Before treating colitis, it is worth learning about its characteristics, types, and causes.
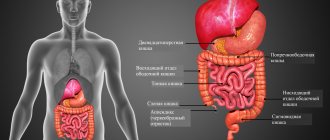
Intestinal colitis is a disease characterized by inflammation of the inner wall of the human large intestine. The mucous layer is damaged due to poor nutrition, stress and other factors, which is the cause of the disease. Inflammation leads to impaired absorption of fluid from food waste and intestinal motility. The shell does not perform its functions or does not perform them fully. The degree of damage determines the type of disease.
Types of intestinal colitis
Depending on the cause of inflammation, the following types of colitis are distinguished:
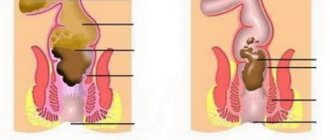
- Ulcerative colitis is a type of colitis characterized by ulcers on the walls of the large intestine.
- Acute - a type in which not only the large intestine is affected, but also the small intestine is inflamed, and the stomach is also affected.
- Ischemic – consequences of poor blood circulation in the intestines.
- Chronic is the consequences of acute, incompletely cured colitis.
- Spastic manifests itself with spasms and bloating. It is not considered a severe form.
- Alcoholism occurs when you are dependent on alcohol.
- Erosive - characterized by ulcers over a larger area of the duodenum.
- Atonic is typical for older people. Intestinal activity is reduced, frequent constipation, hemorrhoids subsequently.
- Hemorrhagic is characterized by bloody discharge - diarrhea.
- Radiation colitis occurs after radiation exposure received for cancer.
- Nonspecific ulcerative - similar to chronic with relapses, origin of the immune type.
Review of suppositories for colitis
Suppositories are often included in a complex of health measures. Unlike tablets, they do not come into contact with the bloodstream or other organs, having a direct effect on the source of inflammation itself.
For colitis there are no restrictions on gender and age. At the same time, the risk of rapid progression and complications is very high.
It is very important to identify the symptoms in time and seek the advice of a specialist.
Suppositories for intestinal colitis are divided into types:
Suppositories that have an anti-inflammatory effect
- Viburcol. It has an antipyretic, sedative, antispasmodic and anesthetic effect. Viburkol copes well with dyspeptic symptoms in the treatment of intestinal colitis. Approved for use in children, pregnant women and lactation.
- Fitor. Characterized by a wide range of actions. Refers to natural remedies. The composition contains vitamins, tannins, acids and flavonoids. Thus, effective elimination of the inflammatory process is noted. The course of treatment is determined by the doctor depending on the degree of progression. To eliminate the pathology, 10-20 days are enough.
- Proctosan. For intestinal colitis in adults, this medicine is very often prescribed. It has an astringent, analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and drying effect. The composition includes the main components: lidocaine, titanium dioxide, bufexamak, bismuth, water, liquid paraffin, lanolin. The course of therapy for the treatment of colitis is 8-10 days. It has a number of contraindications, so it can only be used after consulting a specialist.
Suppositories that have an analgesic effect
- Diclofenac. Used in the treatment of colitis during the acute period. Characterized by a rapid analgesic effect. Has some contraindications.
- Papaverine. Relieves pain and eliminates spasms. The drug has contraindications. The course of therapy is a maximum of 3 days.
Glucocorticosteroid suppositories
- Ultraproct. The most effective remedy of the entire group for intestinal colitis in adults. Fluocortolone is used as a base. Ultraproct is characterized by antiallergic, anti-inflammatory, antipruritic and anesthetic effects.
Other suppositories
- Natalsid. Experts prescribe these suppositories for ulcerative colitis of the intestine. They have a beneficial effect on damaged areas of the mucous membrane. They are used even for bleeding.
- Methyluracil suppositories. The drug is characterized by restorative and regenerating effects. It is used for bleeding, effectively eliminating the inflammatory process. There are contraindications.
Sulfanilamide suppositories.
Eliminate and act directly on the causative agent of intestinal colitis:
- Phthalazol.
- Sulgin.
- Phtazin.
- Doreen.
Symptoms
Symptoms of colitis:
- Dull pain in the lower, side of the abdomen. The time after eating worsens the pain.
- Constipation alternating with diarrhea.
- Symptom of intense gas formation.
- Nausea.
- When defecating, there is a feeling of incomplete emptying of the rectum.
- Unpleasant smell of feces.
- Weight loss.
