Causes of prolonged diarrhea
Prolonged diarrhea in rare cases is an independent disease, as it often appears as a symptom of one or another disorder in the body.
Diarrhea is divided into the following types depending on the etiology of origin:
- The dyspeptic type is characterized by indigestion due to a deficiency of digestive enzymes.
- The alimentary type develops due to an allergic reaction of the body, abuse of alcoholic beverages, consumption of excessively fatty foods and dietary disorders.
- The infectious form occurs due to infection with viruses, helminths, bacteria (Escherichia coli, cholera, salmonella, microsporidia, giardia, dysentery, enterovirus, etc.).
- Medication type . Loose stools develop while taking a certain group of drugs (usually antibiotics).
- Toxic type – poisoning by harmful and toxic substances. Feature - the body exhibits a protective reaction in the form of diarrhea. The etiology of origin can be infectious or non-infectious.
Functional diarrhea
Functional diarrhea is a polysymptomatic intestinal disease without organic causes. It appears constantly or periodically, which is due to certain factors and prerequisites:
- Stressful state, strong experience. In this case, intestinal motility increases as a protective reaction.
- Overexcitability of nerve roots in the intestines.
- Hereditary predisposition.
Functional diarrhea is based on fear. This condition leads to the synthesis of chemicals in the body, which speeds up digestive processes and causes the intestines to reject excess (even water).
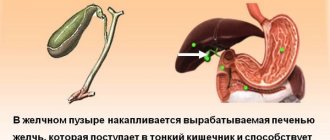
Pancreatitis
Pancreatitis refers to pathologies of the stomach, gall bladder, and pancreas, in which pancreatic enzymes are secreted in insufficient quantities. This leads to pathological reactions in the intestines. Namely, food products are not broken down, nutrients are not absorbed, and the mucous membranes in the digestive system become inflamed.
Inflammatory processes contribute to the alternation of diarrhea and constipation in a chronic form. The main method of therapy is the use of enzymatic agents and dietary nutrition.
Dysbacteriosis
With dysbacteriosis, the quantitative composition of the intestinal microflora is disrupted. The main cause of dysbiosis is long-term use of antibacterial drugs that inhibit lactobacilli, bifidobacteria and other beneficial microorganisms. As a result, the number of pathogenic bacteria increases and immunity decreases.
If we consider the problem from the inside, we can note the following pathological disorders:
- complex proteins are not broken down;
- carbohydrates are not divided into simple molecules;
- there is no synthesis of vitamins, iron, microelements;
- intestinal peristalsis is not subject to regulation;
- harmful substances accumulate and poison the body.
Features of manifestation:
- constant diarrhea;
- bloating;
- spontaneous release of gases;
- pain in the intestines;
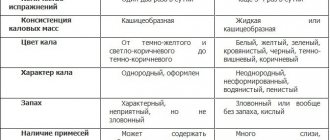
- in feces - impurities of undigested food.
The main method of treatment is taking probiotics.
Ulcerative colitis
With ulcerative colitis, the mucous membranes of the colon become inflamed. There is frequent exacerbation, manifested by the following symptoms:
- prolonged diarrhea;
- pain in the abdominal area;
- weakness of the body;
- blood clots in stool;
- the presence of mucous and purulent inclusions;
- bleeding;
- formation of adhesions;
- perforation.
Ulcerative colitis occurs for a variety of reasons and is treated with aminosalicylates and symptomatic treatments.
Crohn's disease
With Crohn's disease, the entire gastrointestinal tract becomes inflamed according to the granulomatous type, as a result of which the disease is complicated by ulcers and scars, and disruption of the intestinal structure.
The following symptoms are observed in Crohn's disease:
- abdominal pain;
- nausea and vomiting;
- lethargy;
- weakness;
- reduced ability to work;
- watery stool;
- The minimum number of daily bowel movements is 10 times.
Infection with worms
With helminthic infestation, infection occurs with parasites such as pinworms, roundworms, enterococci, tapeworms, etc. Worms settle in the intestines, poisoning the body with waste products.
