According to published medical statistics in our country, doctors are increasingly diagnosing a female disease such as vaginal dysbiosis (in gynecology - “vaginosis”).
Symptoms of the disease manifest themselves differently in women. In general, this condition is characterized by a violation of the ratio of normal microflora of the body and opportunistic microflora.
In adult women, most often with dysbiosis, there is a decrease in lactobacilli in the body and an increase in E. coli and staphylococci.
It is important to know! For successful treatment, it is important to identify this pathology at an early stage of development and prevent its progression. To do this, you should first understand the causes of dysbiosis, and then apply comprehensive treatment of the disease.
Causes of vaginal dysbiosis in gynecology
Vaginal dysbiosis can occur for a number of reasons:
- A large number of sexual partners and lack of contraception or use of hormonal contraceptives.
- Hormonal disorders associated with abortion, menstrual disorders, long absence of sexual intercourse, thyroid dysfunction, as well as any disturbances in the functioning of the ovaries.
Dysbacteriosis in gynecology is quite a common phenomenon, it affects about 75% of women
- Improper personal hygiene - frequent douching, untimely changing of the tampon, abuse of antimicrobial agents.
- Stress, nervous breakdowns, excessive fatigue.
- Long-term use of antibiotics.
- Climate change, hypothermia.
- Chronic vaginal infections.
- General decrease in the body's immunity.
- Intestinal diseases.
- Diabetes.
- Smoking, taking drugs, drinking too much alcohol.
Note! This is not a complete list of reasons characterizing dysbiosis. Symptoms of the disease in women manifest themselves differently, depending on the individual characteristics of the body. Therefore, the causes of the disease, according to information from gynecological reference books, may be different.
Don't miss useful advice from doctors about: Sinusitis: symptoms and treatment at home
Dysbacteriosis
Gastritis
Blackheads (acne)
Fungus
Diarrhea
9410 27 October
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Dysbacteriosis: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
Dysbacteriosis, or dysbiosis, is a qualitative and quantitative change in the microflora in the body. It is characterized by an increase or sharp decrease in bacteria and a decrease in their diversity. Dysbacteriosis can occur in any area where bacteria are present, including the skin, vagina, mouth, etc.
But most often dysbacteriosis means a violation of the intestinal microflora.
Microflora plays an important role in maintaining the functioning of the immune system, but there is also an inverse relationship - with a serious decrease in immunity, dysbiosis occurs.
Causes of dysbacteriosis
The human intestine contains 70 to 80% of the cells of the immune system. Therefore, any instability of the intestinal microflora can disrupt the body's natural defense mechanisms against disease and illness.
Intestinal dysbiosis is associated not only with intestinal disorders, but also with many other conditions that at first glance are not related to digestion - skin problems (acne, eczema), neurological disorders, etc.
Among the reasons for the development of dysbiosis are:
- An increase in the number of pathogenic bacteria and yeasts (for example, candida) and a lack of beneficial microorganisms.
- Penetration of microorganisms normally found in the large intestine into the small intestine. This occurs in chronic diseases characterized by damage to the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract (Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis).
- Other factors include genetic predisposition, an unbalanced diet low in fiber but high in sugar and processed foods, physical and psychological stress, excessive alcohol consumption, frequent use of antibacterial and heartburn medications, and poor oral hygiene.
Classification of dysbiosis Due to the appearance:
- Dysbacteriosis in practically healthy individuals:
- age-related dysbacteriosis – changes in microflora in older people;
- seasonal dysbiosis – changes in microflora during the cold season;
- nutritional dysbiosis – associated with an unbalanced diet;
- occupational dysbacteriosis – with various occupational hazards.
- Dysbacteriosis accompanying various diseases of the digestive system (stomach, pancreas, liver and biliary tract, intestines, malabsorption syndrome (impaired absorption of nutrients)).
- Dysbacteriosis in other diseases:
- infectious,
- immunodeficient,
- with hypo- and avitaminosis (reduced intake or poor absorption of essential vitamins),
- in case of intoxication and exposure of the human body to radionuclides (radioactive isotopes that can be found in places with increased background radiation; in limited quantities and under strict control, they are used for the diagnosis and treatment of certain diseases).
- Drug dysbacteriosis. Occurs as a result of taking antibiotics, immunosuppressants, antacids, antisecretory, laxatives, chemotherapy and other drugs.
