Kinds
Despite the lack of a generally accepted classification of this condition, doctors identify several forms that differ in manifestations and the degree of their neglect. It is worth noting that the disease is always chronic; when its symptoms appear, the condition periodically worsens.
There are focal and diffuse forms of pathology. The first is accompanied by the appearance of only one inflamed focus, the second is characterized by the formation of multiple lesions over the entire area of the organ.
There are other types of disease, the clinical picture of which may differ:
| Variety | Peculiarities |
| Erosive | This form of the disease most often develops into gastritis. The lesions in this type of lesion are multiple, located at a certain distance from each other, and externally resemble bumps. When diagnosing an advanced form of pathology, it is quite difficult to distinguish from gastritis at the initial stage. The disease is accompanied by severe symptoms from the digestive tract and requires timely treatment. |
| Papular | With such a lesion, small papules filled with clear liquid form in the area of inflammation of the mucous membrane. In most cases, the lesions are localized in the lower part of the stomach. With a long course of the disease, the papules are damaged, which leads to the formation of ulceration in their place. Symptoms worsen and complications arise |
| Stagnant | In the congestive form of gastroduodenopathy, there is a disturbance in the movement of gastric juice and enzymes through the digestive tract. Small ulcers form on the walls of the stomach and duodenum, which significantly worsen the patient’s condition, complicate digestion and can lead to other complications. It is worth noting that this type of inflammation often develops in patients suffering from liver pathologies |
| Antral | This form got its name due to the localization of inflammatory foci in the antrum of the stomach. It quite often affects the duodenum and prevents the normal movement of food further along the digestive tract. |
The clinical manifestations of each form are almost the same, so it is almost impossible to determine the type of inflammation without a special examination.
Causes
Erythematous gastritis often develops in patients with a complicated medical history and regular exposure to situations predisposing to the disease. In the life of a modern person there are many factors that can lead to the onset of an inflammatory process in the gastrointestinal tract.
Here are some of them:
- nervous tension;
- unbalanced and unhealthy food;
- taking certain medications;
- viruses, bacteria and fungi in the body;
- concomitant gastrointestinal diseases;
- chronic constipation;
- helminthic infestation;
- bad habits;
- chemical poisoning.
In some clinical cases, the appearance of erythematous exudative gastritis can be facilitated by hereditary predisposition, congenital anomalies of the digestive system, and even severe trauma to the peritoneum.
Stages and degrees
Erythematous gastroduodenopathy, regardless of the type, occurs in several stages, each of which differs in the severity of symptoms. At the initial stage, not all patients show symptoms.
Some note worsening digestion, as well as minor discomfort. In most cases, the patient associates the manifestations with eating the wrong foods, overeating or stressful situations.
Complications do not arise at this stage, the patient does not take medications, since the symptoms disappear quite quickly and do not get worse. At the progressive stage, the manifestations are more pronounced, since the area of the lesion and the depth of tissue damage increases.
The patient talks about indigestion, which develops not only with overeating, but also with adherence to the principles of a healthy diet.
Typically, it is at this stage that patients begin to take various medications that eliminate symptoms. In most cases, they do not see a doctor, which only worsens the disease.
The advanced stage is characterized by the formation of multiple foci on the gastric mucosa and the transition of inflammation to the duodenum. In this case, persistent symptoms of acute gastritis appear. The patient is forced to constantly take medications or consult a doctor, since taking medications improves the condition only for a short period of time.
Erythematous gastroduodenopathy - causes and treatment
Erythematous gastroduodenopathy is a disease that is characterized by the appearance of reddened areas on the gastric mucosa. The disease does not have serious clinical manifestations, but may be accompanied by mild dyspeptic symptoms. Doctors often diagnose erythematous gastritis as superficial inflammation.
Pathology can be detected during fibrogastroduodenoscopy. Thanks to this study, it is possible to notice hyperemic and edematous areas throughout the entire length of the stomach or in some places. With early detection and treatment of the disease, the prognosis is favorable.
Causes
Erythematous gastritis often develops in patients with a complicated medical history and regular exposure to situations predisposing to the disease. In the life of a modern person there are many factors that can lead to the onset of an inflammatory process in the gastrointestinal tract.
Here are some of them:
- nervous tension;
- unbalanced and unhealthy food;
- taking certain medications;
- viruses, bacteria and fungi in the body;
- concomitant gastrointestinal diseases;
- chronic constipation;
- helminthic infestation;
- bad habits;
- chemical poisoning.
In some clinical cases, the appearance of erythematous exudative gastritis can be facilitated by hereditary predisposition, congenital anomalies of the digestive system, and even severe trauma to the peritoneum.
Symptoms
A gastroenterologist treats erythematous gastritis. However, in order to start therapy in a timely manner, it is necessary to notice the primary signs of the disease and immediately consult a doctor.
This is not easy to do, as many people do not pay attention to mild symptoms of indigestion. At the initial stage, the clinical pathology is very poorly expressed, which can complicate the diagnostic process.
How to recognize erythematous gastritis:
- Heartburn appears regularly after eating;
- there may be a large amount of mucus in the stool;
- taste habits change;
- a coating appeared on the tongue;
- after eating there is discomfort, heaviness or slight pain in the stomach;
- disruption of intestinal function (constipation is replaced by diarrhea).
Inflammation of the stomach is often accompanied by a general deterioration in health. Patients complain of severe weakness, increased or decreased blood pressure, dizziness, and poor health.
A sharp decrease in body weight or weight gain will also indicate problems in the gastrointestinal tract.
Types of gastropathy
Erythematous gastritis comes in several types. They all differ in symptoms, the degree of damage caused to the body, and clinical and physical manifestations. Gastropathy is a chronic disease. It can be focal and diffuse, that is, areas of redness of the mucous membrane will be located in some areas or over the entire surface of the stomach.
Pathology also comes in the following forms:
Erosive
Inflamed areas with this type of disease are transformed into lumpy formations. Erosion varies in size and can reach 7-8 mm. The erosive form quickly provokes the occurrence of superficial gastritis.
Papular
Most often, the papular form of gastropathy affects the antrum, that is, the lowest part of the stomach. Papules form at the sites of reddened spots, which gives this type of pathology its name.
Stagnant
Gastropathy in this form is characterized by the appearance of ulcerative formations and the occurrence of enhanced clinical manifestations of the disease. Often, a patient with this diagnosis is diagnosed with concomitant diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and liver.
Antral
The pathology got its name because of its localization - most often it develops in the antrum of the stomach, where food is prepared to move through the intestines.
Diagnostics
The most accurate and fastest way to diagnose erythematous gastritis is using FGDS. This type of study helps to visually assess the condition of the gastrointestinal tract, and also, if necessary, take a tissue biopsy to exclude the growth of malignant cells.
