Intoxication
Poisoning the body with toxins provokes abdominal pain with nausea and loose stools. Poisons can enter the body one time and cause deterioration, or accumulate for years.
Poisoning of the body can be caused by:
- Eating food that has been spoiled or has not been processed properly (toxins may be present on vegetables and fruits due to their processing with chemicals). Poisoning can be caused by eating poisonous mushrooms.
- Side effects from medications. Intoxication can occur due to prolonged use or due to non-compliance with the dosage of the drugs. Poisoning often ends in death.
- Toxic gas poisoning. They enter the respiratory tract, and then into the stomach and cause pain and vomiting. Toxins can accumulate in workers in hazardous industries. Or accidental inhalation of toxic substances.
- Poisoning by poisons. This may occur due to incomplete rinsing of detergent from clean dishes or due to accidental use of products with toxic compounds.
- Infectious diseases and diabetes provoke the release of toxins by the body itself or the causative agent of the disease. As a result, the poisons accumulate, causing pain and vomiting.
- Low-quality alcoholic products or consumption of them in large quantities. Toxins negatively affect the liver and other organs of the gastrointestinal tract, and provoke pain and disruption of the digestive system.
- Smoking on an empty stomach. Nicotine irritates the mucous membrane, causing pain and nausea.
At the first manifestations of food poisoning, it is necessary to take the correct first aid measures (they will be described below). And the faster and more qualified it is provided, the greater the chances of a favorable outcome.
Infectious lesions of the gastrointestinal tract
Food poisoning is a set of symptoms of a digestive tract disorder (nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, high body temperature), which can be combined with other unpleasant symptoms. Most often, the disease can be diagnosed in a child, since the immune system is not fully formed.
The causes of the disease are associated with the consumption of poor quality food and water, poisonous plants, inedible mushrooms, chemicals (salts of heavy metals, dyes, toxins, etc.). Food poisoning, depending on the severity, can begin in different ways: starting with an increase in temperature to 37 degrees and ending at 40.
Malaise, general weakness, stool disorder in the form of frequent bowel movements, severe cramping abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting, decreased blood pressure and cold sticky sweat appear.
In severe cases, symptoms not related to the digestive tract may appear: decreased vision and hearing, headache and muscle pain, convulsions, and others. Treatment requires emergency hospitalization. In such cases, it is necessary to do dehydration therapy.
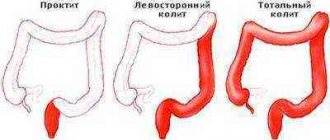
Colitis (enterocolitis)
An inflammatory disease characterized by damage to the mucous membrane of the small or large intestine. The disease can be either infectious or non-infectious. Most often, the disease is combined with acute gastritis and allergies. There are many reasons why the inflammatory process occurs.
Most often it appears as a result of damage to the mucous membrane by any infection, helminths, poisons, or caustic chemicals. But there are other factors that contribute to the development of the disease: poor diet, prolonged and frequent constipation, primary diseases that result in colitis.
Symptoms of damage to the intestinal mucosa begin with abdominal pain in the navel area, stool upset (diarrhea gives way to constipation), increased gas formation and bloating, and weight loss. An admixture of mucus and blood may appear in the stool, which indicates severe inflammation and a violation of the integrity of the mucous membrane.
Shigellosis
An infectious disease caused by bacteria of the genus Shigella. Another name for the pathology is bacterial dysentery. Based on the observations of specialists, it was concluded that people living in large cities are more susceptible to the disease. This is due to the fact that the city has a much higher population density.
People with a low standard of living, who do not have access to clean water and the opportunity to eat quality foods are also more susceptible to infection. Shigella enters the body through food, water or household contact.
Bacterial dysentery begins acutely: nausea and vomiting, cramping pain in the lower abdomen, in which there is a constant urge to defecate, tenesmus after bowel movements, watery diarrhea with streaks of mucus or blood, the number of bowel movements reaches 10 or more times in 24 hours, in which the number of feces is compared to spit.
Due to this condition, patients experience general weakness, malaise, dry skin and mucous membranes as a result of dehydration. The body temperature is high and can reach 39 degrees, severe headache and chills appear. Treatment of the disease is carried out with antibacterial drugs under the supervision of a doctor.
Salmonellosis
Acute intestinal disease caused by bacteria of the genus Salmonella. The source of infection can be carriers or sick people, infected animals (poultry, livestock, cats, dogs, etc.), dirty water, contaminated food. It is worth noting that freezing does not affect the virulence of bacteria.
Salmonellosis can begin to appear several hours after the bacteria enter the body. Of all the forms, the gastroenteric form of the disease is the most common. It manifests itself:
- in the form of a sharp rise in temperature and signs of intoxication (headache, malaise, general weakness, body aches);
- paroxysmal pain appears in the abdomen;
- diarrhea with foamy and foul-smelling green stool.
Nausea and vomiting may occur more than 5–7 times a day, depending on the severity of the illness. Treatment of salmonellosis is possible only with hospitalization.
Problems in the gastrointestinal tract
Nausea and abdominal pain are the most characteristic symptoms of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Additionally, pain may be accompanied by heartburn, constipation/diarrhea and fever. To get rid of the above symptoms, treatment is necessary under the supervision of a therapist; the diseases do not go away on their own.
Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract causing abdominal pain and nausea:
- gastritis in acute and chronic form. Pain occurs due to impaired blood supply to the organ and the condition of its mucosa;
Gastritis is always accompanied by nausea and abdominal pain; in the acute form, vomiting is added - stomach ulcer. The irritated and damaged surface of the stomach reacts painfully to food intake and physical activity;
- intestinal or biliary colic. Pain and nausea are relieved by vomiting and defecation;
- disruption of the intestines with bloating, flatulence. Accumulated air causes pain and nausea;
- infectious diseases of the digestive system. Pathogens irritate organs with waste products and secreted toxins;
- inflammatory processes in the digestive tract. Due to the tumor, the organ increases in size, it is compressed and nearby organs are compressed, which causes pain;
- binge eating. In this case, the stomach is stretched to its maximum size, its functioning is disrupted, which provokes pain and nausea;
- hernia in the esophagus. Eating can cause pinching;
- formation of gallstones;
- benign and malignant tumors;
- injuries to the gastrointestinal tract or ruptures with hemorrhage (may be caused by a tumor or inflammation);
- dysbacteriosis or intestinal obstruction;
- abnormal structure of organs caused by genetic changes.
