When there is an imbalance of obligate beneficial and opportunistic microflora in the intestines, gastroenterologists, based on the results of stool analysis, make a diagnosis of intestinal dysbiosis, the symptoms of which are expressed in diarrhea, constipation, nausea, weight loss, in children, allergic reactions, anxiety, pain in the intestines. stomach, etc. How to treat intestinal dysbiosis? Treatment of this disease should be carried out by a gastroenterologist in several directions:
- firstly, finding out the causes of dysbacteriosis and eliminating them. This may be taking antibiotics, food poisoning due to intestinal infection (stomach flu, dysentery, salmonellosis), acute or exacerbation of chronic gastrointestinal diseases (cholecystitis, hepatitis, pancreatitis, gastric ulcer), as well as chronic stress or eating disorder, climate change, diet. This is possible with the help of pathogenetic treatment aimed at restoring intestinal motor functions, eliminating inflammatory processes, and prescribing enzyme replacement drugs.
- secondly, relieving acute manifestations of dysbacteriosis and normalizing digestion. In this, a diet that normalizes intestinal activity plays a big positive role, this is table No. 4; when followed, the intensity of putrefactive processes decreases.
- thirdly, correction of the composition of the intestinal microflora using non-absorbable antibacterial drugs, bacteriophages, intestinal antiseptics, prebiotics and probiotics that restore normal biocenosis in the intestine (see full description and List of probiotic preparations).
- fourthly, strengthening the body’s defenses, using herbal and synthesized immunomodulators.
Now let’s take a closer look at how to treat intestinal dysbiosis: medications, diet for dysbiosis, all medications, treatment regimens for intestinal dysbiosis:
Treatment of dysbiosis depending on the degree of intensity of the disorder
The intensity of intestinal microflora disorders is divided into 3 groups depending on the patient’s age and the results of a stool test for dysbacteriosis. The table shows the characteristics of these degrees.
| Children under 1 year |
|
| Children over 1 year old |
|
| Adults under 50 years old |
|
| Adults over 50 years of age |
|
If intestinal dysbiosis is detected, treatment in children and adults depends on the severity of the disease, the basic principles of therapy are as follows:
For 1st degree of dysbacteriosis the following is indicated:
- Functional nutrition, vitamin therapy, enterosorbents
- Prebiotics
For degree 2 dysbacteriosis it is recommended:
- Functional nutrition, vitamin therapy, enterosorbents
- Probiotics
For grade 3 intestinal dysbiosis, drug treatment is as follows:
- Functional nutrition, vitamin therapy, enterosorbents
- Antibacterial therapy, bacteriophages, intestinal antiseptics
- Probiotics
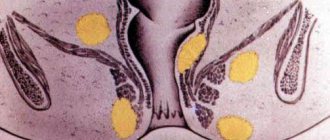
Indications for the use of suppositories
Therapy for microflora disorders (dysbacteriosis) occurs in stages. The patient’s action algorithm should be aimed at:
- Suppression of pathogenic microorganisms:
- elimination of the inflammatory process;
- antimicrobial effect;
- anesthesia.
- Colonization of lesions by beneficial microorganisms.
- Consolidating the result, increasing the barrier functions of the body:
- multivitamins;
- balanced diet;
- the right way of life.
Suppositories for dysbacteriosis are used to cope with the first two tasks. Typically, this is a course of treatment lasting for a decade.
Indications for use:
- inflammatory and infectious pathologies of the urogenital tract;
- chronic cystitis of bacterial origin with relapses;
- nonspecific fungal and mixed vaginitis;
- prevention of infectious complications;
- exacerbation of ulcerative colitis of varying severity;
- remission of ulcerative colitis;
- salmonellosis;
- urinary tract infections;
- dysentery;
- chlamydia;
- colpitis;
- dysbiosis;
- hormonal colpitis.
You cannot prescribe suppositories for yourself, as it is important to take into account the characteristics of the body, contraindications, and age. Only a doctor can develop a therapeutic regimen, taking into account medical history and test results. Which suppositories are appropriate in a particular case is determined by either a gynecologist or a gastroenterologist.