Fibrogastroduodenoscopy is used to examine the digestive system along almost its entire length.
The patient undergoes other functional studies if there are contraindications to FGDS. In this case, the use of ultrasound and x-rays is indicated. Additionally, you will need to submit material for laboratory analysis.
Treatment
Therapy will be effective if carried out in combination and under the supervision of a competent doctor. You will need to follow a diet and also take medications to alleviate the condition and reduce the load on the stomach.
You can be treated with folk remedies and physiotherapy, but you should not completely replace drug therapy with such methods.
Diet
During the period of treatment and rehabilitation you will need to follow a fairly strict diet. She excludes from the diet all foods that provoke the secretion of excess gastric juice and greatly overload the stomach.
Canned food, hot seasonings, strong and carbonated drinks, fast food are completely prohibited; high fat and salt content in dishes is not good for the gastrointestinal tract. Drinking alcohol and smoking are not allowed.
The diet is selected based on the needs of a particular organism. Dishes must contain the required amount of BJU so that the body receives all the important elements.
Medicines
The necessary medications are prescribed by the attending physician. You should not use medications on your own, since erythematous gastroduodenopathy has several varieties and clinical manifestations, respectively.
What medications are used:
- proton pump blockers;
- antispasmodics;
- enzymes;
- antacid drugs;
- vitamins;
- antibiotics (as needed).
The course of medications is selected for each individual clinical case, depending on the patient’s complaints and the severity of the disease. All drugs are designed to help the stomach digest food, while protecting the mucous membrane of the organ.
Folk remedies
Sometimes, with the doctor's permission, you can use homemade "medicine" recipes. There are many proven ways to achieve lasting remission of gastritis. They should not replace drug therapy, as the health condition can only worsen.
To restore the gastric mucosa and protect against the aggressive effects of hydrochloric acid, you will need to consume natural aloe juice or sea buckthorn and linseed oil on an empty stomach. This must be done daily, in a course, no more than a tablespoon at a time. You can relieve inflammation with a decoction of chamomile, plantain or St. John's wort.
Complications
If left untreated, erythematous gastroduodenopathy leads to gastrointestinal health problems. The advanced form of the disease develops into erosive gastritis, which in turn is accompanied by the destruction of the deeper layers of stomach tissue.
In the future, atrophied areas of the mucous membrane may appear, on which the growth of malignant cells begins. To avoid complications, you need to act on the initial stage of the disease in a timely manner.
Prevention
When the first signs of gastritis or a complicated medical history appear, it is recommended to follow the basic rules for the prevention of gastrointestinal diseases. This will significantly reduce the risk of developing inflammation in the stomach.
What can be done to prevent pathology:
- normalize the diet;
- take any medications only after consulting a doctor;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- heal the nervous system;
- strengthen the immune system.
Source: https://ZHKTrakt.ru/gastrit/eritematoznaya-gastroduodenopatiya-prichiny-i-lechenie.html
Symptoms
The first manifestation of the pathology is discomfort in the epigastric region, which appears when eating spicy, salty or fatty foods. Somewhat later, the discomfort gives way to pain, which can occur on an empty stomach. Additionally, the patient is often bothered by nausea, sometimes it provokes vomiting, especially when overeating. It is worth noting that after the stomach is emptied, nausea disappears.
After eating even a small amount of food, the patient feels heaviness in the stomach, which is associated with indigestion, as well as the slow movement of food into the intestines. Additionally, the patient is bothered by heartburn and frequent belching. As the condition progresses, intestinal disorders develop, manifested in the form of flatulence, bloating and pain.
The patient may report persistent constipation or frequent loose stools, depending on the level of acidity. The first is observed with an increased amount of hydrochloric acid, the second - with a decreased amount. It is worth noting that the first option is more common.
If left untreated, the depth of tissue damage increases, which leads to worsening symptoms. Pain appears not only after eating food, but also on an empty stomach, which is associated with gastric juice entering the lesions. In this case, the patient tries to reduce the amount of food so as not to provoke increased pain. Body weight decreases, weakness, headache and dizziness occur.
In some patients, blood pressure decreases. Mental and physical performance also decreases, and memory and concentration deteriorate. Among the external manifestations can be identified pallor of the skin, increased activity of the sweat glands and the appearance of dark circles under the eyes.
Since the patient limits the amount of food, he may experience sleep problems, which only aggravate all symptoms and lead to the development of a nervous disorder. Another external manifestation is a white coating on the tongue, which is present in the morning or during long breaks between meals.
Symptoms of gastroduodenopathy
The symptom complex of gastroduodenopathy is very similar to the symptoms of various intestinal and gastric diseases.
These include:
- attacks of nausea;
- pain in the stomach;
- feeling of fullness in the stomach;
- unpleasant taste in the mouth;
- loss or decrease in appetite;
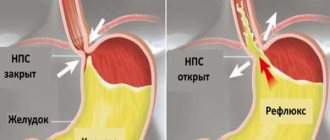
- reflux;
- heartburn;
- diarrhea or constipation.
The first signs of gastroduodenopathy are sudden, often on an empty stomach, sharp, cramp-like pain in the upper abdomen, nausea and vomiting.
Reasons for appearance
Erythematous gastroduodenopathy can occur as a result of various predisposing factors.
The main reasons are considered to be the following:
- Professional activities associated with contact with harmful components, toxins or poisons.
- The need to work night shifts. Experts have proven that patients who work at night are more likely to suffer from pathologies of the stomach and intestines.
- Abuse of alcoholic beverages on a regular basis, smoking.
- Eating spicy, fatty and smoked foods in large quantities.
- Constant overeating.
- Rare meals, when the patient consumes the daily norm at one time, which leads to digestive disorders.
- Long-term treatment with medications that have a negative effect on the gastric mucosa.
- Frequent stressful situations that provoke excessive production of hydrochloric acid and damage to the gastric mucosa.
- The presence of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori in the gastric juice.
- Diabetes mellitus and other endocrine pathologies.
- Poisoning with harmful substances.
In addition, the cause may be other diseases of the digestive tract, for example, cirrhosis of the liver, cholecystitis, pancreatitis.
What is erythematous gastropathy, its symptoms and treatment
After an endoscopic examination, the doctor can make a conclusion: erythematous gastropathy is a pathological condition, is not an independent clinical disease, but acts as an alarming symptom, mainly superficial gastritis.
What is
With erythematous gastropathy, hyperemia (redness) of the upper layer of the gastric mucosa occurs. This happens due to inflammatory processes, which usually do not affect the deep layers of tissue, which provoke swelling and blood flow caused by the expansion of capillaries.
Inflammation with gastropathy is usually less pronounced than with true gastritis, and affects only the superficial layers, therefore it is often referred to as superficial gastritis.