It is impossible to independently identify which organ has malfunctioned without a medical examination. Pain can radiate to all organs of the gastrointestinal tract. The sooner treatment is started, the faster and more effective it will be.
If nausea, headache, weakness, temperature
The simultaneous appearance of symptoms such as fever, nausea, headache, signals the presence of a specific disease. There are currently many diseases with similar manifestations, and establishing a diagnosis helps determine the choice of the right treatment methods.
The very perception of headaches, their intensity and frequency are different for each person with the same disease. If you make a list of the most common diseases that suggest the presence of these signs, you will get the following:
- processes that cause changes and deformation of the vertebral sections with pathological consequences;
- cerebral vascular damage;
- diseases associated with disruption of the circulatory system;
- processes of inflammation of the lining of the brain;
- malignant tumors;
- non-malignant formations;
- diseases resulting from viruses and infections entering the body;
- and many other diseases.
The temperature in such cases varies from 37 degrees and above.
In the structure of the brain there is a center that is responsible for maintaining the temperature of the human body in normal conditions. This center is located directly in the hypothalamus. In the absence of any disturbances in work, body temperature usually does not exceed 37 degrees.
However, if the central work goes out of the usual rhythm, then this indicates the beginning of the development of thermoneurosis. The temperature in this case ranges from 37 to 39 degrees, and can remain at the same level for quite a long period of time.
There is pain in the head area, often with nausea.
Symptoms may be caused by the acquisition of inflammatory diseases, endocrine disorders, infectious diseases and injuries. According to statistics, such manifestations usually appear in people who are uncommunicative, sensitive and melancholic. Treatment is prescribed after a detailed examination and is carried out under medical supervision.
The main methods and techniques include acupuncture procedures, hypnotic and auto-training sessions, adherence to a routine that includes alternating vigorous activity with rest, a balanced diet and adequate restorative sleep.
If you begin to feel sick and dizzy, there is severe weakness, the temperature rises above 38 degrees, loss of appetite, periodic vomiting and rapid weight loss occur, you should consult an oncology clinic.
The reasons for this condition may be:
- blood cancer;
- kidney tumor;
- neoplasms in the lungs and liver;
- diseases associated with disorders of the vascular system;
- brain tumors, both malignant and benign.
If, for some reason, a certain amount of toxins and other harmful substances, as well as viral infections and bacteria that can cause acute poisoning of the body, enters the body, then intoxication occurs.
The symptoms are of the same type and manifest themselves as follows: fever, pallor, nausea with vomiting, chills and severe headache. After vomiting attacks, the patient begins to feel relief. Intoxication can be of varying severity.
If a person begins to lose consciousness and there is no cessation of vomiting even after washing the stomach, then an ambulance should be called.
As for chronic intoxication, its occurrence is caused by renal failure or damage to the nervous system and the presence of brain tumors, as well as processes of inflammation and infectious diseases.
A companion to persistent arterial hypertension is often morning pain in the back of the head with a feeling of fullness and pulsation.
Headache and fever constantly begin to be accompanied by chills, a feeling of heaviness, rapid heartbeat, dizziness, and weakness. Sudden vomiting without nausea may occur.
Older people are susceptible to atherosclerotic changes in blood vessels due to refined food in their diet, sedentary lifestyle, alcohol abuse and smoking.
As a result, the vessels gradually narrow, since all of the above reasons lead to plaque fatty formations, and blood supply processes are disrupted. Because of this, the organs do not receive enough oxygen.
The body is given no choice but to seek compensation to provide internal organs with nutrients and oxygen. For this reason, blood pressure increases.
If this condition appears for the first time, you should immediately consult a doctor or call an ambulance. In case of repetitions, it is necessary to take the medications prescribed by the doctor urgently and periodically measure your blood pressure with half-hour breaks.
This term is used in medical terminology to refer to pain during menstrual cycles. With strong unbearable sensations in the lower abdomen, dysmenorrhea is pathological in nature and has a number of features:
- manifestation of weakness;
- vomiting accompanied by constant nausea;
- excessive salivation;
- attacks of chills alternating with fever;
- dizziness with severe pain;
- the temperature usually rises to 38 degrees.
What is the cause of such conditions can only be determined by a competent specialist. In order to reduce pain, painkillers are most often prescribed, and in the presence of migraines, triptans are prescribed.
Similar symptoms may occur with disorders of the intervertebral discs with further development of pathological changes. This occurs when there is insufficient muscle blood supply and deformation of the discs between the vertebrae.
The diagnosis in this case is most often osteochondrosis of the cervical spine or myogelosis.
Very often, in the presence of a headache and high temperature, the appearance of infectious diseases is assumed. In winter these are usually viral infections, and the flu is no exception. With the flu, the characteristic symptoms are a runny nose and sore throat, a general feeling of severe heaviness and fatigue.
However, you should keep in mind: if the pain intensifies, becomes bursting, begins to feel nauseous, the neck muscles tense, and your general health worsens, it is quite possible that these are signs of meningitis.
For persistent nausea and vomiting with prolonged and severe headaches, hospitalization is required, and the sooner the better.
A relatively new type of infection is stomach flu. Its signs include diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, fever, accompanied by chills.
This disease is contagious and can be contracted through food or water contact. For a middle-aged person with a normal immune system, the disease is not very dangerous.
However, for older people, even death is possible.
There are no miracle drugs to treat this disease. It is recommended to carry out activities more often in order to prevent and prevent the onset of the disease. Do not drink tap water and remember to wash your hands thoroughly. Be always healthy!
source
When nausea occurs against the background of an increase in body temperature, a person develops fatigue syndrome, he feels weakened and lethargic. To eliminate unpleasant discomfort, you need to clarify its causes in order to select the optimal treatment option. The combined appearance of nausea and fever occurs equally in adult patients and children.
