What is hypertrophic gastritis and the mechanism of its development
Hypertrophic gastritis is characterized by thickening of the stomach lining, a decrease in the number of gastric folds and an increase in their thickness. In some cases, inflammation can lead to the growth of polyps (cysts), or erosions may occur in the lower part of the stomach (where food stagnates).
Gastritis develops as follows: dystrophic-degenerative deformations of the gastric walls occur; as gastritis develops, the rate of regeneration processes decreases, epithelial cells atrophy, and rough connective tissue is formed in their place. With this form of gastritis, extensive inflammation of the mucous membrane of the organ occurs, and benign neoplasms appear in the damaged areas.
In the absence of treatment, the risk of degeneration of emerging cysts and polyps into malignant neoplasms increases.
Unlike other types of stomach pathologies, this form of gastritis is characterized by:
- excessive synthesis of mucous substances;
- insufficient production of hydrochloric acid (low acidity) and digestive enzymes.
Hypertrophic gastritis slowly develops from the catarrhal form, which is characterized by slight ulceration on the inner lining of the digestive organ. Lack of treatment contributes to an increase in the area and number of foci of inflammation. At this stage, gastritis with high acidity is detected, which provokes irritation of the mucous membrane.
As a result, the walls of the stomach begin to deform, some bacterial infection joins the negative processes, and fibrous tissue grows in place of the glandular and epithelial cells. The reverse process begins - an insufficient amount of hydrochloric acid is produced to digest food. Food stagnates in the stomach, and this causes fermentation and rotting of proteins and carbohydrates. The walls of the digestive organ thicken, thick folds appear and growths form.
Diet for atrophic gastritis of the stomach: menu, nutrition, treatment
Atrophic gastritis is a pathological condition characterized by inflammation of the gastric mucosa with the disappearance of its secretory cells. As a result, food that enters the gastrointestinal tract stops being absorbed, and the body begins to suffer from a deficiency of vitamins and other nutrients.
And as a final result, all organs and their systems begin to suffer. Diet for atrophic gastritis plays an important role on the path to recovery. With its help, you can relieve abdominal pain and other unpleasant symptoms, improve the functioning of the organ, and speed up the process of regeneration of damaged cells. The selection of treatment and menu selection is prescribed only by a doctor.
The purpose of the diet for atrophic gastritis
With this disease of the stomach, its mucous membrane becomes inflamed, and glandulocytes, which ensure the secretion of the organ, are lost. The place of important glands is replaced by ordinary cells, which leads to the production of mucus by the stomach instead of the juice necessary for digesting food.
Gastritis with low or high acidity in the stomach is often accompanied by heartburn. Many people mistakenly think that diet is an optional condition for therapy, and prefer to drink a soda solution to eliminate the disease.
Such actions only temporarily neutralize the effects of high or low acidity, but increase the risk of stomach cancer. This is explained by the fact that soda remains in the body and is not excreted on its own.
Thus, treatment through diet is necessary.
Nutrition for atrophic gastritis has several main objectives:
- fights high acidity (or low acidity);
- reduces stress on inflamed gastric walls;
- stimulates the digestive process;
- helps eliminate unpleasant manifestations of the disease (belching, pain, rumbling, upset stomach or constipation);
- activates the function of producing enzymes that are required for the breakdown and absorption of incoming food.
Treatment of the disease includes several types of diets, depending on what kind of gastritis a person suffers from:
- atrophic, including chronic form;
- atrophic hyperplastic;
- focal;
- diffuse;
- antral;
- gastritis with high, normal or low acidity.
Chemical composition of food
The daily diet for atrophic gastritis should include no more than 3000 kcal.
Detailed contents of products for the day:
- Protein products ─ no more than 100 grams (up to 60 grams of plant origin).
- Animal fats ─ up to 100 grams.
- Carbohydrates ─ up to 400 grams.
- Table salt ─ no more than 15 grams.
Nutrition should be balanced. The chemical composition recommended by the diet contains such an amount of fats, protein products and carbohydrates that provides the vitamins the body needs and is necessary for its full functioning.
The role of dietary nutrition
For a patient with atrophic gastritis, there should be a gentle diet, since the gastric mucosa, as the pathological process develops, becomes thinner and becomes unprotected.
Dishes should have a neutral taste and be prepared by steaming , boiling or poaching .
The diet should absolutely not include spicy, fried, salty, sour foods, in short, anything that can aggravate the patient’s condition.
