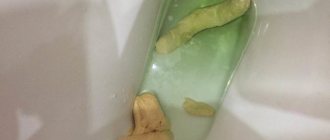
Normal stool color in children is brown or yellow. And even diarrhea, which is already a violation, should not affect the color either. White diarrhea in a child is a fairly rare condition, which already indicates abnormalities.
Discoloration of feces indicates that the production of bilirubin is reduced - a substance that gives excrement a brown color and is the main participant in the quality of food digestion.
Parents should know that this condition of the baby should attract attention, because even if the cause is quite harmless at first, it is better to solve it under the supervision of a doctor. Sometimes a rather serious pathology begins to develop in secret, and it is better to undergo small examinations in order to gain confidence that the baby is safe.
In the first years of life, with proper treatment, quite a lot of even severe pathologies can be permanently eliminated, so you should not delay going to the doctor. Parents should also know what ailments this condition may indicate and when it is time to immediately go to the doctor.
Possible reasons
White diarrhea is one of the rarest phenomena that occurs under the influence of pathological factors, such as:
- Helminthiasis
- Dysbacteriosis
- Pancreatic dysfunction
- Enteritis
- Fistulas
- Oncological disease
- Pancreatitis
- Hepatitis
- Rotavirus infection
- Food poisoning
- Insufficient secretion of lactose.
White, loose stools are often observed in children whose diet included fatty foods. In such cases, the color of stool returns to normal after stopping the consumption of such dishes and products.
Another common reason is a slight overdose of medications, for example, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Ibuprofen), tetracycline antibiotics, etc. However, it should be borne in mind that with the normal functioning of the digestive organs, such a side effect should not occur, which means that a child with frequent white diarrhea should be examined immediately.
Diarrhea can cause dehydration, so postponing a visit to the doctor is strongly not recommended, especially when it comes to infants.
How does white diarrhea occur?
Diarrhea develops when intestinal activity is disrupted - increased peristalsis or improper absorption of water occurs. As a result, the child produces loose stools, sometimes white. Intestinal activity is affected by internal diseases, parasitic infestations, bacterial and viral infections, exposure to chemical toxins, certain foods and medications.
Stool acquires its specific color due to the bile pigment bilirubin. It enters the small intestine along with bile and, through several transformations in the large intestine, is oxidized to stercobilin (pigment), which gives feces a brown color.
In certain pathologies, the flow of bile into the intestines is completely or partially stopped. Feces are not colored and come out of the body with a uniform clay-white hue. This type of stool is called “acholic.”
Pathological causes
If a child not only has diarrhea with frequent white stools, but also exhibits additional pathological symptoms, then you should think about the presence of serious diseases present in the body. With careful attention to children's health, almost any disease can be detected and treated at an early stage.
Hepatitis
With this pathology, in addition to white diarrhea, the child experiences the following symptoms:
- Yellowing of the skin
- Yellowing of the whites of the eyes
- Temperature increase
- Sharp pain in the abdominal area on the right side
- Darkening of urine
- Nausea
- Lack of appetite
- Skin rash
- Headache
Lightening of stool during hepatitis occurs gradually, the color changes from yellow to white and almost colorless.
Lactose intolerance
This pathology is characterized by the absence in the child’s body of a special enzyme designed to digest milk sugar. If signs of the disease appear in an infant less than one month old, they are associated with the immaturity of the digestive system, and over time this condition returns to normal. The presence of deficiency at such an early age can be recognized by the following symptoms:
White loose stool- Bloating
- Increased gas formation
- Insufficient weight gain
- Frequent regurgitation.
One-year-old and older children experience frequent loose stools with a light color and an unpleasant sour odor, as well as weight loss even with a normal balanced diet, and constant abdominal pain.
Rotavirus infection
With a viral infection of the intestines, in some cases there is a lightening of the stool (white or gray color of feces), as well as their liquefaction, frequent and painful urge to defecate. Other signs are vomiting, a significant increase in temperature (up to 39-40 degrees), discomfort in the throat, cough and runny nose, white coating on the tongue, weakness, pain in the head and stomach, and lack of appetite.
