What types of abdominal pain are there?
In terms of duration, pain can be acute, lasting up to 7 days, and chronic – over 7 days. Pain caused by a certain pathological process in the abdominal area is called organic, and pain due to stress, experiences and other psychological factors is called functional. Among other things, this phenomenon is age-related: for example, it is obvious that a 4-year-old girl cannot have menstrual cramps.
The nature of pain in the navel area is perhaps the most varied: there can be pain, colic, a feeling of bloating, burning, pulling, aching and twisting pain. Painful sensations can occur suddenly, or they can increase gradually or appear periodically, in waves.
There are certain signs that indicate a specific cause of pain in the navel or a possible disease, but its definition alone is not enough for a final diagnosis and treatment.
Why does my child have a stomach ache?
Finding out whether a baby has a stomach ache or not is quite simple: babies scream and tuck their legs, older children can hold their stomachs, bend over, and even say, it’s worth finding out more about the nature of the pain from teenagers. Also, accompanying symptoms and factors preceding the onset of pain in the navel area are always taken into account.
Colic
Often occurs in newborns after eating and can last from 1 to 4 hours at a time. On average, such phenomena disappear after 3 months from birth.
Pain due to bloating
Stitching sensations in the navel area in a child may occur due to the accumulation of gases in the intestines, with the gradual release of which the condition normalizes.
Seasickness
This condition indicates that the child is prone to motion sickness, including in ground transport, attractions, swings, etc. It may be accompanied by vomiting and colic.
If your child suffers from seasickness, plan your transportation so that you can make frequent stops and have access to fresh air. When traveling, you should always have regular water without gas.
Bacterial dysentery
In addition to a possible painful condition in the navel area, the baby experiences frequent stools, vomiting and diarrhea are possible. Also, feces may contain impurities of blood and mucus, or the baby “does not walk at all,” and bloody or mucus discharge is noticed from the anus. This symptomatology does not exclude the entry of pathogenic microflora into the digestive system due to contact with a patient or in connection with the consumption of contaminated food or water.
Viral infection
A painful navel area, high fever and vomiting may indicate rotavirus. And pain in the liver area (upper part of the abdominal area on the right) and yellowing of the skin may indicate hepatitis A.
Cough and sore throat due to streptococcus
As a result of a hysterical cough, the abdominal muscles are overstrained, which can cause pain. The disease is accompanied by a painful condition of the throat and navel area, headache, and elevated body temperature.
Abdominal tuberculosis
We can talk about this disease if the baby has been in contact with a patient with an active form of tuberculosis, eats poorly and is losing weight, and also has an enlarged abdomen, which may also be accompanied by a lack of stool.
Constipation
The most common cause of colic. Constipation is characterized by rare, dense stools, periodic sharp and wave-like pain in the navel lasting from 10 minutes to half an hour.
Lactose intolerance or milk protein allergy
The phenomena are not related to each other, but have a common clinical picture and the culprit – dairy products. They are characterized by pain throughout the abdomen, including colic, cramps, as well as bloating and loose stools.
Diarrhea
Accompanied by characteristic rumbling and gurgling sounds. The cause of diarrhea can be anything - a bacterial or viral infection, poisoning or parasitic activity. Other associated symptoms must be taken into account for identification.
Heartburn, gastritis and ulcers
This pain can be observed in almost any part of the abdominal cavity and is characterized by a burning sensation, which children often have difficulty describing.
Parasites
Diarrhea, increased gas formation and spasms with colic are also characteristic of helminthiasis, that is, diseases caused by the activity of parasites or, in common parlance, “worms”.
Dyspepsia (digestive disorder)
It can occur as a result of overeating, eating too quickly, or consuming large amounts of liquid, including carbonated drinks. The pain intensifies when inhaling, and occurs due to excessive or sudden stretching of the walls of the stomach.
Appendicitis
The disease is very rare for babies who are not yet 1 year old. It is characterized by acute pain in the umbilical region, moving to the lower right corner from the navel and may be accompanied by lack of appetite, vomiting, high fever and even diarrhea.
Urinary tract infections
Babies, feeling pain during urination, worry, cry and tense their tummy. Their sleep and appetite are also disturbed. Older children, schoolchildren and preschool children may complain of a burning sensation when urinating.