Clinical picture, symptoms of nausea and increased body temperature to 37, 37.5, 38, 38.5, 39, 39.5. and more than degrees, may be accompanied by other painful symptoms: attacks of vomiting, headaches, dizziness, abdominal pain, stool upset.
Identifying the reasons if nausea, fever and weakness persist for 3-4 days is important to prevent the development of complications.
articles:
If a child or adult has a fever and begins to feel sick, then the causes are nausea, vomiting, headache and low temperature at 37, 37.5, 38 and high temperature at 38.5, 39, 39.
There can be a whole range of 5 and 40 degrees.
Further in the article, we will go into detail about what can cause a feeling in a child or an adult, as if dizzy, chills, what diseases there may be if the baby’s temperature begins to rise and he becomes weak.
The appearance of painful symptoms of nausea and elevated body temperature in most cases is caused by inflammatory processes in the body, often a sign of an infectious etiology of the pathological process.
How serious the situation can be depends on the severity of the painful symptoms and the deterioration of the patient’s general well-being.
An assessment of the totality of symptoms helps determine which of the body systems (digestive, cardiovascular, excretory) are experiencing problems:
1 If you feel sick and nauseous, your body temperature rises, but there is no vomiting or diarrhea, you may be talking about moderate food poisoning.
2 If you feel the urge to vomit and begin to feel sick, vomit, and then there is relief, there is no bowel disorder, most likely the person ate something stale.
3 When you start feeling dizzy and nauseous, your blood pressure may have jumped.
4 If there is a high temperature and severe chills, loss of strength and nausea, increased bowel movements, loose stools, you can suspect the presence of an intestinal infection.
5 When there is a low temperature, weakness and nausea, the chronic pathology of one of the gastrointestinal tract organs may have worsened.
6 If the patient is bothered by an uncomfortable condition, there is nagging and aching pain in the abdomen, side or back, weakness and nausea, there may be a problem with the kidneys.
7 When weakness and dizziness periodically occur, nausea appears, this may be the result of a head injury or the first harbingers of impaired cerebral circulation, which is dangerous for the development of a stroke condition.
8 When abdominal pain and nausea bother you, the temperature begins to rise, the intensity of abdominal colic tends to increase, diarrhea appears, the reasons should be looked for in intestinal pathologies.
9 Low temperature, nausea and weakness, as a symptom complex, are characteristic of chronic gastrointestinal diseases when they enter a period of exacerbation, for example, in spring and autumn.
10 With vascular pathologies, patients complain of periodic mild nausea and a feeling of weakness that occurs against the background of oxygen starvation.
In many cases, nausea and a temperature of 37° C are evidence of exacerbation of chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, which include pathologies:
1 gastritis (chronic or acute form of the disease);
4 irritable bowel syndrome;
5 cholecystitis (chronic);
7 chronic or acute appendicitis (there is pain in the right lower abdomen, chills, possible vomiting).
Gastroenterological disorders are characterized by the presence of the following symptom complex:
1 pain in the abdomen (in the epigastrium, side, hypochondrium), by the location of which the affected organ can be approximately determined;
2 the presence of dyspeptic symptoms: belching, heartburn, rumbling in the abdomen;
3 feeling of fullness in the stomach cavity, bloating in the abdomen;
5 gradual decrease in body weight;
6 paleness of the skin;7
altered perception of familiar tastes and smells.
What can cause high body temperature along with severe nausea? The clinical picture of severe food poisoning is similar to the development of some infectious diseases:
1 fever and aversion to food, weakness appeared;
2 an attack of nausea can come from just looking at food;
3 often a high temperature rises and severe nausea;
4 suffers from repeated vomiting; impurities of bile can be seen in the vomit;
5 is worried about frequent loose stools.
There is no point in hoping that a person was simply poisoned by poor-quality food and that all the symptoms will go away quickly; perhaps an intestinal infection has occurred, and if this is the case, then medical attention cannot be avoided. The diagnosis can only be clarified based on the results of the examination. The danger in this case is:
1 viral infection of the body (rotavirus, enterovirus);
2 intestinal infections (salmonellosis, cholera, dysentery).
As a rule, when a patient suffers from chills, sweats, nausea and a fever, the body is assumed to be infected. The primary diagnosis is assumed based on the results of an objective assessment of the patient’s condition and analysis of his complaints:
1 vomiting and nausea with fever – processes of an inflammatory or infectious nature are suspected in the body;
2 low-grade (37.0-37.3°C) temperature and nausea without vomiting are observed with exacerbation of gastritis, duodenitis, cholecystitis;
3 a feeling of weakness and nausea against the background of periodic dizziness may indicate problems with cerebral circulation;
4 problems with coordination of movements when feeling nauseous - one of the signs of a condition preceding a stroke;
5 reasons for temperature 37, 37.5, 38 and above with attacks of nausea, diarrhea syndrome, abdominal pain, are various, from poisoning to inflammation and intestinal pathologies;
6 if a person has severe tachycardia (increased heart rate), his skin is pale, he constantly feels nauseous, and an incipient state of heart attack or stroke is suspected.
Some conditions accompanied by attacks of nausea and high temperature changes require immediate medical attention, so if the following signs appear, you should call an ambulance:
1 the patient has severe shortness of breath and has difficulty breathing;
2 there are jumps in temperature indicators, sometimes a significant decrease, sometimes a jump towards a sharp increase;
3 when the patient has nausea and a temperature below 40, uncontrollable vomiting mixed with blood;
Source: https://fiwap.ru/golovnaya-bol/esli-toshnota-golova-bolit-slabost-temperatura/
Appendicitis
The inflammatory process in the appendix occurs with pain, nausea (vomiting and changes in the condition of the stool are possible). Appendicitis can occur in acute and chronic forms. The nature of the symptoms varies.
In its acute manifestation, the pain is unbearable. Any movement is painful. At first, unpleasant sensations begin in the umbilical region, gradually moving to the lower abdomen with increasing pain. The temperature rises. In a short period of time, the appendix can rupture and its contents end up in the abdominal cavity, and all organs are poisoned at once. Possible death.