It occurs in diffuse and focal forms.
- The focal form is also called erythematous antral gastropathy and is most often found in the antrum of the stomach. It mainly differs in the local nature of the damage, inflammation and swelling are mild.
- Diffuse (common) gastropathy covers a large part of the mucosal surface in different parts. In the absence of adequate treatment, it leads to gastritis and stomach ulcers.
According to the degree of severity, the first and second stages are conventionally divided. They differ in the degree of damage to the epithelium.
Medicines
If it is determined that the cause of gastropathy is the medications you are taking, it is advisable to ask your doctor to change them. If this is not possible in this situation, medications are used to protect the stomach from harmful factors.
Medicines that can be prescribed for erythematous gastropathy:
- Antisecretory (Omeprazole, Nolpaza, Kvametel, Pariet). Reduce the production of the main irritant of the mucous membrane - hydrochloric acid.
- Gastroprotectors (De-nol, Vikair, Vikalin). Due to the bismuth contained in the composition, they have an astringent and anti-inflammatory effect, protecting the walls of the organ. Helps fight bacteria that cause stomach ulcers.
- Antacids (Almagel, Maalox, Gastal). Reduce acidity, therefore, the aggressiveness of the stomach environment. Binds and removes pathogenic substances.
- Regulating motor skills (Ganaton, Itopride). Can be prescribed in case of stagnation in the stomach and subsequent fermentation and rotting.
Comprehensive treatment with folk remedies gives good results. Herbs are used: gastric herbs, chamomile, fennel. They are mainly aimed at mildly relieving inflammation and improving digestion. Flax seeds and oat jelly are used as an enveloping, stomach-protecting home remedy.
You need to be especially careful with drugs from the NSAID group; due to their ulcerogenic effect, they often cause stomach pathologies.
Nutrition
Proper nutrition remains an important component of treatment. Products that irritate the mucous membrane are excluded: sour, spicy, salty, smoked, fried, soda, alcohol, coffee and others. It is recommended to cook in a double boiler and pay more attention to dishes such as porridge, jelly, and broth. Eating hot or cold food is contraindicated.
Forecast
Gastropathy of the erythematous type is not dangerous, but requires timely treatment, otherwise it can worsen and, without medical treatment, lead to gastritis, ulcers or gastroduodenopathy.
When the first symptoms appear, timely drug therapy and a proper diet can quickly and completely get rid of the disease.
Source: https://vzheludke.ru/zheludok/eritematoznaya-gastropatiya.html
Diagnostics
The erythematous form of chronic recurrent gastroduodenopathy is diagnosed quite simply if the correct methods are used.
The most popular and effective of them are the following:
- A general examination and interview of the patient is carried out in each clinic; payment from the patient is usually not required. The method is considered the first stage of diagnosis; it helps to assess the general condition of the patient and identify associated abnormalities in the internal organs. In this case, the doctor examines the patient’s skin, tongue, and also palpates the abdomen to determine the area of greatest pain.
- Clinical and biochemical blood tests are also considered an important method. The results help to see signs of inflammation, as well as disorders of the liver and pancreas. The study is being conducted in private and public clinics, the price in the first is approximately 400-500 rubles.
- A blood test for the presence of Helicobacter pylori is also considered an important stage of the study. Perhaps these bacteria were the cause of the inflammation, so the assumption should be excluded or refuted. Diagnostics are carried out in public and private clinics, the cost is approximately 300 rubles.
- Examination of gastric juice for acidity levels helps to identify the patient’s tendency to certain intestinal manifestations. For diagnosis, a sample of gastric juice is taken and then studied in the laboratory. The method is used in private and public clinics, the cost of the examination is approximately 400 rubles.
- FGDS - the most effective and informative diagnostic method, in which a probe with a small camera at its tip is inserted into the patient’s stomach. Thanks to this, a specialist can examine the walls of the stomach from the inside, and then determine the cause of the symptoms. Usually on the monitor the doctor sees the lesions, their size, location and number. The study is carried out in any medical institution and costs approximately 300 rubles.
- Ultrasound is an additional diagnostic method that is highly effective. It is necessary to identify abnormalities in internal organs. In this case, the liver, gallbladder and pancreas are examined. The results quite often help establish the diagnosis and probable causes of the disorder. The price of the study ranges from 800-1500 rubles. depending on the extent of the diagnosis. Ultrasound is performed in rooms equipped with appropriate equipment.
FGDS is considered the most effective and informative method, but to obtain a complete picture of the disease, a comprehensive examination should be completed.
Should you be concerned if you have been diagnosed with erythematous gastroduodenopathy?
You will not come across the term erythematous gastroduodenopathy in the office of a gastroenterologist, since this condition is not actually a diagnosis.
Rather, a frightening phrase will appear in the conclusion of the endoscopy result, to which this very doctor referred you. We invite you to figure out together what pathology is hidden under a complex and incomprehensible name.
What does diagnosis mean?
To clearly understand the meaning of the term, let us turn to the literal translation. So:
- Erythema (erythema, Greek) - means redness, redness. Most often, the term is used to refer to redness of the skin and mucous membranes. If in the conclusion of your EGD the description begins with the word “erythematous,” it means that the internal mucous membranes of the organ have a bright red color, which corresponds to inflammation.
- Gastro (gaster, Greek) – stomach. The names of all diseases associated with this organ begin as follows - gastritis, gastroduodenitis, etc.
- The prefix duodeno - (duodena, Greek) denotes a connection with the 12 duodenum. If it is present in the name, it means that the pathology affects the area of the duodenum 12.
- Pathia – (páthos, Greek) – means illness, suffering.
Thus, erythematous gastroduodenopathy means redness (inflammation) of the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum.
To worry or not?
Pathology is not considered an official diagnosis; rather, it denotes endoscopic syndrome, that is, it describes the condition of the superficial tissues of the stomach and duodenum, which does not extend to deeper layers. The condition can be acute or chronic.
Acute inflammation may be associated with temporary irritation of the mucous membranes, which occurs after overeating, drinking alcohol, spicy and spicy foods, and marinades. Persistent irritation is also observed in patients who smoke. Fans of too hot food also periodically suffer from gastropathy, but these symptoms quickly pass.
A chronic form of inflammation is observed in patients with other diseases of the digestive system. Also, endoscopists detect the syndrome of erythematous gastroduodenopathy during or at the recovery stage after acute or chronic gastritis or peptic ulcer.
You should not ignore the pathology, because in the presence of provoking factors, it will not slow down to spread into the deeper layers and transform into a new, acquired disease.
Degrees and types
Endoscopist doctors distinguish 2 forms of pathology:
- Focal erythematous gastroduodenopathy - the term refers to the presence of redness in a limited (local) area of the mucous membrane. In this case, the EFGDS conclusion will contain an exact indication of the department where there is inflammation. This may be the antrum, cardia, fundus of the stomach, duodenal bulb or part of the intestine.
