When the process of food digestion in the gastrointestinal tract is disrupted, fermentation develops in the intestines. The causes and treatment of the pathological condition usually do not cause difficulties. Increased gas formation most often develops in the small intestine and causes considerable discomfort to a person. To solve the problem, you need to know which foods cause fermentation in the intestines and exclude them from the diet for a while.
Causes of intestinal fermentation
Gas formation is a natural physiological process that is an indicator of stable intestinal function. The most common causes of increased gas formation are the following:
- Frequent entry into the intestines of air during smoking, drinking carbonated drinks, drinking water directly during meals, abuse of chewing gum, talking during meals.
- There are a large number of foods on the menu that cause increased gas formation.
- Constant overeating, long breaks between meals, eating food immediately before bed.
- Insufficient production of digestive enzymes. This problem often manifests itself in infants of the first year of life and elderly patients.
- Malignant neoplasms of the gastrointestinal tract.
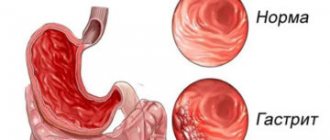
- Chronic ailments of the digestive system: gastritis, pancreatitis, cholecystitis, ulcerative lesions of the stomach and duodenum, cirrhosis, liver failure, cholelithiasis, ulcerative colitis.
- Congenital anomalies of the digestive tract: lactose intolerance, phenylketonuria.
- Disturbance of intestinal microflora due to long-term use of antibacterial drugs and laxatives.
- Infectious and parasitic diseases of the intestine.
- Frequent stressful situations.
- Lack of physical activity, low fiber content in the diet.
- Circulatory disorders that develop due to atherosclerosis.
- Diseases of the spinal column that provoke disruption of the innervation of internal organs: osteochondrosis, poor posture.
List of dangerous products
It must be taken into account that there are a number of products that cause fermentation in the intestines . The list consists of the following food groups:
- Vegetables: white and sauerkraut, potatoes, tomatoes, peas, beans, onions, garlic. Raw foods like these increase gas formation.
- Fresh herbs: parsley, dill, cilantro, sorrel.
- Berries and fruits: citrus fruits, bananas, grapes, pears, apples, peaches, apricots, prunes and others. Consuming on an empty stomach leads to severe flatulence, especially if combined with dairy products.
- Cereals: porridge, muesli, corn, bran. The exception is Fig.
- Yeast products: white and black bread, pies, baked goods.
- Chicken and quail eggs in the form of an omelet or scrambled eggs.
- Dairy and fermented milk products: fresh milk, cheese, kefir, yogurt, homemade butter.
- Meat and offal: pork, lamb, duck, goose, beef. It is especially dangerous to use at night.
- Sugar and various confectionery products certainly increase gas formation.
- Fish and other seafood eaten immediately before bed.
- Carbonated drinks, beer, kvass, packaged juices, jelly.
- Salt and various spices, especially when consumed simultaneously with salty foods.
The list of products is designed for a healthy person. If the patient suffers from digestive disorders or serious diseases of the internal organs, absolutely any food can cause flatulence.
Symptoms of increased gas formation
Violation of the rules of heat treatment of products , as well as gross violations in nutrition lead to increased gas formation. Most often, the disease manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- Increased passage of gases. Normally, the process of removing carbon dioxide from the intestines proceeds unhindered. When the volume of gases formed exceeds the norm, problems with their elimination begin, which causes discomfort to the person.
- Unpleasant odor of gases released. This symptom most often accompanies flatulence. If the pathology is associated with air entering through the stomach, the smell is weak.
- Excessive accumulation of carbon dioxide in the small intestine provokes pain in the abdominal area, up to the development of intestinal colic. It appears most often in children under 1 year of age.
- In some cases, bloating appears. Many people confuse it with increased gas formation, but bloating can also develop with moderate accumulation of carbon dioxide, when there is an obstacle to its removal.
- Rumbling in the stomach due to overeating.
- Stool disorders. Depending on the cause of flatulence, the patient experiences diarrhea or constipation. After the act of defecation, temporary relief occurs.
- Belching with an unpleasant odor and taste of food eaten is considered a malfunction in the digestive process. Normally, belching appears immediately after eating and is odorless and tasteless.
- Increased gas formation provokes compression of the stomach and diaphragm by the intestines. As a result, gastric juice refluxes into the esophagus, which invariably leads to heartburn. Such a symptom always indicates the presence of stomach pathologies.
- In some cases, the patient experiences nausea, accompanied by weakness and chills. The sign is not considered characteristic of flatulence.
