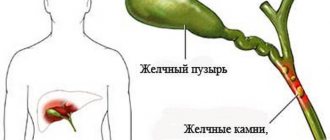
What is cholecystopancreatitis
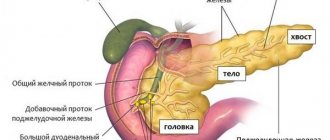
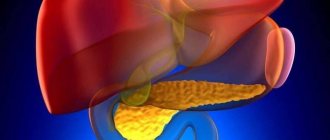
Cholecystopancreatitis is a simultaneous disorder in the functioning of the gallbladder and pancreas, accompanied by an inflammatory reaction.
The process is synchronous, with damage to adjacent organs of the hepatobiliary system. These are pancreatitis and cholecystitis, which began to develop simultaneously for different or related reasons.
Diet for pathology
If the patient does not follow a diet, he will continue to be bothered by the symptoms of cholecystitis for a long time. This is due to the fact that most gastrointestinal diseases occur precisely because of malnutrition. Doctors recommend that even healthy people eat small portions, chewing thoroughly. The last meal should be no later than 3-4 hours before bedtime.
For pancreatitis and cholecystitis, first of all you need to avoid fried, spicy and fatty foods. It is recommended to exclude salted and smoked foods, canned food, sausage, chocolate, cocoa and all drinks containing alcohol.
It is strongly recommended to eat cottage cheese, fermented milk products, stewed vegetables and fruits, steamed meat and fish, and various cereals. You can drink jelly and compotes.
All food that the patient eats should be “light”, quickly digested and not overload the digestive organs.
ICD-10 code
In the international classification of diseases, cholecystopancreatitis is assigned a place in class 11 (diseases of the digestive organs). The disease is in the group K80-K87 - Diseases of the gallbladder, biliary tract and pancreas.
The ICD has its own code K87.0 “Lesions of the gallbladder, biliary tract and pancreas in diseases classified in other headings.”
Treatment
The drugs that are prescribed to the patient for this disease are: antibiotics; painkillers (baralgin, analgin); metabolic drugs (methyluracil); enzymatic agents (pancreatin, festal); means of suppressing juice secretion (cimetidine, omeprazole). Nutrition for illness should be normalized, and certain categories of foods should be excluded. Therefore, nutrition for this disease requires a careful approach - a person needs to completely rebuild his diet in order to avoid repeated exacerbations of the disease.
Folk remedies have a good effect on the digestive organs, so treatment with them is quite justified, but only in combination with diet and drug therapy. As for physiotherapy, it is prescribed purely individually, depending on the severity of the process and the form of the disease. Moreover, in the acute stage it is contraindicated, and in chronic cholecystopancreatitis it is carried out only in the remission stage. Sometimes the only possible method of eliminating pathology is surgical treatment.
Drug treatment
For chronic cholecystitis and pancreatitis, medications are prescribed: antibiotics, painkillers, metabolic agents and enzymatic:
- To relieve pain and improve the functioning of the gallbladder, antispasmodics are prescribed. This is Papaverine, Analgin.
- To improve digestion and produce a sufficient amount of enzymes - Creon, Pancreatin.
- To reduce the production of glandular secretions - Omeprazole.
- Antibacterial drugs – Metronidazole.
- To restore intestinal microflora - Hilak.
All these remedies cannot be used independently; they must be agreed upon in advance with a doctor.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is often used in the treatment of cholecystopancreatitis.
The most effective:
- medicinal electrophoresis;
- reflexology (impact on active points);
- exposure to alternating current;
- magnetotherapy.
Physiotherapy procedures are carried out after the disappearance of pain in the remission phase. For inflammation of the gallbladder and pancreas, mud therapy, hydrotherapy and sanatorium treatment are useful.
Surgical intervention
In case of repeated inflammation, surgery is advisable. This means that gallbladder surgery must be performed within 24 hours of hospitalization.
Acute inflammation of the gallbladder can be cured without surgery. However, complications often occur after conservative therapy. In 30% of cases of treatment of chronic cholecystopancreatitis, the doctor prescribes surgery.
After removing the organ, the abdominal cavity is washed to completely remove the leaked bile.
For older people or those at increased surgical risk due to concomitant diseases, surgery may be postponed to a later date.
