Causes of problems with the intestinal mucosa
The intestine is a very important organ, which is especially susceptible to various diseases. The intestinal mucosa becomes inflamed due to a number of factors, which ultimately brings discomfort and pain to a person. Before understanding how to restore the intestinal mucosa, it is necessary to consider the main causes of dysfunction. So, the manifestation of the inflammatory process may appear in the following cases:
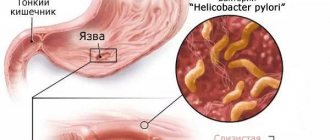
- When the gastrointestinal tract is affected by various parasites. In this case, pathogenic organisms attack the intestinal walls, including the mucous membrane. Parasites absorb nutrients, and as a result of their vital activity, they leave behind damage in the form of ulcers.
- When infected with infectious diseases that cause inflammatory processes. These include various viruses, dysentery, E. coli and others.
- In the absence of healthy microflora. Beneficial bacteria (lacto- and bifido-) ensure the normal condition of the intestines, but in their absence, the mucous membrane is subject to disorders and inflammation. The most common reason for the lack of beneficial bacteria in the intestines is the use of antibiotics.
- With an unbalanced diet.
- For problems with blood circulation.
- With genetic predisposition. Often, intestinal problems are inherited.
- For autoimmune diseases.
Due to the influence of the above factors, mucosal cells die off, which is accompanied by inflammation, can cause pain and prevents the intestines from performing their functions normally. Therefore, it is extremely important to recognize the problem in a timely manner, contact a specialist who will recognize the cause and tell you how to restore the intestinal mucosa. It is important to remember that the earlier treatment was started, the less damage will be caused to the body.
What happens in the intestines
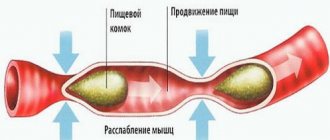
For intestinal inflammation, the symptoms and treatment are almost the same. This is colitis, in which the integrity of the mucous membrane is disrupted. Bacteria, getting on the mucous membrane, continue to damage it, capturing larger and larger areas. In damaged areas, an inflammatory process occurs, which is accompanied by swelling.
This leads to the fact that peristalsis (contractile functions) begins to act more and more slowly, and mucus secretion noticeably decreases. The disease progresses rapidly, which can lead to obstruction: the intestines simply stop performing their functions. With inflammation of the large intestine—the symptoms and treatment of which are the most severe—contaminated blood spreads throughout the body, putting other organs at risk.
The person feels pain, fever, vomiting, diarrhea or constipation. The first thing you want to do in such a situation is to take anabolic steroids. Temporary help can be provided, but while the analgin components are in effect, the bacteria will affect large areas. This is unjustified help.
Important! Minor pain in the intestines accompanied by rumbling, diarrhea or constipation should prompt diagnosis and treatment.
You shouldn't risk your own health. The situation is serious and requires qualified medical assistance.
How to restore the intestinal mucosa with medications
In order to restore the mucous membrane, official medicine uses drugs that are aimed at increasing cell regeneration. It is important to note that such drugs are prescribed by a gastroenterologist. You should not prescribe medications yourself, since the right choice will determine how effective the treatment will be and whether it will worsen the current situation. A number of medications that help restore the mucous membrane include the following:
Each of the above drugs has a different way of influencing the mucous membrane and is prescribed based on the reason, which negatively affects the person’s condition. Even if the patient may not have obvious signs (pain or discomfort) of a disorder in the intestinal mucosa, the doctor, after examination, may prescribe a drug that will help cope with the disorders at the initial stage.
How to restore the intestinal mucosa with folk remedies
As a supplement to the therapy prescribed by a specialist, you can also use folk remedies that will help speed up the restoration of the mucous membrane. Natural remedies are a source of useful substances, so their use will help get rid of unpleasant intestinal problems as quickly as possible and help normalize the functioning of the mucous membrane. Such folk remedies include:
- Celandine. This plant will perfectly help with hyperplastic processes and mucosal atrophy. Celandine should be consumed in the form of a whey infusion, which is prepared as follows: 65 grams of sugar are diluted in 1 liter of whey, and then a gauze bag with dried celandine is placed. The infusion should be left for a day in a dark place at room temperature, and then consumed for 2 weeks after meals, 3 times a day, 50-100 milliliters.
