Basic rules of nutrition for diarrhea
The daily diet is selected taking into account the cause of diarrhea.
There are a number of principles for organizing catering:
- Unloading the intestines. You should eat food in small portions, but often (every three hours).
- Eliminating from the menu foods that increase gas formation and provoke fermentation.
- Reducing the total amount of food consumed during the day by 20-50%.
- Including fermented milk products enriched with beneficial bacteria in the diet.
- Elimination of foods that promote active bile secretion.
- Replenishment of daily nutrient needs. Reducing the volume of carbohydrates and fats. Proteins are the basis of nutrition at this time.
- Drinking enough liquid.
- Refusal of raw fruits and vegetables, because they have a laxative effect and can aggravate the condition.
- Food should be warm (+33…+38 ⁰С). Eating hot or excessively cold food is unacceptable.
- Limiting salt, but not completely abstaining from it.
Authorized Products
If you have an intestinal disorder, you need to eat strictly according to the rules.
During this period, the following products are allowed:
- Cereals. Porridge should always be on the menu, and in case of diarrhea it becomes a salvation. They do not overload the intestines, saturate the body with useful substances, and are easily digested. Porridge is cooked exclusively in water. It is allowed to add salt and a small amount of butter.
- Meat. Preference is given to low-fat varieties. Rabbit, turkey, chicken, veal are suitable. During cooking, the film, tendons, and cartilage are removed.
- Fish. Only low-fat types are used.
- Dairy products. Kefir and cottage cheese can be eaten daily. They must be natural, without any additives.
- Bread. It's best to eat crackers. Eating stale white bread is allowed.
- Berries fruit. They are used to prepare jelly, jelly, and mousse.
- Vegetables. Pumpkin, carrots, potatoes, and zucchini are introduced into the diet in boiled or baked form.
Diet for diarrhea should consist of the following foods:
- Rice. It should be heavily boiled and prepared without salt or other additives.
- Bird cherry compote, blueberry jelly. These drinks have a powerful strengthening effect.
- Weak unsweetened tea with crackers (considered ideal on the first day after the onset of diarrhea).
- Milk serum. Prevents rotting in the intestines, normalizes microflora.
Prohibited Products
Fried and fatty foods are excluded from the diet. They disrupt digestion, make bowel movements more frequent, and dilute the stool.
- all alcohol without exception;
- coffee;
- green tea;
- juices (except apple);
- sweet drinks;
- sparkling water;
If you have diarrhea, you should not eat:
On the second and subsequent days, the menu includes light dishes that do not allow fermentation in the digestive tract - boiled vegetables, mashed potatoes without oil, rice porridge in water without salt and sugar, baked apples. If the patient feels well, the diet for uncomplicated diarrhea in the elderly for 4-5 days is supplemented with boiled or steamed rabbit meat or chicken breast. You can offer vegetable soups, fermented milk products, cottage cheese.
Treatment of diarrhea in older people requires accurate diagnosis, differentiation from other pathologies of the digestive system, and treatment under the guidance of a physician.
The information” on our website is provided by qualified doctors and is for informational purposes only. Don't self-medicate! Be sure to consult a specialist!
An elderly person needs medical care if, in addition to loose stools, he or she experiences the following symptoms:
- Spasms, pain in the intestines or stomach.
- Lack of appetite.
- Bloating.
- Dryness of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity.
- Change in urine color.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Increased fatigue, weakness throughout the body.
Qualified assistance and constant monitoring by caregivers are required for people who, during illness, experience incontinence, that is, involuntary uncontrolled release of feces
It is important to correctly diagnose and establish the cause of the problem
Features of the digestive system of older people
The deterioration of the digestive system is associated with changes in the body that appear in all older people. With age, atrophy of muscle tissue and mucous membranes develops.
In older people, the activity of the salivary glands and the bactericidal effect of saliva decreases. The secreting cells in the pancreas are replaced by connective tissue, which leads to a decrease in fermentation, and food in the stomach is less digestible. Atrophy of the villi and mucosal cells occurs, blood flow to the intestines decreases, leading to a deterioration in the absorption of nutrients and fluids.