- Stress dysbacteriosis. Occurs as a result of prolonged emotional or physical stress.
According to clinical forms:
- Asymptomatic form of dysbacteriosis.
- Local, or local form of dysbacteriosis. It is observed with the development of a local inflammatory process in the intestines (the patient develops symptoms of colitis or enteritis - inflammatory diseases of the large or small intestine).
- A common form of dysbacteriosis. Manifested by severe digestive disorders.
By severity (determined by the number and composition of bacteria):
- 1st degree of severity;
- 2nd degree of severity;
- 3rd degree of severity;
- 4th degree of severity.
Symptoms of dysbiosis
Symptoms of dysbiosis depend on the form and severity of the disease. Patients may complain of stomach upset, nausea, diarrhea or constipation, increased gas and bloating, decreased appetite, unexplained fatigue and problems concentrating, bad breath, and skin rashes.
Diagnosis of the disease
When making a diagnosis, the doctor pays attention to complaints, symptoms of the disease and examination results. But to assess the severity of dysbiosis, laboratory and instrumental examinations are usually required.
- Clinical blood test with a detailed leukocyte formula.
Provoking factors for the occurrence of vaginosis
Gardnerella
In addition to the main causes of dysbiosis, it is important to determine the provoking factors of the disease. These include bacteria, the type of which will help determine the identified symptoms of the disease in women. The main types of bacteria that cause vaginosis:
- Streptococci and staphylococci;
- Gardnerellas;
- Mycoplasma and ureaplasma;
- The causative agent of thrush is Candida fungus;
- Clostridia, Klebsiella, Corynebacterium;
- Escherichia coli.
When bacteria are present in small quantities, they are harmful to health, but when they multiply and spread, they cause illness.
Diagnostic features
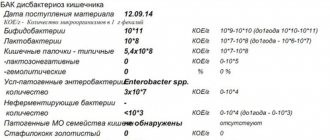
Dysbiosis can be diagnosed in only one way - a biochemical study of stool, which takes into account not only the cavity microflora, but also wall colonies of microorganisms. 72 hours before submitting the material for analysis, the woman is prescribed a special diet that excludes foods that can cause fermentation reactions. These include:
- alcoholic drinks;
- chocolate and other confectionery products with a high sugar content;
- baked goods made from wheat flour;
- dairy products;
- some vegetables (turnips, onions, all types of cabbage).
During this period, you should not take drugs with antibacterial action. If dysbacteriosis is diagnosed, it is recommended to re-test after 2-3 days.
Based on the results of the analysis, the woman is prescribed appropriate treatment and given recommendations on hygiene and care.
Diagnosis of dysbiosis by tests
The main symptoms of vaginal dysbiosis in women
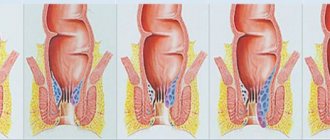
For a long time, vaginosis can occur without any visible symptoms, but as the disease worsens, the following is observed:
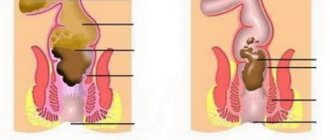
- Vaginal dryness - this condition is very clearly noticeable during sexual intercourse and can give a woman very unpleasant sensations. This condition means the transition of dysbiosis to the pelvic organs. These symptoms can lead to irritability and loss of interest in sex.
- Discharge. Dysbacteriosis in gynecology is also characterized by symptoms in women such as an increase in clear discharge in the initial stage. As the disease develops, namely an increase in the number of staphylococci and E. coli, they acquire a pungent odor and become greenish.
Symptoms of bacterial vaginosis in women may not appear for a long time. Therefore, it is important to undergo regular gynecological examinations
- Itching and burning. If vaginosis is aggravated by thrush, a white coating appears on the walls of the vagina, and itching and burning are possible.
- Pain in the lower abdomen. With a long course of dysbacteriosis, pain in the lower back and lower abdomen may appear; in an aggravated form, frequent painful urination is possible.
You should know! With vaginosis at the initial stage, there are no visible signs of the inflammatory process.
Ignoring vaginal dysbiosis for a long time can lead to more serious illnesses and a significant deterioration in overall health.
Read the popular article on the site: Dry cough in an adult - treatment with drugs and folk remedies.