Very rarely, patients with this diagnosis rise in temperature to low-grade levels. This is associated with the onset of the development of intestinal infection.
Methods for diagnosing pathology
The regular appearance of symptoms of increased gas formation indicates the presence of diseases of the internal organs. In this case, it is recommended to undergo a diagnostic examination. When contacting a gastroenterologist, the patient talks about his symptoms and possible causes of their occurrence.
The first stage of the examination will be palpation of the abdomen, laboratory tests of blood and urine (general, biochemical). After this, it is necessary to undergo an ultrasound examination of the gastrointestinal tract in order to identify pathological changes.
An important point will be the analysis of stool for the presence of pathogenic microflora. To clarify some diagnoses, fibrogastroduodenoscopy and x-ray examination will be required.
If necessary, other diagnostic methods are prescribed individually.
Why does the process begin in the intestines?
Fermentation and putrefaction are two processes that produce gases in the intestines, but they are caused by different factors. Fermentation is a redox process that leads to the formation of alcohol, organic acids, acetone and other organic substances, as well as carbon dioxide and hydrogen.
Fermentation is typical for carbohydrates (organic compounds of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen). Rotting occurs under the influence of microbes; in the process of decomposition of organic nitrogen-containing compounds, ptomains are formed, which have toxic properties.
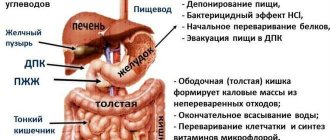
Putrefaction occurs in the large intestine, since there are conditions for the existence of putrefactive bacteria. Thus, carbohydrates that end up in the large intestine ferment and at the same time release gases (carbon dioxide and hydrogen), and proteins rot and form ammonia gas.
The breakdown of carbohydrates begins in the oral cavity under the action of salivary enzymes (amylase and maltase). The process continues in the duodenum, where intestinal and pancreatic juice breaks down carbohydrates into glucose, which will then be oxidized in the cells to water and carbon dioxide or converted into fat or glycogen.
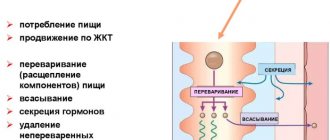
During normal digestion, all food that ends up in the stomach and small intestine must be broken down by hydrolytic enzymes, with the exception of water, vitamins and minerals, which enter the bloodstream unchanged.
Drug therapy regimen
Based on the diagnostic examination, the gastroenterologist draws up a treatment plan. Typically, the treatment regimen includes the following drugs:
- Antacids and enterosorbents promote the safe removal of gases from the intestines. The most popular products in this group are: Enterosgel, Atoxil, Phosphalugel, Almagel, Smecta, activated carbon.
- Antifoam agents, including simethicone. The substance acts on air bubbles and helps reduce discomfort, as well as quickly remove accumulated gases. Adults are most often prescribed Simethicone, Espumisan, children - Bobotik, Infacol.
- To eliminate intestinal spasms, antispasmodics are used: No-shpa (approved for the treatment of children over 6 years old), Riabal (can be used from infancy).
- A mandatory part of the treatment will be taking medications that improve intestinal motility: Motilium, Domperidone. Patients with severe disorders are prescribed a solution for subcutaneous administration of Proserin. The drug is used exclusively in hospital settings.
- The use of combination drugs to eliminate the symptoms of the disease is allowed: Maalox plus, Almakon. The most common active ingredients are antacid and simethicone.
- To improve digestion, enzyme preparations are prescribed: Creon, Festal, Pancreatin.
The use of some medications with a carminative effect is prohibited for newborn children. In this case, herbal remedies are used that have a minimal list of contraindications and side effects: Happy Baby, Babby Calm, Dill Water.
During treatment, fluid intake should be increased to prevent stool retention.
Types of dyspepsia
Depending on the predominant process, several types of pathology are distinguished:
| Type of dyspepsia | Causes |
| Fermentation | if your diet is dominated by carbohydrates |
| Putrid | appears with protein diets, excess meat or consumption of stale foods rich in protein |
| Fatty (soapy) | occurs due to the intake of refractory (animal) fats |
They are also called functional, as they are caused by dietary errors, as well as temporary disturbances in the functioning of the stomach, intestines and pancreas. After normalization of nutrition, the condition will improve. If there is a disease, then dyspepsia will only be a symptom of it; it cannot be completely eliminated without treating the underlying pathology.