- Sea buckthorn oil. This is a wonderful remedy that allows you to restore the cells of the intestinal and stomach mucosa.
- Natural juices of cabbage, beets, carrots and radishes. These products perfectly help restore the functioning of the intestinal mucosa. However, in some cases, you should avoid drinking cabbage juice. A gastroenterologist will help you determine for sure which juice is best to drink.
- With high acidity, flax seeds help well, and with low acidity, infusions of plantain and parsley root help.
- During the restoration of the intestinal mucosa after a burn, Vaseline oil may be prescribed.
Diagnosis of the disease
Usually, after collecting an anamnesis, the doctor can make a preliminary diagnosis of “inflammation of the intestines,” however, to clarify the picture of the disease and make an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct some additional research.
- Clinical blood test. A blood test can reveal an increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate, a classic symptom of inflammatory diseases. An excess number of white blood cells is also determined.
- Coprogram is a study of feces that allows you to determine the amount of food enzymes and evaluate the quality of the stomach.
- Bacteriological analysis of stool - testing for bacteria. Using this analysis, it is possible not only to identify certain pathogenic bacteria, but also to determine their sensitivity to antibiotics.
- Fibroesophagogastroduodenoscopy is a multifunctional study using a fiber optic system (tube with a camera and built-in lighting), which allows you to assess the condition of the mucous membrane of the duodenum and stomach. If necessary, during the analysis, doctors can take a piece of tissue for a biopsy.
- Colonoscopy is a similar test to FEGDS, but the system is inserted through the anus and the lining of the colon is assessed. Inflammations can be diagnosed and assessed.
- Video capsule endoscopy is the most modern research method, during which the patient swallows a capsule that passes through all parts of the intestine. The information perceived by the capsule is transmitted to a special computer via radio waves and processed by a program. In this way, doctors receive all the data about the state of the patient’s gastrointestinal tract.
Diet for mucosal restoration
It is extremely important to regulate nutrition during recovery, since its quality will determine how quickly the problem can be overcome. There are several basic rules:
- It is necessary to exclude alcohol, fatty, spicy, fried foods.
- You should take a large amount of fermented milk products.
- It is important to eat as many plant foods as possible and as few animal products as possible.
- It is necessary to provide gentle nutrition - food should be warm, but not hot, not too salty, pepper and other seasonings should be excluded, food should be mushy or liquid.
- It is necessary to reduce the consumption of flour and sweet products to a minimum.
Doctors' advice
Gastroenterologists recommend adjusting your lifestyle and diet when restoring the intestinal mucosa. First of all, it is necessary to exclude foods that can act as intestinal irritants - alcohol, fatty meats, fried foods, etc.
It is important to drink plenty of clean water. It is best to opt for still mineral water at the time of recovery.
It is necessary to adhere to the prescribed diet and try to eat food at the same time. In addition to actions related to nutrition, it is important to pay attention to lifestyle. You should get into the habit of playing sports, doing gymnastics, or at least devoting 1-2 hours a day to walks in the fresh air.
Traditional methods of restoring the intestinal mucosa
There are many different methods of treating internal organs using traditional medicine. Among them are several effective methods in the fight to cleanse the intestines.
Decoction of oats and yogurt
To restore the intestinal mucosa, you can take a decoction of oats
0.5 cups of oat grains are poured with 250 ml of purified water and kept for half an hour under steaming conditions in a water bath. After cooling and straining, the finished broth is consumed before meals in a dosage of 1 tbsp. spoons 3 times during the day.
To enhance the effect, it is recommended to take bran, which serves as a natural cleaner from harmful substances, as well as flax seeds, which have an absorbent and disinfectant effect on the walls of the inflamed organ.
After using this technique for two weeks, you should begin the next phase, the goal of which is to fill the intestines with beneficial bacteria.