Diet therapy for cholecystopancreatitis
Adults should definitely follow proper nutrition. With the pathology of chronic cholecystopancreatitis, diet is a way of life.
In the acute form of the disease, doctors sometimes allow you to deviate from the rules they have established in terms of nutrition, but this should not be abused.
What does following a diet mean? First of all, this is the exclusion of harmful products. To create a diet, contact your doctor. Here it is important to take into account the course of the disease, the presence of concomitant ailments, test results and the patient’s taste qualities.
Diet is an important stage of treatment. However, this method cannot act as monotherapy. Diet alone will not help cure cholecystopancreatitis.
The meal schedule should be calculated immediately. It is recommended to eat every 2.5–3 hours. For example, breakfast should be 30% of the daily diet, second breakfast - 10%, lunch - 30%, afternoon snack - 15%, dinner - 10%.
Following a diet helps not to overeat, eat well, do not burden the stomach and stop the inflammatory process.
Approximate diet menu:
| Monday | Tuesday | Wednesday | Thursday | Friday | Saturday | Sunday |
| 3 egg whites, oatmeal with water, weak tea, crackers or biscuits | oatmeal, crackers and chamomile infusion | potato omelette, steamed cutlet, soft-boiled egg, tea | soft-boiled egg, macaroni and cheese, tea with milk | steam omelette with vegetable salad, buckwheat porridge with milk, a glass of warm tea with lemon | semolina porridge, green tea, cheesecakes in honey sauce | a portion of oatmeal, cottage cheese and crackers, jelly |
| a glass of kefir or low-fat cottage cheese | marshmallow and mint tea | rosehip decoction with caramel | chamomile tea with dry biscuit | biscuits and low-fat milk | fruits | vegetable salad, meringue |
| vegetable soup, a piece of rabbit or other lean meat, semolina | carrot puree, beef cutlet, rosehip infusion | meatball soup, baked fish in lemon sauce, green tea | baked apples, vegetarian soup, milk | jelly or crackers with kefir, mashed potatoes with butter, yogurt | celery soup, steamed fish, buckwheat porridge and vegetable salad | pumpkin puree soup, compote, meringue |
| glass of kefir with biscuit | jam from non-acidic berries with a piece of yesterday's bread and tea | afternoon snack - baked apples | cottage cheese casserole | curd soufflé, jelly | tea with lemon and steam omelette | apples baked with cottage cheese |
| dried fruit compote, not sweet jam | a glass of low-fat homemade yogurt, biscuits | 200 ml low-fat kefir or milk | vegetable salad of tomatoes and cucumbers, tea with lemon | cup of kefir | curdled milk and baked meat pie | low-fat cottage cheese, tea with lemon |
To create a weekly diet, you need to know what foods are prohibited to use and in what form the food is prepared.
Patients with cholecystopancreatitis are recommended to take pureed food. Steam, bake, boil. It is not advisable to use meat broths.
Spicy foods, smoked meats, pickles, and ready-made store-bought foods (soups in briquettes, instant porridges) are not allowed. It is forbidden to eat fresh bread, fatty meat, cream, legumes, drink coffee and alcohol.
The list of prohibited foods also includes pickled foods, animal fats, baked goods and mushrooms.
Traditional methods
Treatment of chronic cholecystitis and pancreatitis using traditional methods will help.
The most common of them are:
- Infusions of wormwood and yarrow. To do this, take 1 tsp. each of the herbs is poured with a glass of boiling water. You need to infuse the decoction for about 30 minutes, then strain and take half of it 3-4 times a day.
- Infusions of violet, mint, linden, St. John's wort, chamomile. To do this you will need to take 1 tsp. each of them and pour 500 ml of boiled water. Leave for half an hour, strain and take 1 glass 3 times a day before meals.
- Infusions of wormwood, St. John's wort and mint. These herbs have high medicinal properties. They have proven themselves excellent in the treatment of cholecystopancreatitis. To do this you will need to take 1 tsp. each herb and pour all 0.5 liters of boiling water. Leave for 20 minutes, strain and take 1 glass 2 times a day on an empty stomach.
