Loose stools are a common gastrointestinal disorder. Bloody diarrhea in an adult is a rather dangerous symptom of many diseases. What should you do if your stool becomes red and runny? The disease indicates the development of an infectious-inflammatory process in the body and requires immediate medical attention.
What causes bloody discharge in loose stools?
The appearance of blood streaks in the stool indicates damage to the blood vessels of the tissue. This pathological process is caused by various unfavorable factors.
Important! Before starting therapy aimed at eliminating the problem, it is necessary to identify the cause of its development.
Under no circumstances should you be ashamed of a delicate problem and try to treat the disease yourself at home without consulting a doctor. Even if you know for sure that diarrhea appeared after alcohol and it was this that caused it. The presence of blood in the stool may be a sign of a dangerous pathology. It is in case of diarrhea with blood that it is necessary to understand the seriousness of the situation and call an ambulance. It is important to know that bloody diarrhea is not an independent disease, but only a sign of it. Only a medical specialist can establish the exact cause and diagnosis.
Bloody stool can occur with anal fissures. Usually after defecation there is pain and discomfort in the anus. Bloody diarrhea with anal fissure occurs if there is a lack of enzymes.
Also, diarrhea with blood in an adult may indicate inflammation in the lower intestines. The inflammatory process is promoted by a sedentary life, exacerbation of chronic diseases, and neoplasms in the rectum. Tumors in the intestines can lead to bloody diarrhea, which becomes normal.
The presence of a blood clot also provokes dysbacteriosis. The presence of blood streaks can be observed periodically during the disease. The food is not digested sufficiently, and soon bloody discharge is detected in the stool.
Loose stools with blood develop with dysentery, which also causes severe pain in the peritoneum and high fever. In case of illness, the patient is hospitalized and treated in a hospital.
Know! The causes of diarrhea must be determined by a doctor. Any infection that enters the body can cause serious and dangerous complications.
The main causes of bloody discharge in loose stools:
- colitis;
- gastrointestinal diverticulum;
- anal fissure;
- dysbacteriosis;
- dysentery;
- Crohn's disease;
- ulcer;
- infectious-inflammatory process in the gastrointestinal tract;
- oncology.
Treatment of diarrhea with traditional medicine
If there is no allergic dependence on herbal treatment at home, you can use folk remedies, that is, infusions and/or herbal decoctions. Time-tested folk recipes for bloody diarrhea:
- Chamomile infusion. A tablespoon of dry chamomile is poured into 200 ml of boiling water and infused in a thermos for 2-3 hours. Take 50 ml 3 times a day.
- Herbal collection. A tablespoon of a dry mixture of shepherd's purse, burnet root and erect foot is boiled in 250 ml of water for 5 minutes after boiling. The drug is taken 30 ml 5 times a day.
Such herbal treatment of diarrhea is not recommended for pregnant women, people with chronic pathologies of the genitourinary system, and children under one year of age.
A decoction of dry chamomile will eliminate spasms in the intestines
If there is a temperature
Bloody diarrhea is often accompanied by fever. If these two symptoms are accompanied by vomiting, then we can already judge poisoning. After eating poor quality food, diarrhea occurs 1-12 hours later. Temperature may also indicate inflammation of the pancreas. A sick person must see a doctor. This condition is especially dangerous.
Bloody diarrhea, which is accompanied by a high temperature, can last more than a day. During this period, the gastrointestinal tract undergoes significant damage due to the pathological process. A fever may indicate a serious infection or poisoning. A doctor will be able to understand the etiology of diarrhea. Bacterial infection, as well as other diseases, require qualified medical care.
The correct tactics for eliminating loose stools with bloody discharge depends on the established cause of diarrhea. In the treatment of diarrhea with blood, it is important to prevent intoxication of the body, eliminate dehydration and begin to fight the inflammatory process.
Diarrhea with mucus and blood responds well to treatment with the use of certain measures and medications. To help cope with loose stools:
- sorbents;
- modern means - probiotics;
- drinking too much;
- diet.
Drinking plenty of fluids ensures elimination of water imbalance in the body during diarrhea. To stabilize the water-salt level in the body, Regidron solutions are used.
Treatment of bloody diarrhea in an adult
The main goal of treating diarrhea with bloody discharge is to directly address the cause of the disorder, and not to eliminate the frequent urge to defecate. The choice of treatment tactics definitely depends on the source of the pathology. If diarrhea with blood is caused by the action of infectious agents, it is necessary to determine their group and select adequate treatment with antibacterial and antimicrobial agents.
The main goal of treating diarrhea with bloody discharge is to directly address the cause of the disorder, and not to eliminate the frequent urge to defecate.
Although bloody diarrhea is often not a very dangerous disease, sometimes hospitalization of the patient is required, so self-medication is contraindicated. An important stage of treatment is the restoration of water and electrolyte balance in the body. In recent years, many groups of microorganisms have become resistant to many groups of antibacterial agents. Now doctors prefer to use drugs from the group of fluoroquinolones - Lomefloxacin, Norfloxacin, Ofloxacin, Pefloxacin, Ciprofloxacin, Levofloxacin, Sparfloxacin, etc. In special cases, patients require emergency medical care for diarrhea with bleeding.