For this, fermented milk products such as yogurt, kefir, and probiotics are used. The final stage of the cleansing procedure is maintaining a healthy lifestyle and a nutritious diet.
Beetroot
Beetroot restores proper bowel function
Beets are a popular natural remedy for restoring normal bowel function.
The duration of the cleansing course is 1-2 weeks, during which it is recommended to consume 180 ml of freshly squeezed vegetable juice per day, previously kept in the refrigerator for 30 minutes.
It is allowed to take natural medicine with the addition of bee honey, diluted with purified water. During the therapeutic cycle to restore proper bowel function, it is advisable to use boiled beetroot salads with various beneficial ingredients, as well as the drug Enterosgel, in the diet. The final stage of cleansing is the use of probiotics to restore microflora.
Restoring normal functioning of the large intestine
To achieve improved gut health, there are certain effective guidelines that should be followed, which include:
- Diet food. Avoid the use of products that enhance the processes of fermentation and decay, as well as provoke inflammation of the organ mucosa with a high content of acid, salt, spicy and fried food components.
- Cleansing enemas with antiseptic effect. Helps eliminate edema, hyperemia, and neutralize pathogenic microbes. For these purposes, a decoction of chamomile, sage, and calendula is used. Microclysters with sea buckthorn oil have a healing effect.
- Motor activity. If inflammation develops in the intestines, it is not recommended to stay in a sitting position for a long time. Regular lack of body movements leads to stagnation in the large intestine, causing a decrease in blood flow, impairing motility. As a result, constant constipation occurs, as well as intoxication of the body due to fecal deposits. To achieve increased tone and improved blood circulation, it is necessary to resort to simple strength exercises, including physical exercise and walking.
- Use of medicines. Allowed only as prescribed by a doctor after diagnosis of the disease.
General symptoms of inflammatory changes in the intestines
In most cases, inflammation shows signs of itself that bother the patient and force them to go to a medical facility. Symptoms of intestinal inflammation:
- Abdominal pain. Often, patients cannot accurately indicate the location of the pain, but characterize it as squeezing or bursting, not suspecting that their intestines are inflamed. As a rule, pills relieve such pain only for a short period of time. The condition resembles irritable bowel syndrome.
- The appearance of nausea after eating (often this sign indicates inflammation of the small intestine or duodenum).
- Vomiting after eating, indicating inflammation in the upper parts.
- Bloating. This symptom indicates a deficiency of enzymes that are involved in the digestion process.
- Stool disorders (either prolonged constipation or frequent diarrhea).
- Weight loss, indicating insufficient absorption of vital substances by the intestinal walls.
- Anemia, which occurs due to the inability of the affected organ to “take” the required amount of iron from the food entering the body.
- Elevated temperature (from high to low-grade) is a classic sign of suppurative processes in the body.
Inflammatory bowel diseases, according to the nature of their course, are divided into acute (the disease is severe, lasting up to one month) and chronic (the course of the disease can be sluggish with periods of exacerbation, this period lasts up to one year). Based on the localization of the suppurative process, the disease is divided into the following diseases:
- enteritis is an inflammatory process localized in the intestines, affecting both a separate part of it and the entire organ;
- duodenitis – inflammation of the duodenum; the disease in most cases begins from the first section, where the stomach passes into the intestines;
- mesadenitis - inflammation of the lymph nodes, which can provoke pathologies of the mucous membrane; in most cases, suppuration occurs due to the penetration of viruses and infections;
- colitis – inflammation of the mucous membrane of the large intestine; in most cases, inflammation affects the entire organ, but there is also suppuration in individual parts.
Therapeutic actions
To restore the intestinal mucosa, it is necessary to normalize the microflora with the help of probiotics
Drug treatment that helps eliminate inflammation of the intestinal mucosa consists of a list of different groups of drugs:
- antibacterial - help cope with the pathological process;
- adsorbent - remove harmful substances from the body;
- antispasmodic - relieve spasms;
- painkillers - when pain occurs;
- antiemetics - relieve nausea and vomiting syndrome;
- enzymes - improve food absorption;
- probiotics - help restore normal microflora.