In the chronic form, pain can be felt with heavy physical activity, sneezing and defecation. Constipation/diarrhea occurs. Vomiting is also possible, but after the food mass leaves the stomach, there is no improvement. To make an accurate diagnosis, a blood test is necessary.
Myocardial infarction
When a heart attack affects the lower part of the heart, the pain radiates to the diaphragm and stomach. This is accompanied by profuse non-stop vomiting. A distinctive feature of pain during a heart attack from pain due to stomach pathology is that it is localized not only in the abdomen, but also radiates to the heart area.
A person tries to be in a sitting position all the time, but with stomach pain, on the contrary, there is a desire to lie down with his knees bent. If treatment is not started, tissue necrosis occurs, accompanied by a decrease in pressure and pain in the chest. An accurate diagnosis of the presence of a heart attack can be obtained by performing an ECG.
Food intolerance
Nausea and abdominal pain may indicate a food intolerance. Some people's bodies are unable to digest and absorb gluten, lactose and fructose. As a result, they begin to break down under the influence of bacteria, and an increased amount of gases is formed. This leads to bloating.
The enlarged intestine puts pressure on nearby organs, causing pain and nausea with vomiting. The pain intensifies after eating. You can identify what you are intolerant to after taking tests. Or, tracking after taking which product, pain and increased gas formation appear. You can get rid of the disease without taking medications.
Associated symptoms indicating the disease
The development of a certain pathology can be roughly determined by the accompanying symptoms, but it should be understood that the final diagnosis can be made only after examination.
Stomach pain and vomiting
Abdominal pain, which is accompanied by vomiting, always indicates the development of an inflammatory or infectious process. Such symptoms indicate that the human body is trying to remove toxins, and the reasons for this can be very diverse.
Main reasons:
- Food poisoning
. An additional symptom may be increased body temperature. - Liver diseases
. In this case, the pain syndrome is localized in the area of the gallbladder (right hypochondrium). - Appendicitis
. It is very important to recognize this pathology in a timely manner, otherwise it poses a threat to life. The most common location of pain is the lower abdomen. - Strangulated hernia
. In this case, the pain covers the entire abdominal cavity, which makes diagnosis much more difficult. - Exacerbation of stomach ulcers
. This pathology may be accompanied by diarrhea or constipation.
Lower abdomen hurts
When the lower abdomen hurts, it is caused by various diseases of the abdominal cavity. Pain in this localization may occur due to the formation of kidney stones. This pain is very excruciating, it radiates to the back area. In severe cases, the pain syndrome is accompanied by chills and nausea, and blood often appears in the urine.
Other pathologies that cause pain in the lower abdomen:
- Irritable bowel syndrome
a. In this case, spasmodic pain occurs, increased gas formation is observed, as well as alternating constipation and diarrhea. - Appendicitis
. Such pain can be observed for a long time, but under certain circumstances an exacerbation may occur, which requires urgent medical intervention. - Ulcerative colitis
, which is associated with the appearance of ulcers on the walls of the colon and rectum. Along with severe pain, fatigue and weight loss are always observed, and bloody diarrhea appears over time. - Urinary tract infection
. Such diseases are very often observed in women. - Mesenteric adenitis
, which is characterized by inflammation of the glands on the walls of the small intestine as a result of viral infection.
My head is spinning
Cephalgia (headache) and dizziness with abdominal pain can develop due to the fact that acute pain syndrome provokes cerebral vascular spasm. As a result, hypoxia occurs. As a rule, dizziness begins suddenly, the reasons for this can be serious pathologies, such as: perforated ulcer, acute pancreatitis, renal colic, acute cholecystitis, cholelithiasis.
In addition, the stomach and head can hurt at the same time due to allergic manifestations of premenstrual syndrome in women, nervous strain and stress, or increased physical activity.
Diarrhea (diarrhea)
A combination of symptoms such as abdominal pain and diarrhea is most often a sign of poisoning.
In this case, it may be caused by:
- Chemicals that are part of various detergents, paints and solvents, and sometimes even medications.
- Viruses and bacteria, after infection with which manifestations of intoxication are observed.
- Poor quality food.
In addition, various inflammatory processes can cause diarrhea and abdominal pain. Against this background, serious diseases such as colitis, enteritis, and appendicitis develop.
Abdominal pain in the navel area
The most likely cause of pain in the navel area is an inflammatory process. In addition, pain can be localized in this place when pathologies occur in the kidneys, stomach or ureters.
Among the serious diseases that can cause pain near the navel are the following pathologies:
- Omphalitis.
- Neoplasms of a benign or malignant nature.
- Enterocolitis, which is characterized by spasmodic pain.
- Umbilical hernia, the pain intensifies with increased load.
- Irritable bowel syndrome.
Temperature
Abdominal pain, which is accompanied by elevated temperature, most often indicates an exacerbation of chronic pathologies.
This can occur in the presence of: intestinal obstruction, cholecystitis, pancreatitis, appendicitis, hernia.
The same symptoms in the acute nature of the pain syndrome may indicate complications of various pathological processes, such as:
- Perforation of the gallbladder.
- Perforation of a stomach or duodenal ulcer.
- Rupture of the liver or spleen due to trauma.
- Intestinal bleeding.
Intestinal parasites
Due to poor hygiene and consumption of unwashed (or improperly prepared) foods, intestinal parasites can colonize the digestive organs. They cause pain due to disruption of the stomach or liver. During their life, water accumulates in the intestines and stool disturbance occurs, which provokes pain.
The body tries to fight the parasites itself; to do this, more gastric juice is released, which leads to heartburn, vomiting and pain. This happens regardless of the person’s food intake or physical activity. Worms can cause neoplasms, which are also accompanied by pain and nausea.
It is not recommended to self-medicate, as it may not only bring no benefit, but also cause harm. And at this time the parasites will further multiply, populating and poisoning the body more.
Orthopedic deviations
Nausea and abdominal pain may indicate problems with the spine. Its nerve endings are closely connected with the abdominal cavity, so pathological changes can cause pain in the abdomen, accompanied by bloating and sometimes vomiting.
