, pharyngitis – redness of the throat, enlarged tonsils, nasal congestion, temperature may rise;
- dysentery, salmonellosis - green feces with mucus.
Diarrhea and headache in a child
In children, diarrhea in combination with cephalalgia is quite common. Most often, loose stools are a consequence of microbes entering the body.
The immune system reacts violently to foreign agents, triggering defensive reactions. The intestines begin to actively cleanse themselves, accelerating the elimination of pathogens and their toxins. The child’s internal systems are still being formed; they are not perfect. The body’s reaction to even the most “harmless” provocateur becomes violent, and the clinical picture is vivid. It is often accompanied by intoxication, which causes headaches and fever.
You can learn more about the signs of poisoning in children here.
Prevention of diarrhea and cephalalgia in a child:
- compliance with personal hygiene rules;
- general strengthening of the body with the help of vitamins, hardening, fresh air, physical education;
- refusal to try to place the baby in “sterile” conditions, due to which he will not develop acquired immunity;
- adherence to healthy eating rules;
- breastfeeding up to 1-1.5 years.
The combination of symptoms in a child requires urgent evaluation by a doctor, even if they are mild. Dehydration in childhood can develop within a few hours, leading to organic pathologies or death.
What to do
Home treatment can reduce the impact of dangerous symptoms, provided that the following recommendations are followed:
- give the patient plenty of drink - Borzhom or Essentuki mineral water, dried fruit compotes, weak fruit drinks, weak tea with honey;
- follow a dietary diet – boiled cereals, vegetable soups;
- take fermented milk products, non-acidic cheeses, low-fat cottage cheese;
- drink starchy jelly for health;
- eat more boiled vegetables and baked fruits;
- You can bring down the temperature above 38 degrees with Nurofen, Aspirin, Paracetamol;
- take calcium supplements, pro- or prebiotics with pectin, acidophilus.
First aid
If the temperature rises and bowel movements appear, the first aid for the patient will be the following measures:
- at the first signs of intestinal poisoning, induce vomiting to lavage the stomach - drink a solution of potassium permanganate or soda, repeat until the stomach is completely empty, then take an absorbent;
- to prevent signs of dehydration, every 10 minutes give the patient a sip of Regidron (a packet per liter of water), drink plenty of fluids;
- on the first day of treatment for severe weakness, you should refuse to eat, drink more and rest, then follow a light diet and drink broths;
- The temperature during diarrhea should not drop to 37 degrees (it indicates that the body is in the process of independently fighting the infection). In this situation, provide the patient with complete rest.
In case of a complicated course of the disease, diagnostics are required to prescribe the correct drugs for treatment. Diagnosis measures include the use of coprograms, stool tests for dysbacteriosis and helminths, general and biochemical blood tests, and abdominal ultrasound. Depending on the cause of diarrhea, treatment methods include:
- taking sorbents – Smecta, Enterosgel, activated carbon, Polyphepan, Neosmectin, activated carbon (tablet per 10 kg body weight), Balignin, Attapultit
- gastric lavage in case of severe vomiting;
- rehydration therapy for fluid loss - Regidron, Gastrolita, Citroglucosolan, chamomile tea, pharmaceutical saline solution;
- antipyretics for headaches - Paracetamol, Nurofen;
- taking fluoroquinolone antibiotics or cephalosporins - in severe condition, presence of blood in diarrhea
- lacto- and bifidobacteria to restore intestinal microflora during rotavirus infection;
- taking anti-inflammatory drugs on the first day of illness - Indomethacin, Diclofenac, Sulfasalosin;
- When diarrhea occurs, it is useful to take Festal or Mezim to stimulate intestinal function and remove toxins.
Traditional treatment
If diarrhea and high fever appear in an adult or child, you can use traditional medicine recipes to help get rid of dehydration:
- Taking rice or pomegranate broth, mint infusion, fresh blueberries.
- Consuming dry starch dissolved in water, diluted carrot puree, chamomile or mint tea.
