General information
Inflammation in pancreatic cells occurs in an acute form or periods of remission are combined with relapses. In case of severe dysfunction of an important organ, iron produces a smaller volume of enzymes, which leads to the appearance of negative signs.
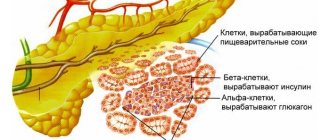
With a lack of pancreatic hormones (glucagon, insulin), jumps in blood sugar levels occur. Stagnation causes a negative effect on the walls of the gland, and inflammation develops. Difficulties digesting food lead to poor health, bloating, diarrhea, pain, nausea, periodic vomiting, and weight loss.
In the absence of disturbances, enzymes do not have a negative effect on the mucous membrane. If the timely outflow of digestive juices does not occur, then caustic substances corrode the gland tissue, and the process of cell destruction begins.
Untreated pancreatitis (ICD code 10 K86) causes complications: inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis), abscess and phlegmon of the pancreas. Dangerous conditions are possible: intraperitoneal bleeding, necrotization of tissue of an important organ, peritonitis. If treated incorrectly, pancreatitis becomes chronic, increasing the risk of developing diabetes mellitus due to impaired insulin production.
Pancreatitis
Multislice computed tomography (MSCT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the abdominal organs, sometimes with contrast, which allows for a more detailed assessment than ultrasound of the size and structure of the pancreas, the condition of its ducts, the presence of complications, and to exclude pathology of other abdominal organs cavities. Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) of the abdominal organs is a highly informative method, even with minimal changes in the pancreas, used to determine indications for surgical treatment.
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP), which involves a combination of radiological and endoscopic instruments to assess the condition of the pancreatic duct and its branches. The study allows you to obtain pancreatic secretions, as well as carry out a number of therapeutic manipulations - dilate the ducts, remove a stone, etc.
Endoscopic elastography of the pancreas makes it possible to determine the stiffness and rigidity of the tissue, assess the degree of fibrosis (irreversible changes) and the exocrine function of the pancreas.
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) is performed to assess the condition of the mucous membrane of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum.
Which doctors should I contact?
The diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic pancreatitis is carried out either by general practitioners or by doctors.
It is important to understand that the cause of abdominal pain can be not only diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, but also cardiological, urological, gynecological diseases, as well as lesions of the musculoskeletal system.
Any abdominal pain necessarily requires a medical examination to determine treatment tactics. Treatment of pancreatitis
A prerequisite for the treatment of acute and chronic pancreatitis is the cessation of drinking alcohol and smoking.
During the period of exacerbation of the disease, fasting is recommended. During the subsidence of the exacerbation and during the period of remission, patients are advised to eat nutritious meals 5-6 times a day in small portions.
Preference should be given to foods high in proteins and complex carbohydrates, dietary fiber, and vitamins. The decision to limit fat is made individually.
Drug therapy includes several groups of drugs.
Painkillers can be taken only after examination by a doctor - if pain occurs (as needed) or as a course.
If the pancreas does not produce enough enzymes, the doctor prescribes enzyme replacement therapy.
Drugs that reduce the secretion of hydrochloric acid in the stomach and lead to a decrease in the production of pancreatic juice are indicated to relieve exacerbation of pancreatitis.
In addition, the doctor may recommend taking vitamins and antidepressants (to reduce the symptoms of depression and the severity of pain). With the development of diabetes mellitus, carbohydrate metabolism disorders are corrected.
In some cases, surgical treatment may be required.
Complications
The most common complications of pancreatitis are considered to be cholestasis (impaired outflow of bile), infectious diseases (phlegmon and abscess of the pancreas, septic conditions), rupture of the pseudocyst (fluid-filled cavity) and pancreatic duct, intra-abdominal bleeding, erosions (superficial defects of the mucous membrane) and ulcers in the esophagus, stomach and duodenum, pancreatic adenocarcinoma, diabetes mellitus, carbohydrate metabolism disorders, malabsorption of nutrients.
A variety of cardiovascular, pulmonary, hematologic, and metabolic complications are possible.
Prevention of pancreatitis
To prevent exacerbation of pancreatitis, it is recommended to eat at least 4-5 times a day in equal portions and not to overeat. The diet should be varied and include a sufficient amount of dietary fiber, which is found in grains, vegetables and fruits. Animal fats (fatty meats, rich soups, high-fat dairy products) should be limited.
An important component of preventing pancreatitis is limiting alcohol consumption and quitting smoking.
Sources:
- V.T. Ivashkin, I.V. Maev, A.V. Okhlobystin et al. Recommendations of the Russian Gastroenterological Association for the diagnosis and treatment of chronic pancreatitis. Russian Journal of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, Coloproctology No. 4, 2014, p. 70-97.
- Clinical recommendations. Chronic pancreatitis in adults. Russian Gastroenterological Association, 2021.
- THOSE. Polunina. Chronic pancreatitis: exocrine insufficiency and its correction. Attending physician No. 6, magazine, 2021, p. 71-77.
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor.
Causes
In most cases, the inflammatory process in the pancreas develops against the background of gallbladder pathologies. Most often, pancreatitis is combined with gallstone disease.