In older people, the mucous membrane gradually smoothes out along the entire length of the digestive tract. A lack of enzymes provokes the development of lactose intolerance and makes it difficult to digest fatty foods. Significant proliferation of pathogenic bacteria in the small intestine provokes diarrhea, flatulence, and bloating in old people.
Age-related changes in the body
Diarrhea (diarrhea) due to nervousness: can it happen, how to treat it
Along with wisdom and life experience, approaching old age, people often notice various signs of aging of the body. Depending on each organism, they are all different and appear at different times. Old age is observed not only by external signs, but also affects all organs and systems of the human body. Features of the development of diarrhea in older people are associated with excision of the resources of the digestive system. The following factors of decreased performance are observed:
- Digestion primarily involves chewing food in the mouth. The muscles of facial expression and mastication decrease in strength with old age, resulting in poor grinding of food products that enter the stomach in the form of pieces;
- By adulthood, the esophagus lengthens and its muscle fibers become deformed. This greatly complicates the swallowing function, and the formation of hernias is possible;
- The production of enzymes that help break down food decreases. As a result, the intensity of digestion in the small intestine decreases;
- The volume of the stomach decreases and its position changes from vertical to horizontal. The production of gastric juice and enzymes decreases. Organ motility, blood supply and metabolic processes slow down;
- The risk of “senile constipation” increases, which leads to the formation of fecal stones. The situation may change suddenly and diarrhea may begin. In the case of an operation to remove fossilized feces, the patient may begin to suffer from chronic diarrhea;
- The balance of the microflora of the intestinal cavity is disrupted. Pathogenic microorganisms begin to outnumber lactobacilli. The synthesis of vitamins is disrupted. As a result of the negative activity of pathogenic bacteria, intoxication of the body appears, which causes severe diarrhea in an elderly person. The body's protective function is triggered, trying to rid the body of toxins;
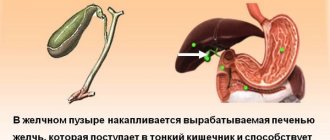
- Metabolic processes are disrupted as a result of a decrease in liver volume. At the same time, the gallbladder enlarges and its walls thicken. The normal release of bile into the upper sections is disrupted. The formation of excrement is often recorded;
- The glandular cells of the pancreas are reduced in number. As a result of insufficient blood circulation, the organ ceases to produce the required amount of enzymes.
A large list of deterioration in the functioning of organs involved in digestion leads to a disorder that provokes the dilution of stool. In case of such a delicate problem, do not hesitate to contact a doctor. A timely response to the disease can prevent serious complications. Nocturnal diarrhea in older people indicates not only indigestion, but also a malfunction of other organs. As a rule, it is accompanied by severe abdominal pain. If it occurs suddenly, then it may be food poisoning from foods eaten at dinner. When the temperature rises, it indicates the development of an infectious disease.
Age-related changes in the digestive system
The appearance of regular diarrhea in the elderly is directly related to the aging process of the body. The following changes occur:
• The amount of saliva, which is necessary for digesting food and good absorption of nutrients, decreases. Lack of saliva causes dry mouth, chewing muscles also weaken, and the esophagus becomes longer. Because of this, poorly chewed food enters the stomach, which can lead to both diarrhea and constipation. • The stomach muscles weaken and lose elasticity. The stomach itself also changes in size. Gastric juice is produced more slowly. Food is poorly broken down and often ferments in the stomach. Poorly digested, it passes into the intestines, thereby irritating it. The entire digestion process results in loose stools. • The gallbladder enlarges, producing either more or less bile. • Problems with the pancreas are caused by a lack of digestive enzymes. Food is poorly digested and the body quickly gets rid of it. Due to problems with the pancreas, a person feels nauseous, has heaviness in the stomach and loose stools. • Lactase deficiency leads to poor absorption and lactose intolerance. For this reason, consuming dairy products can cause gas, abdominal pain and diarrhea. • The work of the small intestine slows down, which prevents high-quality digestion of food. • Fecal stones are a common occurrence in the elderly. Stones occur due to deposits on the walls of the large intestine. They interfere with the normal movement of food, causing food to be excreted partially digested. Stones provoke the development of harmful bacteria, which create pathogenic microflora in the intestines. All this leads to severe diarrhea. • Decreased size and strength of the liver. It begins to work worse, which disrupts the metabolism of proteins and carbohydrates. This weakens bowel function.
ethnoscience
Viral diarrhea: causes, how to treat the disease
Loose stools are usually treated with medications, but in the case of older people they are not always effective, since not all drugs can be used for them. This treatment should also be discussed with your doctor.