The changes are most often age-related; the older the person, the thinner the discs between the vertebrae become. This provokes the appearance of growths that can irritate the digestive organs. The pain is constantly present and intensifies with sudden bending or lifting heavy objects.
Symptoms
A person who complains of abdominal pain may have different symptoms. Most often it manifests itself in the form of spasms and colic.
- Colic is an attack of primarily stabbing (hence the name) pain. In case of colitis, a person has colitis in both sides, in case of appendicitis or inflammation of the ovaries - in the lower abdomen, in case of poisoning, the localization of colic can be in different parts of the abdomen and most often an additional symptom appears (vomiting, diarrhea).
- Spasms are pain that is accompanied by involuntary muscle contraction. At the same time, the skin turns pale. The pain may cause the person to lose consciousness. If the spasms are due to inflammatory diseases of the intestines or stomach, they are accompanied by fever. Gynecological problems are indicated by spasms accompanied by bleeding.
- Anginal pain is an unpleasant sensation with a strong burning sensation.
- Sharp pain in the area above the navel is a common occurrence with appendicitis.
- A feeling of “fullness” in the lower back may indicate problems with the colon
- Cyclic pain (either intensifies or subsides) is a characteristic symptom of diseases of the bladder and intestines.
- Pain accompanied by severe gas formation indicates improper functioning of the colon.
- Painful sensations accompanied by itching of the anus are symptoms of damage to the rectum.
- Unpleasant sensations in the abdomen , intensifying at rest and disappearing with movement, are the result of problems with blood circulation.
Stress
With severe and frequent stress, the body's immune system weakens and this primarily affects the digestive organs. As a result, pathological conditions begin to develop.
Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract provoke the appearance of pain, vomiting and fever. The pain may intensify with another stressful condition. Severe stress can cause muscle spasms, which manifests itself as abdominal pain.
Infectious diseases
As for infectious diseases accompanied by abdominal pain and fever in adults and children, these include
- dysentery;
- salmonellosis;
- food poisoning;
- viral hepatitis;
- helminthic infestations.
The most typical disease is dysentery, accompanied by symptoms of general intoxication, such as weakness, malaise, loss of appetite, fever, and headache. Abdominal pain is initially diffuse, then becomes cramping, intensifying before defecation. Characteristic is the presence of tenesmus, nagging pain in the rectum, radiating to the sacrum. There may be stools more than 10-15 times a day. In severe cases - up to 50. In this case, feces are replaced by mucus and blood.
In atypical forms, the presence of blood and mucus in the stool may not be noted, which complicates diagnosis. Differential diagnosis in this case must be carried out with other intestinal infections, such as stomach pain, diarrhea and fever. In addition to clinical data, confirmation of the diagnosis can be based on the isolation of the pathogen from feces and bacteriological examination. Sowing the intestinal contents helps to identify the cause of the disease in cases of subclinical forms or chronic dysentery, manifested by periodic abdominal pain, diarrhea and a temperature of 37-37.2 degrees.
Since the causative agent of the disease is a bacterium of the genus Shigella, a course of antibiotic therapy will prevent the disease from becoming chronic and will promote recovery.
Salmonellosis is an acute infectious disease characterized by various forms from asymptomatic to the development of infectious-toxic shock. The most typical is the gastrointestinal form, characterized by an acute onset, the presence of intoxication, an increase in body temperature to high levels, stomach pain, nausea, and vomiting. After a few hours, foul-smelling stools appear, without tenesmus and blood. The presence of repeated vomiting and stool up to 10-15 times a day can cause the development of dehydration syndrome.
It is characterized by thirst, dry, wrinkled skin, lack of urine, and decreased blood pressure. Seizures may develop. In addition to gastric lavage, therapeutic measures necessarily include replenishing fluid lost by the body. For diagnosis, an important role is played by identifying the pathogen in food debris, feces, vomit, as well as the spread of the disease in a group of people who consumed a certain contaminated product.
Foodborne illness is another very common disease characterized by symptoms such as abdominal pain, vomiting, and fever. Diarrhea develops in half of sick patients. The most common pathogen in this case is staphylococcus or its metabolic products, enterotoxins. Patients complain of stomach pain, nausea, temperature 37, severe weakness. The pain is sharp and cramping in nature. Weakness and malaise are very pronounced. There is a decrease in the temperature of the extremities, pallor of the skin, and a decrease in blood pressure. Despite such pronounced symptoms, by the end of the day there is usually an improvement in the condition and recovery.
The initial period of botulism is also accompanied by nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain at normal temperatures. The neurological symptoms that characterize this disease can appear only after a day. Given the serious prognosis of the disease, urgent medical attention is necessary.
The presence of abdominal pain, temperature of 37-38 degrees, and dyspeptic disorders is also characteristic of viral hepatitis. Diagnosis can be difficult in the pre-icteric period. With the appearance of a pathognomonic symptom, differential diagnosis is carried out between hepatitis of other etiologies and diseases accompanied by the development of jaundice, which is very important for determining treatment tactics and carrying out measures in the outbreak.
Diseases of the reproductive system
With the onset of menstruation in women, pain can be caused by its onset. They are localized in the lower abdomen. The severity of pain depends on the general condition of the woman’s body. When discharge occurs, the symptom begins to subside.
If the pain is severe and is accompanied by a change in the nature of menstruation, then this may indicate the development of an inflammatory process or tumor in the reproductive organs. In this case, consultation with a gynecologist and treatment are necessary.
With the onset of pregnancy, pain and nausea can be caused by hormonal changes in the body. If they are strong, then this may mean a threat of miscarriage. In the last months of pregnancy, pain can be due to a greatly enlarged uterus, which puts pressure on nearby organs.
In men, pain can be caused by the prostate gland. If it is located close to the bladder, then when it fills, pain will occur in the lower abdomen.
Causes
What are the causes of abdominal pain, dysfunction of the abdominal organs and retroperitoneal space?