Another reason for damage to an important organ is alcohol abuse. The risk of inflammation and toxic poisoning increases when drinking cheap, low-quality alcohol.
What is hyperprolactinemia and how to treat the disease?
Read useful information. How to drink Duphaston? Instructions for using the hormonal drug are described on this page.
There are other factors that provoke the development of pancreatitis:
- hormonal imbalances,
- unhealthy diet: excess carbohydrates and fats, frequent consumption of marinades, pickles, smoked foods, fried foods, baked goods,
- pathological processes in the duodenum,
- wounds and injuries in the abdominal area,
- viral hepatitis, mumps,
- genetic predisposition,
- long-term smoker experience,
- elevated levels of triglycerides in the blood,
- long-term use of estrogens, sulfonamides, antibiotics, diuretics,
- the presence of helminthic infestations in the body,
- metabolic problems,
- tumor lesions, narrowing of the pancreatic duct,
- underwent surgery on the pancreas,
- chronic vascular diseases.
Note! In a third of patients, doctors cannot identify the exact cause of the inflammatory process.
Causes
There are many etiological factors leading to the development of acute pancreatitis, the most common are:
- Pathology of the biliary system (60% of all cases). The excretory ducts of the gallbladder and pancreas have a common duct. Consequently, any pathology of the biliary tract (calculous cholecystitis, papillitis, etc.) can cause a violation of the outflow of pancreatic juice. The secretion with numerous enzymes begins to linger and cause breakdown of the gland tissue.
- Traumatic lesions of the pancreas.
- Pathologies of the duodenum. With a peptic ulcer, penetration (a breakthrough into the tissue of another organ) of the ulcer may occur.
- Alcohol abuse and frequent consumption of fatty or spicy foods. Such products create an increased load on the organ, during which an acute inflammatory process can occur.
- Penetration of bacteria and viruses (for example, Coxsackie) into organ tissue by hematogenous, lymphogenous or ascending routes.
- Taking medications (thiazide diuretics, azathioprine, prednisolone, etc.) that have a pronounced pancreatotoxic effect. Against the background of massive necrosis of organ cells, inflammation develops.
- Congenital developmental defects. Any anomalies can disrupt the adequate functioning of the organ and lead to stagnation of enzymes.
- Genetically determined predisposition.
Expert opinion
Shoshorin Yuri
General practitioner, site expert
Less commonly, the cause is autoimmune diseases, disorders of the blood supply to the organ (atherosclerosis, thrombosis), allergic reactions, tumors. Up to 10% of all cases of pancreatitis remain unrecognized.
Symptoms
The main sign of inflammation of the pancreatic tissue is pain. In the acute form, the manifestations are so painful that some patients cannot move due to painful colic, and loss of consciousness due to painful shock is possible.
A visit to a gastroenterologist is necessary if negative signs appear:
- discomfort of varying intensity in the upper abdomen or left hypochondrium area,
- increased sweating,
- nausea,
- bloating,
- vomit,
- heaviness in the stomach after eating,
- cardiopalmus,
- pain often spreads to the lumbar region or becomes encircling in nature,
- the skin and whites of the eyes change shade: turn yellow,
- pain appears in the middle part of the back (this symptom is also disturbing against the background of other pathologies: appendicitis, intestinal obstruction, ulcerative lesions of the digestive tract).
Kinds
Pancreatitis occurs in mild, moderate and severe forms. During an exacerbation, the symptoms are pronounced and severe pain appears. In most cases, a mild form of acute pancreatitis develops, but due to the influence of a complex of negative factors, tissue necrosis or severe organ damage is possible. If the pancreas does not function, then in the absence of urgent measures, death is possible.
Acute inflammation
Signs of acute inflammation of the pancreas in women:
- pain in the abdomen (upper part) or in the area under the ribs on the left side,
- cold sweat appears,
- nausea develops, uncontrollable vomiting is possible,
- stool is disrupted and diarrhea develops.
An attack of acute pancreatitis can be fatal if the patient is not urgently taken to the hospital for intensive care. It is important to reduce the level of alpha-amylase, which often increases 10 times or more, to restore strength, and to normalize the food processing process.
Chronic form
The course of the pathology depends on many factors: diet, the presence of other chronic pathologies and addictions, the degree of damage to the cells of the problem organ. Complications often develop, and pain of moderate intensity is troubling. If the diet is violated, the load on the weakened organ increases, and the discomfort intensifies.
A characteristic symptom is diarrhea. The stool contains undigested pieces of food, the stool takes on a mushy form, the smell becomes pungent, and after using the toilet it is difficult to wash off the remains. Appetite decreases, the patient loses weight, and is often bothered by vomiting and bloating.
On a note! The transition of pancreatitis to a chronic form is a consequence of inadequate or untimely treatment of an acute process. Often the patient himself provokes severe damage to the pancreas if he does not follow the doctor’s orders or refuses to follow a diet.
An attack of pancreatitis - what to do?
The manifestation of symptoms of PP is grounds for immediate consultation with a doctor. In most cases, an attack occurs suddenly, so the best option is to call an ambulance. Before specialists arrive, the patient must perform a number of actions to alleviate his condition. Home treatment is permissible only in cases of mild attacks of the chronic form of the disease.