The most effective remedy for diarrhea, even when the discharge is bloody, is considered to be powder made from dried films of chicken ventricles. This powder should be taken 2-3 times a day, 1 teaspoon with liquid. Rice water and infusion of chamomile flowers are also considered good remedies. But before using such methods, you should consult your doctor. This treatment also requires a diet.
Symptoms and complications
Quite often, stool disorder is not limited to changes in the consistency of feces; it is accompanied by additional symptoms:
- loss of appetite;
- dry mouth;
- cutting or spasmodic, cutting, stabbing pain in the projection of the stomach and intestines;
- weakness, increased fatigue;
- nausea and vomiting;
- bloating;
- change in urine color.
In order not to miss the development of serious diseases, if atypical symptoms appear, you need to consult a therapist or gastroenterologist. This should be done as soon as possible if diarrhea in older people is accompanied by high fever, the appearance of blood in the stool, and severe pain. The body of an elderly person, just like the body of a child, has a low margin of safety, therefore, if the condition suddenly worsens, immediate medical attention is needed.
The most common complication of diarrhea is dehydration, leading to rapidly increasing loss of water and the inability of most systems to function. A severely weakened elderly person, who almost certainly has several somatic diseases in old age, may develop complications that are incompatible with life due to dehydration. Therefore, if there is a decrease in skin tone, dry lips and mouth, sunken eye sockets, a sharp decrease in blood pressure and the number of urinations, you must immediately take measures to replenish the water balance.
If an elderly bedridden patient suffers from diarrhea, due to reduced tissue trophism, maceration and irritation of the anal area quickly occurs. In order to prevent skin damage in elderly patients due to diarrhea for a long time, it is recommended to carefully treat it with antiseptics, regenerating ointments, and not ignore hygiene procedures.
What should the diet be like?
Why does diarrhea occur after drinking beer and how to treat it? Diarrhea after beer: possible causes and treatment features
In old age, it is extremely important to eat properly, since not every food is suitable, and many foods are not worth eating at all. In some cases, even a diet is required
A diet is understood as a specially designed diet not for the purpose of losing weight, but with the goal of eliminating from the diet foods that are harmful to the “elderly” body. Properly selected products will help avoid serious illnesses, as well as the possible occurrence of diarrhea and its complications.
Food products for older people should be varied, easily perceived and digestible, biologically valuable, but compared to what the younger generation consumes, food should be less energetically valuable. At the same time, the food must contain enough proteins, vitamins, minerals, salts, in particular iron, potassium and calcium.
Authorized products:
- corn, sunflower, soybean oils;
- lean meat (chicken, turkey);
- low-fat cottage cheese, cheese, fermented milk products, milk;
- egg whites;
- vegetable, fish and lean meat (chicken) soups;
- low-fat fish;
- seafood;
- vegetables, berries, fruits;
- porridge (preferably whole grain cereals, such as pearl barley);
- vegetable salads (preferably with vegetable oil);
- meat by-products, in particular liver (for example, beef);
- bread made from wholemeal flour or bran;
- fruit drinks, decoctions (for example, from rose hips), juices;
- weak tea and coffee (it is better to replace coffee with chicory), etc.
Not recommended products:
- fatty cheese, cottage cheese;
- sour cream, cream (possible in limited quantities);
- fatty meat (pork);
- fried food;
- egg yolks;
- sugar;
- sweet flour dishes (cakes);
- various confectionery products (sweets, chocolate, cream products);
- sweet, carbonated drinks, kvass;
- pasta;
- rice (causes constipation);
- legumes (peas, beans);
- smoked, salted, spicy foods;
- mustard, mayonnaise, horseradish%
- margarine, etc.