How does vaginal dysbiosis manifest?
An imbalance of microorganisms in the vaginal microflora always has certain signs and symptoms. An asymptomatic course of dysbiosis is possible, but only in rare cases when a woman does not have problems with the activity of the immune system.
Doctors consider an increase in the volume of vaginal discharge during the period between menstruation to be one of the main clinical manifestations of dysbiosis in women. This situation may be normal in the middle of the cycle, when a woman ovulates. The amount of mucus increases during this period, the consistency of the discharge also changes: it becomes thicker and more viscous. On the 4-5th day after the release of a mature egg from the ovary, the discharge usually returns to normal, but there are a number of symptoms that should alert a woman and become a reason to contact a supervising gynecologist.
What is vaginal dysbiosis
- Color. Normal discharge is colorless and appears as clear white mucus. If pathogenic flora actively develops in the vaginal environment, their color will change to yellow, green, brown or white.
- Consistency . Normal discharge can be compared to egg white - it has the same consistency and viscosity (sometimes the discharge may be more liquid, but if there are no pathological signs of infectious diseases, this is also considered normal). With bacterial infections, the discharge becomes thick and resembles fatty sour cream with a yellow or swamp tint. With thrush, plaque on the walls of the vagina and external genitalia looks like curdled cottage cheese.
- Smell. If the discharge has a strong odor of fish or rotting products, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Symptoms of flora disorders due to vaginal dysbiosis
The symptoms of dysbiosis depend on what type of microorganism began to grow in the vaginal environment. Pathogenic flora can be bacterial or fungal in nature - in each case there will be certain clinical symptoms and signs.
| Type of dysbacteriosis | Which microorganisms predominate? | Symptoms |
| Fungal | Mainly microscopic organisms – yeast-like fungi Candida | White discharge with the consistency of a thick cream or curdled mass. There may be small inclusions. An unpleasant odor may be present, but it is usually mild and resembles sour milk. Women's main complaints are burning and itching in the perineum and anal canal. You may experience discomfort during urination (if the infection has spread to the urogenital tract). The skin of the genital organs is red and inflamed |
| Bacterial | Trichomonas, gardnerella, chlamydia | The discharge becomes very thick and profuse, accompanied by severe itching and inflammation of the skin of the labia and mucous membranes of the vulva. The color of the discharge is brown, green or yellow. A distinctive feature of bacterial infections is a sharp, unpleasant odor (also called a “fishy” odor) |
Note! Previously, vaginal dysbiosis was not considered a disease, and therapy consisted mainly of using alternative medicine methods. Dysbiosis is now listed in the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10) as “inflammatory diseases of the vulva and vagina (including unspecified inflammatory processes).
Factors that affect the vaginal microflora
Vaginal itching
Itching and burning are observed in 100% of cases of vaginal dysbiosis. Skin manifestations can have different localization and intensity. Sometimes severe itching in a woman appears only in the perineal area and affects the external genitalia. The opposite clinical picture is when a burning sensation occurs in the vaginal tract and intensifies after urination, intimacy and other provoking factors. In half of the cases, the pathology takes a combined form, when pathological manifestations occur in both the perineum and the vagina. If the number of pathogenic microorganisms grows rapidly, itching may also appear in the anorectal area: around the anus and in the rectum.
Symptoms of vaginal dysbiosis in girls
According to the accepted data of modern gynecology, symptoms of vaginal dysbiosis in girls can appear at any age.
The main reasons for the development of the disease in adolescents:
- hypothermia;
- errors in personal hygiene, most often incorrect use of tampons and gels for intimate hygiene;
- weak immunity;
- poor nutrition, lack of rest and fresh air, stress;
- hormonal imbalance during puberty.
In most cases, until adulthood, the main symptoms of the disease are itching and burning in the groin area. Discharge and a specific odor appear in older girls.
If you suspect the development of this disease in a child, you should consult a doctor to determine the causes and treatment program.
Diagnosis of dysbacteriosis
In gastroenterology, the diagnosis of intestinal dysbiosis begins with determining the nature of the disorders based on the patient’s complaints. Sometimes symptoms of intestinal dysbiosis occur against the background of a primary disease that is present in the anamnesis, and it is also found out which drugs that suppress microflora were used for treatment.