- Taking rehydration solutions - take a tablespoon of sugar, a teaspoon of salt and half a teaspoon of soda per liter of boiled water. Or dissolve eight teaspoons of sugar, a teaspoon of salt, and the fresh juice of two oranges or grapefruits in a liter. It is necessary to give the patient food every five minutes in small portions.
Treatment
Such manifestations as fever and diarrhea should in any case cause concern, regardless of who they appear in: adults, teenagers or a small child.
Before starting treatment for diarrhea and fever, it is necessary to determine what kind of disease the patient is suffering from. And it is best for a specialist to handle this task.
In the acute course of the disease, it is necessary to undergo diagnostic procedures that allow you to prescribe medications depending on the occurrence and development of the disease. The diagnosis is made after conducting stool examinations, analyzing it for dysbacteriosis, biochemical and general blood tests, and ultrasound.
Treatment methods:
- Gastric lavage;
- Rehydration therapy (water and electrolyte therapy);
- Taking sorbents (enterosgel, activated carbon);
- Taking antipyretic drugs (nurofen, paracetamol);
- Taking antibiotics;
- Taking anti-inflammatory drugs;
- Taking enzymes;
- Taking lacto and bifidobacteria.
Diarrhea page
Diagnostic methods
If you have diarrhea and chills, doctors give a referral for:
- clinical blood test;
- blood for antibodies to helminths;
- fecal analysis.
In a clinical blood test, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate, as well as the number of leukocytes and eosinophils, are studied. In this way, helminthiasis or intestinal flu can be detected.
Fecal examination examines the material for the presence of parasites, occult blood, fats, or food particles. You can find out which organ was affected.
After completing laboratory tests, the patient is selected for the required instrumental examinations. Only after this the patient is prescribed adequate and safe treatment.
This video will help you in treating diarrhea in children:
Prevention
To prevent weakness, fever, diarrhea and vomiting, you need to follow simple but effective rules of prevention:
- When preparing food, observe the shelf life of products;
- Avoid self-treatment with antibiotics;
- store ingredients only in the refrigerator in compliance with the commodity proximity, do not keep raw meat next to fresh vegetables;
- choose only high-quality food products, without expired expiration dates;
- do not eat raw fish in rolls, cook steaks without blood, do not drink unpasteurized milk, untested water;
- wash your hands more often;
- eliminate insects in the kitchen;
- wash dishes thoroughly.
To prevent the appearance of symptoms such as vomiting, fever, weakness and diarrhea, the following precautions and prevention rules must be observed:
- Wash your hands frequently;
- Wash dishes thoroughly;
- Prevent insects from appearing in the kitchen;
- Eat only high-quality and unexpired products;
- Do not eat raw fish, rare steaks, or unpasteurized milk;
- Store food in the refrigerator;
- Do not self-medicate with antibiotics;
- Observe product expiration dates.
Possible causes of chills and temperature with diarrhea and methods of treating the condition
Traditional medicine recipes can be used if diarrhea and fever occur; they help get rid of dehydration:
- Taking rehydration solutions: Take 1 tablespoon of sugar, 1 teaspoon of salt, dissolve 0.5 teaspoon of soda in 1 liter. boiled water. Take small portions every five minutes;
- Dissolve one tsp in one liter of water. salt, 8 teaspoons of sugar, add fresh juice of two grapefruits or oranges. Take every 5 minutes in small portions;
- Taking pomegranate, rice water, and mint infusion;
- Drinking mint and chamomile tea, as well as dry starch dissolved in water.
Video on the topic: Abdominal pain and fever
Diarrhea page
Rotavirus infection
Rotavirus infection is an intestinal flu caused by infection with rotavirus. The stomach and intestines suffer, so in addition to the classic flu symptoms, diarrhea and vomiting also occur.
Unlike intestinal infections, rotavirus is infected mainly in the autumn-winter season. The infection can be contracted through the oral-fecal or airborne route. The incubation period can last up to five days. Then the following symptoms appear:
- Diarrhea and vomiting;
- Stomach ache;
- Headaches and sore throat when swallowing;
- Increased body temperature;
- Redness of the laryngeal mucosa;
- Runny nose and nasal congestion.