Causes of diarrhea
In old age, loose stools can be caused by a variety of reasons, ranging from a harmless disorder to serious pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract. And, the older the patient’s age, the longer the list of probable diseases. This is due to changes occurring in various parts of the digestive tract:
- depletion of facial muscles and disorders of the masticatory apparatus, preventing high-quality chewing of food;
- elongation of the esophagus with subsequent deformation of all its tissues and, as a result, difficulty swallowing;
- change in the size of the stomach and insufficient production of gastric juice;
- decreased completeness of processing of consumed food in the small intestine;
- the formation of fecal stones in the large intestine, which leads to the growth of pathogenic microflora and disruption of the synthesis of vitamin K and B;
- changes in the specific gravity of the liver and a decrease in the quality of its functions (regulation of protein and carbohydrate metabolism, detoxification);
- an increase in the size of the gallbladder and disruptions in the production of bile;
- dystrophic or pathological changes in the pancreas, lack of enzymes produced to digest food.
The causes of diarrhea can also be classic, for example, eating low-quality food, intestinal infections, sudden climate change, antibacterial therapy or stress.
But, as practice shows, all these diseases are typical for younger patients. But grandparents feel the symptoms of diarrhea due to more serious changes occurring in their body. In addition to the above, if a patient complains of diarrhea for a long time, this may indicate the development of the following diseases:
- chronic inflammation in the small or large intestine (Crohn's disease);
- damage to the mucous membrane of the large intestine of various types (ulcerative colitis);
- endocrinological diseases;
- diabetes;
- chronic insufficiency of the adrenal cortex (Addison's disease);
- chronic inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis);
- malignant neoplasms;
- previous operations;
- intoxication with protein breakdown products due to impaired renal function (uremia);
- lack of zinc in the body.
A decrease in the sensitivity of taste buds leads to the consumption of overly spicy, sweet or salty foods. This negatively affects the functioning of not only the digestive tract, but also all other organs.
Treatment of diarrhea in the elderly
Rehydration
During diarrhea, a huge amount of fluid is lost, which is excreted along with feces and through vomiting. Often drinking large amounts of water does not help cope with dehydration, and therefore you have to resort to other methods and means of helping the body.
To help the body normalize the water-salt balance, it is necessary to resort to the help of medications. For this purpose, proven and effective drugs are used, which can be purchased at any pharmacy, for example Regidron or Citroglucosolan.
At home, you can prepare a glucose-salt composition. To do this, stir 1 tsp in 1 liter of boiling water. salt, 4 tbsp. sugar and 175 ml. orange juice, homemade from fresh fruit. The composition should be drunk half a glass 4 times a day 15 - 20 minutes before meals. As a rule, on the second day the spasms stop and the stool returns to normal.
Detoxification
It is important to know! Toxins and accumulated gases must be removed from the intestines to avoid intoxication of the body. Sorbents are taken for infectious type of intestinal disorder
If intestinal absorption is impaired, such drugs should be taken only after consultation with a specialist.
Sorbents should be taken by persons over 60 years of age:
- Enterosgel. The bioorganic silicon contained in the composition allows the drug to be absorbed into the intestinal walls as much as possible, while removing all waste, toxins and pathogens from it. In this case, the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract does not suffer. The drug does not cause addiction or negative consequences during its use.
- Polysorb. The drug contains colloidal silicon dioxide, which is the most effective against diarrhea on the entire domestic market.
- Smecta. Does an excellent job of preventing the spread of toxins and wastes inside the intestines.
- Cholestyramine. It binds bile acids well, so it is ideal for patients who have diarrhea due to surgery on the stomach or gall bladder.
- Activated carbon. A cheap and effective drug that has won the trust of many patients.
Reduced intestinal secretion and decreased intestinal motility
To reduce intestinal secretion, you need to take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as Indomethacin or Diclofenac. These remedies will have a good effect on bacterial type of diarrhea. Elderly people suffering from Crohn's disease need to take steroid medications such as Metypred or prednisolone.
To slow down the movement of food through the intestines and, thus, reduce the motor function of this organ, you need to take Octreotide. For severe pain symptoms, resort to antispasmodics. For irritable bowel disease and Crohn's disease, take Lopedium.
Important point! Slowing intestinal motility cannot be carried out in case of various infectious types of gastrointestinal disorders.
Restoration of intestinal microflora
To restore the intestinal microflora and normalize the absorption of nutrients and vitamins, you should take one of the following medications:
- Enterol;
- Acylact;
- Hilak-forte;
- Lactobacterin.