Nutrition for atrophic gastritis of the stomach should relieve the diseased organ as much as possible and help it produce gastric juice and digestive enzymes.
Basic diet rules
The same diet may be slightly different for each patient. The diet for atrophic gastritis corresponds to treatment table No. 2. A specialist can adjust nutrition taking into account the individual characteristics of the body.
The diet for atrophic gastritis is based on several general recommendations:
- Food consumption should be fractional. You need to take about 5 or 6 doses per day, each of which is limited to small portions.
- Avoid hot and very cold foods so as not to damage the mucous walls of the stomach.
- You should not eat products made from coarse fiber.
- The temperature for cooking should not exceed 50 degrees.
- Food can be consumed steamed, it is recommended to boil or stew in a slow cooker. It is allowed to fry dishes, but so as not to form a crust.
- Products must be crushed to eliminate mechanical stress on the digestive system and stimulate the enzymatic function of the stomach.
In what form to use
The raw plant should not be consumed. Firstly, it is subject to heat treatment. Secondly, a hard vegetable is difficult to digest for an inflamed stomach.
Boiled or stewed pieces will be healthy and proper dishes. It is forbidden to fry the plant, like any food when sick. A good option would be to try to squeeze out the liquid. It is important to drink the drink for gastritis with low acidity. The juice is easily digested. The advantage of pumpkin drink is that it can be stored for a long time in the refrigerator while maintaining its valuable properties.
The pulp is indicated for people with chronic gastritis; the vegetable contains an abundance of vitamins. Unlike other foods, pumpkin is well absorbed along with nutrients.
The most important thing is the spices. It is not recommended to use for cooking or it is suggested to greatly limit it. Spices irritate the walls of the stomach. If you want to diversify your diet, it is recommended to prepare dietary dishes. If you have any type of digestive system disease, you should not eat hot food. To avoid having to be treated for complications, it is better to cool the food before eating.
Features of the diet for atrophic gastritis
If you are ill, you should exclude all products that need to be intensively digested by the stomach. The diet should include only foods that stimulate acid production. For patients suffering from loss of appetite, dishes from the diet menu should help increase it slightly.
Authorized Products
The therapeutic nutrition menu includes the following products:
Source: https://bugmk.ru/pitanie/pri-atroficheskom-gastrite.html
Classification of gastritis
Hypertrophic gastritis is divided into several types, which are characterized by the duration and intensity of the development of the pathology. The main feature by which they can be combined is the transformation of the mucosal relief; it appears against the background of secretory insufficiency.
Under the influence of irritants, the gastric mucosa becomes inflamed and regenerates; these ongoing processes lead to the appearance of one of the types of hypertrophic gastritis:
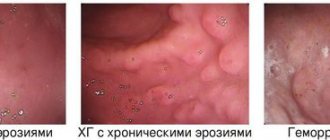
- warty. A characteristic feature of this form is the presence of growths on the mucous membrane that resemble papillomas (warts) in appearance;
- giant gastritis (Menetrier's disease). With this type of gastritis, very large folds are present - up to 3 cm, atrophy of the secretory glands occurs, and the number of mucus-forming glands increases. This type of gastritis is divided into 3 forms: asymptomatic, pseudo-tumor, dyspeptic;
- granular form of gastritis. It is characterized by the formation of small (less than 1 cm) growths resembling grains. Pathological cavities appear inside the gastric walls, which are filled with liquid contents. This form of hypertrophic gastritis is formed against the background of the appearance of cysts of different types and sizes (from 2–3 mm to 1.5–2 cm);
- polypous form. It is typically characterized by the presence of both single and multiple growths (polyps) of connective tissue, which are formed as a result of increased regeneration (the size of the lesions is 0.5-2 cm in diameter).
Growths that form in the stomach can be of various types: benign or formations of a complicated inflammatory process. The hypertrophic process can penetrate into the parenchyma of the walls, that is, into the muscular layer of the digestive organ.
In addition, the pathology is divided into acute and chronic forms:
- The acute form is a dangerous pathology, due to the fact that the cause of its appearance is chemical intoxication. Penetration of caustic alkalis and acids into the gastrointestinal tract promotes deformation of the gastric walls and leads to tissue degeneration.
- The chronic form of gastritis is a sluggish pathology that has stages of exacerbation and remission.
What causes the appearance of hypertrophic gastritis?
The causes of chronic hypertrophic gastritis are quite diverse and have a wide range of infectious, parasitic, and nutritional factors.