With rotavirus infection, stool can be up to 15 times a day, the stool is yellowish in color, reminiscent of clay soaked in water. The patient becomes lethargic and irritable.
Since there is no appetite with this pathology, as the disease progresses, the patient suffers greatly from debilitating vomiting on an empty stomach.
If classic flu symptoms are observed, but the patient has frequent and loose stools, rotavirus is first suspected.
Intestinal infection
When an adult’s temperature rises and diarrhea appears, this may be the cause of an infectious intestinal infection.
These include pathogenic bacteria and viruses, for example:
- Rotavirus.
- Enterovirus.
- Adenovirus.
Bacterial infections include:
- Cholera.
- Dysentery.
- Salmonellosis.
- Escherichiosis.
When infections begin to affect the gastrointestinal tract, other important organs begin to become inflamed, resulting in unpleasant diseases:
- Gastritis. The disease appears when the stomach is damaged.
- Duodenitis. Damage to the duodenum.
- Enteritis. Disease of the small intestine.
- Colitis. Pathology of the large intestine.
In some cases, in an adult, diarrhea with fever can be caused by food poisoning or other substances, which also falls under the category of bacterial infection of the intestines, since such a condition is provoked by bacteria from foods and other substances.
Infectious contamination can occur very simply, and the pathogens are found on products and in the food itself.
For example, if an ingredient is used that has already expired or was stored incorrectly under inappropriate conditions.
In this case, the infection in the products begins to multiply, and after consuming the product it enters the body and causes diarrhea.
Less commonly, infection can occur through the air; more likely, infection can occur through products that have been used by an already sick person.
Most often, diarrhea and fever appear as a result of consuming products of animal origin, while the animal itself was already a carrier of the pathogen before slaughter or production of eggs or milk.
Diarrhea and fever in an adult occur as a result of using canned food that has expired. Often the problem occurs when using an old homemade seamer.
In this case, botulism appears. This disease is very dangerous for the health and life of people. An adult may lose vision and experience paralysis.
The first symptoms in an adult with a bacterial infection will be the same for any type of virus.
Initially, intoxication of the body begins, after which the immune system begins to work and protect itself.
Due to this, diarrhea and fever appear. Thus, the human body tries to get rid of and cleanse itself of infection and bacteria.
Factors causing deviation
Diarrhea can be acute or chronic. In the first case, its cause is usually an infection: viral, bacterial or parasitic. In the second case, diarrhea can be a sign of a number of pathologies.
Diarrhea that lasts more than 2 days may be ordinary food poisoning, which does not go away due to improper behavior after illness: for example, eating fatty, difficult-to-digest foods.
Muscle chills usually indicate intoxication.
Endocrine system disorders
The endocrine system controls all organs and processes in the body, so hormonal imbalance often provokes severe chills and regular diarrhea.
Diabetes mellitus can cause diarrhea that lasts more than 10 days. Against the background of the disease, there is a feeling of severe physical weakness, which can be expressed in a combination of decreased body temperature and tremor, which is felt as chills.
The second common cause of regular bowel disorder is thyrotoxicosis or hyperthyroidism. Increased production of thyroid hormones or an overdose of levothyroxine accelerates internal processes, including peristalsis. The condition is most often characterized by a subjective feeling of heat in the body, but chills are also possible.
A combination of two symptoms is possible during menopause. Restructuring of the hormonal system can provoke functional disorders of any organs.
Intoxication of the body
Intoxication or poisoning occurs when it enters the body:
- Alcohol.
- Arsenic, mercury.
- Poor quality food.
- Medicines.
- Mushrooms, poisonous berries.
The clinical picture appears on average 1.5-2 hours after the toxin enters the blood; in children it may appear faster. Signs of poisoning include loose stools, headache and chills. An increase in temperature does not always occur, but the fact of hyperthermia is an alarming sign.
Diarrhea and chills without fever can occur with reduced immune function: immunodeficiency and taking immunosuppressive drugs. In this case, the health hazard will be even higher, since the body will be defenseless against the toxin. The condition can lead to kidney failure, liver damage, and increased intestinal motility can lead to dehydration.