What to look for besides diarrhea:
- itching in the anus;
- formation of acne, warts, papillomas;
- sudden weight loss;
- increased appetite;
- asthma attacks;
- intoxication symptoms - nausea and vomiting, headache, insomnia, weakness;
- depressed mood, irritability;
- heaviness in the abdominal area;
- frequent belching;
- flatulence;
- alternating constipation and diarrhea.
Not only children, but also adults can become infected with worms, since parasitic agents are found in food, water, air, and on household objects. Specific treatment is required.
Other reasons
In addition to the main causes of prolonged diarrhea, diarrhea occurs against the background of the following pathological disorders and factors:
- enteritis of a polyetiological nature in different parts of the intestine;
- enterocolitis, in which the inflammatory process affects both the large and small intestine;
- lactose intolerance;
- fibrosis of the pancreas, which occurs against the background of impaired growth of connective tissues;
- irritable bowel syndrome caused by unfixed factors;
- malignant and benign neoplasms;
- hyperthyroidism, in which the thyroid gland produces excessive amounts of hormones;
- a sharp decrease in immunity;
- impaired intestinal integrity due to surgery, trauma;
- alcohol and drug abuse;
- allergies to food and other allergens.
general characteristics
Chronic diarrhea occurs in approximately every third person. The pathology becomes chronic when it lasts more than 3-4 weeks.
Chronic diarrhea does not necessarily mean that a person suffers from it all the time. Symptoms may subside for a long time, followed by periods of exacerbation.
If you have diarrhea of this nature, you cannot refuse treatment. Usually this problem is dealt with by a gastroenterologist and proctologist. Depending on the cause of the pathology, it may be necessary to involve other specialists, for example, an endocrinologist, an infectious disease specialist.
Dangerous symptoms
The main symptom of prolonged diarrhea is loose stools over a long period of time, which cannot be eliminated using conventional methods and means. Since diarrhea is a symptom of other diseases and conditions, the associated symptoms may be different. But there are general symptoms that require the patient to immediately consult a doctor:
- cramps and pain in the abdominal area;
- intestinal rumbling;
- increased body temperature;
- bloating, flatulence;
- the presence of mucus, pus and blood in the stool;
- unnatural color of stool;
- weight loss;
- severe weakness of the body;
- mental disorders;
- dehydration (convulsions, poor coordination of movements, dizziness, dry mucous membranes and skin, low blood pressure).
If these signs appear, you need to urgently go to a specialist and undergo a comprehensive examination, which will reveal the true cause of prolonged diarrhea. Based on the results obtained, a treatment regimen is prescribed.
Diagnostic measures
Diagnosis of the suspected pathology is carried out by a doctor after a preliminary conversation with the patient. The specialist finds out the nature of the disorder (acute or chronic), then takes stool for analysis and checks whether the problem remains if the person completely refuses food. A set of diagnostic procedures allows you to find out the exact cause of persistent diarrhea.
We recommend: What is diarrhea and how to treat it
If the disorder is chronic, you must quickly undergo the required blood tests:
- general;
- identifying the concentration of vitamin B12 (diarrhea when taking vitamins);
- Ca concentration level;
- folic acid level;
- checking the correctness and completeness of the functioning of the thyroid gland and liver;
- Fe concentration;
- study of biomaterial for celiac disease.
The causes of chronic diarrhea necessitate additional tests that will help confirm the diagnosis and prescribe adequate, effective treatment. Taking into account the patient’s complaints, the doctor prescribes special examinations:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity.
- Colonoscopy, during which a biopsy of the intestinal mucosa is taken for further histopathological examination.
- X-ray of the abdominal cavity.
What could be the consequences?