- The diffuse form is diagnosed if the redness is widespread and visible in many areas of the gastric and duodenal mucosa.
The syndrome is also divided into degrees:
- Grade 1 pathology is common and is associated with temporary, shallow irritations of the mucous membranes. Stage 1 responds well to therapy, sometimes to eliminate it it is enough just to correct the diet; you do not need to take medications;
- Grade 2 means that the process has a chronic course, that is, redness and inflammation of the mucous membranes is always present. Grade 2 occurs in patients with chronic gastritis and other diseases of the digestive tract.
About the reasons in detail
The cause of erythematous gastroduodenopathy is not always a diet disorder or an existing disease of the digestive system. The condition may have a different origin. The following factors provoke hyperemia of the mucous membrane:
- Microbial or fungal infections of the mucous membrane.
- Taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications. Hormones, anticoagulants for a long time.
- Chronic metabolic disorders.
- Vitamin deficiencies.
- Constant stress and overwork, high physical activity.
- Hereditary factor.
- Increased acidity of the stomach contents.
- Starvation diets.
- Bad habits.
At grade 1, gastroduodenopathy does not manifest itself sharply - clinical symptoms appear periodically and disappear as soon as the diet is normalized. Grade 2 erythematous gastroduodenopathy is characterized by a more pronounced clinical picture, which is similar to the manifestations of chronic gastritis.
Important! The condition is not a reason for hospitalization of the patient, and does not exempt him from military service.
Symptoms of erythematous gastroduodenopathy
The most common symptom of erythematous gastroduodenopathy is heaviness in the stomach that occurs after eating. Moreover, for the symptom to appear, the patient does not have to overeat; heaviness occurs even after a snack.
Sometimes this condition is accompanied by severe nausea, which is difficult to cope with.
This is due to the fact that when the mucous membrane becomes inflamed, the production of enzymes is disrupted, food digestion proceeds slowly, causing discomfort.
If the foci of redness are located in the antrum and spread to the area of the duodenal bulb, peristalsis suffers: the food bolus has difficulty moving through the digestive tract, stagnates in the lower parts of the stomach, causing the patient bloating, unpleasant belching of air, heaviness in the epigastrium and disorders intestinal activity. Pathology in this case provokes constipation or diarrhea.
If erythematous gastroduodenopathy with an erosive component is detected, pain syndrome is added to the above symptoms. This condition is dangerous due to its rapid degeneration into erosive gastritis or peptic ulcer.
Therefore, the doctor must explain to the patient the need to follow a gentle diet. When hyperemia is combined with atrophy, the prevailing symptom is heaviness in the epigastrium and flatulence.
In this case, the doctor prescribes enzyme preparations (Omez, Festal, Mezim) to stimulate the activity of the stomach.
The common symptoms of erythematous gastroduodenopathy include the following:
- weakness, fatigue, increased irritability;
- lack of appetite, stomach discomfort;
- anemia associated with impaired absorption of nutrients;
- weight loss;
- periodic vomiting not associated with poisoning;
- plaque on the mucous membranes of the mouth, especially on the tongue.
Painful symptoms disappear if the patient’s regimen and diet are normalized. If you ignore periodic ailments, the pathology will quickly develop complications and first transform into gastritis, and later into peptic ulcers.
The signs of erythematous gastroduodenopathy in the acute stage or during initial detection are similar to the symptoms of exacerbation of chronic gastritis.
Therefore, treatment and nutrition for acute conditions are similar to treatment recommendations and diet for chronic gastritis.
Treatment and diet
Drug treatment for erythematous gastroduodenopathy is rarely prescribed. The main therapeutic method in this case is diet. Don't be alarmed and think that your diet should be reduced to diet soup and cereals, this is not so. On the contrary, the daily food set should be varied in order to provide the body with the necessary substances.
The restrictions apply only to frankly unhealthy foods - smoked meats, marinades, too hot and too cold dishes. You should not drink alcoholic and carbonated drinks, overeat heavily, or “sit” on coffee alone throughout the day. A sick stomach should not be empty, so carefully consider your daily diet.
To help, we suggest you familiarize yourself with the material, where we examined in detail the principles of nutrition for superficial gastritis. Dietary recommendations for this disease and erythematous gastroduodenopathy are identical.
Folk remedies
For erythematous gastroduodenopathy, it is allowed to be treated with traditional methods. Herbal infusions gently relieve inflammation of the mucous membrane and help restore damaged mucous membranes. We offer you several simple herbal medicine options for the stomach.
A simple collection to relieve inflammation
The main component of this collection is yarrow. 50 grams of dried crushed yarrow flowers and herbs are poured into 400 ml of water and boiled over low heat for 40 minutes. After the broth has cooled, it is filtered and taken warm, a third of a glass, before main meals.
Composition for stimulating digestion
To prepare this decoction, prepare a mixture of the following components:
- centaury;
- yellow gentian;
- chicory flowers;
- fumaria officinalis;
- yarrow;
- St. John's wort.
Do not be alarmed by such variety - the raw materials for preparing the decoction are sold in any pharmacy. Mix the ingredients in equal quantities, take 3 tablespoons of the prepared mixture and pour 400 ml of boiling water. Seal tightly and leave for 4 hours. Strain the broth and take it warm before your main meals - breakfast, lunch and dinner.
These recipes are given in the “Newest Therapist's Handbook”, written by the famous Russian doctor, E. A. Nikolaev.
We invite you to watch a video about healing herbs for the stomach.
Before starting treatment with herbal remedies, it is better to consult with your doctor.
In each case, it is important to take into account the individual characteristics of the body, allergies, the presence of concomitant diseases and other factors.
Be attentive to yourself, do not neglect visiting the clinic. And remember: with erythematous gastroduodenopathy, your main task is proper and healthy nutrition.
Source: https://MedBrat.online/zheludok/eritematoznaya-gastroduodenopatiya.html
Prevention
Erythematous gastroduodenopathy quite often develops into a more dangerous disease , so it is easier to prevent it than to treat it. The most important method of prevention is adherence to the principles of a healthy diet. Portions should be small, meals should be frequent, and unhealthy foods should be completely excluded from the menu.
In addition, it is important to avoid stressful situations that can provoke excessive production of gastric juice. It is also necessary to normalize the work and rest regime, to prevent overwork, which can lead to the development of inflammation.
Another method of prevention is to take medications only as prescribed by a doctor and strictly adhere to the dosage. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, hormonal drugs and some other groups of drugs provoke inflammation of the gastric mucosa, so uncontrolled use leads to complications.