Intestinal obstruction
The painful condition occurs due to distension of the abdomen, accompanied by constipation, rapid vomiting with bile and possible admixture of feces.
Intussusception
A type of intestinal obstruction typical for children in the age range of 3 months – 3 years. A sharp sensation of pain occurs, lasting about 3 minutes and repeating every 10-20 minutes. There may be bloody bowel movements, pale skin and nervousness of the baby.
Medications
Most often, a painful reaction can occur after taking antibiotics, but it is also possible with the use of many other medications.
Irritable bowel syndrome
It can last quite a long time - from several weeks to several months. More often registered in adolescents. At such moments, there is acute pain at the navel, which intensifies with palpation, nausea, a feeling of fullness and bloating. It usually occurs after eating and goes away with the release of gas.
Menstrual cramps
They can also occur a few days before menstruation. They have varying degrees of severity, and may be accompanied by painful sensations in the lumbar region.
Psychological factors
In this category, two factors are distinguished: behavioral pain sensations, contrived to attract the attention of adults (usually observed at the age of 4-7 years) and an anxiety state in a stressful situation, which may be accompanied by diarrhea (typical for 5-10 years of age).
Other possible causes of pain
- Hernia;
- ulcer;
- inflammatory bowel disorders (for example, colitis);
- tumors;
- pancreatitis;
- cholelithiasis;
- mononucleosis;
- coelica;
- Sickle cell anemia is an inherited blood cell disorder.
Causes of pain
When this disease develops, it is worth analyzing exactly when discomfort occurs. The source may be too tight clothing that puts pressure on the stomach.
This unpleasant phenomenon can also occur as a result of serious pathological processes in the human body, some of which require urgent hospitalization.
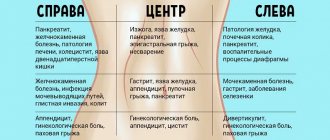
Common causes of belly button pain:
There are many causes of pain in the abdominal area.
1 Enteritis, gastroenteritis . Enteritis is an inflammatory process in the small intestine. Gastroenteritis is an inflammation of not only the small intestine, but also the stomach. These diseases are considered the most common causes of abdominal pain in the navel area. In this case, the following appears: nausea followed by vomiting, broken stools (diarrhea), accumulation of gases in the intestines, bloating and rumbling in the abdomen.
Acute enteritis develops as a result of infection entering the body and is accompanied by elevated body temperature. Enteritis can become chronic as a result of infection with Giardia or helminths, as well as due to non-compliance with the correct diet.
2 Intestinal colic . It can occur as a result of severe distension of the intestine, impaired peristalsis, irritation of nerve endings and muscles, or the presence of an obstruction in the intestine. The causes of intestinal infection are written in detail here.
3 Abdominal (abdominal) migraine . A headache and paroxysmal pain appears in the child’s navel area. Flatulence, bloating, nausea, diarrhea, and vomiting develop. Children of preschool age are most often affected.
4 Umbilical hernia. Characterized by acute pain in the navel area, as well as the appearance of an oblong formation (hernia) in this area. Self-medication or untimely therapy can lead to tragic consequences, therefore, if you suspect the appearance of this disease, you must immediately call an ambulance.
5 Malabsorption syndrome . This is a chronic gastrointestinal disease caused by impaired digestion. Malabsorption syndrome may be associated with a lack of enzymes, lack of complete absorption of nutrients and their subsequent transportation.
6 Diverticulitis of the small intestine . Protrusions (diverticula) appear. Visually, they look like an inflated bag, the size of which varies from 3 mm to 15 cm in diameter. In this case, the intestinal lining protrudes through the intestinal muscles. The affected areas are very painful, radiating to the left area of the abdomen. Possible increase in body temperature. If a child has blood in his stool, then this is a serious symptom that under no circumstances should be ignored.
7 Appendicitis . Sudden pain appears in the abdomen above the navel, around it, or in the pit of the stomach. Over time, it intensifies and moves to the right side of the body. Dry tongue and tachycardia occur, but a sharp increase in body temperature does not always occur.