Prolonged diarrhea has a negative impact not only on the intestines and digestive system, but also on the entire body. If you do not go to the clinic, the following complications may occur:
- When loose stools last for a long time, all beneficial substances (vitamins, minerals, micro- and macroelements) are washed out of the body, and the water-salt balance is disrupted. The result is dehydration. Dehydration causes blood fluid to thicken, which slows blood circulation, which has a negative effect on the brain and heart. Against this background, arrhythmia, atherosclerosis of blood vessels and other diseases occur. Dehydration itself eventually leads to the death of the patient.
- Malfunction of the central nervous system organs due to loss of fluid. The blood is not saturated with oxygen and nutrients, which develops hypoxia (oxygen starvation). This leads to depression, memory impairment, motor coordination and similar reactions.
- Dehydration contributes to cramps, as muscle tissue loses elasticity and nerve roots lose sensitivity. The level of fluid in the ligamentous and muscular apparatus decreases, which leads to dryness. Involuntary muscle contractions occur due to incorrect interpretation of signals sent by the brain to the muscular system.
- Impaired functionality of all internal organs due to lack of nutrients and water in the body.
As dehydration progresses, the patient's condition worsens significantly - tears do not flow from the eyes, the visual apparatus seems sunken, and the eyelids do not close completely. Next, a white coating forms on the tongue, and the tongue itself becomes swollen. The patient urinates extremely rarely, the color of the urine darkens.
Nonspecific ulcerative colitis
The causes of diarrhea are often associated with diseases of the large intestine.
Loose stools are a manifestation of ulcerative colitis.
With this disease, inflammation of the mucous membrane and the formation of ulcers are observed. Mostly young people aged 20 to 40 years are affected. There are several theories for the development of this pathology (autoimmune, genetic, infectious). Ulcerative colitis is characterized by the following symptoms:
- bowel dysfunction;
- the presence of blood and mucus in the stool;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- bloating.
During exacerbation, body temperature rises. Patients lose weight. They experience weakness and muscle pain. The function of the organ of vision is often impaired. Diarrhea is one of the most persistent symptoms. 95% of patients complain about it.
The frequency of bowel movements is on average 3-4 times a day. With exacerbation, the urge to go to the toilet becomes more frequent. Blood and large amounts of mucus are found in the stool. Diarrhea in ulcerative colitis is sometimes combined with constipation.
First aid for diarrhea
The first thing to do is to eliminate the risk of dehydration, since it is dehydration that leads to complications. To prevent this, the body is supplied with salt and water. The following rehydration solutions are used:
- Regidron is the most common. Normalizes electrolyte balance, accelerates the conduction of nerve impulses. Additionally, it restores the heartbeat, as it consists of a large amount of potassium, glucose, and chlorine. In addition, the functionality of the brain improves, muscle weakness is eliminated, and irritability is reduced.
- Reosolan consists of salts, which eliminates vomiting, nausea, and weakness.
- Orsol is most often taken for heart disease and potassium deficiency, since in addition to its rehydrating properties, it protects the heart muscle from damage.
- Normohydron accelerates metabolic processes, relieves pain and spasms, and normalizes blood supply.
- Gastrolite mineralizes soft tissues, reduces gastric acidity, eliminates nausea and flatulence.
- Citraglucosolan is used mainly in the initial stages of dehydration.
Ways to use rehydrating drugs:
- orally - at home (you should strictly follow the dosages indicated in the instructions);
- intravenous drip method - in the clinic.
Rules for taking Regidron and similar drugs:
- take 1 tbsp every 5-10 minutes. l.;
- the temperature of the solution should be warm (35-38 degrees);
- do not eat during the day.
If these drugs are not found in the first aid kit, use a folk rehydrating remedy that is recommended by doctors:
- slightly heat boiled water – 1 liter;
- add 2-3 tbsp. l. Sahara;
- put 1 tbsp. l. table salt;
- mix thoroughly;
- give the patient 100 ml to drink after each bowel movement;
- The maximum daily dosage of the solution is 2 liters.
If diarrhea occurs due to intoxication or infection, you will have to take emergency measures - rinse the stomach. To do this, the patient must drink 1-1.5 liters of water or 1-2 glasses of rehydration solution at a time, which leads to immediate vomiting.