The cause of colic can be appendicitis, inflammation of the ovaries (in these cases, colic in the lower abdomen), poisoning, or colitis. With colitis, a person has colitis in both sides. If the colic is cramping and is localized both in the abdomen and in the lower back, the pain is more intense, the cause is most often urolithiasis, kidney injuries or pyelonephritis. Colic in the navel area may be a response to irritants of the sensitive mesenteric plexus of the intestine.
Among the common causes of paroxysmal spasms are intestinal obstruction and gastroduodenitis. And uterine endometriosis is most often behind spasms during urination in women.
If abdominal pain is accompanied by increased gas formation and a frequent urge to defecate, then the cause will most often be associated with diseases of the colon.
If you have abdominal pain - anginal, and the patient is bothered by an expressive burning sensation - the cause is most often gastritis (inflammation of the stomach lining) or pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas). If pain and burning are accompanied by severe tension in the muscles of the abdominal wall, and a person complains of pressure in the chest, the cause may be associated with heart pathologies: in particular, such pain is typical for 60% of patients with myocardial infarction.
The cause of abdominal pain accompanied by low-grade fever (the temperature remains at 37.1–37.5 °C for a long time) is most often inflammatory bowel disease.
What does the type of pain indicate?
Nausea and abdominal pain differ in the nature of their manifestation for different diseases. When examining a patient, the doctor always asks how the pain was expressed and makes a preliminary diagnosis.
Based on this, the next examination will be scheduled.
What diseases are typical for different types of pain?
| Type of pain | Disease | Notes |
| Acute pain expressed in the stomach area | Pancreatitis, ulcer, pathology in the gallbladder | Urgent examination and treatment is required |
| Sudden severe pain | Chemical burn of mucous membranes or poisoning | Urgent hospitalization |
| Unbearably sharp, sudden pain | Breakthrough gastric or duodenal ulcer | Emergency ambulance call |
| Severe but short-term pain, which may occur when breathing | Diaphragm spasms | Consultation with a specialist is required |
| Severe pain in the form of contractions | Infections in the gastrointestinal tract | A visit to a therapist/gastroenterologist is required |
| Severe pain in the umbilical area, which gradually moves down the abdomen and intensifies | Appendicitis | Emergency assistance must be called immediately |
| Moderate pain that gradually decreases but does not go away completely | Pathological abnormalities in the large intestine | A visit to a specialist is required |
| Moderate pain similar to contractions, most often occurring at night or after eating | Ulcer or inflammation of the duodenum | Urgent examination by a specialist |
| Constant mild pain, aching in nature | Neoplasms in the stomach, including tumors | Consultation with a gastroenterologist |
| Pain in the form of a burning sensation in the stomach, worsens when hungry or after eating | Diseases in the stomach that occur in a chronic or initial stage | Consultation with a therapist |
These symptoms may not necessarily mean the listed diseases; an accurate diagnosis is made after a complete examination. It is important that knowing what pain is typical for various pathologies, you can determine how urgently help should be provided.
Weakness and nausea with gastritis
Dizziness and nausea may occur when taking PPIs.
Don't be surprised, but nausea and weakness can be symptoms of gastritis. Inflammation of the gastric walls causes general intoxication of the body, which cannot but affect the general condition of a person.
Severe weakness due to gastritis requires medical intervention; in especially severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary. The website https://gastritinform.ru describes the causes of weakness and nausea with gastritis.
You will also learn how long weakness with gastritis lasts and how to deal with it.
Nausea as a symptom of gastrointestinal disorders
Nausea, as a symptom, is common, especially when the gastrointestinal tract is disrupted, however, it is not a symptom that should not be ignored. Therefore, if you regularly experience nausea or nausea accompanied by vomiting, it is imperative to consult a doctor who can find the cause and prescribe the correct treatment.
Nausea as a symptom is common, especially when the gastrointestinal tract is disrupted.
If nausea occurs after eating, it is necessary to clearly monitor what kind of food it is, when nausea occurs (hours or minutes after eating), what accompanying symptoms arise - all this will allow the doctor to determine the direction of diagnostic searches and identify the cause.
If nausea is accompanied by pain in the epigastric region (upper central part of the abdomen at the level of the lower ribs), we may be talking about gastritis or gastroduodenitis (inflammation of the stomach and duodenum). If the pain is localized lower - in the navel area and is also accompanied by vomiting or intestinal disorders, this can often be a sign of food poisoning.
Nausea after smoking with gastritis and cigarettes is sometimes a sign of erosive gastritis/gastroduodenitis, gastric ulcer, however, it can also be a consequence of gastroesophageal reflux disease (the release of stomach contents into the esophagus), since smoking reduces the tone of the valve that separates the stomach and esophagus and at the same time The peristalsis of the entire stomach decreases, which can be felt as nausea.
Nausea with gastritis
The main initial sign of gastritis is constant nausea and pain in the stomach; after a person vomits, the pain disappears, and a sour and very unpleasant taste remains in the mouth. Added to all the listed symptoms is heartburn, a terrible feeling in the stomach, as if the food has not been digested and does not want to be digested.
Heartburn goes away only if you walk or do something; when you lie or sit, it intensifies. If we talk about intoxication, it is worth noting that it can be a consequence of gastritis. The person experiences general weakness, dizziness, discomfort in the body and inability to concentrate.
Intoxication (general weakness) of the body
Intoxication is a general reaction of the human body to the introduction of any toxins: microbial, bacterial, food. Toxic syndrome most often develops in diseases of the digestive system of bacterial origin and acute respiratory infections.
Intoxication develops to one degree or another in almost all inflammatory and infectious diseases. The severity of symptoms of intoxication depends primarily on the reasons that caused it.
As a rule, a toxic symptom is manifested by headaches, muscle weakness, aches in the lower back and muscles, vomiting, nausea, increased body temperature, increased sweating, abdominal pain, changes in blood pressure, diarrhea, and pale skin.
Weakness due to gastritis
The main source of acute gastritis is food poisoning or simply poisoning with poor-quality food
Gastritis is an inflammation of the stomach lining. It occurs for several reasons.