Leading an unhealthy lifestyle, not following a healthy nutritional diet, and taking certain potent medications increases the risk of disturbances in the functioning of the digestive system.
Resumption of normal intestinal activity, including restoration of the mucous membrane, is possible through the use of drug therapy, traditional methods of treatment, and diet.
Products that restore the intestinal mucosa
Proper nutrition is the key to good bowel function
In achieving effectiveness in improving bowel function, proper nutrition is of great importance.
At the same time, you should include in your daily menu food elements that help normalize microflora, such as kefir, yogurt, symbiter, narine, as well as prebiotics that activate the growth of beneficial bacteria. They are contained in the following products:
- bananas;
- chicory;
- asparagus;
- Rye bread;
- Jerusalem artichoke;
- garlic;
- beet;
- tomatoes;
- oats;
- leek;
- dandelion leaves;
- bran;
- sauerkraut;
- artichoke;
- barley;
- onion;
- beans.
Restoration of the colon mucosa
When stagnant processes occur in the large intestine, the condition of the entire organism is jeopardized, as it becomes easily vulnerable. The negative impact of pathogenic bacteria causes a number of unpleasant manifestations and symptoms, such as:
- fermentation;
- stool disorder;
- flatulence;
- skin rashes;
- belching;
- hair loss;
- bloating;
- bad breath;
- failures in the metabolic system;
- anemia;
- state of apathy;
- excessive fatigue;
- decreased immune strength.
In some cases, severe intestinal slagging occurs, requiring cycles of therapeutic manipulations. Among them:
- Herbal decoction in combination with products with a laxative effect. An infusion of chamomile or calendula in a dosage of 400 g at a time will have a stimulating effect on the release of bile and will provoke an improvement in colon emptying.
- Vegetable oil (olive, flaxseed, sunflower, castor, corn) It is recommended to use it in the morning on an empty stomach in combination with flaxseed infusion, using the product in the amount of 1 tbsp. spoons before meals.
- Cleansing enemas. For filling, purified boiled water and decoctions of anti-inflammatory medicinal herbs are used. The therapeutic course involves the use of 3-5 infusions throughout the day, achieving a feeling of complete relief.
- Colon hydrotherapy. A common method of washing all parts of the colon, performed using a special apparatus and a large volume of water, as well as certain solutions. The cleaning process takes place under the supervision of a specialist and viewed on a computer monitor. This method is carried out only in conditions of stay in specialized medical institutions. It helps eliminate solid deposits, including fine particles and compacted sediment. Treatment is carried out in stages, with gradual penetration of fluid into various parts of the intestine. For complete cleansing, 10 treatment sessions are required.
- Saline solution. To prepare the product, you need to dissolve 1 tbsp. a spoonful of table salt in 1 liter of water. In the morning, take 400 ml of the resulting mixture on an empty stomach, and then drink another 2 liters of solution over the course of several hours. Throughout the entire procedure, you should perform feasible physical exercises. The result of cleaning is the emptying of clean liquid, without any residues or impurities.
To achieve a successful result in restoring the intestinal mucosa, it is advisable to carry out therapeutic actions on this issue under medical supervision. Traditional methods are used as additional manipulations to drug treatments.
You can learn about restoring the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract from the video:
Noticed a mistake? Select it and press Ctrl+Enter to let us know.
The overall health of the body depends on the condition of the intestines. Proper digestion of food consumed, effective and maximum extraction of beneficial nutrients, timely elimination of residues and toxins are the key to health and active functioning of the body.
Antibacterial and other potent medications, an unhealthy lifestyle, and poor diet can negatively affect the intestinal mucosa and cause disruption of the digestive tract. You can speed up recovery with the help of medications, folk remedies, and proper nutrition.
Crohn's disease
A severe intestinal disease accompanied by necrosis and granulomatosis is called Crohn's disease. Pathological lesions extend not only to the intestinal mucosa, but also to tissues lying deeper. In advanced cases, the pathological process can lead to the formation of fistulas, subsequent tissue scarring, and the occurrence of adhesions. Crohn's disease causes severe pain and frequent diarrhea. This occurs due to impaired absorption of nutrients.