Folk remedies
Traditional methods will also help you cope with diarrhea:
- Rice broth. It is necessary to pour two glasses of boiling water over a teaspoon of rice and boil over low heat for about 15 - 20 minutes. The resulting broth is filtered through a fine sieve or bandage and taken at regular intervals, 2 tablespoons before or during meals.
- Tincture of oak bark. Add a tablespoon of crushed oak bark mixture to a glass of boiling water and leave to infuse in a warm, dark place for 2 hours. The resulting mixture is filtered and taken 1 tsp. every 2 - 3 hours for 2 - 3 days until bowel function normalizes and stool becomes stronger.
- Sage decoction. Brew a tablespoon of herb leaves into 300 ml. boiling water With the lid tightly closed, leave the mixture for 2 - 3 hours. Strain the broth and use a teaspoon during attacks of diarrhea. The intestinal microflora quickly normalizes and diarrhea stops.
Reference! All of the above products should be taken only if you are not allergic to the ingredients.
Nature of the disease in the elderly
Older people experience various stomach problems, which often results in diarrhea. Diarrhea is a symptom of internal disorders in the body that must be diagnosed. This problem cannot be ignored: diarrhea leads to dehydration, which is dangerous in old age. Against the background of age-related changes and chronic diseases, this dehydration leads to negative consequences.
Many people under 60 years old are characterized by ailments that are accompanied by periodic diarrhea. These problems can be caused by poisoning from poor-quality food, stomach bacteria or infections, or certain medications.
Age-related changes in the functioning of the body play a major role, causing disruptions in metabolism. This problem is typical for older people. Diarrhea can occur as a reaction to fear or shock. In this state, high-quality digestion of food does not occur; it passes from the stomach to the intestines and is excreted from it.
Regular diarrhea in old age may indicate Addison's disease or diabetes. You need to pay attention to diarrhea in a bedridden person. People who are bedridden are characterized by constipation. The appearance of diarrhea may indicate hormonal problems and gastrointestinal diseases.
Menu options for the day
It is worth eating frequently, about 4–6 times a day, but in small portions.
Food should be easy to chew. It is forbidden to overeat, as too much stress on the gastrointestinal tract can cause consequences.
1 menu option
1 meal (breakfast): omelet, oatmeal porridge with milk, weak tea with milk.
Meal 2 (second breakfast): 1 – 2 fruits (baked apple, banana or pear).
Meal 3 (lunch): vegetable soup, chicken cutlets with mashed potatoes, dried apricots and raisins compote.
Meal 4 (afternoon snack): rosehip decoction, any juice.
Meal 5 (dinner): boiled fish with stewed cabbage, vinaigrette, tea.
Meal 6 (at night): yogurt.
2 menu option
1 meal (breakfast): buckwheat porridge, cottage cheese with low-fat sour cream and sugar, tea with milk.
Meal 2 (second breakfast): salad of cucumbers and tomatoes with vegetable oil.
3rd meal (lunch): chicken soup, pilaf with boiled meat and vegetables, compote.
Meal 4 (afternoon snack): rosehip decoction, any juice.
Meal 5 (dinner): boiled meat with vegetables, apple soufflé, tea.
Meal 6 (at night): kefir.
During the day, in addition to the main menu, you can have bread (250 - 300 g), sugar (20 - 30 g), butter (10 g).
The menu is approximate. Everyone must independently or with the help of doctors determine their daily diet, diet
It is important to monitor your weight - do not overeat or deplete your body, and take all measures to normalize your weight.
Diet for an elderly person with diarrhea, what can and cannot be eaten with diarrhea?
The greatest threat for older people with loose stools is dehydration. In this regard, treatment and diet are needed when the first signs of illness are detected. The diet should be followed starting from the first day of the disease. Initially, you need to refuse food altogether, drinking only plenty of liquid. The food that the patient eats should be easily digestible, not have a weakening effect and not cause fermentation.
It is allowed to eat crackers and biscuits, mashed porridges, mashed potatoes, and baked apples. The introduction of meat products into the diet is carried out no earlier than 3-5 days, depending on the patient’s condition. Meat should be cooked exclusively by steaming. The most recommended during such a diet are vegetable soups or soups made with lean meat. The consumption of dairy products, raw vegetables and fruits, sweets, fried and fatty foods is prohibited. You can drink weak tea, as well as unsweetened compotes and jelly.