- Prostration.
Acute form:
- Loss of appetite.
- Diarrhea.
- High body temperature.
- Drawing pain in the lower abdomen.
Treatment of the disease
Diagnosis leads to treatment. Therapy provides an integrated approach to this matter. Experts advise going through all the steps:
- Diet.
- Sessions with a psychotherapist.
- Sanatoriums.
- Drug treatment.
Treatment with medications involves prescribing a set of medications. Let's take a closer look at this.
Prescribing antibiotics
Antibiotics are not always used to treat colitis. The reason for this is contraindications for different types of colitis.
Antibiotics are drugs aimed at destroying bacteria that cause infectious diseases. They are prescribed if the use of other methods has proven ineffective.
Antibiotics are not prescribed together with antibacterial drugs due to unexpected reactions.
Furazolidone is a representative of antibiotics and has a pronounced antimicrobial function. An effective drug whose properties depend on the dose. The tablets are taken without chewing. The treatment course is individual. The average course is a week when taking the medicine four times a day.
Levomycetin is an antibiotic available in the form of tablets and powder. Effective as furazolidone. The course is prescribed by the doctor.
Metronidazole is another antibiotic with an antimicrobial effect. It has contraindications: pregnancy, problems with the central nervous system.
The described remedies are used for mild to moderate severity of the disease.
Painkillers (antispasmodics)
Painkillers help relieve pain caused by the acute form of the disease. Used for ulcerative, acute colitis.
No-spa - suitable for moderate pain, has contraindications for heart failure, preschool age, and individual intolerance to the composition of the drug. Available in the form of a solution, yellow tablets.
Dicetel - solves the problem of spasms, thereby eliminating pain. Take the tablets three times a day. Contraindicated for children. Available in orange tablets.
Mebeverine is an antispasmodic that soothes intestinal irritation and relieves pain. Used internally. Contraindication – hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
Anti-inflammatory drugs
Inflammation is the main feature of the disease. To relieve it, the doctor prescribes anti-inflammatory medications that improve the general condition of a person.
Prednisolone is prescribed for ulcerative colitis, a chronic form of the disease. The drug relieves inflammation and inhibits the process of its development. The dosage is individual.
Restoration of microflora
Disease and drug use destroy the normal microflora of the human intestine. Antibiotics, in addition to destroying bacteria, destroy beneficial microflora, the absence of which leads to depression, obesity, asthma, allergies and dysbacteriosis.
Medicine does not yet have in its arsenal a medicine without side effects. Therefore, having cured one thing, you have to solve the problem with the consequences. It turns out that it is almost impossible to completely cure a form of chronic colitis.
Microflora restorers: Bifikol, Bifidumbacterin. Treatment time with drugs is up to one and a half months. This also includes Linex, Lactobacterin.
Linex is a medicine in capsule form that restores microflora. Take capsules three times after meals. Contraindications – allergy to the components of the drug.
Lactobacterin is a prebiotic in powder form. Use one hour before eating as a drink. Treatment should be carried out for a month.
Bifikol is a lyophilisate intended for preparing a suspension. Use half an hour before meals twice a day. Used to restore microflora after ulcerative colitis. Contraindications: simultaneous use with antibiotics.
Bifidumbacterin is available in capsules, tablets, lyophilisates for the preparation of suspensions and liquid concentrates. Application depends on the prescribed form of the medicine. The dosage is individual. Do not use for children under three years of age.
Solving problems with intestinal motility
After restoration of the microflora or simultaneously with it, medications are prescribed to improve intestinal motility.
Mezim-Forte is a drug in the form of tablets that activates the digestion process - a high level of absorption of proteins, carbohydrates, fats. The drug is contraindicated for pancreatitis.
Creon is a medicine in the form of gelatin capsules to improve digestion. The dosage depends on the severity of the disease. Like Mezim, it is contraindicated in chronic pancreatitis.
Terms of use
Suppositories are inserted through the anus deep into the rectum. Depending on the doctor’s instructions, the procedure is performed one to three times a day, after bowel movements or a cleansing enema. Hands should be washed clean; if there is a manicure with long nails, sterile medical gloves should be worn. The candle can be inserted in two positions:
- Lying on your left side. You need to pull your right leg towards your stomach, relaxing your anus as much as possible. Lubricate the anus with Vaseline so as not to injure the mucous membrane. Push the drug with your index finger (or little finger, if the suppository is being administered to a child) to a depth of 2-3 cm. Squeeze the buttocks and rest quietly for a few minutes.