Experts strongly recommend that patients give up cigarettes and reduce the amount of alcohol consumed to a minimum. Additionally, contact with toxic substances should be avoided. If a patient suffers from any diseases of the digestive system, it is necessary to visit a doctor in a timely manner and undergo an examination to detect complications at an early stage.
Erythematous gastropathy: causes, symptoms and treatment
Erythematous gastropathy is a pathology in which slight redness of the gastric mucosa is detected - erythema, the appearance of which is provoked by blood flow to the affected area. Such lesions do not penetrate into the deep layers, but are located on the surface.
What is erythematous gastropathy
The inflammatory process in gastropathy is often less pronounced than in true gastritis, and only the superficial layers are affected, which is why it is often called superficial gastritis.
The appearance of inflamed areas on the surface of the stomach is often accompanied by pain that occurs in the center of the abdomen. This pathology may be accompanied by swelling of the epithelium, increased sensitivity, and excessive mucus synthesis.
The appearance of erythematous gastropathy is due to the influence of various damaging factors on the gastric mucosa. As a result of the negative influence of such factors, the formation of erythema occurs - redness caused by blood flow to the affected areas of the membrane.
Erythematous gastropathy is not a full-fledged disease, but it often appears with superficial erythematous gastritis. If treatment is not started in a timely manner, there is a risk of serious pathologies – for example, peptic ulcers.
Often, simultaneously with this disease, erythematous gastroduodenopathy appears - redness and the formation of an inflammatory process in the mucous membrane of the pylorus of the stomach and duodenum.
Both conditions are not independent diseases; these symptoms are diagnosed during clinical examinations for other diseases. If they are detected, it is recommended to start drug treatment as soon as possible and change your lifestyle and diet.
But in the presence of the above pathologies, there is a risk of developing a third symptom - erythematous bulbopathy - an inflammatory process in the loop connecting the duodenum with the intestine.
Types of pathology
This pathology occurs in the following forms: diffuse and focal.
Focal also known as erythematous antral gastropathy, it can often be found in the antrum area of the stomach. Its difference is the local type of damage, and swelling and inflammation are mild. This type of pathology rarely degenerates into gastritis. This form appears when there is a malnutrition or develops as a reaction to the use of certain types of medications.
The diffuse (common) form of the pathology affects a large area of the mucosal surface in various parts of the digestive organ. In such a situation, erythema is located in different parts of the organ and can affect large tissue surfaces. In the absence of adequate treatment, it can lead to the development of gastritis and stomach ulcers.
According to the degree of severity, the first and second stages can be distinguished, which differ in the degree of damage to the epithelial layer.
Erythematous gastropathy of the 1st degree is characterized by initial manifestations of damage to the epithelial layer of the digestive organ. There are no symptoms of neglect.
Grade 2 erythematous gastropathy is characterized by progression of the process. This is due to the ongoing influence of damaging factors. The inflammatory process in adults becomes chronic.
In addition, there is a division into other types of pathology, which have their own characteristics:
Erythematous gastropathy of the antrum.
This section of the stomach is located in the lower part, its task is to mix food and maintain the acid-base balance (pathology is characterized by low acidity).
Due to damage to this zone, the movement of food through the pylorus into the duodenum slows down. This provokes the occurrence of stagnant processes and the beginning of the fermentation process.
Papular . It forms in the lower region of the stomach. It is characterized by the appearance of small ulcers on the surface of the mucosa, which arise due to increased synthesis of hydrochloric acid. Symptoms are not clearly expressed.
Erythematous erosive gastropathy . This type of anomaly develops accompanied by hyperemia and the formation of superficial erosions. They are diagnosed using endoscopic examination.
The pathology occurs as an acute or chronic disease . In the first case, the diameter of the erosions is no more than 2 mm. When the factor causing them is eliminated, they heal within a week.
The chronic course of the disease is accompanied by the formation of fairly large defects - more than 7 mm. Excessive acid synthesis leads to disturbances in the blood circulation of the mucous layer of the digestive organ.
Signs of this type of pathology include heartburn, sour belching, pain, a feeling of heaviness in the right hypochondrium and flatulence.
Congestive erythematous gastropathy . This form of gastropathy is characterized by disruption of the digestive organs. More often, its symptoms are not clearly expressed, so they are difficult to diagnose against the background of the main illness.
Causes of the disease
Erythematous gastropathy can be caused by the following reasons:
- Disruption of the circulatory process.
- Presence of pathogenic microorganisms or fungal infection. More often, the cause of the disease is the active activity of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. In this case, treatment is aimed at getting rid of the provoking factor.
- Chemical burns.
- Infectious diseases.
- Medicinal (medicinal gastritis). The causes of this type of gastropathy include taking aspirin and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Heredity.
- Poor nutrition.
- Excessive drinking and smoking.
- Daily routine and stress resistance are of no small importance. Under the influence of psychotraumatic factors, the synthesis of adrenaline increases. It affects the growth of hydrochloric acid production, and its prolonged exposure leads to irritation of the mucous membrane of the digestive organ, provokes redness, inflammation, and in some cases causes the formation of ulcers and erosions.
Diagnosis of pathology
Gastropathy is detected more often during examination for the presence of other disorders.
Endoscopic examination can sometimes also cause erythematous gastropathy, it is called endoscopic syndrome, but this condition usually does not require special treatment.
Fibrogastroduodenoscopy is considered the main diagnostic method for gastropathy. During the examination, the doctor uses an endoscope to examine the esophagus, duodenum and stomach. Sometimes it becomes necessary to take tissue samples for histology.
Before conducting this type of diagnostic examination, it is advised to follow some recommendations. A few days before the study, exclude alcohol, carbonated drinks, fatty foods from the diet, and do not smoke.
In addition to fibrogastroduodenoscopy, the following types of examinations and laboratory tests are performed:
- blood and urine tests;
- gastroscopy;
- Ultrasound of the gastrointestinal tract;
- CT.
How to treat pathology
To select the correct treatment regimen, it is necessary to establish the factors that provoked the onset of the disease. Another important point when prescribing treatment is the presence of concomitant pathologies, this could be erosive or chronic gastritis, gastroduodenitis.
When it is determined that the cause of gastropathy is the medications used, it is recommended to replace them. If this is not possible, medications are used that protect the stomach from the influence of negative factors.
Medicines prescribed for erythematous gastropathy:
- antisecretory agents - “Kvamatel”, “Nolpaza”, “Omeprazole”, “Pariet”. They reduce the synthesis of the main irritant of the mucous membrane - hydrochloric acid.
- gastroprotectors – “Vicair”, “De-Nol”, “Vikalin”. They protect the walls of the organ, have an astringent and anti-inflammatory effect.