The main source of acute gastritis is food poisoning, or simply poisoning with low-quality food. After two to three hours, acute inflammation of the gastric mucosa occurs, which is accompanied by high fever and vomiting.
Nausea, dizziness, and diarrhea may also occur.
Symptoms of acute gastritis usually appear 4-8 hours after exposure to a pathogenic factor. There is a characteristic feeling of heaviness and fullness in the epigastric region. Then weakness, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea appear.
With acute gastritis, not only the condition of the stomach and intestines changes: the skin and visible mucous membranes become pale, the tongue becomes covered with a grayish-white coating. There may be drooling or, conversely, severe dry mouth.
When palpated, it hurts “in the pit of the stomach” - in the place where the ribs form an angle under the sternum. If the effect of harmful factors is repeated, then acute gastritis usually becomes chronic.
Then the treatment will need to be much more complex and lengthy, so acute gastritis should be dealt with decisively and mercilessly.
Dizziness with gastritis
Dizziness and headaches only at first glance seem unrelated to inflammation of the stomach. Many chronic diseases of internal organs can contribute to the development of non-systemic dizziness.
Chronic gastritis with a complicated course also belongs to such ailments. The appearance of frequent dizziness with gastritis usually signals the severity of the disease and the involvement of the whole organism in the disease.
An additional factor in the deterioration of well-being due to inflammation of the gastric mucosa is a decrease in blood glucose levels. This is what often explains the symptoms of low mood, nausea or dizziness. At the same time, the patient may have a headache, everything will fall out of his hands, or he may become impossibly picky and capricious.
Intoxication headache or dizziness with gastritis are among the most well-known consequences of the presence of any toxic substances in the body.
Dizziness due to astheno-vegetative syndrome with gastritis differs from reflex pain.
In this case, dizziness will not be associated with food or accompanied by nausea, but will appear with increasing load, often intensifying in the evening.
In addition to headaches with asthenic syndrome, there may be a feeling of fatigue, weakness or weakness. It is not uncommon to experience dizziness towards the end of a busy work day.
Especially often, women complain of dizziness with chronic gastritis, in whom this condition is accompanied by irritability, increased sweating, chilliness of the hands and feet, and sleep disturbances. Dizziness with gastritis can manifest itself as a result of (intoxication, reflex pain or astheno-vegetative syndrome, or be a consequence of their complex combination.
Can there be weakness with gastritis?
Frequent companions of ordinary gastritis are constant weakness, frequent headaches and low-grade fever.
The main symptoms of gastritis are abdominal pain (aching, sharp, sharp), loss of strength, loss of appetite, weakness, poor health, dizziness, nausea and vomiting, heartburn, increased sweating, disruption of the gastrointestinal tract, gases, sudden weight loss, low blood pressure, belching, sour taste in the mouth, dry mouth or, conversely, excessive salivation. With chronic gastritis, anemia may develop.
The main symptoms of acute gastritis are pain in the upper abdomen, general weakness, dizziness, nausea and vomiting. At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor. Without proper treatment, acute gastritis becomes chronic. Although 50% of chronic cases are considered as a separate disease.
Frequent accompanying gastritis is constant weakness, frequent headaches and low-grade fever.
Localization of pain
The cause of pain can also be determined by its location. Therefore, it is important to listen to pain symptoms when they appear. Knowing where the pain is localized and the nature of its manifestation, you can more accurately determine the disease.
| Location of pain | Possible reason | Notes |
| In the upper abdomen | Gastritis, peritonitis, heart attack | Urgent ambulance call |
| In the middle of the belly | Gallbladder, intestines, appendicitis, hernia | It is necessary to be examined by a gastroenterologist |
| Underbelly | Diseases of the urinary system, reproductive organs, ectopic pregnancy | Initially you need to visit a therapist, then a gynecologist |
| Below the ribs on the right side | Liver, heart attack, biliary tract dysfunction | If there is a greater suspicion of a heart attack, you should immediately call an ambulance |
| Right side | Appendicitis, inflammation of the right appendage | Acute pain requires urgent hospitalization |
| Below the ribs on the left side | Pathological changes in the pancreas | You need to visit a gastroenterologist |
| Left side | Inflammation of the urinary tract, inflammation of the left appendage, inflammatory process in the intestines |
If the patient cannot determine where the pain is localized, then the specialist must also be informed about this. A preliminary diagnosis can be made based on the nature of the pain. Without additional examinations, treatment is not prescribed.
First aid for abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting with fever and chills
Abdominal pain and nausea can be caused by various reasons. Therefore, first aid measures differ from each other. Based on the pain syndrome, as well as what the person was doing before the pain appeared, it is possible to roughly determine what could be the source of the symptoms.
In case of poisoning, it is first recommended to cleanse the stomach (vomit is induced until clean water begins to come out) and take activated charcoal.
After this, the patient is provided with plenty of fluids and rest. When a temperature appears, it is advisable to bring it down by rubbing or administering medication intravenously/intramuscularly, trying not to irritate the stomach.
If the poisoning was caused by serious chemicals, then inducing vomiting is contraindicated. They can repeatedly burn the digestive tract and oral cavity, as well as enter the respiratory tract.
To cleanse the body of toxins, the victim needs to drink a laxative so that the poison comes out with the feces. Activated carbon is also given. You need to drink more liquid to dilute the toxins in your stomach.
If the pain is caused by an exacerbation of a chronic disease, the patient is given painkillers. At high temperatures, antipyretics are allowed. Be sure to remain calm.
If an infection or the presence of parasites is suspected, the stomach is cleansed with activated charcoal. At temperatures above 38.5 degrees, an antipyretic is given. Fresh, cool air must be provided. For severe pain, you can take painkillers.
If the pain is sharp with profuse vomiting and fever, then the patient must be kept at rest and not take any action until the ambulance arrives. Painkillers will not give an accurate diagnosis, and rinsing can only worsen the situation, since inducing vomiting provokes muscle contraction and increases pain.
Antibiotics, alcohol-containing drugs or traditional medicine recipes are strictly prohibited until the patient has been examined by a doctor and treatment has been prescribed. Self-medication with medications for fear of going to the hospital can worsen the situation. Even after the attack of pain is relieved, a visit to the doctor is necessary.