- In a vertical body position. Leaning forward, spread the buttocks with your fingers and insert the suppository. Then you need to lie down for half an hour to distribute the medicine evenly.
Candles are stored in refrigerators and administered quickly to prevent them from melting in the palms. To protect underwear from contamination, use a clean soft cloth or panty liner. If an incomplete dosage of the drug is required, the suppository is cut longitudinally with a sharp knife.
Pharmacy counters offer a wide range of rectal products for the treatment of inflammation of the large intestine. But you should remember that they must be prescribed by a doctor. Self-selecting medications can lead to negative health consequences.
Vitamin intake
In case of chronic colitis, in addition to medications, vitamins of groups C, B, PP, and U are prescribed. These organic compounds are consumed orally, parenterally, or in the form of injections. Injections are given with some B vitamins.
B1 is used to better cleanse the body.
Vitamin B3 improves the production of stomach acid and harmonizes the functionality of the intestinal tract.
U is used as a building material. With its help, damaged areas of the intestine are restored. PP involves the secretory activity of the human stomach.
Nutritional Features
When treating colitis, following a diet is almost the most important component of recovery. If you have an intestinal disease, you can eat the following foods:
- Yesterday's coarse wheat bread, crackers. Fresh white bread and baked goods increase the production of gases, peristalsis accelerates - this will negatively affect the patient’s condition.
- Soup, porridge with water, vegetable broth. Soup and not only animal fats burden the work of the stomach, intestines, and liver.
- Meat, fish in the form of steamed cutlets.
- Consume low-fat dairy products.
- Confectionery in moderation.
- Tea, cocoa, soft coffee.
- No more than two spoons of sugar per day, a few sweets.
It is worth giving up:
- legumes, pasta - cause excessive gas formation;
- raw fruits and vegetables – fiber enhances peristalsis;
- canned food, pickles, smoked, pickled - these products irritate the intestinal lining and cause inflammation;
- fast food;
- spices, seasonings.
It is known that treatment of colitis with medications is an integral part of the fight against this disease. It is necessary to consider in more detail the various cases of manifestation of colitis and select medications that correspond to them.
Colitis - general information
Intestinal colitis is a serious gastroenterological pathology that requires medical attention. Today, pharmacists offer a wide selection of drugs, the use of which will help stop the inflammatory process and normalize digestion. However, you cannot prescribe them for yourself. Remember that treatment of intestinal colitis should be an exclusively medical matter.
Taking medications is an integral part of such therapy. In this material we will talk about how chronic intestinal colitis is treated with medications, and also consider the most effective drugs (list) with which you can relieve the symptoms of this pathology.
The disease is the presence of inflammation on the mucous membrane of the digestive organs.
The inflammatory process leads to the destruction of the organs of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as to disruption of the integrity of their tissue surface.
Intestinal colitis can occur in 2 forms: acute and chronic. The first requires urgent treatment measures, because the manifestation of symptoms in this type of pathology deprives the patient of working capacity.
Characteristics of the disease
Colitis is a local inflammation that occurs on the mucous membrane of the colon, resulting in disturbances in the absorption and motor functions of the intestine. Separately, it is worth highlighting spastic colitis, which is long-term painful intestinal spasms.
Detection of this disease requires not only medication, but also a complete adjustment of a person’s lifestyle. First of all, you need to follow a complex diet.
Men over 40 years of age and women over 20 years of age are most susceptible to the disease.
To make a preliminary diagnosis, a stool test is required. To clarify the diagnosis, the doctor prescribes endoscopic examinations, such as retromanoscopy and colonoscopy.
Diagnosis of nonspecific ulcerative colitis
Diagnosis begins with an examination of the patient, identification of complaints and medical history, a detailed interview with the patient, including, in particular, collection of information about trips to southern countries, intolerance to any foods, medications taken (in particular, antibiotics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)), smoking and the presence of inflammatory and malignant bowel diseases in relatives. Laboratory diagnostic methods
- Complete blood count, hematocrit, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), C-reactive protein, hemocoagulogram, total protein, albumin, liver tests, electrolytes. In the acute course of UC (the first attack of the disease), it is necessary to perform a bacteriological and microscopic examination of stool to exclude acute intestinal infection. Both at the onset of the disease and during exacerbations, a study of C. difficile toxins A and B is recommended.