Stomach flu
Intestinal flu is a general name for gastrointestinal pathologies caused by the activity of viruses. In more than 60% of cases, patients with diarrhea of this etiology are diagnosed with rotavirus, norovirus or adenovirus.
Attention! Stomach flu is an illness usually caused by poor hand hygiene.
Diarrhea and chills with fever require medical intervention, as it is important to exclude salmonellosis, dysentery, cholera, malaria and other dangerous pathologies.
Other reasons
Diarrhea and chills in an adult without fever can occur due to:
- Hypertensive crisis.
- Enteritis is inflammation of the small intestine.
- Colitis is inflammation of the colon and rectum.
- Helminthiasis is an infection of the intestines with parasites.
- Syphilis.
- Allergic reaction.
Diarrhea and low-grade fever
Low-grade fever in an adult is the position of the thermometer scale between 37 and 37.5 degrees.
If an adult develops diarrhea and such a temperature, then doctors can make a preliminary diagnosis of gastroenteritis. This condition is also called “stomach flu”.
Gastroenteritis appears as a result of viruses and their waste products in the intestines. Thus, the mucous membrane and intestinal walls become injured and begin to become inflamed.
If proper treatment is provided, all symptoms will quickly go away. Until the doctor says that the disease is completely cured, the patient remains a carrier of the infection.
This can become dangerous for other people who live with the infected person.
The main symptoms of gastroenteritis are as follows:
- Diarrhea.
- Temperature 37 degrees.
- Chills.
- In some cases, vomiting.
- Feces in mucus.
- The color of the stool changes to gray-yellow.
- Mild abdominal pain and cough may occur.
It is worth noting that diarrhea and fever can also indicate other diseases, for example, cholera or mild salmonellosis.
Diarrhea and headache in an adult
As a person grows up, his body learns to regulate internal processes, so it no longer reacts so brightly to the same stimuli. For this reason, the development of such a clinical picture should be treated with increased attention. In an adult, the simultaneous appearance of headache and diarrhea may indicate not only poisoning or infectious diseases. The combination of symptoms is characteristic of chronic inflammatory processes in the large intestine, pancreatitis, appendicitis, and gastric ulcers. The doctor must also exclude such common serious diseases as sore throat, sepsis, and influenza.
Diarrhea and high fever
Viral infection
In some cases, people may have a temperature of 38 degrees and, moreover, diarrhea appears, all this indicates dysentery or staphylococcus.
For these reasons, people may have the following symptoms:
- Severe and frequent diarrhea.
- Stool contains mucus and blood.
- The color of the stool may be green.
- Weakness appears in the body.
- The fever begins and the temperature reaches 39 degrees.
Similar symptoms can be observed with HIV diseases, as well as various tumors.
Other symptoms are possible in the presence of other pathologies not related to the intestines and gastrointestinal tract, for example, a problem arises with inflammation of appendicitis.
When diarrhea and a temperature of about 39 degrees appear, the person must be urgently hospitalized. It is almost impossible to recover on your own, especially if you do not know the reasons for your deterioration in health.
What to use for diarrhea
In case of food poisoning caused by poor-quality products, as well as intestinal flu, you simply need to not interfere with the body getting rid of harmful bacteria.
Vomiting and diarrhea appear; they can provoke dehydration, so it is recommended to drink more water, tea, infusions of medicinal herbs, as well as saline solutions, for example, Regidron.
It is imperative to rest and lie down more. When the diarrhea stops, you will need to take measures to restore the intestinal microflora. The general treatment plan is as follows:
- A proper diet is used, which removes foods that can have an irritating effect on the intestinal walls. It is recommended to use table No. 4.
- It is imperative to take sorbents to remove toxins and strengthen stool.
- Enzymes are used to normalize the flora.
- To normalize the temperature, you can take antipyretics.
- Additionally, it is necessary to use probiotics, as well as kefir and other fermented milk products.
This treatment allows you to get rid of symptoms and normalize stool in just 5 days. If the diarrhea does not stop, then a visit to the doctor should be urgent.