The most informative method of laboratory diagnosis of intestinal dysbiosis is bacterial culture of stool and analysis for dysbacteriosis. Coprogram, gas-liquid analysis and stool biochemistry can reveal indirect signs of the disease.
Diagnosis of vaginal dysbiosis
Standard diagnosis of dysbiosis includes:
- gynecological examination;
- microflora smear;
- polymerase chain reaction analysis;
- vaginal seeding.
Before taking a smear, it is important to abstain from sexual intercourse, use of vaginal suppositories and douching for several days.
A smear is taken before the start of treatment and at the end of it.
A PRC analysis must be taken to determine the causative agent of the infection and the number of bacteria in the body. In turn, taking a culture helps determine the properties inherent in the pathogen. It is also necessary to determine the body's sensitivity to antimicrobial agents.
How to treat vaginal dysbiosis?
To diagnose vaginal dysbiosis, a gynecologist may prescribe the following tests and studies:
- flora smear - is a microscopic examination that allows you to identify the qualitative and quantitative composition of the microflora and detect dysbiosis. A scraping is taken during a gynecological examination of the vagina and cervix; the procedure is painless and does not require the use of anesthetics or special preparation;
- polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a laboratory test that detects the DNA of pathogens in the test sample. Usually used to exclude sexually transmitted diseases: patients with dysbacteriosis are at increased risk of contracting STDs;
- rapid test for the pH environment of the vagina. One of the fastest methods for detecting dysbiosis, allowing the gynecologist to judge the state of the microflora after the first examination of the patient. If the number of lactobacilli is insufficient, the pH changes.
Also common diagnostic methods in gynecology include ultrasound and video colposcopy. A doctor may prescribe them if he believes that dysbiosis is caused by poor circulation in the pelvis or abnormal development of the genital organs. After receiving the results, the gynecologist develops a treatment regimen.
Treatment of vaginal dysbiosis is aimed simultaneously at suppressing pathogenic microflora, increasing the number of lactobacilli, and restoring local immunity responsible for the regulation of microorganisms.
For this we use:
- local antiseptic drugs. Modern gynecology refuses to use antibiotics to suppress pathogenic microflora (except in exceptional cases when dangerous and severe microbial infections have developed against the background of dysbacteriosis). Instead, local antiseptic drugs are prescribed that do not harm the normal flora. This therapy is the most gentle, suitable for pregnant women and nursing mothers, and allows you to get quick and pronounced results;
- probiotics are products containing live lactobacilli or their metabolic products. Medicines in this group allow you to restore normal microflora. But taking them will not give results if the pathogens are not first suppressed. Therefore, treatment of dysbiosis should be comprehensive, developed by a gynecologist depending on the individual characteristics of the patient’s body, her age, hormonal status, and the causes of dysbiosis;
- immunomodulators. The doctor selects drugs that increase the local immune response. Dysbacteriosis is often associated with a decrease in the natural protection of the reproductive system. If it is not restored, dysbiosis will return immediately after stopping antiseptics and probiotics. For effective therapy, immunocorrection is necessary.
The final stage is the development of individual recommendations that allow a woman to maintain intimate health. If necessary, the gynecologist helps you select individual hygiene products to maintain normal vaginal pH. Typically, treatment lasts no more than three weeks, unless dysbiosis has led to more serious gynecological problems.
Vaginal dysbiosis during pregnancy
Quite often, dysbiosis in gynecology is characterized by the presence of similar symptoms in pregnant women:
- discomfort and itching in the vagina;
- an abundance of discharge that has an unpleasant, sometimes pungent odor.
Stress caused by worry about the child, excessive fatigue, and poor nutrition can lead to dysbacteriosis. The most common cause is hormonal imbalances, which lead to decreased immunity.
During pregnancy, self-medication is prohibited; all procedures must be agreed with the attending physician so as not to harm the baby.
Vaginal dysbiosis occurred after antibiotics
Antibiotics are widely used to fight infections. They stop reproduction in a short time and kill pathogenic microbes, but at the same time destroy beneficial ones. This is why dysbiosis develops.
To prevent this from happening, you need to strictly follow the therapy regimen, do not skip injections/take pills, and do not cancel or extend the course yourself. At the same time, they take products to restore balance, which contain complexes of beneficial bacteria. It is recommended to adhere to a diet during antibiotic therapy: introduce more fermented milk, vegetables, fruits into the menu, give up alcohol and sweets.