- Leaves of the Golden Whisker. Grind 2-3 leaves of the plant, pour 500 ml of boiling water, boil over medium heat for 10-15 minutes. Leave for 8 hours. It is recommended to drink warm tincture 3 times a day before meals, 50 ml. Course 30 days. This treatment helps relieve inflammation of the biliary tract and is used for gallbladder diseases.
- Strawberries. Pour boiling water (250 ml) over wild strawberry roots (1 tablespoon). Let it brew for 1 hour. Drink 100 ml morning and evening. Used for cholecystitis, gastritis, and pancreatitis.
- Dill. Dill water is used for problems with the gastrointestinal tract. Pour boiling water over the dill seeds and let it brew. Drink 100 ml 3 times a day. Ready-made dill water can be purchased at the pharmacy.
In addition to drug treatment of chronic cholecystopancreatitis, rose hip decoction, flaxseed oil, and a mixture of castor oil with any freshly squeezed juice are used. All this must be taken 30 minutes before meals. To cleanse the gastrointestinal tract, ginseng, nutmeg and basil are added to food.
Classification
There are several ways to classify cholecystopancreatitis. The latter was proposed in 1978. This classification method provides for possible combinations of diseases of the biliary tract and pancreas.
Highlight:
- acute inflammation of the walls of the gallbladder with reactive edema of the pancreas;
- acute cholecystitis with focal pancreatitis;
- total destructive cholecystopancreatitis;
- the occurrence of stones not only in the bile duct itself, but also in the common bile ducts, accompanied by an acute aseptic inflammatory reaction in the pancreas;
- a complication of acute pancreatitis with the development of multiple organ failure, accompanied by acute reactive cholecystitis.
This classification is important in determining treatment tactics.
Principles of therapeutic nutrition
The main effort for successful treatment of pancreatitis is applied to proper nutrition of the patient. You must adhere to a strict diet. This is required in the acute phase of the disease.
In the first days of the acute phase of the disease, the patient is prescribed a starvation diet. On the second day, you are allowed to drink water without gases and a weak rosehip decoction. Gradually, liquid vegetable soups are added to the menu, and then semi-liquid dishes - purees and porridges. The patient's diet is expanded to include stewed and boiled vegetables and lean meats and fish. Fermented milk products are useful.
Spicy and salty foods, as well as fatty and smoked foods are strictly prohibited. It is necessary to give up coffee, chocolate and cocoa, as well as fatty and sweet confectionery products.
It is useful to cook porridge with low-fat milk and bake or stew vegetables and dietary meats. Cook food by steaming or in a water bath. It is better to remove the skin from poultry meat first. It is better to give preference to chicken, nutria or rabbit meat, as well as veal.
Fruits are gradually added to the diet, but not sour ones and only ripe ones. At first, it is allowed to eat baked apples and pears, as well as pumpkin. As the condition improves, they gradually move on to fresh fruits in small quantities.
Wheat white bread is not recommended to be eaten fresh - it is better to give preference to yesterday's products. Unsweetened biscuits and crackers are welcome.
Causes of cholecystopancreatitis in adults
Unlike most inflammations that can occur in other parts of the body, cholecystopancreatitis is not always the result of an infection.
Stones in the bile ducts and the bladder itself are one of the main causes of cholecystopancreatitis.
If the gallbladder fails to empty properly (for example, due to scarring, injury, or obstruction), bile accumulates and stones form.
Stones block the duct partially or completely, which leads to the development of an inflammatory process.
Secondary common causes:
- infection with bacteria that penetrate the liver and blood;
- endocrine diseases such as diabetes mellitus type 1 or 2 and HIV can cause swelling of the bile and pancreas;
- Cancer diseases can also affect the development of a simultaneous inflammatory reaction in the pancreas and gall bladder. In these cases, the pathology is formed due to the blocking of the bile ducts by the tumor;
- stomach ulcer and the presence of parasites in the body.
Risk factors for the disease include: age (over 60 years), estrogen replacement therapy, consumption of fatty foods.
Treatment with folk remedies
Some traditional methods can alleviate the condition during exacerbation of cholecystopancreatitis. But they should be practiced under the supervision of a doctor and only after his approval.
- Infusion of yarrow and wormwood. To prepare this remedy, you need 1 tsp. Pour 1 cup of boiling water over each herb and leave for about half an hour. Drink 1 glass twice a day on an empty stomach.
