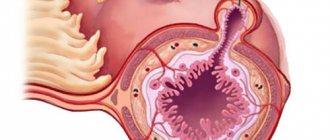
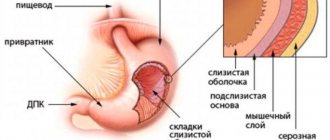
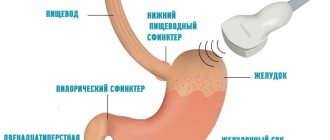
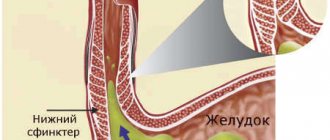
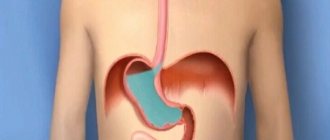
The intestinal valve is a tightly closed fold of natural origin formed at the junction of the small and large intestines. Its functional purpose is to ensure the movement of intestinal contents in the direction from the ileum to the cecum.
Insufficiency of the ileocecal valve (another name for this organ) causes the reflux of food masses in the opposite direction. The Bauginian valve, when its functionality is impaired, leads to congestion of the small intestine with the microflora of the large intestine and, as a consequence, its inflammation. Regular manifestation of this pathology causes a disease called chronic enteritis.
Causes of the disease
The Bauhinian valve, the shape of the opening of which can be open round, closed-lip-shaped, semi-open-slit-shaped, may stop performing its natural functions for the following reasons:
- congenital anatomical anomalies and defects;
- consequences of surgery;
- inflammatory processes in nearby organs, for example the ovaries;
- the presence in the body of pathogenic microbes that enter with food;
- neurological diseases.
Diagnostic methods
Irrigoscopy. Injection of a contrast agent through the rectum followed by radiography. Using this study, it is possible to visualize the transition of the large intestine to the small intestine, its boundaries, and functional state. Colonoscopy. With a total colonoscopy, the Bauhinian valve can be seen. This is a fairly accurate way to determine the functional state of the ileocecal valve. In addition to examining the bauginian valve during colonoscopy, it is also recommended to insert the end of the colonoscope into the small intestine. In this case, the distal part of the ileum is examined. The mucous membrane of the small intestine is characterized by the presence of signs of inflammation.
The Bauhinian valve should close tightly, periodically expelling the contents of the small intestine in peristaltic waves. When it is insufficient, the sponges do not close tightly, forming a slit-like space. Through this gap, the contents of the cecum along with bacteria can penetrate into the ileum, causing inflammation.
Capsule endoscopy. A modern and quite expensive method of endoscopic examination. It is performed by the patient swallowing a miniature video camera with a power source. At the moment, this is the most reliable method for studying the small intestine. Moreover, it is the only one that allows you to examine the entire small intestine as a whole.
X-ray examination with control of barium passage. The subject drinks a large amount of contrast agent containing barium. After this, X-rays of the abdominal cavity are taken at regular intervals to determine the distribution of the contrast agent.
It must be remembered that X-ray methods only allow one to suspect insufficiency of the Bauhinian valve. Only endoscopic examination can confirm or refute them.
The method of treating inflammatory processes in the area of the Bauginian valve is determined by the specific course of the disease. The general condition of the patient’s body, as well as the nature of the complications that the disease could provoke, play an important role.
If the nature of the disease is infectious, the patient is placed in an infectious diseases hospital. For this disease, antiparasitic and antibacterial therapy takes place. It is a common practice to prescribe so-called broad-spectrum antibiotics to patients, belonging to the group of sulfonamides or tetracyclines. These medications should be taken for at least 7 days.
Insufficiency due to psychosomatics
Separately, I would like to highlight the causes of a psychosomatic nature, which are the provocateurs of almost half of all diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Psyche and somatics (soul and body) are an integral, unified system with a strong interconnection of components. Any deep emotional experience affects a person’s physical health, and, conversely, poor health directly affects thoughts, mood, and behavior. The Bauginian valve, the treatment of pathologies of which is successful in most cases, is also no exception and can become inflamed for psychosomatic reasons.
Causes of deficiency
The main causes of this disease are:
- Anatomical developmental defects, collagenosis, congenital anomalies.
- Psychosomatic reasons. It's no secret that all diseases of the gastrointestinal tract are approximately 50% caused by the human psyche. At the moment, the world medical community has identified a whole group: psychosomatic intestinal diseases.
- Consequences of surgery or inflammatory disease. A scarring process or adhesions in the abdominal cavity can disrupt the function of the ileocecal valve and deform it. First of all, this includes operations on the appendix, especially with advanced appendicitis.
- Inflammatory diseases of adjacent organs, for example, the right ovary.
- Neurological diseases.