Digestion of food with aging occurs much more slowly than with young people, so exiting the diet should be done very carefully and gradually. It should be noted that the definition of diseases in older people is quite complex, and therefore, actions regarding any treatment must be agreed upon with a qualified specialist. It is also important to know that an elderly person during illness, unfortunately, may be unable to control the occurrence of bowel movements, which leads to the need for his relatives or guardians to monitor this. When leaving your place of residence, you need to ensure that your time away from home is as short as possible or make sure that there is a restroom at the place of your visit. Diarrhea in older people in more than 70% of cases is evidence of illness, and therefore requires diagnosis and consultation with a doctor.
Folk remedies for diarrhea
Elderly people often prefer traditional recipes to medicines
In this case, it is important to remember that without identifying the cause, the problem cannot be solved. Before taking herbal remedies, you still need to see a doctor, undergo an examination and determine the diagnosis.
For the most part, natural remedies are aimed at restoring intestinal microflora, normalizing digestive processes, and relieving inflammation. The most common traditional medicine to combat diarrhea are:
- Infusion of oak bark. It has an anti-inflammatory effect, and also strengthens the stool and stops fluid loss. To prepare the medicine, pour boiling water over a small amount of crushed bark and leave for an hour. Then drink the infusion in small sips throughout the day.
- Strawberry leaves. They help fight infection, strengthen the immune system and have a beneficial effect on the digestive system. Pour a tablespoon of strawberry leaves into a glass of boiling water, leave for 20 minutes, filter and cool. The resulting medicine is taken 50 ml every hour. The course of treatment lasts until the symptoms stop completely.
- Sage. Sage is beneficial for many systems and organs, including the intestines. It is believed that it can normalize hormone levels in the body. An infusion is made from the herb and kept in a thermos for two hours. The medicine is taken in small sips throughout the day.
- Rice water. Boil a couple of tablespoons of peeled brown rice in half a liter of water for 30 minutes. Then filter the water, cool and drink throughout the day. This product strengthens perfectly and prevents the body from losing fluid. It is also suitable for bedridden patients and those who have difficulty chewing.
The basic rule when choosing folk remedies is that they should have a gentle effect on the elderly body. Strong drugs and remedies should be avoided. The likelihood that diarrhea will develop into chronic constipation is very high. Old age requires a special approach to treatment. Otherwise, the body's reaction may be unexpected.
source
Features of treatment
Diarrhea in the elderly requires immediate treatment. After all, at this age, the immune system, like the entire body as a whole, is not able to fully resist infections. Therefore, even one-day diarrhea can provoke dehydration and rapid deterioration of the patient’s condition.
But treating diarrhea without an established cause is not easy. Moreover, in old people the general clinical picture of diseases of the digestive organs is poorly expressed, and often diarrhea is the only symptom indicating ongoing pathological processes. Therefore, the first thing you need to pay attention to is the nature of the bowel movements. For example, liquid stool mixed with mucous contents that is disturbing only during the daytime may indicate irritable bowel syndrome. But the cause of round-the-clock diarrhea with mucus and pus is most likely infectious colitis.
Based on the diagnostic results and after the cause of diarrhea in older people has been established, treatment is selected on an individual basis. And a favorable prognosis can only be guaranteed if you consult a doctor in a timely manner. At the same time, the lack of qualified help significantly reduces the chances of a full recovery.
Rehydration and detoxification
The processes of restoring lost fluids and minerals must begin before going to the doctor, continuing until diarrhea in older people completely stops. The classic version, water or compotes, are ineffective in this regard. After all, with their help, only water reserves in the body are replenished, and the electrolyte balance remains disturbed. Therefore, the best remedy in this situation is pharmaceutical drugs, for example, Regidron or Citroglucosolan.
But in the question of how to stop diarrhea, sorbents come to the rescue, binding toxic substances and preventing their further penetration into the blood. This can be activated carbon, Smecta, Polysorb and others. But it should be understood that taking these drugs is a temporary measure that does not exclude a full examination. After all, if a patient is constantly bothered by diarrhea due to oncology, then the likelihood of recovery on sorbents is zero.