- An infusion of mint, St. John's wort and wormwood. Take 1 tsp. each type of raw material and pour 2 cups of boiling water. Leave for half an hour, drink 1 glass twice a day before meals.
- Infusion of St. John's wort, chamomile, tricolor violet, linden blossom and mint. Take 1 tsp. each herb and pour 0.75 liters of boiling water over everything. After infusing for half an hour, drink a glass of the product on an empty stomach. Drink 1 glass twice a day.
- Linseed oil. Helps cleanse the gallbladder. To do this, you regularly need to take 1 tbsp. l. oil in the morning or add it to dishes.
- Infusion of celandine. To prepare it, you need to take one part of celandine, two parts each of tansy flowers, toadflax and peppermint leaves, four parts each of dandelion roots and erect cinquefoil. The ground mixture should be poured with boiling water at the rate of one glass per tablespoon. After infusing for half an hour, the product must be strained. Drink about a third of a glass three times a day, half an hour before meals. The course of admission is three weeks.
- Corn silk tea. 1 tbsp. Pour a spoonful of the product into 1 glass of water and bring to a boil. Drink a quarter glass four times a day before meals. At the same time, follow a diet.
Complications
Lack of treatment for chronic cholecystopancreatitis or its acute form leads to serious consequences.
Complications such as:
- pancreas cancer;
- reactive hepatitis;
- pancreatic necrosis of the pancreas.
As a result of the progression of pathologies, absorption is impaired and obstructive jaundice develops.
Treatment methods
Mineral water will help relieve the acute form of chronic cholecystopancreatitis.
To relieve the acute form of chronic cholecystopancreatitis, it is prescribed to drink hydrocarbonate-chloride mineral water, 250 g five times a day.
A diet without fatty, spicy foods, soda and sour apples, smoked meats, marinades, strong tea and coffee is recommended. Meals should be fractional and gentle on inflamed organs. Drug treatment is as follows:
- To block pain and improve the movement of bile and pancreatic juice, antispasmodics (papaverine, duspatalin) and analgesics (injectable analgin and tramadol) are used.
- To ensure normal digestion, drugs are used - enzymes (Creon, Pancreatin), which are taken before meals.
- To reduce the production of gland secretions, medications such as omeprazole and pantoprazole are allowed.
- Antibacterial agents are used (metronidazole, azithromycin).
- To restore the intestinal microflora, they are prescribed (bifiform, hilak).
Physiotherapy is prescribed:
- laser therapy;
- low-intensity UHF procedure;
- high frequency UHF.
Procedures to relieve pain:
- diadynamic therapy;
- cryotherapy;
- Ural Federal District.
Measures to relieve muscle spasms:
- high frequency magnetic therapy;
- electropheresis with antispasmodics (no-spa, papaverine);
- applying paraffin to areas.
Diagnostics
For diagnosis, along with physical examination, various laboratory tests and imaging methods are used.
To confirm the pathology, blood tests are prescribed. In the presence of an inflammatory process, some indicators will change. Acute cholecystopancreatitis is characterized by the following symptoms:
- increased number of leukocytes;
- acceleration of ESR;
- the concentration of C-reactive protein increases.
The trigger for the development of gallbladder inflammation, usually stones, causes stagnation of bile. Then the level of total bilirubin and alkaline phosphatase in the blood increases. ALAT, ASAT, GGT are higher than normal in the development of a disease such as acute cholecystopancreatitis.
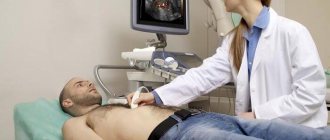
The standard imaging procedure for diagnosing inflammation is ultrasound. The doctor looks at the ultrasound:
- whether the bladder wall is supplied with blood;
- whether there are stones in the gall bladder;
- the gallbladder wall is perforated or not;
- whether a liver abscess has formed.
Additional CT scans indicate possible causes and complications. X-ray examination is not useful for cholecystopancreatitis, since the majority of gallstones (more than 85%) cannot be detected on the image.
Clinical symptoms
The clinical picture of pancreatitis and cholecystitis reveals pronounced and severe symptoms.
- The main clinical manifestations are the occurrence of a dull aching pain in the abdominal area.
- Pain with pancreatitis is girdling in nature or limited to the right hypochondrium.