- Changes in laboratory parameters in UC are usually nonspecific. Anemia, leukocytosis, and electrolyte changes in the blood may occur.
Instrumental diagnostic methods
- Examination of the perianal area, digital examination of the rectum, sigmoidoscopy.
- Plain radiography of the abdominal cavity to exclude complications.
- Colonoscopy
with ileoscopy is a mandatory procedure to establish the diagnosis of UC, as well as to decide on colectomy. - A biopsy of the colon mucosa is also required during the study in most cases.
- Ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs, retroperitoneal space, pelvis.
- If it is impossible to conduct an endoscopic examination of the colon and ileum, it is possible to perform a computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging with ascertainment of the intestine.
For additional indications the following is carried out:
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy;
- video capsule endoscopy;
- single or double balloon enteroscopy.
Treatment of nonspecific ulcerative colitis of the intestine
Treatment options for UC include medications, surgery, psychosocial support, and dietary advice.
Mild and local forms of the disease can be treated on an outpatient basis; moderate and severe forms of the disease require hospitalization:
- Diet and its regularity are important. In remission, the diet should contain a sufficient amount of plant fiber, fresh vegetables and fruits. Patients with UC do not need significant restrictions during the period of remission. During the period of exacerbation and diarrhea, it is possible to limit foods that stimulate motility (dairy, fermented milk, fresh vegetables and fruits).
- Depending on the form and severity of the disease, anti-inflammatory drugs, hormones, immunosuppressants, antibiotics, and biological therapy can be taken alone or in combination.
Some complications of the disease require surgical treatment. We are talking about the following conditions:
- perforation of the intestinal wall,
- toxic intestinal dilatation,
- intestinal stenosis,
- bleeding,
- malignant neoplasms.
Surgical treatment of ulcerative colitis can also be used in cases of severe disease and ineffective therapeutic treatment.
Eliminating the causes of illness
To identify the causes of colitis, the doctor will need to collect information about the patient’s condition. To do this, he will ask him some questions about his health, and also write a referral for tests.
If spastic colitis has been diagnosed, then most often it is enough to adjust the diet and diet.
In the case where the cause of the disease is parasites that have settled in the intestines (for example, worms), the patient is first prescribed medications to destroy them. These drugs include Albendazole, Azinox, Vormil or Dekaris. They effectively destroy all protozoan parasites.
If the patient has other problems with the gastrointestinal tract, the doctor should prescribe their diagnosis. It is often possible to cure colitis and other problems in this area with medications alone.
Regardless of the cause of the disease, the patient is recommended to follow a strict diet, limit exercise, and abstain from smoking and alcohol. Medicines used for other diseases may also be discontinued.
Benefits of rectal suppositories
Unlike local and systemic drugs for proctitis and colitis, rectal suppositories are effective against any form of inflammation of various parts of the intestine, due to the targeted effect of active medicinal components. The drugs directly affect the affected area, disinfect and create a protective film on the mucous membranes. The main advantages of rectal suppositories are:
- no negative effect on the gastrointestinal microflora;
- maintaining the therapeutic effectiveness of the drug components inside the intestine;
- speed of directed influence;
- ease of use in children and adults;
- dosage accuracy. Suppositories for treating the intestines are easily inserted into the anus without causing any discomfort.
Despite the absence of absolute contraindications, independent use of drugs is unacceptable. Inadequate dosage can contribute to traumatization of mucous membranes, persistent diarrhea and complicate the recovery process.
Use of antibiotics
Treatment of intestinal colitis with antibiotics is recommended only when therapy does not seem effective without their use. In addition to parasitic microorganisms in the intestines, any antibiotic destroys all beneficial microflora. At the same time, the presence of an inflammatory process on the mucous membrane of the colon is itself poorly tolerated by the intestinal microflora. When an antibiotic acts on weakened microorganisms, their death exceeds all permissible values. In other words, the patient begins to develop dysbacteriosis, which progresses rapidly.
Treatment without antibiotics can be done if the diagnosis is spastic colitis. In other cases, as a rule, the use of antibiotics is necessary. In this case, sulfonamides are prescribed as medicine, for example, Fthalazol and Sulgin. They are used strictly as prescribed by the doctor. Most often they are prescribed according to the following scheme:
- the first period of active suppression of inflammation (the number of days when taking it depends on the neglect of the process and the body’s own resistance) - 6 times a day;
- the second period of suppression of residual inflammation (2 days) - 4 times a day;
- the third period is consolidating (2 days) - 3 times a day.