- antacids - “Maalox”, “Almagel”, “Gastal”. These drugs help lower acidity, reduce the aggressiveness of the gastric environment, bind and remove pathogenic substances.
- regulating motor skills - “Itoprid”, “Ganaton”. They are prescribed in case of stagnation, fermentation and rotting in the stomach.
When the bacterium Helicobacter pylori is present, antibiotic therapy is prescribed.
In very rare cases, there is a need for surgical intervention. To do this, resection of the affected areas is performed.
Diet for erythematous gastropathy
Therapy for erythematous gastropathy will not be effective without diet correction.
Compliance with the following rules will help normalize nutrition and get rid of irritating effects on the organ:
- It is recommended to steam food;
- it is important to avoid eating irritating foods, such as: spices, smoked foods, spicy foods, pickles;
- It is prohibited to drink carbonated drinks, coffee, or alcoholic drinks. It is recommended to replace black tea with green, herbal infusion or plain water;
- The basis of nutrition consists of lean meats and fish, lean broths, liquid porridges, and jelly. It is allowed to eat jelly, cottage cheese, egg whites;
- All dishes should be eaten at room temperature. Too cold or hot dishes can cause irritation of the mucous membranes and lead to spasm of smooth muscles;
- It is recommended to eat at intervals of several hours;
- portions should be small - no more than 350 g. This helps to avoid increased stress on the digestive organs;
- you should not overeat. Excessive food volume contributes to the onset of rotting in the stomach. This causes a feeling of heaviness, nausea, and belching.
The presence of pronounced negative symptoms or deterioration of the patient’s condition requires adherence to a strict “Table No. 1” diet.
Only with a combination of drug therapy and dietary nutrition, as well as lifestyle correction, can you quickly get rid of the pathology.
Traditional methods of treatment
Folk remedies can be used as complementary to drug treatment. Traditional methods of treatment include the use of herbal infusions, decoctions, freshly squeezed juices, etc. For example, oat decoction has an enveloping effect. For low acidity, it is good to drink fresh cabbage juice.
You can use various herbs and medicinal plants: chamomile, fennel. The use of these remedies is aimed mainly at gently relieving inflammation and improving digestion.
Treatment methods
To eliminate the symptoms of the pathology, you need to undergo a course of treatment. The use of folk remedies and other methods is allowed.
Medications
Treatment of the disease is carried out using drugs from different groups to achieve a complex effect and prevent complications.
The most commonly prescribed medications are:
- Almagel is an antacid in the form of a suspension for oral administration, which is used in case of increased acidity of gastric juice and heartburn. Helps eliminate symptoms, improve digestion and prevent the negative effects of acid on the stomach walls. The medication is taken for 10-14 days, 1 measuring spoon 2-3 times a day. A measuring spoon is included with the bottle. The price of the medicine is from 300 rubles.
- Maalox is another antacid medicine in the form of an oral suspension. For the treatment of gastroduodenopathy with high acidity of gastric juice, it is used for 2 weeks. You need to take the medicine 3 times a day, 1 sachet containing a single dosage of the medicine. The medication is highly effective, quickly eliminates heartburn, and alleviates the patient’s condition. Price – from 200 rub.
- Motilium is an antiemetic in tablet form, which additionally activates intestinal motility, eliminates flatulence and bloating, and promotes the normal movement of food through the intestines. It is used to alleviate the patient’s condition and is effective. The patient takes 1 tablet 3 times per day, the duration of the course should not exceed 7 days. The price of the product is from 400 rubles.
- Duphalac is a laxative that is used to relieve persistent constipation in patients with advanced gastroduodenopathy. The syrup softens stool and stimulates its movement through the intestines, which alleviates the patient’s condition. You can take it for 5-7 days, 20 ml before bedtime. The price of the product is from 300 rubles.
- Loperamide is an antidiarrheal drug that is used to treat frequent loose stools. Can be used for no more than 3 days in a row. The patient needs to take 1 tablet 2 times a day until the consistency and frequency of stool normalizes. The drug is very effective, but can cause persistent constipation if used incorrectly. The price of the product is from 100 rubles.
- De-nol is a tablet medication that is used when the Helicobacter pylori bacterium is detected in the body. You must take the medicine for at least 30 days. During this period, the active components destroy the bacteria and improve the patient's condition. The product is very effective, the daily dosage is 4 tablets, you can take them 4 times or divide them into 2 doses. The price of the medicine is from 350 rubles.
- Omez is a drug from the group of proton pump inhibitors that allows you to reduce the negative effects of hydrochloric acid on the walls of the stomach by reducing its amount. The drug helps prevent the development of ulcers and is considered very effective. It must be taken for at least 30 days, 1 tablet 3 times a day, 30 minutes before meals. Price – from 120 rub. for 10 tablets.
- No-spa is an effective antispasmodic medication that relieves spasm of the smooth muscles of the digestive tract and alleviates the patient’s condition. You need to take the product 1 tablet 3 times a day, the course lasts up to 2 weeks. The price of the medicine is from 150 rubles.
- Pancreatin is a pancreatic enzyme substitute that is used to improve digestion and is considered very effective. The drug helps process food and normalize enzyme levels. Take 2 tablets with meals, repeat 3 times a day. Course duration is from 2 to 4 weeks. The price of the medicine is from 30 rubles.
- Creon is another enzyme preparation that is highly effective. You should take it 1 tablet 2 times a day with meals, repeat for 2 weeks in a row. The medication stimulates the production of digestive enzymes and improves blood circulation. Price – from 500 rub.
Such products help improve digestion, normalize the production of enzymes and gastric juice in the right quantities, and prevent complications. For each patient, the treatment regimen is selected individually depending on the symptoms and complications.
Traditional methods
Erythematous gastroduodenopathy cannot be treated using traditional methods, but they are allowed to be used to alleviate the patient’s condition.
Chamomile decoction is a universal medicine for any pathology of the digestive tract. You can prepare it from 20 g of dry raw materials and 500 ml of water, cook for 3 minutes, leave to infuse for 40 minutes. Divide the filtered medicine into 2 servings and consume throughout the day. Repeat the manipulation for 10-14 days.
A decoction based on yarrow and calendula flowers also helps relieve the condition. It is necessary to combine 10 g of each plant, add 1 liter of water and cook the composition for 5-7 minutes. After this, leave to infuse for 2 hours. Take the filtered product 100 ml 2 times a day. The course of treatment lasts up to 2 weeks.
The simplest folk method is treatment with honey. You should consume 15 g of natural honey daily on an empty stomach. It is better to take a liquid product that does not contain sugar crystals. The minimum course duration is 4 weeks.
Diet
The disease cannot be cured without following an appropriate diet. It involves the complete exclusion of smoked meats, baked goods and confectionery from the menu. It is also worth giving up marinades, sauces and seasonings.