In addition to the reasons listed, there are many others. These include:
- dysbacteriosis;
- IBS (irritable bowel syndrome);
- passage of kidney stones;
- UC (nonspecific ulcerative colitis);
- jeunitis;
- Crohn's disease;
- intestinal ischemia;
- oncology of the small intestine;
- volvulus.
Causes of pain in the navel area in women: cystitis, impaired blood circulation in the pelvic organs, endometritis, endometriosis, intestinal disorder, benign or malignant neoplasms in the appendages and uterus.
Characteristics that will give a clear picture of the child’s condition
Length of pain
Pain that lasts no longer than a day can be caused, for example, by flatulence or another short-term gastrointestinal disorder, which is not a cause for serious concern. If your stomach hurts for more than 24 hours, this is sufficient reason to contact a specialist.
Specific location of the painful area
Often, pain near the navel goes away on its own, but if the area below or on the side is painful, especially for a long time, this may indicate some kind of disease, and in this case it is better to consult a doctor in a timely manner.
General condition of the baby
If the baby, in addition to the pain he is experiencing, is lethargic, refuses to eat and drink, is pale, and is covered in cold, sticky sweat, this also means that a medical examination is in order.
Vomiting and/or diarrhea
In non-serious cases, vomiting does not last longer than a day, and diarrhea does not last more than 3 days. The presence of impurities of various types in vomit or feces is also important. This could be, for example, blood, and the vomit may also contain yellowish, greenish or suspicious dark inclusions.
Temperature
An increase in temperature does not indicate serious problems. Rather, on the contrary, often with a serious illness and abdominal pain, the temperature does not rise.
Groin pain
May occur due to testicular torsion in boys. Moreover, the child may say that his stomach hurts not where the navel is or below, but that he feels pain in the gastric region. In addition, the baby may experience some embarrassment and not admit where exactly the pain is bothering him , so you should ask the boys especially carefully, explaining how important it is to know the specific location of the pain for its further treatment. It is important not to delay with this phenomenon!
Rashes on the body
Abdominal pain and rash may be a sign of scarlet fever, so contact your doctor immediately.
Enteritis
Sometimes inflammation of the mucous membrane of the small intestine becomes protracted. Then we are talking about chronic enteritis, which during an exacerbation has the same symptoms as this disease in its acute form.
Abdominal migraine
Pain that affects the umbilical region of the abdomen also occurs with abdominal migraine. In this case, pain is accompanied by discomfort in the head, weakness, numbness of the limbs, etc. This condition may be psychosomatic in nature.
What to do, the opinion of Dr. Komarovsky
Dr. Komarovsky warns that you should never apply a heating pad to your stomach without a doctor’s prescription. In the case of purulent-inflammatory processes in the abdominal cavity, the use of heat can cause perforation of the intestinal wall and diffuse purulent peritonitis.
Pediatricians recommend allowing the child to take a position that is comfortable for him, observing bed rest, limiting the amount of food consumed, and giving the baby plenty of rehydration solutions (Regidron and others). If the baby's condition worsens, you should call an ambulance.
Pain around the navel is an alarming sign, which may indicate diseases of the stomach or intestines and requires the intervention of a competent specialist. Therefore, if your child complains of discomfort in this area, you should take him for a consultation with a gastroenterologist as soon as possible.
When do you need a doctor for abdominal pain in a child? – Doctor Komarovsky
What to do if your child has a stomach ache
If you find that your baby has colic, medications that contain simethicone or Kuplaton, as well as dill water or fennel tea will help get rid of them. A special gas outlet tube, which can be purchased at any pharmacy, also helps to remove gases.
Give your baby a massage of the navel area with circular strokes in a clockwise direction, and apply a warm diaper to the tummy. Shortly before bedtime, you can bathe the baby in a bath with the addition of chamomile infusion or other herbal teas with a calming and relaxing effect, which can also be bought at the pharmacy.
With an older child, the situation is different: first of all, what can be done to alleviate his condition is to provide frequent drinking of still water in small quantities and, if necessary, to drink special means for rehydration; in addition, lay him on his back with his head on a pillow, place a blanket or pillow under your knees. This position will remove the tension in the abdominal muscles as much as possible.