The clinical picture of Crohn's disease is varied - from the mildest to the most severe. Symptoms appear either suddenly or gradually. Crohn's disease can be suspected by the following signs:
- frequent bouts of diarrhea;
- cramps and pain in the abdomen;
- decreased appetite;
- blood in the stool;
- nausea, vomiting;
- sudden weight loss;
- the appearance of ulcers.
Role in the body
The main cause of most diseases of the gastrointestinal tract is inflammation of the intestinal mucosa. It manifests itself in disruption of the processes of assimilation of valuable nutrients that the body receives with food. This is a perfectly streamlined and quite complex process.
For the gastrointestinal system to function normally, it is necessary that the intestinal cells and its mucous membrane are in ideal condition. Then they will be able to send the maximum amount of nutrients into the bloodstream and retain toxins.
When the intestinal mucosa is inflamed, susceptible to disease, and saturated with toxins, bacteria and other harmful substances can enter the bloodstream. Therefore, it is especially important that the mucous membrane of the intestines and stomach functions normally and is healthy.
How to improve the health of the intestinal mucosa
The danger of hyperpermeability
Intestinal hyperpermeability is the process by which certain substances enter our body that have not been filtered out in the intestinal lining, and thus we can get sick. When these harmful elements are captured by our immune system, it initiates an inflammatory response to begin to fight the risk or threat of infection. If this process lasts long enough, then we are already talking about chronic inflammation.
What causes intestinal hyperpermeability?
- Allergies or intolerance to certain foods, such as milk.
Sometimes, we are allergic to certain drinks, vegetables, fish or even seasonings, and we don’t even know it. We notice that we feel bad after eating them, but we still continue to eat them. Dairy products, for example, often cause similar problems.
Subscribe to our INSTAGRAM account!
- There are various agricultural additives, preservatives and food colorings that damage our intestinal mucosa.
- It is also interesting to know that many medications cause damage to our intestinal lining, and can even interfere with the normal absorption of nutrients.
Medicines to protect the stomach, which are prescribed along with painkillers, antibiotics or the effects of chemotherapy, often lead to such problems.
- We also shouldn't neglect the health of our gut flora. If our intestines are not populated with enough acidophilus bacteria that fight germs or candida fungus, we may suffer from the problem of hyperpermeability of the intestinal mucosa.
Cause of intestinal inflammation
The intestinal mucosa can be damaged as a result of various diseases, when taking potent drugs and poor nutrition. The disease practically does not manifest itself. The patient may experience stool retention, pain and discomfort in the gastrointestinal tract. At the same time, restoration of the mucous membrane is a long process and takes more than one month.
If you have the above symptoms, you should visit a gastroenterologist. He will examine the pancreas, stomach and other digestive organs to rule out possible causes of discomfort. Tests should be taken to identify the underlying disease. Treatment should be prescribed by a specialist.
Be attentive to your health and if symptoms of the disease appear, do not delay your visit to the doctor. Bowel cancer is a common disease.
Causes of inflammatory diseases
Pathology can be caused by a number of reasons. The most common ones are:
- Infections – inflammation is caused by protozoa, viruses or bacteria. Most often, rotavirus, salmonella, E. coli, and amoebic dysentery are found in patients.
- Worm infestations (most often this cause occurs in children).
- Autoimmune disorders, in which the cells of the intestinal mucosa are perceived by the body as foreign, so the production of antibodies begins, which cause inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Congenital digestive defects. For example, a deficiency of certain enzymes in parents can be genetically transmitted and found in the child.
- Poor nutrition – abuse of fried foods, spices, sour sauces, smoked and fatty foods.
- Alcoholism and smoking.
- Imbalance of intestinal microflora, drugs that “kill” beneficial microflora.
Let's look at the symptoms of the most common and severe lesions - ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease.
How does the mucous membrane recover?
Let's look at how to restore the intestinal mucosa and effectively get rid of discomfort. All known methods that guarantee recovery boil down to the following points:
- Cleansing from harmful bacteria, toxins, allergens and undigested food residues.