You should not eat canned food, fatty meats, as well as fresh vegetables and fruits in large quantities. It is important to give up alcohol, strong coffee and tea. This will reduce the negative impact on the stomach.
The menu should include the following products and dishes:
- Lean meat and boiled fish.
- Stewed vegetables and baked fruits, such as apples.
- Soups with water or chicken broth.
- Buckwheat and oatmeal porridge.
- Steamed lean meat cutlets.
- Dried fruits in small quantities
- Low-fat fermented milk products.
- A small amount of nuts.
- Compotes, green tea, herbal infusions.
- Biscuits, stale bread.
- Mashed potatoes.
- Scrambled eggs.
- Kissel.
An approximate daily menu must be drawn up taking into account all the recommendations. For example, for breakfast the patient can have a choice of oatmeal, 2 soft-boiled eggs or buckwheat porridge. For drinks, you can choose compote or weak black tea.
Lunch should include a first course, such as rice soup with chicken broth, noodle soup with water, or chicken broth with herbs. However, do not fry carrots and onions before adding them to the soup. The second course may include mashed potatoes and a steamed chicken cutlet.
Dinner may consist of a small amount of boiled fish or chicken breast. You can prepare stewed cabbage as a side dish. Just before bed, you can eat some dried fruits or 200 ml of low-fat kefir. It is important to eat food slowly and in small portions.
Other methods
Additional treatment methods include magnetic therapy and electrophoresis. Both methods are used to stimulate tissue repair and prevent complications.
Magnetic therapy is carried out in a medical institution, the session lasts 20 minutes. During the procedure, the stomach area is exposed to magnetic radiation, which stimulates tissue repair processes. The minimum course consists of 10 sessions.
Electrophoresis involves exposing the affected area to low frequency electric current. As a result, the mucous membrane is restored. The duration of the procedure is 15-20 minutes, it is carried out 3 times a week for a month.
Treatment
Despite the fact that erythematous gastropathy does not pose a threat to life, its presence in itself is unpleasant. At the same time, it’s very easy to get rid of it – you just need to adjust your diet.
All unhealthy foods should be excluded from the diet: fried, pickled, smoked, very spicy and sour.
Replace it with healthy ones, that is, with foods rich in minerals and vitamins, fresh vegetables and fruits, boiled or stewed food. One of the important factors of treatment is quitting smoking and alcohol. It is very important to maintain a water regime, you need to drink more clean water, at least two liters of clean water a day, natural herbal decoctions.
No special drug treatment is required here. However, there are a few things I can recommend.
The following drugs will help restore the mucous membrane
- Gastrofarm;
- Maalox;
- Almagel.
Their astringent effect protects the stomach and speeds up the healing process. Folk remedies are quite effective. The simplest and most accessible is a gastric collection, which is sold in any pharmacy. You should infuse it according to the instructions and drink it.
Video
Possible complications
Without treatment, the likelihood of complications increases.
The most common consequences:
- Development of gastritis, gastroduodenitis or peptic ulcer.
- Damage to the intestinal walls as a result of constant gas formation, constipation and other disorders.
- Enteritis and colitis of varying severity.
- Progressive gastric ulcer with perforation of the organ wall and the development of peritonitis.
- Internal bleeding.
- Impaired functions of the liver, pancreas and gall bladder.
To prevent complications, it is worth visiting a doctor in a timely manner and undergoing treatment.
The erythematous form of chronic gastroduodenopathy is not a dangerous disease if treatment is started immediately after the first symptoms appear. However, if the symptoms are ignored, the condition worsens, which can lead to serious consequences.
Treatment and diet
Drug treatment for erythematous gastroduodenopathy is rarely prescribed. The main therapeutic method in this case is diet. Don't be alarmed and think that your diet should be reduced to diet soup and cereals, this is not so. On the contrary, the daily food set should be varied in order to provide the body with the necessary substances.
The restrictions apply only to frankly unhealthy foods - smoked meats, marinades, too hot and too cold dishes. You should not drink alcoholic and carbonated drinks, overeat heavily, or “sit” on coffee alone throughout the day. A sick stomach should not be empty, so carefully consider your daily diet.
To help, we suggest you familiarize yourself with the material, where we examined in detail the principles of nutrition for superficial gastritis. Dietary recommendations for this disease and erythematous gastroduodenopathy are identical.
Erythematous gastropathy: what it is and how to treat it, Competently about health on iLive
You will not come across the term erythematous gastroduodenopathy in the office of a gastroenterologist, since this condition is not actually a diagnosis.
Rather, a frightening phrase will appear in the conclusion of the endoscopy result, to which this very doctor referred you. We invite you to figure out together what pathology is hidden under a complex and incomprehensible name.
Consequences
There are two most common complications of erythematous gastropathy: gastritis and peptic ulcer. Sometimes, if this pathology is not treated, the mucous layer of the stomach may atrophy. In turn, against the background of atrophy of the mucous membrane, a malignant tumor of the stomach may appear.
Having seen the diagnosis of erythematous gastropathy in the conclusion of FEGDS, you should not be afraid, but you also should not ignore it. In this case, it is recommended to consult a gastroeterologist or general practitioner. If necessary, specialists will conduct additional research and give treatment recommendations that will allow you to avoid the above complications.
Possible complications of this disease include pathologies such as stomach ulcers or gastritis; stomach cancer rarely develops.
Classification of the disease
The method for diagnosing this pathology is fibrogastroduodenoscopy. This is the most reliable way to determine hyperemic areas in the digestive tract. The doctor uses a special device - an endoscope - to examine the esophagus, stomach cavity and duodenum. In some cases, biomaterial is collected for histological examination.
During the procedure, various parameters of damage to the mucous membrane of the digestive tract are assessed in order to make a correct diagnosis and assess the patient’s condition. Depending on them, there is the following classification of erythematous gastropathy.
According to the form of manifestation
In this case, the extent of the area of hyperemia is assessed.
- The focal form is characterized by limited (local) damage, the inflammatory process occupies a small area of the mucosa. This condition rarely develops into gastritis; it often occurs situationally due to errors in nutrition or as a reaction to taking certain medications.
- The widespread, or diffuse form, has a diffuse nature; erythema can be detected in different gastric sections, covering a large surface of the tissue. In the absence of proper treatment, it can lead to complications - gastritis and peptic ulcers.
Classification in this case includes an assessment of the condition of the mucosa, measures of the impact of damaging factors on the membrane.
- Erythematous gastropathy of the first degree of inflammation is characterized by initial manifestations of damage to the gastric epithelium, with no signs of advanced disease;
- The second degree indicates the progression of the process as a result of the ongoing negative impact of damaging factors on the epithelium. In this case, the process becomes a chronic form of gastropathy or gastritis.