Such situations include:
- old age;
- infants under 1 year of age;
- hyperthermia above 38 C;
- excruciating and severe pain in the abdomen;
- presence of vomiting containing blood or black vomit;
- impaired consciousness, severe dehydration.
If you have digestive disorders, then there is an option to turn to traditional methods of treatment. You can make an infusion of chamomile leaves or drink various herbal infusions.
Any disease can be prevented. Likewise, digestive disorders can be “cured” even before they appear. Follow a diet, eat small portions 5-7 times a day, and do not overeat before bed. Following these simple recommendations will prevent the development of many diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, a clear symptom of which is diarrhea mixed with blood.
Sources
https://prootravlenie .ru/simptomy/ponos-s-krovyu-prichiny-lechenie
https://gemoparazit.ru/raznoe/ponos-s-krovyu#i-3
https://vrachta jna.ru/ponos-s-krovju-u-vzroslogo-chto-delat-pri-ego-pojavlenii-lechenie.html
https://gastrogid.ru/ponos-s-krovyu-prichiny-lechenie-i-posledstviya/#i-2
Ulcer
Ulcerative damage to the mucous membrane of the digestive organ provokes the development of bleeding. For peptic ulcers, it is important to use medications for exacerbation. The ulcer is often accompanied by black, loose stools.
Once an ulcer is detected, treatment for diarrhea includes diet and medications to heal the ulcer. The action of the medications used should be aimed at stopping bleeding or bleeding.
Diarrhea with blood and mucus causes dangerous disturbances in the body and severe dehydration. Large fluid loss can lead to seizures and other dangerous consequences. It is important to take food and water in small, frequent portions. Fenyuls, Ferrum-lek, Maltofer will help increase hemoglobin in the blood.
Nutrition and prevention
One of the treatment options for diarrhea is diet. In the first days of diarrhea, the patient should eat this way:
- 24 hours – only sorbents;
- second day - crackers and bananas, a glass of strong tea;
- third - a boiled egg is added;
- from the fourth day - boiled meat, fish, boiled vegetables, slimy porridges: rice, oatmeal.
Diarrhea with blood is dangerous for the body, so the sooner it is stopped, the better.
Prevention measures include proper nutrition and personal hygiene. It is necessary to exclude dyes and enzymes, strengthen the immune system, drink only boiled water, wash your hands more often, before eating - be sure.
Haemorrhoids
Damage to blood vessels and the formation of anal fissures cause bloody discharge in the stool. Hemorrhoids often cause bloody stools. Blood on toilet paper is observed due to the fact that internal hemorrhoids bleed, anal fissures occur, and blood circulation in the intestines and anal canal is disrupted.
Diarrhea due to hemorrhoids with blood is treated with drugs that eliminate inflammation of the nodes and stabilize the stool. If a prolapsed hemorrhoid is detected, it is necessary to use healing anti-inflammatory ointments and rectal suppositories. As soon as the medication begins to act, bleeding in the anal canal will disappear. Sea buckthorn suppositories and propolis-based suppositories help eliminate bleeding and diarrhea. You can use the drug Relief.
What not to do, and what is the danger of the phenomenon
With anal bleeding and diarrhea, dehydration quickly sets in. The body not only loses moisture along with feces, but also cannot absorb water and is left without a circulating blood volume. This can lead to a sharp increase in the load on the cardiovascular system and death. Another possible complication is anemia. Most often, pathology develops as a result of small but frequent blood loss.
In case of diarrhea with blood, it is strictly forbidden to self-medicate. This is due to a large list of reasons that can trigger the occurrence of this condition.
As a result of self-administration of medications, a person’s well-being can sharply deteriorate. For example, this often happens when using antibiotics. They help cope with infection and prevent infection of soft tissues and mucous membranes, but have a powerful irritating effect on the internal walls. Open wounds make the situation worse: bleeding may increase.
Oncology
Blood from the anus is often observed with tumors of the digestive organs. The higher the tumor is located, the darker the stool will be. Bloody discharge from a tumor is often found on the surface of the stool. Often blood in stool can be seen in cases of intestinal and stomach cancer.
Oncology requires special specific treatment. When diarrhea becomes the norm with a malignant tumor, it is necessary to direct therapy to eliminate anemia and take iron-containing drugs. Surgery can help eliminate a malignant tumor.
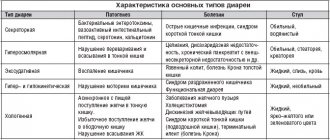
Types of diarrhea
A simplified understanding of diarrhea is loose stool that accompanies various conditions of the human body, usually infectious diseases.
The consistency does not fully characterize diarrhea. The second sign is the frequency of bowel movements: diarrhea is said to occur when it reaches more than three times a day.
The third most important characteristic is the volume of feces exceeding the daily norm (200 ml).
Another sign of diarrhea is that the stool must contain feces, for example, with cholera, frequent loose stools can reach 10 liters per day, but they consist of mucus, not feces, so technically it is not diarrhea.