- Colonization of the intestinal and stomach mucosa with beneficial digestive bacteria that have a beneficial effect on the microflora.
- The healing process of damaged mucosa.
Increased digestive enzymes
Every person should remember the intestines not only when there is a feeling of discomfort, inflammation, gases and pain in the gastrointestinal tract. To protect against harmful substances and strengthen the mucous membrane, you should follow a few simple rules every day.
Along with food, the body should receive products that will help the body secrete the maximum amount of valuable digestive enzymes. These include raw vegetables: broccoli, parsley, celery. It is recommended to constantly consume honey and fruits: kiwi, papaya, grapes, pineapple. Papaya is indicated if the pancreas is not able to produce enough enzymes. Pineapple effectively reduces mucosal inflammation.
Symptoms
Inflammation of the large intestine
Symptoms of inflammation of the large intestine are as follows:
- spasmodic abdominal pain;
- increased abdominal volume and increased flatulence;
- nausea and vomiting;
- abdominal pain may be accompanied by unstable stool;
- an admixture of mucus and blood may appear in the stool;
- painful act of defecation;
- constipation, which can suddenly be replaced by bouts of diarrhea;
- lethargy, increasing weakness;
- increased, in some cases high, body temperature.
Symptoms of inflammation of the small intestine:
- the pain is localized in the navel area;
- diarrhea that is not caused by dietary habits;
- seizures in the corners of the mouth;
- bleeding gums;
- increased dry skin, brittle hair;
- the stool is liquid, foamy, foul-smelling, and contains undigested food particles;
- increasing weakness, low-grade body temperature.
Inflammation of the intestinal lymph nodes has similar symptoms, but the nature of the pain changes - the pain syndrome intensifies when walking, riding and other types of physical activity.
When the cecum is affected, the following clinical picture may be present:
- sudden weight loss;
- increased flatulence;
- anemia;
- blood in stool;
- weakness, pallor of the skin;
- almost constant pain in the lower abdomen;
- changes in stool frequency and consistency.
The inflammatory process in the area of the sigmoid colon will be characterized as follows:
- rumbling in the stomach, bloating;
- abdominal pain may radiate to the left leg;
- there may be an admixture of pus in the stool;
- pain may be present on the left side of the chest;
- nausea with repeated vomiting;
- temperature increase;
- symptoms of food poisoning.
As for the inflammatory process in the duodenum, symptoms may not appear at all for a long time. In general, the symptomatic complex will be characterized as follows:
- the pain is localized in the upper abdomen;
- a feeling of fullness in the stomach even with a minimal amount of food;
- Nausea and vomiting may occur periodically;
- increased flatulence;
- “hunger pains”;
- belching with an unpleasant odor;
- symptoms of anemia.
It is possible to properly relieve intestinal inflammation if you establish the cause of its occurrence and its exact location. Therapy must be comprehensive. You cannot take antibiotics and other medications on your own if inflammation of the small intestine (or other localization) is diagnosed - this can lead to the development of complications.
Daily cleansing of mucous membranes
A layer of harmful bacteria that accumulates on the intestinal and stomach mucosa prevents the body from properly absorbing valuable nutrients. This layer is called "biofilm". To systematically remove the film from the intestinal walls, you need to:
- Drink 2 liters of water every day;
- Start the morning with a glass of warm purified water with the addition of lemon juice;
- Eat red fruits, without added sugar;
- Periodically drink infusions of dandelion and parsley;
- Eat carbohydrate-rich whole grains: oats, buckwheat, brown rice and others;
- Add flax seed to food;
- Eliminate sugar, sweet drinks, unhealthy fats, and dyes from your daily diet;
- Practice a physically active lifestyle: play sports, walk in the fresh air, swim, ride a bike.
Symptoms and diagnosis of intestinal inflammation
Inflammatory bowel diseases can be localized in the wall of the small or large intestine, along the entire length or in a specific area.