Hypertrophic inflammation of the inner membrane is associated with damage by microorganisms, the most famous of which is the bacterium Helicobacter pilori . It is also possible to be affected by the fungus Candida , Cryptococcus , Histoplasma capsulatum . Long-term invasion by these microorganisms is manifested by inflammatory reactions in the stomach cavity, duodenum and small intestine. The following conditions contribute to pathological growth of the mucous membrane:
- autoimmune diseases (lupus, scleroderma, rheumatoid arthritis);
- chronic reflux gastritis;
- lack of proper eating behavior;
- decreased general and local immunity.
- long-term use of proton pump inhibitors, nonsteroidal medications for inflammation, anticancer cytostatics, corticosteroids, and iron supplements sometimes lead to the growth of folds on the surface of the stomach.
Provoking mechanisms that increase the risk of hypertrophic gastritis include poor nutrition, frequent alcohol consumption, smoking, and stressful situations. A genetic disposition cannot be ruled out; sometimes deformation of the mucosa is associated with a gene mutation that causes familial adenomatous polyposis syndrome.
Causes
When hypertrophic gastritis occurs, harmful factors, both external and internal, play a basic role. In some cases, the pathology appears as a consequence of an acute form of gastritis, and in others it develops as an independent disease, as a result of the prolonged and constant influence of various irritating factors.
The most common cause of gastritis is considered to be the presence of Helicobacter pylori in the human body, although its presence is not a mandatory provoking factor for the onset of the inflammatory process, but only predisposes to it. This bacterium enters the human body with poor-quality food and, moving through the stomach, reaches the mucous membrane, where it attaches to the surface of cells. By releasing a substance during its life activity that increases gastric acidity, the bacterium promotes the production of gastrin.
The next reason for the occurrence of pathology is associated with a disruption in the process of movement of stomach contents through the digestive canal. In a patient with reflux, the contents of the duodenum are refluxed into the stomach. The main irritating component is bile, which can cause severe chemical burns in the stomach.
High nervousness and emotional instability can also cause gastritis. The activity of the autonomic system is disrupted, which becomes a provoking moment for the onset of the formation of many diseases of the digestive system.
Other irritants are:
- alcohol consumption;
- poor dental condition;
- binge eating;
- dry food, “on the go”.
In addition, there are other factors that have a negative impact on the stomach and lead to inflammation of its walls:
- smoking;
- long intervals between meals;
- insufficient amount of complete proteins in the patient’s diet;
- use of medications (mercury, salicylic drugs) for a long period of time;
- tendency to food allergies;
- the presence of acute infectious diseases (tuberculosis, intestinal infections, influenza, diphtheria) or focal infections (tonsillitis, adnexitis, sinusitis);
- dysfunctional disorder of the digestive organs (intestines, biliary tract, pancreas);
- the presence in the body of parasites and diseases associated with them (helminthiasis, ascariasis, trichuriasis);
- professional reasons (inhalation of toxic fumes - acids, ammonia, mercury);
- hereditary predisposition;
- low immunity.
Causes
The causes of pathological hypertrophy of the gastric mucosa are as follows:
- Nutritional factor. This includes malnutrition with deficiencies in protein and other nutrients. Nutritional errors are unusual in modern society, but they are possible among antisocial individuals and people who are overly keen on various starvation diets.
- Chronic intoxication. Exposure to lead, alcohol, and other toxic substances matters.
- Hypovitaminosis of various etiologies.
- Smoking.
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Congenital defects in mucosal development.
- History of infectious diseases - hepatitis, dysentery, typhoid fever.
- Metabolic disorders.
- Neurogenic defects.
- Chronic gastritis of other forms.
- Benign tumors.
It is interesting that the list of causes that provoke hypertrophic gastritis is identical to Ménétrier’s disease, although the latter is not considered sufficiently studied by modern medical science.
Symptoms of pathology
The intensity of symptoms may depend on the stage of development of the disease, the age of the patient, and the state of his immune system.
The main symptom of the disease is dyspepsia, which is similar to the erosive chronic form. The following symptoms are observed:
- Belching with the smell of rotten eggs.
- “Hunger” pain an hour after eating.
- Heaviness in the stomach.
- Heartburn.
- Having an unpleasant taste in the mouth.
- Diarrhea.
- Possible vomiting.
With severe deformations of the gastric tissue, severe pain occurs immediately after eating. Appetite disappears, weight decreases sharply, the body becomes exhausted, anemia and pale skin are observed. The main distinguishing signs of this pathology are shortness of breath and tachycardia, which occur half an hour after eating food.