But when determining normality and pathology, it is not the frequency, consistency and other characteristics that are important, but changes in the usual order of bowel movements.
The individual characteristics of some people allow bowel movements three times a day, and others - three times a week, but both of them can be quite healthy.
You should be concerned about changes in the frequency of bowel movements, the degree of stool formation, odor, color, and the appearance of additional impurities - streaks of blood, pus, remnants of undigested food, and so on.
Diarrhea causes a deficiency of fluid and electrolytes in the body, and this is its main danger.
The balance is disrupted with unformed stools, but with liquid stools the process is more rapid. Diarrhea up to two weeks is considered acute, and over three weeks is considered chronic.
Any medical student can easily identify the source of diarrhea. Every day, 8 liters of liquid enter the intestines. 85% is absorbed from the small intestine, the remaining 15% (about a liter) from the large intestine.
With profuse diarrhea, the small intestine “leaks”, the watery stool has a sharp and foul smell, you can see pieces of undigested food in it, and in most cases the stomach does not hurt. Pain may indicate damage to the colon.
Video:
Another difference in diarrhea depending on the place of occurrence is the frequency of bowel movements. The closer the source of diarrhea is to the anus, the less able a person is to hold back bowel movements.
If there is a lot of feces, but trips to the toilet are rare, then the problem is probably in the small intestine. If the functioning of the large intestine is impaired, feces are usually scanty, but you have to run to the toilet much more often.
There are 4 main causes (mechanisms) of diarrhea:
- secretory activity of the intestinal walls;
- increased osmotic pressure in the intestine;
- exudation as a result of increased permeability of the intestinal walls;
- decrease or excessive increase in intestinal motility.
Depending on the mechanism, four types of diarrhea are distinguished. Copious, too loose stools are distinguished by secretory diarrhea.
The same high-water, but greasy (sticks to the smooth faience of the toilet) stool is characteristic of osmotic diarrhea.
Scanty, loose stools mixed with blood and mucus are a reason to suspect exudative diarrhea. Liquid or poorly formed scanty stool characterizes diarrhea due to accelerated or slowed intestinal motility.
Injury
Trauma to the intestine or other internal organ causes damage to its walls. Bleeding of varying intensity occurs. Blood in the stool can be found after a bruise to the soft tissue of the intestines or stomach. Timely medical assistance in treating the injury will stop the bleeding. In case of injury, it is better to remain calm and follow all medical instructions.
If the causes of diarrhea with blood in an adult are quite dangerous, then the patient should undergo treatment in a hospital. The patient is given intravenous infusions of prescribed medications and saline solutions, and intramuscular injections are given.
When diarrhea with blood in an adult, the cause of which has not been identified, you can feel burning and itching in the posterior canal, as well as pain of varying intensity. It is important to undergo medical diagnostics to determine the exact cause of the development of a dangerous symptom.
How to treat bloody diarrhea
When diagnosing infectious diseases, treatment is carried out only in a hospital setting in the infectious diseases department. The doctor prescribes antibacterial therapy and also takes measures to prevent dehydration and eliminate intoxication.
For this purpose, the following may be prescribed:
- Ofloxacin. The drug should not be used by pregnant and lactating women suffering from epilepsy and enteritis, as well as children under 15 years of age.
- Ciprofloxacin. A strong antibiotic is contraindicated in pregnant and lactating women, as well as children under 15 years of age.
With diarrhea with blood, beneficial substances are not absorbed by the inflamed intestines, which leads to vitamin deficiency. Water with the addition of Ringer's solution or Regidron powder will help you recover. These preparations contain the daily amount of microelements and salts necessary for the body.
Complex treatment in other cases directly depends on the cause of the appearance of blood in the stool:
- In case of hemorrhoids, treatment is carried out with wound healing and hemostatic drugs. Hemostatic drugs such as Vikasol are prescribed; suppositories with adrenaline are used.
- If a peptic ulcer or intestinal tumor is diagnosed, in addition to drug therapy, surgical intervention may be required. After removing the tumor or closing the defect on the stomach wall, bloody diarrhea stops.
- In case of dysbacteriosis, treatment is carried out with drugs containing bifidobacteria and lactobacilli - Bifidobacterin, Linex, Bifiform, Lactobacterin. Such products restore intestinal microflora. This disease requires an appropriate diet.
- For mild diverticulitis, treatment is possible at home. Bed rest, taking antibiotics (Timentin, Cefoxitin), drinking plenty of fluids and a strict diet are recommended. The doctor may prescribe pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs. If the disease occurs in an acute form, urgent hospitalization of the patient is necessary and, most likely, surgical intervention.
- Treatment of poisoning comes down to drinking plenty of fluids, diet and medications that remove toxins from the body, for example, Reosorbilact. It is mandatory to take products that restore intestinal microflora, for example, Linex.
The cessation of diarrhea does not mean that the person is healthy and therapy can be interrupted. The process of intestinal restoration is long and cannot be neglected. Otherwise, the diarrhea will return. Vitamin complexes are also needed to restore the body's strength.