Ruptures and possible injuries of the colon
Symptoms of the disease
Insufficiency of the Bauginian valve is a little-studied disease, as it is characterized by rather nonspecific symptoms:
- flatulence (excessive accumulation of gases),
- bowel dysfunction: diarrhea and constipation;
- seething in the abdomen, which is especially well heard when pressing on the abdomen, namely in the area of the right hypochondrium;
- bad breath, presence of bitterness in the mouth;
- heartburn, nausea, belching;
- pain in the right side. The pain is mild, intermittent, and often occurs some time after eating;
- dizziness;
- cardiopalmus;
- increased fatigue;
- weight loss.
In most cases, insufficiency of the bauhinium valve is detected completely by accident (during an examination of the body or during screening) and can be mistaken for another disease.
Brief introduction to the disease
It is worth noting that insufficiency of the bauhinium valve is a fairly common diagnosis found in medical practice. However, identifying this disease is not an easy task, even taking into account the introduction of cutting-edge diagnostic methods into practice. This fact is explained by the fact that the symptoms of this pathology are often confused with other diseases. For example, insufficiency of the bauginian valve is often mistaken for irritable bowel syndrome.
Insufficiency of the bauhinium valve is a fairly common diagnosis found in medical practice.
The not very successful diagnosis and treatment of insufficiency of the bauhinium valve is also explained by the fact that this disease has not been fully studied, and therefore causes some difficulties even for very experienced doctors.
So, in order to have a clearer picture of this disease, it is necessary to consider the main reasons that can lead to its development and the accompanying symptoms. It is important to study effective diagnostic methods and, of course, treatment methods.
Bauhin's valve: diagnostic methods
You can see the Bauhinian valve and accurately determine its functionality by performing a colonoscopy, which allows you to examine in detail the ileum, the mucous membrane of the small intestine, and also identify inflammatory processes present in the body.
The pathology of the ileocecal valve can be diagnosed using several methods, one of which is irrigoscopy, which involves injecting a barium-containing contrast agent into the rectum and then taking x-rays. The manipulations performed allow us to see the distribution of the contrast agent and make a presumptive diagnosis based on what we see, which can be confirmed by endoscopic examination.
A fairly effective and expensive diagnostic method is capsule endoscopy, during which the patient is required to swallow a miniature video camera equipped with a power source. To date, this method is the most reliable and the only one that allows you to completely examine the inside of the small intestine.
Diagnostics
- Irrigoscopy. The study is a method of contrast radiological diagnostics. During irrigoscopy, a contrast agent (barium suspension) is injected into the patient's intestines through the anus. After the organ cavity is completely filled, a series of x-rays are taken, on which the condition of the ileocecal valve can be assessed and a violation of the passage of contrast through the intestines can be detected.
- X-ray with oral contrast. In some cases, contrast contrast with the introduction of barium suspension through the mouth may be used. The technique allows you to evaluate the distribution of contrast under physiological conditions - when moving from the small intestine to the large intestine. Despite good visualization of the valve, both radiological techniques cannot unambiguously confirm the diagnosis of valve insufficiency. This is due to the fact that it is a functional disorder, and x-rays can only statically evaluate the organs; they do not provide data on valve movements.
- Colonoscopy. The technique is a mandatory component of diagnosing valve insufficiency. During a colonoscopy, the doctor examines the intestinal cavity in real time using a special device - a colonoscope. The image is displayed on the screen in high resolution. If the valve is functioning normally, it will contract and relax rhythmically, releasing small portions of chyme. The damper will close tightly, without any clearance. The presence of even a small gap during the rest period indicates valve insufficiency.
- Capsule endoscopy. The patient must swallow a disposable mini-camera that passes through the entire digestive system and records data on the condition of the organs. The recording is examined and transcribed by doctors who note ileocecal valve insufficiency. The technique is highly informative; among endoscopic methods, it is the only one that allows you to examine the entire length of the small intestine. However, capsule endoscopy has a number of disadvantages. The obvious disadvantage of the technique is its price - at the moment, not every patient is able to pay for the study. In addition, the procedure cannot take a biopsy, which can be taken during a colonoscopy.
Insufficiency of the Bauhinium valve: treatment
Identified pathology of the ileocecal valve is treated exclusively in a hospital setting and only using an integrated approach. If the development of inflammation occurs due to the presence of an infection in the body, doctors prescribe antiviral drugs and antibacterial agents. If the disease is anatomical, treatment is carried out not only with drugs (containing magnesium), but also with surgical intervention, which consists of narrowing the bauhinium valve. Such manipulations can reduce the volume of contents returning back to the small intestine.
Functions
The main function of the bauhinium valve is to regulate the movement of the bolus of food from the small intestine to the large intestine and to delimit the overlying parts of the organ from the colon populated by bacteria.