Treatment methods
In case of autoimmune origin of chronic inflammation of the stomach, it is necessary, first of all, to treat anemia, since severe deficiency of vitamin B12 can lead to irreversible neurological disorders. This substance is prescribed by a doctor and taken as an intravenous injection. The dose and frequency of administration depend on the degree of deficiency.
Maintenance therapy, i.e. taking vitamin B12 once a month, may be needed for the rest of your life. Typically, resolution of neurological symptoms can be observed within 6 months after treatment. Unfortunately, in severe cases, when it comes to spinal cord damage, the changes are irreversible.
Hypertrophic gastritis caused by Helicobacter pylori requires combined treatment. It is recommended to take two antibiotics with a proton pump inhibitor for 7 days. It is estimated that approximately 80% of patients experience a complete recovery. If an allergy to antibiotics occurs (or if the bacteria does not respond to this group of drugs), the treatment regimen should be changed.
For chronic inflammation of the stomach caused by excessive use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, drugs are prescribed that reduce the secretion of hydrochloric acid. The most commonly used group of medications are proton pump inhibitors (eg, Omeprazole, Lanzoprazole). They protect the gastric mucosa from damage and reduce discomfort.
For reflux disease, you can take medications that have the task of reducing stomach acidity by chemically binding hydrochloric acid. Treatment is supplemented with drugs with a protective effect (Sucralfate). They form a thick layer on the surface of the stomach wall, as a barrier between the mucous membrane and the acidic contents of the organ.
In cases where pain and discomfort are severe, when bleeding occurs or the presence of a cancerous tumor in the stomach area cannot be ruled out, surgical treatment is necessary. It consists of resection of part or all of the organ and nearby lymph nodes, if the presence of a malignant tumor has been determined.
Diagnosis
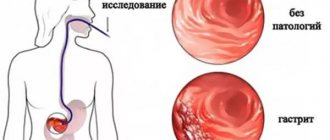
The main method for making a diagnosis is gastroscopy. It helps to identify the extent of damage to the mucosa. For a more detailed examination, the following methods are used:
- blood analysis;
- biopsy;
- examination of the secretory activity of the stomach (performed using a probe);
- examination of mucosal cells to detect the presence of infections and the bacteria Helicobacter pylori.
In addition to the results of instrumental and laboratory studies, you can see external manifestations of hypertrophic gastritis:
- cracks in the corners of the mouth;
- thick plaque on the tongue and teeth;
- pain on palpation of the abdomen.
Diagnostics
If these symptoms occur, you should immediately contact a medical facility for diagnosis and diagnosis. The first stage is initial consultation and examination. The doctor collects the patient’s life history and medical history, clarifies the presence of certain symptoms, as well as their intensity. In addition, the condition of the skin is assessed and the abdomen is palpated. After this, the patient is sent for laboratory and instrumental diagnostics. The most informative methods for making a diagnosis are:
- carrying out endoscopic examination;
- X-ray of the stomach with the introduction of a contrast agent;
- Clinical blood test;
- blood biochemistry;
- pH-metry of the stomach.
Based on the diagnostic results, the most effective treatment tactics are prescribed.
Treatment of pathology
For mild gastritis, treatment is carried out conservatively. It is generally recommended to follow a diet high in proteins and vitamins.
Drug treatment is carried out using the following medications:
- Antibacterial (if bacteria are present) - Amoxicillin, Amoxiclav, Clarithromycin.
- Anticholinergic (reducing protein loss).
- Enveloping and astringent (to eliminate heartburn).
- Painkillers (to relieve pain attacks).
- Enzymatic (to improve digestion) - “Panzinorm”, “Festal”, “Mezim Forte”.
In addition, for diarrhea, probiotics and prebiotics are prescribed - “Bifiform”, “Linex”, “Enterol”, “Acipol”.
In the complicated form of gastritis (when bleeding, pain, swelling is present), the disease requires surgical intervention. In this case, the overgrown tissue is removed. When there is a risk to the patient's life, a complete or partial gastrectomy (excision of the stomach) may be used.
Diet for hypertrophic gastritis
The main condition for the treatment of hypertrophic gastritis is compliance with a special gentle diet.
With hypertrophic gastritis, it is very important to follow the principle of fractional nutrition - food intake is carried out in small portions, at least 5-6 times a day.