Inflammation of the large intestine will have the following symptoms:
- stomach ache;
- diarrhea - sometimes with mucus and blood discharge;
- fever or febrile condition;
- impaired absorption of nutrients, vitamins, mineral salts, as well as symptoms of their deficiency.
Inflammation of the intestine is diagnosed based on an interview with a doctor and special tests, for example, a colonoscopy to obtain a histological sample of the inflamed tissue or a radiological examination of the intestine.
Sometimes it is possible to diagnose intestinal inflammation only during surgery. A still difficult and less common test is virtual colonoscopy, which is performed by swallowing a capsule equipped with a video camera.
Cleansing with Enterosgel
The advantages of cleansing the intestines and stomach with Enterosgel are undeniable:
- The product is completely safe even with long-term use;
- The drug thoroughly and maximally removes poisons and toxins.
During the treatment process, Enterosgel does not damage beneficial microflora and does not wash minerals and vitamins out of the body.
You need to take the drug Enterosgel 1.5 tbsp. spoon 3 times a day. The full course of cleansing is 2 weeks.
After taking a course of Enterosgel, beneficial intestinal bacteria actively multiply in the body. Taking pharmaceutical probiotics will speed up the process. After a course of cleansing and restoration of the intestines and stomach with the help of Enterosgel, nausea, skin rashes, stool disorders, allergic reactions disappear, and sometimes excess weight is reduced.
Intestinal diseases, their symptoms and treatment
With improper nutrition, garbage begins to accumulate on the walls of the intestines - undigested food debris, which, when decomposed, are a source of toxins that spread further throughout the body.
Many foods, including white cabbage, legumes, kvass and carbonated drinks, increase gas formation in the clogged intestines. Constipation occurs due to a lack of fiber and water in the diet, from heavy meat and flour foods. With the help of a healthy diet, you can get rid of intestinal diseases and these problems, as well as restoring the intestinal microflora and cleansing the intestines of toxins.
Depending on the condition of the intestines and the type of disease, food (menu) is selected. If the disease is more than serious (perforated ulcer, ulcerative colitis, peritonitis), then the doctor will prescribe all the dietary features for the patient. Usually porridge with water, steamed or boiled vegetables, jelly and steamed lean meat. Such nutrition is mandatory for diseases for which it is necessary to receive medical help.
In general, nutrition and lifestyle when treating less serious diseases (gastritis, dysbiosis) and maintaining intestinal health should be as follows:
- eat small portions, 4-5 times a day;
- Chewing your food thoroughly is very important;
- drink water 30 minutes before meals and 1.5-2 hours after;
- drink 1-2 glasses of water in the morning on an empty stomach (helps lightly cleanse the stomach and intestines and “wake up” them;
- include fresh vegetables and fruits in your menu (they contain fiber and other substances that promote the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as vitamins and minerals);
- eat porridge from unprocessed cereals, fish, seafood, lean meat;
- Your regular menu should not contain fried, sweet, smoked, salty, flour, alcohol and fast food, semi-finished products and products with chemical additives (preservatives, dyes, flavor enhancers) from sausages, palm oil and yeast. These products adversely affect the health of the intestinal microflora;
- sweets can be replaced with dried fruits and honey, bread with yeast - with yeast-free, whole grain or bread;
- do sports (exercise, running or brisk walking and any physical activity that you enjoy). This improves metabolism and the flow of blood, oxygen and nutrients to organs and tissues, including the intestines, and also strengthens joints, heart and blood vessels, muscles and ligaments.
How to restore bowel function: folk recipes
Restoration is effective using oats and yogurt. It is necessary to boil oats: 3 tbsp. l. The grains are poured with water 1:2, heated for half an hour in a water bath and drained. A decoction of 30 ml is taken three times a day, half an hour before meals. Flax seeds and bran, which work as a natural sorbent, will help enhance the cleansing effect of oat decoction.
2 weeks after cleansing the mucous membrane with oat decoction, you can move on to the next stage: colonizing the intestines with beneficial microflora. Homemade fermented milk products will help with this: yogurt, kefir. Pharmaceutical probiotics are also effective. The final stage is proper nutrition, a healthy and rational lifestyle, and the elimination of bad habits.