Helminthiasis
Often severe pain in the abdominal cavity with a significant increase in temperature is caused by helminthic infestations. The most common among them are:
- ascariasis;
- giardiasis;
- opisthorchiasis;
- echinococcosis;
- hookworm disease.
Helminth infections are characterized by severe abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and fever. In addition, the patient may experience yellowing of the skin, chills, and sudden changes in mood.
The danger of helminthic infestations is that they may not show themselves for quite a long time.
The symptoms are mild, and the pain is rarely severe. The threat is the development of dangerous complications in the absence of medical care for a long period.
In order for the doctor to prescribe correct and effective treatment, it is necessary to observe the patient. Typically, with helminthiasis, the disease occurs in paroxysmal stages, which is associated with the development cycle of the parasite.
Therefore, you need to consult a doctor even during the period when symptoms subside. At this time, helminths do not disappear from the body, continuing to suck the juices out of a person, destroying his tissues and releasing their waste products into the blood.
Differential diagnosis is usually carried out by analyzing stool for worm eggs and protozoan cysts.
If pain in the lower abdomen and temperature are observed, then a clinical blood test is usually also prescribed for the presence of eosinophils and PCR reactions to individual helminths.
Sometimes radiography and ultrasound are required to determine damage to the liver, gallbladder and pancreas.
Medications
To eliminate symptoms, it is not recommended to start taking medications on your own without consulting a doctor.
If abdominal pain occurs, accompanied by vomiting, loose stools and fever, the following medications may be prescribed:
1. It is necessary to cleanse the body of toxins; if the medicine cannot be taken orally due to excessive vomiting, then you can do an enema with it.
Medicines for cleansing:
- smecta;
- polysorb;
- enterosgel.
It is not entirely recommended to take activated carbon, as it changes the color of stool.
Because of this color, you may not see streaks of blood in the stool (if there was bleeding). If the risk of bleeding is excluded, then charcoal is allowed to be taken.
2. If you have loose stools for more than 1 day.
Then you need to drink fixatives:
- tetracycline;
- enterofuril;
- loperamide
On the first day, their use is prohibited, since the body is cleansed of toxins with the help of liquid feces. Consolidation of the stool can provoke even more severe intoxication and deterioration of the condition.
3. With copious and frequent vomiting, dehydration may occur; to prevent this, you must drink during the day:
- rehydron;
- gastrolit;
- a solution of sugar (40 g), salt (10 g) and water.
Drink at least a liter per day, in small doses. You can also drink warm sweet tea.
4. If you have stomach problems or overeating, products containing enzymes will help:
- mezim;
- pancreatin;
- festal
They should be taken immediately after meals. Since on an empty stomach they can increase pain.
5. If an infection is suspected, antibiotics should be taken. But only a therapist can prescribe them.
Since it is necessary to find out the nature of the pathogen. After a course of antibiotics, you need to take medications that normalize the functioning of the intestinal tract.
6. At temperatures above 38.8, you need to take antipyretics. But with severe vomiting or loose stools, this can be problematic. You can wipe the patient, or administer the medicine intramuscularly (done in a hospital or when calling an ambulance).
7. If the disease is known, and the pain is severe, then it can be relieved with the help of medications:
- no-shpa;
- analgin;
- spazgan.
Medicines that improve digestion also relieve pain. After eliminating vomiting, the pain will also subside. With properly selected complex treatment, symptoms quickly stop.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies can also be used in treatment. On their own, they will not be able to get rid of the cause of pain and nausea. Before using them, you should consult a therapist.
List of tested recipes:
- Dried pomegranate peel will help relieve pain, disinfect and strengthen stool. To use, take 15-20 g of crushed peel and steam it in 200 ml of boiling water. The drink is divided into 2 doses.
- Grated ginger root helps get rid of loose stools and reduces the urge to vomit. Before use, pour boiling water over the ginger (so that the water hides the ginger) and leave until it cools. A single serving is no more than 80 ml.
- Tea made from mint and currants helps reduce pain, improve immunity and reduce fever.
- Dill seeds relieve bloating and pain. To do this, you need to steam 10 g of seeds in 250 ml of boiling water. The infusion is divided into three servings.
- To get rid of heartburn, bloating and pain, you can drink a drink of soda (7 g) and water (180-200 ml). You should only drink it when it is prepared. For taste, you can add 3-5 drops of lemon juice.
- To relieve pain, inflammation and eliminate infection, you can drink chamomile tea, which can be purchased in a pharmacy in ready-made form. Consume before meals up to 3 times during the day.
Infusions and decoctions are good to use for the prevention of pain and after the end of drug treatment. The course and dosage are prescribed by the therapist. Before taking, you need to make sure there are no allergies.
Nutrition
Proper nutrition will help reduce pain and vomiting, even if the symptoms are not due to digestive problems. With the correct load on the gastrointestinal tract, the body will work at full strength, and the disease will recede faster.
Rules for eating in the presence of pain, vomiting and loose stools:
- food should be light but satisfying;
- portions should be small and the temperature should not exceed 60-70 degrees;
- It is desirable that the food is sufficiently chopped. It will be good to use broths, cereals and puree soups;
- overeating should not be allowed; an enlarged stomach causes pain and also puts pressure on other organs, which can further increase the pain effect;
- cooked food should be fresh and it is advisable to switch to a home menu, avoid going to restaurants;
- Do not drink water during meals, it dilutes gastric juice and interferes with normal digestion of food;
- eat at regular intervals and avoid snacking;
- It is recommended to rinse your mouth with mint or chamomile before eating. You can drink teas from them;
- To relieve pain symptoms, you need to choose the right medicine, giving preference to those that irritate the organs of the digestive tract less.
Until the nausea and pain subside, you must stick to a diet and eliminate junk food. If medications do not bring relief or discomfort is felt in the abdomen, then only a specialist can replace medications. It is important to be able to recognize pain that requires emergency medical attention.
Author: Kotlyachkova Svetlana
Article design: Mila Friedan