After the operation, the patient should eat food during the first six months only in pureed form and in compliance with the temperature regime (food should not be too cold or too hot).
| Prohibited products include | Recommended for use |
| strong coffee and tea, chocolate | pureed cereal soups |
| mushrooms | cottage cheese (non-sour), cheeses (low-fat and mild) |
| alcohol | lean meats (rabbit), poultry (boiled turkey, skinless chicken) and fish |
| sausages and canned goods | lean beef as mince for cutlets |
| fatty meats, poultry and fish | steamed omelette or soft-boiled eggs |
| sour cream | white bread (only yesterday's bread) |
| hot seasonings and sauces | oatmeal porridge |
| brown bread, pastry products | jelly |
| grape | dried fruit compotes |
For gastritis, an apple is considered a useful product. Thanks to the pectin it contains, the functioning of the entire digestive tract improves. During the acute phase, it is recommended to consume the apple baked.
Also, for gastritis, it is recommended to drink milk with a spoon of honey. It helps with gastritis with high acidity. An important condition for this is to consume the mixture warm, preferably before bedtime. Milk helps reduce acidity and coats the mucous membrane, and honey, thanks to the microelements and vitamins it contains, has an anti-inflammatory effect on the patient’s body as a whole.
Treatment with folk remedies
Therapy with traditional methods is allowed only at the rehabilitation stage. To restore the damaged gastric wall, aloe juice, medicinal herbs, honey and other folk recipes are used.
Potato juice is used as an enveloping agent that has a beneficial effect on the gastric mucosa; it can be used to eliminate erosions and small ulcers on the surface of the mucosa. To obtain the product, squeeze the juice from several potatoes and drink half a glass 30 minutes before meals. In addition, it is good to drink this remedy on an empty stomach, 1 glass an hour before breakfast. Duration of therapy is 10 days.
Drinking mineral water helps reduce stomach acidity and suppress the effects of hydrochloric acid. The effect of mineral water depends on its temperature; when it is necessary to reduce acidity, drink warm water. It is recommended to drink 1 glass of mineral water at one time.
When increased synthesis of gastric juice is required, mineral water is drunk cold in the amount of 0.5 cups, and should be drunk very slowly. When drinking water, you should rid it of gases by shaking or heating it a little. The duration of the course of therapy is a month.
Sea buckthorn oil is considered another powerful remedy in the treatment of atrophic gastritis, as it has wound-healing, anti-inflammatory and enveloping effects. It should be consumed to heal ulcers and erosions before meals, a dessert spoon at a time.
The use of flax seeds as a decoction helps restore the mucous membrane, protects and envelops it. To prepare the remedy, use 1 tbsp. Pour a spoonful of flaxseed into hot water and boil for 5 minutes, then leave to infuse for about 2 hours. The strained broth is consumed before meals, 1 tbsp. spoon. You can also use another recipe to prepare the product: mix 1 tbsp. spoon of flax seeds with 0.5 liters of hot water, leave for several hours. Drink a glass of the strained product 1 hour before meals.
If your stomach has high acidity, it is recommended to drink 1 glass of warm boiled water before breakfast. In addition, it is recommended to use a decoction of the following herbs: St. John's wort, chamomile, yarrow - 2 tbsp. spoons, celandine - 1 tbsp. spoon. 1 tbsp. A spoonful of this mixture is poured with boiling water and left to cool. You should drink the resulting infusion 5-6 times a day before meals, a quarter glass. Course – 2 months.
Fresh cabbage juice helps with low acidity. It should be consumed slightly warmed, half a glass 1-2 times a day.
Prevention
If the patient follows all the recommendations of the gastroenterologist, then the prognosis for recovery is favorable. Complete recovery is facilitated by following a gentle, balanced diet.
You will have to completely give up drinking alcohol, smoked and fried foods, strong coffee and tea. Nutritionists recommend more often including the following foods in your diet:
- milk, kefir, Varenets, cottage cheese;
- chicken breast, lamb, lean beef;
- lean fish, seafood;
- dried white bread, vanilla crackers;
- potatoes, Chinese cabbage, carrots, pumpkin.
To never know what it is, it is necessary to prevent hypertrophic gastritis. You should quit smoking and snack on fast food on the run. Long walks in the fresh air, physical exercise, and a lack of stress help improve digestion.
Prevention of gastritis
To prevent this type of gastritis, you must follow the following rules:
- eat fully and rationally;
- get rid of bad habits;
- treat diseases of the digestive system in a timely manner.