Diet
The next stage is diet. Following a diet for diarrhea in older people is a mandatory component of treatment, regardless of the cause of the disorder. Basic rules on how and what to feed a patient with diarrhea:
- Complete refusal to eat on the first day after signs of diarrhea appear. During this time, you can “eat” with water, jelly, tea, fresh compote and pharmaceutical solutions for rehydration.
- From the second day, meals for diarrhea consist of easily digestible dishes and foods that do not cause gas formation or fermentation in the intestines. This could be oatmeal or rice porridge, mashed potatoes, homemade crackers, baked apples and boiled vegetables.
- Meat is introduced into the diet only on the fourth or fifth day. These can be low-fat varieties such as rabbit or chicken fillet, boiled or steamed.
- At the same time, soups were introduced into the diet. It is recommended to cook them in vegetable broth. If meat is used, only skinless chicken or turkey is acceptable. The meat broth must be secondary, that is, after the first boil, it is drained.
- Gradually, natural-based fermented milk products are being added to the menu. Use starter cultures for homemade yoghurt, cottage cheese and kefir, as this is where live bacteria are contained.
Old people who suffer from diarrhea for a long time should not be fed raw fruits and vegetables, fresh milk, fried and fatty foods. The ban is also imposed on all kinds of spices and spices that have an irritating effect on the stomach and intestines.
Folk remedies
Treatment with folk remedies in people over 50 years of age can only be carried out in combination with drug therapy and strictly under the supervision of a doctor. Popular recipes:
Rice cereal decoction
To prepare it, add 1.5 teaspoons of rice with water (0.5 l). Cook the porridge over low heat for 30–40 minutes. Strain the finished broth and take 50 ml every 2-3 hours. A bedridden patient must be fed with a teaspoon. Read more about the benefits and uses of rice water here.
Oak bark infusion
Pour 200 ml of boiling water over one tablespoon of dry raw material and leave to steep for a while. Strain the finished product and take 5-10 ml every 2-3 hours. The daily dose of oak infusion is up to 250 ml. We wrote other recipes with oak bark for diarrhea here.
Methods for diagnosing the causes of diarrhea
The doctor prescribes treatment only after establishing the true cause of diarrhea. To do this, he recommends that the patient undergo examination:
- clinical blood test - identifying indirect signs of an inflammatory process that can cause diarrhea;
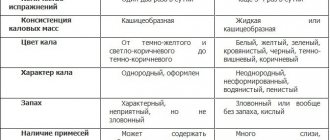
- coprogram - analysis of stool for enzymatic activity and digestive ability of the stomach, intestines and pancreas;
- bacterial culture for microflora and its sensitivity to antibiotics;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs - helps to assess their condition and detect possible chronic processes, and not only of the digestive system;
- sigmoidoscopy – endoscopic examination of the mucous membrane of the rectum and distal parts of the sigmoid colon;
- colonoscopy - examination of the large intestine;
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy - examination of the mucous membrane of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum.
Instrumental diagnostics are aimed at visually identifying pathological processes that cause digestive disorders, while laboratory methods only allow us to suspect problems with it. Therefore, in no case should you refuse an examination prescribed by a doctor and try to get by only by taking tests.
Diagnostics
Any symptoms of diarrhea in older people require clarification of the cause before prescribing treatment. The following methods are used to diagnose the disease:
- analysis of patient complaints;
- microscopic examination of stool (coprogram) to identify atypical inclusions;
- bacterial culture;
- blood test for the presence of inflammation, biomarkers of liver and pancreas dysfunction;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs
- gastroscopy, colonoscopy, sigmoidoscopy to identify damage to the intestinal and gastric mucosa, ulcers, neoplasms, and sources of bleeding.
Analysis of diagnostic results allows the doctor to determine treatment methods and find out the cause of diarrhea.