Pathologies of the bile ducts and pancreas
The following symptoms indicate blockage of the ducts, bending or twisting of the gallbladder, as well as problems with the pancreas (pancreatitis):
- Frequent, loose, light-colored stools with an unpleasant, uncharacteristic odor
- Acute pain in the upper abdomen
- Nausea
- Tachycardia
- Increased sweating
- Vomit
- Dark color of urine
- Belching
- Yellowish skin tone
- Feverish condition.
Pancreatitis and hepatitis in the initial stages have similar symptoms.
Normal stool in children
There is no fixed stool rate for children. The frequency of bowel movements, consistency and color of stool depend on age, nutrition, amount of fluid consumed and characteristics of the body.
Age standards for stool:
- Breastfed children. Mushy or liquid stool that is golden or yellow-green in color with a sour odor.
- Formula-fed children. Pasty or semi-solid stool that is yellowish or light brown in color with a sour odor.
- Children over 1 year old. Sausage-shaped or snake-shaped feces with a smooth or cracked surface. It can be dark yellow or all shades of brown with a specific but not fetid odor.
With adequate weight gain and good health, the following are considered normal options: a greenish tint to the stool, undigested inclusions and mucus.
Average frequency of bowel movements in healthy children based on survey results.
| Age | Number of bowel movements per week | Number of bowel movements per day |
| 0-3 months breastfeeding | 5-40 | 2,9 |
| 0-3 months artificial feeding | 5-20 | 2 |
| 6-12 months | 5-28 | 1,8 |
| 1-3 years | 4-21 | 1,4 |
| 4 years and older | 3-14 | 1 |
As you can see from the table, the range of bowel movements that is normal is large. Therefore, you cannot rely on it to identify violations.
Diarrhea is determined by the consistency of the stool. With diarrhea, it is porous and loose in the form of fluffy lumps or watery and completely liquid. Basically, this is at least 3 excrements of a child with unusual watery stools with a pungent and fetid odor.
Since infants' stool is mostly liquid, conventional signs of diarrhea are accepted. This is 10 g of liquid feces per kg of body weight per day. To get a clear idea of how much it is, you need to multiply the child’s weight by 10 and pour the same amount of water into the container. Be sure to pay attention to additional signs.
Physiological reasons
Natural factors that influence the color and consistency of children's feces include dietary habits, improper or untimely introduction of complementary foods in infancy, as well as excess consumption of carbohydrates, fatty foods, dairy products, etc. In such cases, if the child is in normal health, correcting the diet helps. In older people, the causes of white diarrhea are often factors such as failure to comply with basic hygiene rules, drinking low-quality drinking water, climate change, etc. Usually, the symptom in question goes away on its own without treatment.
First aid for diarrhea
Treating the underlying disease that caused the stool disorder will help get rid of diarrhea. But first of all, measures should be taken to prevent dehydration of the body, since this happens very quickly in childhood. The child should drink little and often. It is important that the liquid consumed is at a comfortable temperature, not cold or hot. You can give a small patient a sorbent drug, for example, Polysorb, Enterosgel, activated carbon. Regidron or regular saline solution will help prevent dehydration, and taking Smecta is recommended to quickly remove toxins from the intestines and stop diarrhea.
If diarrhea lasts more than two days, the child requires qualified medical care. Even after prolonged diarrhea has stopped, it is advisable to conduct an examination to exclude the possibility of any serious pathology.
Treatment depending on the age of the child
To replenish lost fluid in the body, it is necessary to use Regidron or Humana Electrolyte anti-diarrhea medications. Rehydration for diarrhea at home can be done by diluting a teaspoon of salt, the same amount of sugar and half a spoon of soda in a liter of boiled water. This solution is given to children without restriction at any age.