References: https://www.smed.ru/guides/43946/doctor/ Belousov A. S., Vodolagin V. D., Zhakov V. P. Diagnosis, differential diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the digestive system. - M.: Medicine, 2002. Clinical recommendations. Gastroenterology / Ed. V. T. Ivashkina. - M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2006. https://spina.co.ua/lechenie/gastrit/ A. T. Barmagambetova Clinical symptoms, diagnosis, treatment of gastritis and prevalence level among the population of the Republic of Kazakhstan // Bulletin of KazNMU. 2013. No. 2. https://doc.ua/bolezn/gastrit Notes from the author of the article, based on personal experience. This material is purely subjective and is not a guide to action. Only a qualified specialist can determine an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Last modified: 03/17/2020
Symptoms
As a rule, the first symptoms of a disease such as hypertrophic gastritis appear immediately after the onset of inflammatory processes due to damage to the gastric mucosa. However, in the chronic form, the disease can be practically asymptomatic for quite a long time until remission occurs. The first signs in this case are often confused with food poisoning or a cold. The acute form appears immediately and develops very rapidly and quickly.
The main symptoms include heartburn, nausea and vomiting. The patient loses his appetite. After eating, severe pain is felt in the abdomen. The patient eats less and loses weight quickly. Swelling and flatulence appear. Salivation increases. Often the disease is accompanied by bowel dysfunction. Some patients develop diarrhea, others suffer from constipation. There is a general weakness of the whole body. Bleeding in the stomach is possible.
If any of these signs occur, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible and undergo a medical examination. It is not a fact that with such symptoms hypertrophic gastritis will necessarily be detected. Timely diagnosis and detection of gastritis will allow you to avoid unpleasant symptoms and quickly eliminate the disease by undergoing a course of treatment.
Treatment of chronic gastritis
Treatment of gastritis is always complex. Patients are prescribed a diet: table No. 1 or 2 according to Pevzner (depending on the preservation of the secretory function of the stomach).
If a patient is diagnosed with Helicobacter pylori infection, he is prescribed drugs from the group of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and two antibacterial agents. PPIs reduce the acidity of gastric contents, making the bacterium more vulnerable, and a complex of two (and sometimes three) antibiotics is necessary, since it is extremely resistant to drug effects. Such therapy is carried out for 1-2 weeks, after which tests for Helicobacter pylori are repeated. If for some reason proton pump inhibitors cannot be recommended, drugs from the group of H2 blockers (ranitidine, famotidine) are prescribed for these purposes.
To stimulate the restoration of the mucous membrane, gastroprotectors based on rebamipide (Rebagit) are prescribed. It improves blood circulation in the mucous membrane, promotes the regeneration of its cells, and reduces the activity of inflammation. In addition, rebamipide improves the effectiveness of eradication (destruction) of Helicobacter. The drug acts throughout the gastrointestinal tract and at any of the three structural levels of the mucosa.
To reduce the feeling of heaviness and fullness of the stomach, and reduce the frequency of reflux, prokinetics (itopride) are prescribed. These drugs normalize gastrointestinal motility. For reflux gastritis, ursodeoxycholic acid preparations (ursosan) help reduce the damaging effects of bile.
Diet
It is important to follow a diet specially developed by your doctor, since otherwise you can only worsen the situation. Some foods can cause further damage to the stomach and serious negative consequences for the gastrointestinal tract. Meat, fish, rye bread, puff pastry, broths, borscht, cabbage soup, and soups (mushroom and cheese) should be excluded from the diet. It is also necessary to exclude fatty and fried foods, carbonated drinks, alcohol, and sweets.
How to get rid of abdominal pain due to gastritis
Despite such a large number of dietary restrictions, patients are usually allowed to eat many other healthy and tasty foods and dishes. In particular, with this type of gastritis, you can eat milk porridge, vegetable soups, wheat bread, lean meat (boiled or steamed), omelettes and soft-boiled eggs. It is acceptable to consume natural dairy products. Patients can drink kefir and eat butter. It is useful for this disease to eat boiled vegetables (carrots, beets and potatoes).
A disease such as atrophic gastritis is a rather complex pathology, since along with the inflammatory process, atrophy of the mucous membrane and glandular tissue occurs. The cells and tissues of the stomach gradually change their structure until they die completely or partially, which directly affects digestive function. The following are disrupted: secretion of the mucous membrane, production of enzymes, breakdown and absorption of substances necessary for the body. Over time, the stomach stops “accepting” any food, and the percentage of nutrients entering the body becomes unacceptably small. As a result, not only the digestive system suffers, but the entire human body.