Alternative medicine against fermentation
When traditional medicine was at the beginning of its development, it was possible to get rid of the disease only with the help of folk remedies. Ancient healers knew exactly how to remove fermentation in the intestines, so some recipes are still used today:
- The most common remedy designed to stop fermentation is dill water. It’s easy to prepare: pour a tablespoon of dill seeds into 350 ml of boiling water and leave for 3 hours. After this, strain and drink before meals, throughout the day, dividing the entire volume into 4 doses. The good thing about this recipe is that it is suitable for use by infants. The dosage in this case will be less.
- A decoction based on chamomile has antiseptic, anti-inflammatory and carminative properties. To prepare it, boil a tablespoon of pharmaceutical raw materials in a glass of water for 5 minutes, and filter after 3 hours of infusion. Take 20 ml 4 times a day. Continue therapy until symptoms disappear completely.
- If food continues to ferment in the intestines and pharmaceutical remedies do not help, ordinary green tea with the addition of 5 g of chamomile and 3 g of thyme will correct the situation. The ingredients are brewed with boiling water, simmered for 10 minutes and taken warm 2-3 times a day.
- Drinking ginger tea on an empty stomach will relieve spasms and improve digestion. Making the drink is simple: add half a teaspoon of grated ginger root and the same amount of cinnamon powder to a glass of boiling water, leave for 30 minutes. Use immediately after waking up until recovery.
- Lemon peel and lemon juice will eliminate fermentation. To enhance the effect, you can drink 30 ml of lemon juice daily with a pinch of cinnamon. Duration of treatment is 10 days. This recipe is not suitable for patients with gastric ulcers, as it can provoke an exacerbation.
- An infusion based on dandelion rhizome will help alleviate the patient’s condition. To obtain it, 10 g of crushed raw materials are infused for 12 hours in a glass of cold, boiled water. The composition is taken 50 ml 4 times a day for 7 days. The product will help not only cope with flatulence, but also improve the condition of the gastric mucosa.
- A decoction of parsley seeds can provide first aid at the first signs of bloating and increased gas formation. It should be prepared from 20 g of raw materials and 300 ml of water. Boil the composition for 5-7 minutes, leave for 1 hour, take a tablespoon 5 times a day until the symptoms disappear.
As a rule, after 10 days of home therapy, fermentation processes stop. It is recommended to coordinate the use of folk remedies with your doctor to avoid unpleasant consequences.
Symptoms of fermentation in the stomach
The symptoms accompanying fermentation in the stomach can be varied. Some complain of minor discomfort. Others experience the disease much more clearly on themselves.
Signs of a pathological process may be hidden in the following:
- bloating;
- flatulence and increased gas formation;
- rumbling;
- stool disorder. However, the character may be different. The pathology may be accompanied by both constipation and diarrhea;
- colic and pain in the stomach.
With adhesions and the development of neoplasms, other symptoms may occur. The patient complains of headaches, dizziness, increased temperature, and the appearance of undigested food particles in the stool.
If an organ is injured, harmful bacteria colonize it, causing intoxication of the body and disruption of the microflora.
Dietary recommendations
Proper heat treatment and reducing the amount of products that increase gas formation will help reduce the risk of recurrence of the disease.
It is recommended to eat boiled and baked vegetables and fruits, and exclude smoked meats, marinades, spices, baked goods, and legumes from the diet. You should not combine carbohydrate and protein foods in one meal, drink during meals, overeat, or consume large quantities of specific foods (oysters, shrimp, exotic fruits).
Dishes must be freshly prepared; consumption of expired products is prohibited. Once a week, it is recommended to take a fasting day and give up heavy food, replacing it with rice, buckwheat, and baked apples.
Fermentation in the intestines is not considered a serious pathology, but in some cases it can serve as the beginning of the development of diseases of the digestive system . Don't ignore the symptoms. Early diagnosis and treatment are the key to successfully getting rid of the problem.
Fermentable foods
- bakery products: white wheat bread, black bread, shortbread cookies, buns, products made from yeast and puff pastry;
- cereals: semolina, millet porridge, corn flakes, pasta, spaghetti, bran;
- legumes: peas, lentils, beans, beans, chickpeas;
- vegetables: potatoes, zucchini, white cabbage, broccoli, cauliflower, green peas, pumpkin, asparagus, carrots, bell peppers, Brussels sprouts;
- fruits: sweet apples, pineapples, bananas, grapes, persimmons, pears, melon;
- dried fruits: raisins, dates, prunes, dried apricots, figs;
- sweets: honey, sweets, chocolate, cakes;
- malt-based drinks: kvass, beer, sweet carbonated drinks, fruit juices;
- dairy products: milk, ice cream.