Diet for dysbiosis - functional nutrition
How to treat intestinal dysbiosis? With a mild degree of imbalance in the intestinal microflora, it may be sufficient to eliminate these causes through a balanced diet, taking prebiotics or probiotics. In case of severe disorders, dietary nutrition is also indicated simultaneously with complex antimicrobial therapy:
A diet for dysbacteriosis should be balanced in the content of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates, and also rich in microelements and vitamins; the amount of fluid drunk for an adult should be at least 2 liters per day. Moreover, it is very good to drink 1-2 glasses of clean water 30-40 minutes before meals, ideally if it is warm mineral water without gases.
It is very important to follow a diet in accordance with the biorhythms of the human body, that is, it is advisable to eat food at the same time - breakfast, 2nd breakfast, lunch, afternoon snack and dinner.
The daily diet of a person with dysbacteriosis should include amino acids such as glutamine (a source of high-energy compounds, nitrogen, purine), arginine, which has immunostimulating and anabolic effects, as well as fermented milk products enriched with active bifidobacteria and lactobacilli - cottage cheese, kefir, cheese, homemade yogurt, natural butter. Store-bought butter in our supermarkets most often contains palm and other refined oils, including solid beef fat, which is very harmful to the pancreas and the entire gastrointestinal tract, so you should buy proven or homemade butter without numerous additives, or completely abandon it. Dietary fiber and pectins must be present - these are beets, carrots, bran, cabbage, seaweed.
Not everyone knows that many foods are natural prebiotics or probiotics and have a weak antibacterial effect, for example, the following foods are destructive for some types of pathogenic microorganisms:
- Sweet peppers, onions and pomegranates act on E. coli.
- For staphylococcus in the intestines - strawberries, raspberries, aronia and red rowan, barberry.
- Apples, radishes, apricots, garlic, sage, dill, blueberries, rowan, and horseradish have a suppressive effect on Klebsiella, Protea, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
- Lingonberries and fresh carrots have a destructive effect on fungi, in particular candidiasis.
How to adjust the diet for dysbiosis depending on the nature of the intestinal pathology:
If the stool is dark and foul-smelling
analysis of the coprogram shows an alkaline reaction, a mass of undigested fibers - this is putrefactive dyspepsia. In this case, you should limit the consumption of fats and meat, increase boiled vegetables, cereals, and sour milk in your diet. Jelly or cranberry juice, apricot compotes, dried apricots, and fresh apricots are also useful. With such intestinal dysbiosis, herbal treatment is based on the use of wormwood, lemon balm, sage and caraway.
If the stool is yellowish
The feces are yellow, the analysis shows an acidic reaction, there is a lot of starch and undigested fiber - this is fermentative dyspepsia. In this case, you should exclude milk, limit carbohydrates and raw vegetables, more protein foods are indicated - cottage cheese, boiled meat, steamed fish, eggs. Vegetables can only be consumed boiled, and fermented milk products and various cereals also help well; spices such as bay leaves, pepper, and cloves inhibit fermentation processes. Herbal teas made from chamomile and mint are useful in herbal medicine; they reduce spasms and have an anti-inflammatory effect.
If the disease is accompanied by diarrhea
The diet for dysbacteriosis consists of eating boiled and pureed food, and the food should be of medium temperature, neither cold nor hot. Among herbal remedies, it is optimal to use pomegranate peels, oak bark, blueberry compote, and bird cherry. Read more about all medications for diarrhea in our article.
If dysbiosis is characterized by constant constipation
Then the diet should contain a lot of fiber, which is found in maximum quantities in apricots, white cabbage, eggplant, carrots, apples, and pumpkin. Rhubarb compote improves intestinal motility, as well as pure bran, which should be taken 1 tsp or tbsp. spoon 3 times a day, ideally washed down with a fermented milk product - yogurt, kefir, bifilin.
Other means to restore bowel function
In addition to taking pills for intestinal dysbiosis after antibiotics, it is necessary to adjust your usual lifestyle and diet. The first step to restoring microflora is physical activity. Blood circulation supplies the organs with essential nutrients. It is useful to do exercises in the morning, swim, and walk more. To increase blood circulation in the pelvic area, fitness and dancing (oriental for women) are suitable. With low activity, the blood begins to stagnate, moves more slowly through the bloodstream, and worsens the functioning of organs and their restoration.
Be sure to drink 1.5-2 liters of water per day. This thins the blood and removes harmful bacteria from the body. Helps get rid of constipation. When treating any disease, water is an integral part of therapy. You need to eat small portions several times a day. This will help the gastrointestinal tract digest food better. It is necessary to exclude junk food:
- preservatives;
- fat;
- roast;
- semi-finished products;
- chocolate;
- baked goods;
- alcoholic drinks;
- soda;
- coffee.