Comprehensive treatment of vaginal dysbiosis
To achieve a positive result, it is necessary to stop the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms, after which the presence of beneficial microorganisms in the vagina should be increased.
To consolidate the result, you need to strengthen the body's immunity. Treatment of vaginal dysbiosis consists of taking prescribed medications and therapy to restore normal microflora. Let's look at each stage in more detail.
Drug treatment
Let us highlight some drugs that help treat vaginal dysbiosis and restore microflora:
| Drug, price | Method of administration | Cause |
| Tiberal (price about 700 rubles) | A week twice a day, 500 ml | Destruction of pathogenic microorganisms |
| Tinidazole (pack about 45 rubles) | 3-4 tablets per day, 6 days | |
| Clindamycin (approximate price 600 rubles) | Per day from 600 to 1800 mg three times a day, for a week | Against staphylococci and E. coli |
| Terzhinan (price from 350 rubles) | 1 tablet in the evening in the vagina, 10 days | |
| Essentiale forte (price from 700 rubles) | 2 capsules, three times a day | Recovery process |
Doctors warn that taking medications that were not prescribed by a specialist can negatively affect the functioning of the body and worsen overall well-being.
Microflora restoration therapy
Violation of the vaginal microflora is directly related to a woman’s immunity, so during treatment it is necessary to pay enough attention to strengthening the immune system.
Most often, restoration of microflora takes no more than 1 month. After completing the course, a re-examination by a specialist is required. If the disease is not in an advanced state, the use of immunomodulators is sufficient for treatment.
In more complex cases, for example, to restore microflora after thrush, it is necessary to take products containing lactobacilli and a component that restores epithelium.
Drugs that help restore the normal vaginal environment:
| A drug | Mode of application |
| Gynoflor | For a week, one tablet into the vagina before bedtime |
| Laktogin | For women over 18 years old, one capsule, 10 days |
| Ecofemin | 1 capsule twice a day. Take from two weeks to a month |
| Lactobacterin | Ten days, one vaginal suppository before bed |
A rehabilitation course of medication should be discussed with your doctor.
Read the popular site article: Clotrimazole ointment, suppositories - instructions for use for women
How to treat?
Intestinal dysbiosis can be treated in several ways, but complex therapy is often used to achieve maximum effect.
Drug therapy
Treatment using medications is aimed at eliminating the symptoms of dysbiosis, strengthening the immune system, colonizing the intestines with beneficial microorganisms and preventing complications. Women may be prescribed drugs from different pharmacological groups, which are listed below.
| Pharmacological group | What are they for? | Drugs |
| Sorbents | Removes toxins, toxic fumes, allergens, waste, eliminates intoxication. Cleanses the blood and helps strengthen the body’s protective functions | "Polysorb", "Activated carbon", "Enterodes", "Enterosgel", "Smecta" |
| Multivitamin and vitamin-mineral complexes | Restores the balance of vitamins and minerals, improves well-being, increases the body’s resistance to infectious diseases | "Alphabet", "Duovit", "Vitamax", "Biomax", "Vitrum", "Sana-sol" |
| Digestive enzymes | Eliminate signs of digestive disorders, improve digestion and the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, relieve heartburn, bloating, flatulence | "Creon 10000", "Pancreatin" |
| Prebiotics, probiotics, lactobacilli | Suppress the activity of pathogenic flora, destroy pathogenic bacteria, restore the balance of microflora by populating the intestines with beneficial bacteria | "Linex", "Hilak Forte", "Yogulakt", "Bifidumbacterin", "Normobakt" |
| Antifungal drugs | Prescribed when fungi are detected in stool | "Levorin" |
Bifidumbacterin for the treatment of intestinal dysbiosis in women
If vaginal dysbiosis is combined with intestinal dysbiosis, the woman is prescribed topical treatment agents, which can be used in the form of vaginal suppositories, gels or ointments. Preparations containing beneficial lactobacilli - suppositories " Bifidumbacterin"
" and "
Acylact
". Medicines have only one drawback - they are sold only in large populated areas, so residents of small towns and villages have to choose other means for the treatment of vaginal dysbiosis.