Rice water and starch do not have any age restrictions for children. It should be brewed with just water or made into jelly, but only slightly sweetened and do not use fresh berries and fruits, but only dried ones. Such remedies can quickly eliminate diarrhea.
Drugs
Remedies for diarrhea are divided into five groups:
- Probiotics are drugs that are used to relieve symptoms of dysbiosis, one of which is diarrhea:
- Linex – capsules, price – from 400 rubles;
- Bifidumbacterin - powder, price - from 80 rubles.
- Medicines aimed at slowing down the wave-like contractions of the walls of the rectum (peristalsis):
- Imodium – capsules, price – from 250 rubles;
- Loperamide - syrup (it is prescribed to children in this form of release), price - from 25 rubles.
- Antibiotics that eliminate the cause of diarrhea - intestinal infections:
- Levomycetin - tablets, powder, price - from 76 rubles. (children from 3 to 16 years old are prescribed 25 mg per kilogram of weight twice a day);
- Metronidazole – tablets, solution for infusion, price – from 40 rubles. (take one tablet twice a day);
- Amoxicillin - tablets, powder for injection, price - from 27 rubles. (children under 5 years old need to take 0.125 g of the drug three times a day).
- Enterosorbents are means for binding exogenous and endogenous substances in the gastrointestinal tract by increasing adsorption, absorption, complexation and ion exchange:
- Activated carbon - tablets, powder, price - from 10 rubles. (taken at the rate: 1 tablet for every 10 kg of weight);
- Smecta - powder for preparing a suspension, price - from 130 rubles. (children under one year old are given one sachet, from one to two years old - 2 sachets, over 2 years old - 2-3 sachets).
- Preparations of plant origin, which in most cases have an astringent and tanning effect on the intestinal contents:
- bird cherry fruits (price - from 50 rubles);
- blueberries (price – from 80 rub.);
- burnet root (price - from 50 rubles).
Nutritional Features
Compliance with a special diet applies not only to a small child, but also to a young mother if the child is fed exclusively on breast milk. In this case, the woman is advised to exclude foods that have a laxative effect from her diet. These can be carrots, apricots, citrus fruits, onions, radishes, zucchini.
If diarrhea appears as a result of an infectious disease, then the child’s body very quickly loses potassium along with loose stools. This element is necessary for healthy heart function. Potassium deficiency can be replenished by giving special decoctions of:
- dried apricots;
- carrots;
- potatoes;
- raisins
To prepare, just grate the food and pour hot water for half an hour, then strain and cool. In the same way, you can prepare decoctions from any vegetables and fruits.
You can give your child egg yolk as it strengthens the stomach. Rice, oatmeal or jelly can also be left in the diet. It is very important that the menu contains enough plant fiber and a minimum of carbohydrates. This could be fruit, mashed potatoes, semolina porridge or cookies.
For mild disorders, you need to stop the restorative diet after 4-5 days, for serious disorders - after 10 days.
Folk remedies
There are a lot of fixatives for diarrhea from traditional medicine: rice water, flax seeds, wormwood, caraway seeds, garlic and other components that are infused with ethyl alcohol, brewed or consumed whole.
Here are some folk recipes used for white diarrhea in a child:
- Pour 1 glass of rice with 7 glasses of water, cook until fully cooked. When the rice is ready, strain it through a sieve or cheesecloth. The resulting liquid should be given to the child 50-100 ml 3-4 times a day, regardless of the baby’s age.
- Blueberry tea. Pour boiling water over a handful of dried berries, bring to a boil and simmer over low heat for 5 minutes. The child should drink a cup of tea with berries 3 times a day.
- Decoction of pomegranate peel. Pour 2 tablespoons of dried peel into 500 ml of water, bring to a boil and cook in a sealed container for 15 minutes. Take half a teaspoon of the decoction 3 times a day 20 minutes before meals.
An important nuance when using pomegranate for a child is consultation with a pediatrician, since this product is considered an allergen.