You need to include in your diet as many fresh vegetables and fruits, cereals, and vegetable soups as possible. It is better to eat meat boiled or baked; fried foods are difficult to digest. You should eat more foods rich in fiber (spinach, green beans, broccoli, carrots, nuts).
It is recommended to drink freshly squeezed juices, green tea, herbal infusions and decoctions. Herbs have a beneficial effect on the microflora: strawberry leaves, rowan, fruits, rose hips, fruits and leaves of black currant, string.
At the pharmacy you can buy ready-made herbal mixtures to restore intestinal balance: Zolotoy Altai, Herbalist Timasheva, Fitogastrol. You need to add dietary supplements to your diet. During the recovery period, the body must receive a sufficient amount of vitamins and minerals. A light abdominal massage will have a positive effect. You can do it yourself. In the morning on an empty stomach, drink a glass of clean water, then make circular stroking movements in the abdominal area, with light pressure. This activates the work of the gastrointestinal tract and has a beneficial effect on digestion.
The use of prebiotics for dysbiosis
The modern pharmacological industry is very rich in drugs that help establish the balance of intestinal microflora. These drugs include probiotics and prebiotics, which contain either living microorganisms themselves or their metabolic products.
To stimulate the natural growth of beneficial bacteria, gastroenterologists prescribe prebiotics - these are substances that enter the body along with food of non-microbial origin; they are not digested, but are designed to stimulate the development of normal microflora, since they serve as a nutrient medium for obligate, beneficial flora.
Prebiotics not only help improve the metabolic activity of natural microflora, but also suppress the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria, the body does not reject them. Unlike probiotics, they do not require special storage conditions or special packaging. Prebiotics include:
- Indigestible disaccharides are Lactulose (Normaze, Duphalac, Goodluck, Prelax, Lactusan), Lactitol (Exportal), gastrointestinal transit prebiotic (contains fructooligosaccharides, artichoke, lemon and green tea extracts), lactic acids - Hilak forte.
- These substances are found in natural products: cereals - corn, chicory, onions and garlic, as well as dairy products.
Effective tablets
Dysbacteriosis is a special pathology of the gastrointestinal tract that causes a lot of discomfort. If signs of this disease are detected, it is necessary to immediately seek help from a doctor and begin treatment. Today, a huge number of medications are produced to eliminate the symptoms of dysbacteriosis. They differ in the active substance they contain, cost, duration of use and other characteristics. You should not choose your medications on your own. Treatment should be prescribed by a doctor, taking into account test results, the severity of the pathology and the individual characteristics of the body. You can learn more about dysbiosis and its symptoms in adults in an article on the topic.
Tablet drugs are conventionally divided into the following groups:
- Probiotics – help normal intestinal flora reproduce faster, increase immunity;
- Antibacterial drugs – eliminate the main provoking factor of pathology, namely harmful microorganisms.
Before prescribing treatment, the doctor must find out the cause of the disease. It is often provoked by E. coli, staphylococcal, enterococcal and candiomycosis infections.
The following drugs are used to treat dysbiosis: Intetris, Enteroseptol, Pimafucin and Polysorb, Enterol, Levomycetin, Nystatin and Furazolin, Iberogast. These medications are affordable and highly effective. It is important to remember that the treatment regimen for dysbiosis is prescribed by the attending doctor after a complete diagnosis and determination of the sensitivity of a particular pathogen.
To treat dysbiosis in adults, you can take the following tablets:
Sorbents
These include Pepidol, Polysorb, activated carbon and Polypefan. These sorption preparations promote the binding of toxic substances and also prevent the active spread of putrefaction processes in the intestines. The course of treatment suggests using these remedies at the initial stage.
Enzymes
The most common enzyme tablets for dysbiosis: Digestal, Polyzyme, Mezim and Panzinorm Forte. They help normalize the digestive process, digestion of food, as well as the absorption of nutrients in the gastrointestinal tract.
BS based on a live strain
To effectively treat dysbiosis, you will need such drugs as Enterol, Bificol, Colibacterin, Baktisubtil. Their use is indicated at stages 1 and 2 of pathology. They are made from living microorganisms that create healthy intestinal microflora.