Diet for dysbiosis
Diet for intestinal microflora disorders
Women are recommended to eat foods rich in fiber and coarse plant fibers. These are vegetables, herbs, berries, fruits, cereals, rye flour, bran. These products improve intestinal function, cleanse it and improve the absorption of nutrients, which prevents disturbances of the intestinal microflora. The diet must include fermented milk products: kefir, yogurt, fermented baked milk. There is now a huge selection of products in stores with the addition of healthy dairy crops, so creating the right menu will not be difficult.
Products that are recommended to be limited or completely excluded from the daily diet:
- semi-finished products;
- sausages;
- products containing monosodium glutamate, flavorings, dyes and preservatives;
- alcoholic drinks;
- chips, crackers;
- carbonated drinks;
- herbs and spices.
Important! This diet is recommended for women not only during the period of treatment of dysbiosis - constant adherence to the recommendations will help improve the condition of the skin, improve the functioning of the digestive system, increase immunity and lose excess weight, if any.
Nutrition for dysbiosis
Folk recipes
The following remedies have been successfully used to treat dysbiosis in women:
- oak bark decoction (drink 1 glass on an empty stomach until symptoms are completely eliminated);
- a mixture of garlic and honey (take a teaspoon 2-3 times a day 30-60 minutes before meals for 5-7 days);
- rice water (drink half a glass 2 times a day, regardless of meals, for 10 days).
Intestinal dysbiosis is a common pathology that can be asymptomatic or cause the appearance of uncharacteristic clinical signs. Timely treatment will help women not only avoid serious complications and infections of the gastrointestinal tract, but also maintain “women’s” health, which directly depends on the state of the intestinal microflora. Read medications for the treatment of gastritis in adults on our website.
Possible complications of vaginal dysbiosis
If the disease is not treated for a long time, complications are possible, which include:
- endometritis – inflammation of the uterine cavity;
- vaginitis – inflammation of the vaginal walls;
- cervicitis - development of the inflammatory process of the uterus;
- development of cystitis as a result of bladder infection;
- adnexitis - inflammation of the appendages.
Most often, the first signs of the onset of the development of such diseases are caused by the appearance of burning and itching, as well as an increase in the amount of discharge.
Read the popular article on the site: Menopause in women: symptoms, age-related characteristics, treatment with effective methods.
Traditional recipes for the treatment of vaginal dysbiosis
| Dysbacteriosis in gynecology. The use of traditional recipes to treat identified symptoms in women | |||
| Name | Ingredients | Recipe | Reception |
| Douching - no more than 15 minutes. Normalization of the body's condition | 1. Chamomile and plantain | 1 tbsp. spoons of herbs, pour a liter of boiling water, leave for half an hour, strain | In the morning and before bed |
| 2.Oak bark | 1 tbsp. spoon, pour 200 ml of boiling water, leave for three hours, strain, cool | During the week at night | |
| 3. Bird cherry | 1 tbsp. spoon per 400 ml of water, boil, cook for 20 minutes over low heat, strain and cool | Once a day for a week | |
| Therapeutic sitz baths (waist-deep) – have a calming effect and relieve inflammation | 1.Oak bark | 250 gr. leave the collection in cold water for four hours, boil, add to the bath | Daily for 20 minutes |
| 2.Flower honey | 2 tbsp. dilute spoons of honey with 500 ml of hot water and add the mixture to the bath | 20 minutes every two days | |
| Tinctures to strengthen the immune system | 1.Quince, cherry, garlic, lemon and apples | Mash the cherries, grate the quinces and apples, finely chop the lemon, squeeze out the garlic. Mix all the ingredients, pour in 1.5 liters of water, close and let it brew for 30 minutes, then strain | Four times a day, 100 ml |
| 2. Dried rowan, honey, onion | Pour 2 tablespoons of berries into 400 ml of water, cook for 25 minutes, add 2 tablespoons of honey and grated onion | One spoon 4 times a day | |
| 3. Purslane leaves, egg white | Grind leaves and mix with egg white | Drink three times a day, course 15 days | |
One should not neglect the fact that to improve the effect of treatment, in addition to the above methods, fresh fruits, vegetables and dairy products should be introduced into the daily diet.
You should take vitamins E and C, which have a positive effect on the balance of microflora.
When using traditional methods of treatment, one should not neglect the consultation of a qualified specialist. This will help you get better treatment.