- Symptoms usually appear several hours after eating. The attack is triggered by eating spicy or fatty foods.
- Sometimes severe, uncontrollable vomiting develops.
- The pain radiates to the right shoulder blade or shoulder.
- A common clinical sign is dryness and bitterness in the mouth, bitter belching.
- With pancreatitis, the abdomen is often swollen.
- Stool disorders manifest themselves in the form of constipation or diarrhea.
The disease begins acutely, the course is protracted and chronic. Periods of exacerbations are followed by periods of remission.
Objective examination data
Upon examination, the doctor finds objective signs of the disease:
- On palpation, the patient complains of pain in the epigastrium and right hypochondrium.
- The liver is enlarged on palpation and protrudes from under the edge of the costal arch.
- Ortner's and Mussi-Georgievsky's symptoms are considered characteristic signs.
Forms of the disease
Depending on the clinical course, it is customary to distinguish two forms of the disease - purulent-ulcerative, which exhibits an acute, severe course, and a protracted, sluggish form of the process. If you detect at least some of these signs, you should immediately contact a doctor.
To clarify the diagnosis of pancreatitis, the doctor will prescribe a series of clinical and laboratory and instrumental studies. Ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging acquire diagnostic significance. The latest types of diagnostics are used much less frequently due to their high cost.
The diagnosis can be confirmed using a biochemical blood test, urine tests and coprogram.
Treatment of cholecystopancreatitis
The effectiveness of treatment primarily depends on the patient himself. It is important not only to take prescribed medications, but also to limit yourself from stressful situations, follow a healthy diet and lead a healthy lifestyle. All risk factors that aggravate the course of the disease should be excluded.
Drug therapy
Treatment in adults involves the use of painkillers, antacids, enzymes and vitamins.
The symptoms of cholecystopancreatitis will not improve if proper nutrition is neglected along with drug therapy.
Forecast and prevention of cholecystopancreatitis
Chronic and acute cholecystopancreatitis responds well to treatment. With timely assistance, the pathological condition enters the relapse stage.
How long the disease will remain in a chronic state without manifestation of the inflammatory process depends on compliance with preventive measures:
- proper nutrition;
- weight loss;
- the right way of life.
The prognosis for acute and chronic disease is good. Rarely does the disease end in death. In most cases, patients manage to maintain a relapse by visiting a doctor on time and undergoing sanatorium treatment.
Need to know
Painful sensations in chronic cholecystopancreatitis can be caused by:
- inflammatory processes near nerves;
- pancreatic tissue destruction, which can be triggered by various factors;
- narrowing of the bile duct.
A disruption in the production of certain hormones can cause a chronic illness, in which the process of digesting fats can be significantly disrupted, which is why they can even be excreted in unprocessed form along with feces.
At the initial stages of development of inflammatory processes of the pancreas, the patient may have impaired glucose tolerance.
It may not cause any symptoms at first and can only be detected by laboratory tests.
If you seek medical attention promptly, a diagnosis can be made before your blood sugar levels rise above normal.
One of the main signs of high blood sugar is deformation of the fundus vessels.
In severe cases, when lactic acid accumulates in the gastrointestinal tract, the patient may experience signs of complications of diabetes mellitus. If the blood glucose level reaches 200 mg/dl, the patient experiences damage to the nerve fibers, nervous system disorders, and mental illness may occur.
There are also more rare symptoms indicating a disease such as chronic cholecystopancreatitis:
- yellowing of the skin;
- ascites;
- protrusion of the pleural part;
- formation of false cysts;
- arthritis, which affects the small joints of the hands.
According to nosology, deaths are 50%
Therefore, it is important not to self-medicate. Only a doctor knows how to treat these diseases correctly
The likelihood of death may increase if the patient has the following complications:
- formation of blood clots in the veins;
- significant obstruction of the bile duct;
- the presence of malignant neoplasms in the pancreatic duct;
- damage to peripheral nerve fibers;
- diseases of the endocrine system.
When examining a patient with chronic cholecystopancreatitis, the doctor may detect a white coating on the tongue, “seizures” in the corners of the mouth, excessive dryness of the skin, and delamination of the nail plates. The presence of red spots on the abdominal cavity may indicate poor circulation.