First aid and relief
During PP, patients should not take a horizontal position (the pain will increase). The best option is the “embryo” pose. The second way to reduce pain is to sit down with your torso strongly tilted forward. After relief of the condition, it is necessary to carry out a number of actions to stop the attack.
If the pain syndrome persists, then the patient needs qualified medical care (a team of doctors must be called).
First aid measures:
- ensuring the patient complete rest (sudden movements are prohibited);
- exclusion of food consumption (at least for 24 hours);
- preventing dehydration of the body (you can drink alkaline mineral water every hour, a quarter glass);
- stopping an attack with antispasmodic drugs (No-Shpa);
- To relieve pain, you can use a cold compress (for example, any frozen food from the refrigerator).
Home treatment
Self-medication for pancreatitis is prohibited. The disease provokes complications that are incompatible with life. At home, you can carry out preventive measures, carry out courses of therapy drawn up by a doctor and provide first aid in case of exacerbation of the inflammatory process.
You cannot use folk remedies as the main method of treating pancreatitis or to relieve PP.
Acceptable home treatment options:
- diet therapy (a mandatory point in the treatment of the inflammatory process);
- taking medications prescribed by a doctor;
- changing lifestyle (observing a rest regime, ensuring sufficient physical activity, preventing stressful situations);
- implementation of preventive measures.
Specialized medical care
In most cases, PN involves inpatient treatment. The first task of doctors is to temporarily exclude the pancreas from the digestive system. This state of the organ is ensured by fasting. During the first day (or 48 hours), the patient should not eat food. The fluid supply is replenished with alkaline mineral waters. In severe cases of pancreatitis, the period of fasting can reach three days. The further treatment regimen depends on the individual clinical picture of the patient’s health status.
Stages of medical care for PP:
- elimination of signs of intoxication of the body;
- increasing the level of enzymes in the blood to normal levels (Pancreatin, Creon);
- elimination of the consequences of dehydration;
- drug treatment (antibiotics, antiseptics, antispasmodics, analgesics, enzyme medications, vitamin complexes, etc.);
- restorative therapy.
The hospitalization period is on average two weeks. After discharge, the patient is given recommendations on how to prevent repeated PN (daily routine, dietary habits, preventive measures). Additionally, the doctor explains what actions should be taken in the event of a relapse of the attack.
If the patient follows the specialist’s recommendations, the risk of exacerbation of pancreatitis is reduced. Remissions for this disease can be quite long.
Video on the topic: Health. Chronic pancreatitis. You can't stomach it!
Complications of the disease
Pancreatitis provokes the gradual destruction of the pancreas. Violation of the functional state of the organ leads to failures in other body systems. The inflammatory process can cause the death of the patient if there is no adequate therapy and preventive measures are not taken.
Possible complications:
- pancreatic necrosis (purulent destruction of the pancreas);
- peritonitis;
- vein thrombosis;
- sepsis;
- abscesses and cystic formations;
- pancreas cancer;
- obstructive jaundice;
- retroperitoneal phlegmon;
- diabetes;
- internal bleeding.
Diagnostics
If you suspect pancreatitis, you need to visit several specialists: an endocrinologist, a gastroenterologist, a therapist. In case of serious condition, an attack of acute pancreatitis, you will need the help of an emergency team.
First, the doctor conducts an examination, clarifies complaints, and palpates the painful area. It is important to find out whether there is a yellow tint to the sclera of the eyes. The patient must indicate how many attacks there were, how long the negative symptoms last in an acute condition.
Blood test to clarify indicators:
- lipases,
- amylase,
- liver enzymes,
- bilirubin,
- blood indicators.
Clinical researches:
- Ultrasound of all organs in the abdominal cavity.
- Endoscopy to examine the walls of the stomach and identify stones in the bile ducts.
- CT with contrast or MRI.
- Retrograde and magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography.
- Puncture from the inflamed area of the affected gland.
General rules and methods of treatment
How to relieve inflammation of the pancreas? Depending on the form of the pathology, the treatment regimen differs. In an acute process, it is necessary to relieve pain, relieve inflammation, prevent the accumulation of purulent masses and the development of peritonitis. During an attack, you need to refuse to eat and give the patient a light analgesic so that emergency doctors can understand the true picture of negative symptoms. The sooner the patient is taken to the hospital, the lower the risk of peritonitis.
In the chronic form of pancreatitis, a complex intake of drugs is required:
- Insulin. In case of tissue necrosis, disruption or complete cessation of the production of an important enzyme, daily insulin injections are indicated.
- Enzyme preparations. The more active the inflammatory process, the less often the gland produces substances for the complete digestion of food. Congestion causes heaviness in the stomach and accumulation of stones in the gall bladder. Enzymes are needed to activate digestion. Effective drugs: Mezim, Pancreatin, Enzistal.
- Analgesics for pain relief. For moderate discomfort, Ibuprofen and Paracetamol are prescribed. To eliminate acute, shooting pains, more powerful drugs are needed, which the gastroenterologist selects individually, taking into account contraindications.