The activity of the ileocecal valve has several stages, which depend on the intake of food into the body:
- outside the digestive process, the Bauhinian valve is closed;
- approximately 5 minutes after eating, the valve begins to open and allow small portions of food to pass through - 10-15 ml of chyme;
- the activity of the valve is regulated by peristalsis - a wave of muscle contraction, passing through the ileum, changes the pressure in the cavity of the organ, which leads to the opening of the valve;
- the entry of food into the large intestine leads to an increase in pressure in the cavity of the cecum and closure of the valve;
- throughout the entire digestion period, the valve opens and closes cyclically every minute;
- after all the chyme has passed into the large intestine, the valve closes and remains in this position until the next meal.
Be sure to read: More about Crohn's disease: symptoms and methods of treating pathology
On average, the Bauhinian valve allows up to 4 liters of chyme to pass from the small intestine into the large intestine per day.
The key to health is the correct daily routine
Therapy is aimed both at eliminating symptoms and at relieving inflammation and swelling. The problem of the pathological condition of the ileocecal valve is almost always solved by normalizing lifestyle, provided that the causes of the disease are due to functional reasons. Therefore, first of all, you need to establish a daily routine and normalize your own diet. You need to eat in small portions, about 6-7 times a day. This will normalize the functioning of the valve system of the gastrointestinal tract and regulate the mechanism of unilateral movement of food masses. The menu should be diversified with mechanically gentle food: slimy soups, steamed fish and meat cutlets, meatballs. It is recommended to consume fruits in the form of purees, juices, and compotes. Baked apples are very useful. It is important to give up fried and spicy foods, black bread, beets, cabbage, limit coffee consumption, and also give up bad habits: alcohol and smoking. Patients are under medical supervision for six months.
Since the Bauhinian valve can often become inflamed due to psychosomatic disturbances, it is necessary to prevent stress factors from entering your life. For help in this matter, you can contact a psychologist or psychotherapist.
Its pathology in each specific case requires an individual therapeutic approach, which is determined only by the attending physician, taking into account the diagnosis and assessment of risk factors.
Treatment
General recommendations
- maintain a sleep schedule, get up and go to bed at the same time every day;
- eat 5-6 times a day, in small portions;
- maintain a water regime, drink at least 1.5-2 liters of water daily;
- give up bad habits - drinking alcohol, smoking;
- reduce your stress level and, if necessary, consult a psychotherapist.
| Recommended Products | Not Recommended Products |
|
|
Medical treatment
The choice of treatment method depends on the severity of the symptoms of the disease and the presence of backflow of intestinal contents into the overlying sections - reflux. The decision on the need for one or another therapy is made individually by the patient’s attending physician.
Treatment of the cause of its occurrence is of great importance in the fight against the disease. Inflammatory processes in the intestines are controlled by antibacterial therapy, autoimmune processes by the administration of glucocorticosteroids, in the presence of psychosomatic disorders, neurotropic drugs are used and rational psychotherapy is carried out. In some cases, the condition resolves after eliminating the etiological factor. Thus, with a mild course of the disease, valve insufficiency can be eliminated through lifestyle correction and appropriate etiotropic treatment.
In case of severe disorders, drug therapy with magnesium orotate is prescribed. This drug is especially effective in cases where the insufficiency of the ileocecal valve is of primary origin, that is, it does not depend on other intestinal pathologies. Magnesium orotate adversely affects normal microflora, therefore, after its course, probiotics or prebiotics are prescribed to restore balance in the bacterial system.
If medications are ineffective and the patient develops active reflux, then surgery is required. The procedure is minimally invasive and can be done during endoscopy or using laparoscopic instrumentation. During the operation, the bauhinium valve narrows, thereby eliminating the return passage of chyme into the small intestine.
Failure of the Bauginian valve of an organic or functional nature, in which the contents of the large intestine are thrown into the small intestine. Symptoms of the disease include: intoxication, dyspeptic disorders, as well as pain in the right segment of the iliac region, which intensifies after eating. To establish the cause of the pathology and confirm the diagnosis, the doctor analyzes the clinical picture, interviews the patient, conducts a physical examination and refers him to additional laboratory and instrumental examinations. As a rule, a coprogram, irrigoscopy, capsule endoscopy, complete blood count and breathing tests are performed. If there are no gross anatomical changes in the area of the ileo-cecal junction, conservative therapy is prescribed, including pharmaceuticals that affect certain parts of the mechanism of the onset and development of the disease. According to indications, surgical intervention is possible. If you seek medical help early and receive adequate treatment for the disease, the prognosis for recovery is favorable.
Causes of insufficiency of the bauhinium valve
The pathology can be congenital and develop during fetal development. In this case, the causes of the disease are considered to be TORCH infections (rubella, toxoplasmosis, syphilis, chickenpox, herpes simplex), radiation and the use of teratogenic medications. Also, the disease can develop against the background of undifferentiated connective tissue dysplasia, infectious and non-infectious enteritis, colitis, bauginitis, coprostasis, high pressure in the colon, dolichocolon, Hirschsprung's disease and acute colonic obstruction. In addition, the disease can form after damage to the ileocecal valve during surgery on the small and large intestine.