IMPORTANT! This condition usually occurs in the absence of treatment or with inadequate therapy.
The essence of pathology
Erythematous gastropathy is hyperemia of the gastric mucosa, identified during fibrogastroduodenoscopy. Additionally, during the study, swelling of the epithelium, its vulnerability, and increased mucus production may be present.
This endoscopic syndrome occurs as a result of the damaging effects of various factors on the lining of the digestive tract. As a result, erythema occurs - redness caused by a rush of blood to the affected area. Damage is observed on the surface of the tissue and does not affect the deeper layers.
This condition is not a disease, but it is characteristic of superficial chronic erythematous gastritis. With this option, gastropathy persists for a long time; in the absence of adequate therapy, it can develop into more serious diseases, for example, an ulcer.
If there is hyperemia of the epithelium in the endoscopic picture, additional diagnostic tests may be required: for the presence of a bacterial infection (Helicobacter), for determining acidity, in some cases, a biopsy is taken from the affected areas.
Sometimes this symptom does not manifest itself at all and is discovered by chance during a routine examination.
Prognosis and prevention
If the disease is treated promptly and effectively, it does not pose a threat to life. A negative prognosis will occur when the disease is advanced and leads to the development of malignant neoplasms, as well as in the presence of pernicious anemia.
Having studied the causes of the development of gastropathy, it is recommended to design prevention methods in such a way as to protect your body from negative external and internal influences. First of all, you need to monitor your diet, give up bad habits, not abuse medications, and avoid stressful situations. In order to minimize the risks of relapses in gastropathy and prevent further development, patients need to:
- follow all recommendations and prescriptions of the doctor;
- eradicate bad habits;
- constantly fight excess weight;
- adjust nutrition.
Sources: https://gastri.ru/gastropatiya-chto-eto-takoe.html https://teamhelp.ru/gastroenterologiya/giperemicheskaya-gastropatiya-chto-eto-takoe.html gastrit.guru/lechenie/gastropatiya-chto- eto-takoe.html https://ilive.com.ua/health/gastropatiya-zheludka-chto-eto-takoe-i-kak-lechit_124297i15938.html https://etozheludok.ru/zabolevania/osnovnye/gastropatiya-zheludka. html gastrit.pro/lechenie/gastropatiya/ lovenlive.ru/gastropatiya-zheludka-chto-eto-takoe-i-kak-lechit.html This material is exclusively subjective and is not a guide to action. Only a qualified specialist can determine an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Last modified: 03/19/2020
Diagnosis of pathology
To detect the disease - even if there are almost no problems with the stomach - make an appointment with a gastroenterologist.
A comprehensive diagnosis is required, since there is no specific clinical picture. A gastroenterologist, after a visual examination and history taking, may prescribe the following:
- general clinical and biochemical blood test;
- general urine analysis;
- general analysis of stool;
- pH-metry;
- PCR testing;
- endoscopic examination of the gastrointestinal tract;
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy;
- X-ray of the stomach with a contrast agent;
- ELISA.
At the discretion of the doctor, the diagnostic program can be supplemented with other laboratory or instrumental research methods.
Causes
Pathological phenomena in digestion can occur due to hereditary predisposition. Gastropathy is considered a consequence of the influence of external (exogenous) or internal (endogenous) irritating factors. Exogenous include:
- poor nutrition;
- consumption of strong alcohol and drugs;
- smoking.
By endogenous we mean:
- reflux of bile from the duodenum;
- taking medications, including non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- long stagnant processes;
- burns and injuries;
- insufficient blood supply to the stomach walls.
Symptoms of erythematous gastroduodenitis and its treatment options
Erythematous gastroduodenitis is a disease of the gastrointestinal tract, characterized by damage to the gastric mucosa by hydrochloric acid, which begins to corrode it, causing inflammation. To prevent the development of the inflammatory process, it is important to know what it is and begin timely treatment of the disease.
Symptoms
As a rule, in the early stages of erythematous gastroduodenitis, clinical manifestations are mild, and in some cases completely absent. The following signs of the disease should alert a person:
- feeling of discomfort in the stomach after eating;
- burning sensation in the stomach;
- nauseating state;
- general weakness;
- decreased appetite;
- stool disorders;
- increased gas formation;
- belching;
- heartburn.
Advice! The reason to visit a doctor should be the presence of at least one of the symptoms.
Treatment
Therapy for this type of gastroduodenitis should be carried out under the supervision of the attending physician, because the disease requires an integrated approach. The treatment plan includes:
- taking medications;
- compliance with a therapeutic diet;
- use of folk remedies.
Advice! There is no need to ignore your doctor's recommendations. After all, you can get rid of erythematous gastroduodenitis by combining all these methods.
Medicines
Drug therapy is mandatory for this disease. The treatment regimen usually includes antibiotics. They are prescribed to eliminate the bacteria H. Pylori. But therapy is also impossible without taking the following groups of drugs:
- antacid medications;
- bismuth preparations;
- proton pump inhibitors;
- enzyme agents;
- antispasmodics;
- sedatives;
- prebiotics;
- vitamins.
Advice! Drug therapy is selected exclusively by the attending physician. It is not recommended to take medications without his consultation.
Diet
It is impossible to cure pathology without therapeutic nutrition. Therefore, diet is considered the basis of therapy. All unhealthy foods (fried, smoked, pickled, etc.), as well as the following products, are excluded from the diet:
- meat and fish of fatty varieties;
- carbonated and alcoholic drinks;
- sweets;
- flour products;
- strong tea, coffee;
- spices;
- sauces;
- sour berries, fruits.
Allowed foods are best steamed, boiled or baked in the oven. If the disease is acute, it is recommended to take pureed food. You need to eat often (up to 6 times a day) and in small portions. The last meal should be taken 3 hours before bedtime.
Advice! It is advisable to include medicinal mineral water in the diet, for example, Essentuki or Borjomi. Regular consumption of these drinks will significantly reduce acidity in the stomach.
Prevention
Proper and balanced nutrition is the basis for the prevention of erythematous gastroduodenitis. In addition, throughout your life you must adhere to the following rules:
- maintain a sleep and rest schedule;
- engage in a feasible sport;
- treat diseases in a timely manner;
- observe the rules of personal hygiene;
- take medications only with the permission of a doctor;
- stop smoking and drinking alcohol;
- avoid stress.
These recommendations will significantly reduce the risk of developing the disease. It is not difficult to cope with erythematous gastroduodenitis; it is important to follow all the doctor’s recommendations and adhere to a therapeutic diet. But it should be borne in mind that in patients who did not adhere to all prescriptions, their condition may worsen and complications in the form of erosions and ulcers in the stomach may appear.
Source: https://vnorg.ru/zheludok/gastroduodenit/280-eritematoznyy.html