Similarly, the patient can be prescribed targeted antibiotics that specifically target the pathogenic intestinal microflora.
Attention should be paid to antibiotics containing hydroxyquinoline. Their peculiarity is their effect on microorganisms that are resistant to other antibacterial drugs. As an example, we can mention Intestopan and Enteroseptol. The dosage and regimen depends on the course of the disease. The disease will have to be treated for 10-12 days.
Benefits of using suppositories
Along with food, various bacteria enter a person. If they are pathogenic and enter in large quantities, then an unfavorable environment for pathologies is created.
Any injury to the mucous membrane and the presence of pathogenic microflora in combination cause inflammation. Colitis is a disease of the intestinal mucosa characterized by an inflammatory process.
The disease must be treated comprehensively. Rectal suppositories for colitis act effectively, quickly alleviate the human condition and are easily tolerated by the body. It should be noted that the contraindications for such drugs are minimal, as are the side effects.
That is why they are prescribed to pregnant women, during lactation and even to children.
Objectives of suppositories:
- Return normal stool.
- Alleviate the patient's condition.
- Restore cell regeneration.
- Make it easier to defecate.
At the same time, it is very important to understand that all therapy must be prescribed by a doctor.
Since colitis has the same symptoms as many other intestinal pathologies, only a specialist can identify the real disease, focusing on diagnostic results.
Choosing any drug is a responsible matter. Only adequate dosage and correctly selected medicine will bring the desired result in the treatment of intestinal colitis.
This is especially true for suppositories that have a laxative effect. Constant loose stools prevent the intestinal mucosa from recovering, so here the help of a specialist who will determine the dose is most welcome.
Suppositories for intestinal colitis – advantages:
- Quick results.
- Minimum contraindications and side effects.
- They act directly on the source of inflammation.
- Safe for children and pregnant women.
- They have regenerating and restorative properties.
Formation of microflora
During treatment with antibiotics, the intestinal microflora is seriously damaged. Therefore, after completing their course, it is necessary to conduct a restorative course of treatment of dysbiosis and enzymatic disorders. For this purpose, your doctor will prescribe probiotics. They are not a medicine.
In addition to restoring intestinal microflora, these drugs help remove toxins. As a result of their intake, stool normalization occurs, gas formation decreases and appetite improves.
There are many different probiotics available today. The essence of their action is the same. The differences lie in slight fluctuations in the doses of active substances, flavoring additives and manufacturing companies. When choosing a drug, you should rely on the doctor’s advice or purchase it based on the price range.
The most frequently recommended are: Bifidumbacterin, Lactobacterin, Probifor, Lactofiltrum, Bifiliz and some others.
With dysbacteriosis, all kinds of enzymatic disorders are often observed. To combat them, drugs containing pancreatin are prescribed. The most common among them are Mezim, Festal and Panzinorm.
Problems with intestinal motility
With any colitis, spasm of intestinal smooth muscles often occurs. To eliminate this condition, antispasmodic drugs are used, for example No-shpu, Drotaverine or Papaverine. For a more effective effect, it is possible to use Platiphylline.
To improve motor skills, take Motilium or Cerucal.
In case of diarrhea, astringents are recommended. The most common and completely safe among them is calcium carbonate.
In case of constipation, mild laxatives that are not irritants to the intestinal mucosa can be used. Vaseline oil is considered the safest drug, which, when taken orally, coats the colon mucosa and facilitates the movement of feces due to their softening.
If the patient experiences flatulence, it is recommended to use such remedies as infusion of fennel or chamomile fruits, calcium carbonate or Carbolen.
Another problem with irritable bowel syndrome is the excess mucus produced by the intestinal wall as a protective response to the presence of inflammation. Its excess worsens already poor peristalsis. To combat it, astringents are used. These include Phosphalugel, Almagel and some others. To bind excess mucus, substances that adsorb it are used. These include calcium carbonate and bismuth compounds.
Vitamin support for the body and antidepressants
Colitis can be quite painful for a person. As a result of internal discomfort, irritability develops, a persistent feeling of fatigue, and insomnia. To normalize the patient’s condition, it is desirable that therapy include sedative and mild sedative tablets, for example, Persen or Glycine.
To reduce the burden on the body, patients are often recommended to take B vitamins, primarily B6 and B12. They are most often prescribed in the form of tablets or ampoules for oral administration. It is possible to administer injections, but they are very painful.