You should try to understand the cause of the painful condition, taking into account the nature of the stool and its frequency. Perhaps the fact that your child ate or drank something unusual the day before may give you an idea of the cause. In any case, adjust your baby’s diet - let him refrain from eating heavy food for a while.
When is medical intervention necessary?
Call an ambulance if:
- a newborn under 3 months of age experiences vomiting and diarrhea;
- the child does not have stool, but nevertheless vomits;
- the baby suddenly developed acute pain in the navel area;
- the child has a tense, hard and painful abdomen;
- the baby has rapid or slow breathing;
- the abdominal area was recently injured;
- the baby feels pain when urinating, the urine has taken on an unnatural dark color;
- the boy has pain in the groin area;
- The baby is undergoing treatment for cancer.
Causes of abdominal pain in children
Provoking factors that cause pain in the child’s mesogastrium are mainly malfunctions of organs and systems located in the specified area. More often, deviations occur in the gastrointestinal tract and urinary system.
Diseases that cause pain in the umbilical area:
- Colic is cramping in the baby's stomach after eating.
- Bloating is an accumulation of gases that causes abdominal pain due to stretching of the intestinal walls.
- Acute appendix is an inflammatory process in the vermiform appendix of the cecum. Nagging pain symptoms begin near the navel and radiate to the right side. Pain is a signal of the danger of peritonitis. Nausea, flatulence, vomiting, bloating, and fever appear.
- Volvulus is an intestinal obstruction caused by helminthic infestation, trauma, or impaired intestinal motility. The pain appears in the mesogastrium and spreads lower, gradually intensifying. Defecation becomes difficult, vomiting occurs, the temperature rises, blood pressure drops, the baby turns pale, and lethargy appears. This pathology is treated surgically.
Intestinal obstruction in a child - Cholecystitis is an acute inflammation of the gallbladder. In addition to the pain attack localized in the central abdominal cavity, the baby noticeably darkens the urine, increases gas production, and increases the temperature.
- Cystitis is inflammation in the genitourinary system. Characterized by cutting sensations below the navel, high temperature, and frequent urge to urinate.
- Hepatitis A is a viral infection that causes pain in the abdominal cavity, radiating to the right. Fever, diarrhea, and yellowing of the skin appear.
- Enteritis is an inflammatory process of the small intestinal mucosa that can cause pain in the center of the abdominal cavity during phases of exacerbation of the disease.
- Intestinal hernia is a release of part of the intestine through the abdominal wall in the area near the navel due to parasitic diseases, weak muscles, and hereditary pathologies. Only a doctor can repair a hernia. Compression of the intestine as a result of pathology or sudden movements leads to severe pain, especially when touched, and intoxication develops. Urgent surgery required.
- Gastritis is an inflammatory process on the gastric mucosa. Accompanied by severe pain in the center of the abdomen after eating, vomiting, belching, nausea and heartburn. In a teenager, the likelihood of exacerbation of the disease increases due to poor diet and hormonal changes in the body.
- Small intestinal cancer is a tumor formation that causes painful attacks in the center of the abdominal cavity, accompanied by bloating, nausea and vomiting.
Small intestinal tumor - Helminth infestations - a painful symptom caused by intestinal damage by parasites. During the acute course of the disease - fever, bowel dysfunction, flatulence, nausea, urticaria.
- An umbilical hernia is a protruding formation in the mesogastrium, the cause is weakness of the abdominal wall muscles in infants. The pathology goes away on its own in children. After 5 years, surgical intervention is required, as the risk of pinching the hernia increases, which will cause pain in the umbilical area.
- Food poisoning - caused by putrefactive bacteria and provokes painful attacks in the abdominal area, nausea, diarrhea, fever, vomiting.
- Intestinal obstruction - appears as a result of blockage of the intestinal lumen by a swallowed object, small toy or parasites. Characterized by severe pain in the groin, vomiting of feces, and intoxication. Urgent surgical treatment is required.
External factors provoking painful symptoms in the mesogastrium
Adults should understand that the occurrence of painful symptoms in the navel area is associated not only with pathologies in the functioning of the baby’s organs and systems. A number of causes of abdominal pain symptoms are external in nature:
- Mechanical trauma to the abdominal cavity.
- Eating foods that do not go together.
- Expired food products.
- Long-term treatment with medications.