Probiotics
The best drugs for dysbiosis: Narine, Bifiform, Linex, Bifidumbacterin, Lactobacterin. Such probiotics are a broad group of medications that can be taken during any stage of the disease. The tablets contain strains with beneficial microorganisms that normalize microflora and eliminate pathological microorganisms.
Prebiotics
Normaze, Duphalac and Hilak Forte form a favorable environment for the existence of beneficial bacteria in case of dysbacteriosis. It is important to note that they do not contain strains of microorganisms. They can be taken at any stage.
Restoring motor function
For dysbacteriosis, it is recommended to take the following drugs: Immudon, Duspalatin, Meteospasmil, Trimetad. They contribute to the rapid restoration of intestinal motility and peristalsis, which eliminates symptoms such as flatulence, loose stools and bloating.
Immunomodulators
This group of drugs includes Dekaris, Levomizole. These drugs normalize the local immunity of the gastrointestinal tract. It is advisable to take it at the final stage of the treatment course to consolidate the effect.
Treatment of intestinal dysbiosis - probiotics
Probiotics are drugs for the effective treatment of intestinal dysbiosis, which contain live microorganisms; they are used for the prevention and treatment of dysbiosis, since their action is based on the regulation of intestinal microflora. All probiotics can be divided into several groups:
Multicomponent
they consist of several types of bacteria, colibacteria, bifidumbacteria, lactobacilli - these are Linex, Bifiform, Bifikol. On average, the course of treatment for dysbiosis with such drugs is 14 days.
Monocomponent
consisting of one type of bacteria - bifidobacteria, lactobacilli, colibacteria - Bifidumbacterin, Lactobacterin, Colibacterin. The course of treatment can last from 2 to 4 weeks.
Combined
they include symbiotic communities of major bacteria and strains that are resistant to most antibiotics in combination with culture media and immunoglobulin complexes. These drugs accelerate the growth process of beneficial microflora, these include Linex, Rioflora immuno, they contain streptococcus, bifidobacteria, lactobacilli, as well as Bificol, which contains E. coli and bifidobacteria.
Recombinant or genetically engineered
in addition to the obligatory microorganisms, they contain cloned genes that control the synthesis of alpha-interferon - this is Bifiliz (bifidobacteria and lysocin), the course of treatment of which is up to 14 days.
Synbiotics
For a more lasting effect, both prebiotics and probiotics are prescribed simultaneously. To treat intestinal dysbiosis, synbiotic preparations are produced with a competent combination of pre- and probiotics, forming ready-made complex medicines, for example, Bifidobac, Maltodophilus, Laminolact. The course of treatment with such drugs should be at least 21 days.
Antagonists
Probiotics can conditionally be classified as antagonists; these are microorganisms that can also suppress the development of opportunistic flora; these include antidiarrheal drugs such as Enterol, Bactisporin, Baktisubtil. The course of treatment of intestinal dysbiosis with these medications should not last more than 5-7 days.
Read more about all probiotics and Linex analogues here.
However, in severe forms of dysbacteriosis, the use of probiotics and prebiotics alone is not enough. They are not capable of destroying pathogenic organisms, since they are only intended to compete with opportunistic flora, suppressing its reproduction, and in the event of a serious imbalance, additional use of antibacterial agents and intestinal antiseptics is necessary.
Rules of application
Suppositories for the treatment of dysbacteriosis are used according to the instructions that come with each drug. General rules for all suppositories used for dysbiosis:
- mainly administered before bedtime, after hygiene procedures;
- when administering rectal suppositories, the intestines are emptied;
- hands are treated with an antiseptic or thoroughly washed with laundry soap;
- the introduction of suppositories is carried out while lying on your back;
- after the procedure, it is recommended to lie down for a quarter of an hour;
- some drugs should be moistened with water before use;
- at the same time as the drug is administered, do not use pads or tampons.
Before starting a course of treatment, study the list of contraindications and side effects.
Antibacterial drugs, intestinal antiseptics, bacteriophages
Their use should be very careful, prescribed only by a gastroenterologist, when the degree and form of dysbiosis is known, based on the laboratory-determined sensitivity of the bacterium to a specific drug:
Antibacterial drugs
- Staphylococcus - for example, if dysbiosis is caused by the proliferation of staphylococcus, then staphylococcal or pyobacteriophage is indicated, treatment for 14 days. If we are dealing with a combined lesion (inflammation of the navel in a newborn, risks of sepsis in premature infants), then macrolides (azithromycin, clarithromycin, josamycin) or aminoglycosides.