According to modern gynecology, dysbacteriosis, regardless of the identified symptoms in women, is not transmitted during sexual intercourse and is not classified as a venereal disease. However, it must be treated immediately when the first symptoms are detected.
Author of the material: Tatyana Markina
Treatment of intestinal dysbiosis in adults
Contrary to the stereotypes imposed by commercials, taking probiotics does not solve the problem at the root. It is necessary first of all to find and eliminate the cause of dysbiosis, since the phenomenon itself is secondary.
Treatment of intestinal dysbiosis should be based on the following principles:
- Elimination of external risk factors (correction of nutrition, drinking clean water, minimizing contact with harmful substances, and so on).
- Suppression of excessive growth of opportunistic microflora.
- Taking probiotics and prebiotics.
- Consolidating a positive result and achieving stable remission.
Let's take a closer look at all these principles.
Diet
Source: freepik.com/poringdown
Proper nutrition plays an important role in stabilizing the microbiocenosis of the intestinal microflora. Therefore, treatment should begin with diet correction. It is necessary to reduce the consumption of foods that cause fermentation processes (or even better, completely abandon them). This also applies to products that are not recommended for consumption for chronic gastrointestinal diseases. The reason for this is that, as we already know, dysbiosis is always secondary to the underlying disease, such as colitis, gastritis or hepatitis.
Improper nutrition provokes exacerbation of diseases of the liver and gastrointestinal tract, which will aggravate the imbalance of intestinal microflora. Therefore, without correcting the diet, all attempts to combat dysbiosis are doomed to failure.
| Unwanted Products | Recommended Products |
| Baking, confectionery Alcohol (especially beer and sweet wine) Beans and grapes Kvass Spicy seasonings Cheeses with fat content above 40% | Fermented milk products (kefir, yogurt, fermented baked milk) Sauerkraut Berries and fruits that reduce fermentation (apricots, black currants, cranberries) Porridge (except pearl barley) Soups with fresh broth Lean meat and fish Vegetables (carrots, pumpkin, zucchini, potatoes) |
Much attention should be paid to fiber - dietary fiber stimulates intestinal motility and absorbs toxins. In fact, fiber is a prebiotic, since the obligate intestinal microflora uses dietary fiber as a nutrient medium.
Medications
Before moving on to the description of medications used for dysbiosis, we emphasize that first of all it is necessary to treat the underlying disease. This is called etiological treatment - influencing the cause, not the effect, of the disease. As for drugs used directly to eliminate dysbiosis, they can be divided into several groups.
Antibiotics
The use of antibacterial drugs is advisable in case of excessive growth of pathogenic microflora in the intestine, which is accompanied by a deterioration in the functional state (impaired motility and absorption). The following groups of antibiotics are used:
- penicillins (amoxicillin);
- fluoroquinolones (ofloxacin, norfloxacin);
- tetracyclines (doxycycline);
- broad spectrum (rifaximin).
The average course of treatment is 7 days.
Probiotics
Expert opinions regarding the effectiveness of these drugs are contradictory. Many domestic gastroenterologists consider the administration of probiotics to be an integral part of the fight against dysbiosis, however, in foreign clinical practice, the advisability of using these drugs is now increasingly criticized. Opponents of the use of probiotics argue their position by the fact that most of it simply does not take root in the patient’s body. There are also opinions that the use of these drugs may contribute to the growth of fungal infections in the blood.
The basis of the composition of probiotics is represented by lacto- and bifidobacteria, but Escherichia, streptococci and enterococci can be used as a supplement. Probiotic release form:
- capsules;
- powders;
- drops;
- rectal suppositories (suppositories).
Drugs to improve digestion
This includes pancreatic enzymes (pancreatin and drugs containing it), as well as drugs to improve intestinal motility (domperidone, metoclopramide). In addition, to normalize the intestinal absorption function and improve the functional state of the liver, hepatoprotectors (phospholipids, preparations with milk thistle extract) are prescribed.
Folk remedies
Here it is important to determine the interpretation of this definition in the context of eliminating dysbiosis. For example, some consider the consumption of fermented milk products or sauerkraut as a folk method of treating dysbiosis, although in fact this is only one aspect of normalizing the diet.
As for decoctions of medicinal herbs or yeast infusions, which are used both for oral consumption and for microenemas, it is better not to use such methods without the consent of a doctor. Often such remedies do more harm than good.