- Psychological factors (stress, anxiety).
Diagnostics
To determine the cause of pain in the navel area, an anamnesis is collected, that is, it is found out, starting with what the baby ingested the day before, and ending with known hereditary diseases.
A physical examination is performed, during which the doctor palpates (feels) the abdominal area and may even perform a rectal examination to check for bleeding from the anus. Then the necessary tests are prescribed (blood, urine, feces) and an x-ray or ultrasound is not excluded.
Treatment of abdominal pain
You have already learned above what to do with infants who suffer from colic. If the baby has a temperature above 38˚Ϲ, give an antipyretic (Nurofen, Panadol or Paracetamol). These drugs also have an analgesic effect.
In case of poisoning, Atoxil can help in the dosage according to the instructions, depending on age. In general, with regard to taking medications, they should be used according to the doctor’s recommendations so as not to complicate the situation when self-medicating.
Causes of pain in the navel area
Pain in the navel area can occur due to many factors, many of which threaten the child’s life and can be fatal. Parents should know how to distinguish between cases when medical intervention is not required from those when medical attention is urgently needed.
The main reasons why children experience pain in the umbilical area are::
- Constipation;
- Intestinal infection;
- Acute or chronic enteritis;
- Intestinal obstruction;
- Umbilical hernia;
- Intestinal hernia;
- Acute appendicitis;
- Gastritis and gastroduodenitis;
- Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum;
- Abdominal migraine (psychogenic pain);
- Dysbacteriosis;
- Taking medications that irritate the mucous membrane of the thyroid gland, poisoning;
- Intoxication due to ARVI and other infections.
It is important to assess the intensity of the pain, its duration and nature - ask the child to describe his sensations in as much detail as possible. Depending on the characteristics of the manifestation, the following types of pain syndrome are distinguished:
- Aching;
- Cutting;
- Pricking;
- Pulling;
- Cramping.
Tips for preventing childhood abdominal pain
To avoid possible complications from the digestive system, teach your child the rules of personal hygiene, in particular, washing hands when coming from outside and before eating. Don't let your baby overeat; teach him to eat more vegetables and fruits to avoid constipation.
Do not forget that eating just before bed is undesirable or even harmful not only for adults, but also for children (this does not apply to infants). To prevent the formation of hard stool in the intestines and their accumulation, the child should drink enough water.
Prevention of abdominal pain
Preventive measures depend on the nature of the pathology that caused abdominal pain. Observing the rules of personal hygiene allows you to avoid contracting an intestinal infection. It is necessary to teach a teenager to always wash their hands thoroughly before eating and after visiting the toilet, and while eating to use only personal dishes and cutlery. Fresh vegetables and fruits should also be thoroughly washed with a brush under running water before consumption. Where hygiene is not possible, it is better not to eat food.
Video
The phenomenon of abdominal pain near the navel in a child is very common, and it is important to determine its nature in time in order to be able to prevent possible serious consequences and alleviate the patient’s condition. A well-known pediatrician of the highest category with many years of experience will help you understand this issue, watch the video below:
Tell me, was the article useful to you? Were you able to determine the cause of abdominal pain around the navel in a child and did you eliminate it yourself or did you have to turn to specialists? Leave your detailed comment below, and I wish you and your children to be healthy!
An article about colic in a newborn will help you explore the topic of abdominal pain in more detail. Find out why a newborn’s tummy may still hurt, and whether you should worry if green feces are detected in your baby. It will be useful for you to know what an umbilical hernia is in children and when you should worry if you find a characteristic protrusion of the navel in a baby.
Volvulus
Due to injuries, helminthic infestation or dysfunction of intestinal motility, intestinal obstruction may develop. This is a dangerous condition in which the child will complain more and more every hour. Intestinal volvulus is treated only in a hospital in the surgical department.
Sharp pains occur in the abdomen, around the navel and below, they intensify over time, eventually becoming unbearable. Defecation and passage of gases are difficult. Vomiting is frequent, at first the vomit contains food, then it acquires an unpleasant odor and feces are found in it.
In this condition, the temperature progressively rises, and general weakness and intoxication increase. The child is pale, lethargic, heart rate is rapid, blood pressure is low. Possible disturbances of consciousness.