Diarrhea in the elderly
A common disorder of intestinal function in old age is diarrhea, which, if prolonged, can lead to serious consequences - dehydration, loss of electrolytes and vitamins, and cause exacerbation of chronic pathologies. Diarrhea in old age, unlike in young people, is less likely to be caused by poisoning or intestinal infections. Their most common cause is disturbances in enzymatic activity due to age, which impairs the complete breakdown and absorption of food components. As a result, food residues enter the large intestine undigested, where they are actively broken down by microbial flora with the formation of irritating and toxic metabolic products. This leads to increased peristalsis, irritation and inflammation of the intestinal wall, and ultimately diarrhea is formed. Another reason may be a decrease in the activity of taste buds, which leads to a distortion of eating habits with an overabundance of sweet, spicy, and salty foods. This irritates the intestinal wall, causing diarrhea.
The basic principles of treating diarrhea in older people are:
- treatment of the underlying disease that caused diarrhea;
- carrying out rehydration and detoxification of the body;
- prescribing a special diet for diarrhea.
Treatment of the underlying disease
After diagnosis, the doctor prescribes appropriate treatment. All patients with diarrhea are recommended to take medications that restore normal intestinal microflora.
In cases of intestinal infection or food poisoning, antibacterial agents and antiseptics, plenty of fluids and a gentle diet are prescribed. The presence of a chronic process in the intestines (Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis) requires the prescription of hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs, vitamins, and a proper diet.
You can use folk remedies to treat the underlying disease and diarrhea in elderly patients only after consultation with your doctor.
Rehydration and detoxification therapy
One of the main directions in treatment is to replenish lost fluid. For this purpose, plenty of drinking is prescribed, which can be represented by ordinary alkaline mineral water without gas, or by special preparations (Regidron, Oralit). At the same time, parenteral administration of saline solutions is carried out.
It is important to note that rehydration therapy should be carried out throughout the entire period of diarrhea until it completely stops. To detoxify the body, intestinal sorbents are used, and intravenous infusions of glucose, Reosorbilact, and saline solutions are also performed. To detoxify the body, intestinal sorbents are used, and intravenous infusions of glucose, Reosorbilact, and saline solutions are also performed.
To detoxify the body, intestinal sorbents are used, and intravenous infusions of glucose, Reosorbilact, and saline solutions are also performed.
Diet
Special attention is paid to nutrition for diarrhea in older people. The patient is explained the basic principles of the diet for diarrhea, which are as follows: On the first day after the onset of diarrhea, you should completely abstain from food.
It is recommended to consume more liquid in the form of compotes, weak tea, juices, alkaline water, and oral rehydration preparations. On the second day, the patient is allowed to eat only easily digestible foods. For example, porridge with water, vegetable soup, crackers, baked apples. Eating lean meat and fish is allowed only 4-5 days after the onset of diarrhea
On the first day after the onset of diarrhea, you should completely abstain from food. It is recommended to consume more liquid in the form of compotes, weak tea, juices, alkaline water, and oral rehydration preparations. On the second day, the patient is allowed to eat only easily digestible foods. For example, porridge with water, vegetable soup, crackers, baked apples. Eating lean meat and fish is allowed only 4-5 days after the onset of diarrhea
In this case, dishes must be steamed, boiled or baked in the oven
Fermented milk products are introduced with caution. The patient is recommended to start consuming kefir, cottage cheese and yogurt, which are least likely to cause diarrhea and, moreover, help restore normal intestinal flora
It should be noted that the occurrence of loose stools in an elderly bedridden patient is provoked by the constant horizontal position of the patient. Therefore, it is advisable to follow a gentle diet constantly. In this case, it is better to grind all dishes in a blender or knead through a sieve.
Causes of diarrhea in old age
As a result of a slowdown in the functionality of metabolic processes, the main cause of diarrhea in older people is age-related changes and impaired enzymatic activity. Another reason for diarrhea is that the number of taste buds decreases at this age. In order to return the former sensations from food, an old person provokes stool disorder by including excessively spicy, salty foods and a large number of sweets in his menu.
The main causes of diarrhea and indigestion in older people:
- consequences of taking antibiotics, side effects of certain medications;
- complications of existing endocrine diseases (diabetes mellitus);
- history of Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis;
- reaction to stress, emotional tension;
- hygiene violations;
- poor quality nutrition;
- poor chewing of food due to missing teeth.
If an elderly person's stool contains blood, he may have stomach bleeding or an infection of the digestive system as a result of dysentery or salmonellosis. When pain occurs in the stomach or intestines, loose stools and constipation alternate, an urgent diagnosis is needed to identify a malignant tumor.