- Enterococci - if enterococci predominate (the most common of which is Klebsiella), then Klebsiella bacteriophage or nitrofurans (Ersefuril, Furazolidone, Stop-diar, Enterofuril), macrolides, levomycetin or semi-synthetic penicillins are indicated.
- Protea - modified E. coli or Protea are most often sensitive to nitrofurans - the most effective are nitrofurans (Ersefuril, Enterofuril), nalidixic acid derivatives - Nevigramon, as well as Sulgin, Fthalazol - sulfonamide drugs.
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa - to suppress its reproduction, polymyxin, carbenicillin or aminoglycosides - Kanamycin, Gentamicin - are most often used.
- Candidiasis - dysbacteriosis caused by the growth of fungi of the genus Candida or other fungal agents is treated with antifungal drugs, such as Fluconazole (Diflucan, Mikosist, Flucosan, Fluconorm, etc.), Terbinafine (Lamisil, Terbizil, Terbinox, Exittern, Bramisil), amphotericin B (Ambisome, Amphocil, Amphoglucamine, Ampholip, Fungizone).
- Clostridia - when it comes to pseudomembranous colitis caused by clostridia, a course of metronidazole (Trichopol) is first prescribed, and if it is ineffective, a course of the antibiotic vancomycin is prescribed.
Bacteriophages
Bacteriophages are special viruses that act on a specific type of bacteria; they can be used as an independent treatment or in combination with other antimicrobial therapy, used in the form of enemas or for oral administration. Currently, the following bacteriophages are produced: Proteus, staphylococcal, coliproteus and Pseudomonas (more about treatment with bacteriophages).
Immunomodulators, vitamins, enterosorbents and other drugs for intestinal dysbiosis
- Immunomodulators to accelerate the restoration of intestinal microflora can only be taken as prescribed by a doctor; it is best to use herbal preparations, such as Propolis, Dibazol, Immunal, tincture of echinacea, schisandra, and eleutherococcus. No other immunostimulant drugs should be taken without a doctor’s prescription (see whether drugs are needed to enhance immunity).
- Vitamins - during intestinal dysbiosis, the absorption and synthesis of vitamins slows down or stops altogether, therefore, with prolonged intestinal dysbiosis, treatment should be supplemented by taking vitamin complexes, in order to avoid the occurrence of serious hypovitaminosis, especially deficiency of vitamins E, D, A.
- Enterosorbents - for intestinal dysbiosis, treatment can be supplemented by taking enterosorbents, such as Polysorb, Polyphepan, Activated carbon, Enterosgel, Filtrum STI (instructions). However, their use should be short-term, no more than 7-14 days, and in between taking other medications, it is best to take them at night, 1 hour before or 2-3 hours after meals and taking other medications and vitamin complexes.
- Antispasmodics - if the patient is very worried about diarrhea, then, in addition to other therapy, you can take antispasmodics, such as No-shpa, Papaverine, as well as anti-diarrhea tablets - Loperamide, etc., astringent herbal preparations. If the patient suffers from constipation, then antispasmodics and drugs with Lactulose, laxatives - Forlax, Vaseline oil, suppositories for constipation are also indicated.
- Choleretic drugs - immortelle, choleretic preparations, Hofitol, hepatoprotectors - Karsil, Esentialle, Legalon, Liv 52 (see list of all medicines for the liver). According to indications, it is possible to use enzyme preparations - Pancreatin, Mezim, Festal, Creon.
- Antihistamines - against the background of intestinal dysbiosis, various allergic reactions can develop in children and adults, so it is also possible to use antihistamines and allergy tablets, such as Cetrin, Zyrtec, Zodak, Claritin. If the patient develops neurasthenic conditions, you can take sedatives, such as tincture of valerian and motherwort.
Author:
Selezneva Valentina Anatolyevna physician-therapist
Tablets for dysbacteriosis
Despite the effectiveness of suppositories in the treatment of dysbiosis in adults and children, doctors more often prescribe therapy to patients with drugs in tablet and capsule form. Why? The answer is obvious - they are more universal, have a wide spectrum of action and are highly effective in those parts of the body where it is impossible to use topical drugs.
The above-described medications can be divided into two large groups - these are drugs to eliminate the underlying disease and the cause of dysbiosis, as well as medications that normalize the microflora, increase immunity, eliminate the symptoms and negative effects of the disease.