How to determine the body's recovery:
- skin tone is normalized;
- urination is restored;
- mucous membranes are moisturized;
- weakness disappears.
Methods for treating persistent diarrhea
The treatment regimen is selected after a thorough examination based on the results obtained, that is, depending on the etiology of the origin of diarrhea. Therefore, drugs specific to the cause of diarrhea are prescribed.
Taking medications
Treatment should be aimed at restoring peristalsis, normalizing the functionality of the digestive system, restoring the balance of microflora, saturating the body with useful substances, and eliminating unpleasant symptoms.
What medications does the doctor prescribe:
- Antidiarrheals that bind feces: Loperamide, Imodium, Levomycetin, Enterodes.
- Antispasmodics that relieve spasms and pain: Papaverine, Halidor, No-shpa, Duspatalin.
- For physiological diarrhea, antidepressants (Amitriptyline, Imizin, Fluoroacyzin) and sedatives (Novo-passit, motherwort tincture, Persen, valerian tincture) are used.
- For allergic reactions, antihistamines are used: Claritin, Diazolin.
- In case of intoxication, sorbents are prescribed: Activated carbon, Sorbex, Enterosgel, Polysorb.
- To restore peristalsis and motility, drugs with hyperidin are used.
- Probiotics and prebiotics help normalize the microflora: Linek-s, Enterol, Hilak, Lactofiltrum, Bifidumbacterin, Normospectrum, Acipol.
- To saturate the body with useful substances, vitamin and mineral complexes are used (the choice depends on the level of deficiency of a particular substance).
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine is used primarily as an adjuvant therapy for long-term diarrhea, since the approach to treatment must be comprehensive. What you can use:
- Mint tea is used to restore digestion, but it needs to be brewed differently. Place a few mint leaves in a glass of boiling water, boil for 1-2 minutes, let it brew under the lid until warm. Drink 2-3 glasses per day.
- To reduce inflammatory processes, chamomile is brewed. For 250 ml of boiling water, 1 tbsp is required. l. herbs with flowers. Cook over low heat for 10-15 minutes, strain. Take in small sips before meals for half an hour.
- Strong tea stops diarrhea (1-2 tsp of tea per 200 ml of boiling water). The daily norm is 3 cups.
- Brew St. John's wort (250 ml of water per 1 tablespoon of herb). Drink in small portions throughout the day.
- Eat 5-6 grains of black peppercorns.
- Use starch: for 200 ml of water you need 2 tbsp. l. starch powder. Mix thoroughly, divide the glass into 3 parts.
- Mix 100 ml of vodka with half a teaspoon of salt. Drink at once.
- Swallow a clove of garlic three times a day.
- Sugar mixed with caraway oil is beneficial (2-3 drops per 20 g).
- For helminthic infestation, brew wormwood. To do this, add 1 tbsp into a thermos (a glass of boiling water). l. herbs. Leave for an hour and a half. Drink the resulting solution 2 times.
- Grind the carrot seeds, separate 1 tbsp. l., take the same amount of green part of the dill. Take orally once a day.
- Oatmeal cooked in water can help bind feces. For 0.5 liters of water you need 100 g of flakes. Cook for 5 minutes, then add the dried pears and cook until done. Eat a portion at 2 times.
- The most universal way is a decoction of rice cereal. For 500 ml of water, take 1 tbsp. l. rice, cook for 15 minutes, let sit until completely cool. Strain the liquid, take 50 ml every couple of hours.
- Boil pomegranate peels and drink as a tea drink. Do the same with walnut leaves.
- Pour 1 tsp into a thermos. ground red pepper and cinnamon powder, pour a liter of boiling water. Leave for 60 minutes. Take the drug every half hour, 2 tbsp. l.
Do not forget to consult with your doctor about the use of folk remedies, since in each individual case (based on the etiology of the origin of diarrhea) different recipes are used.
Diet
Dietary nutrition is a prerequisite for the treatment of diarrhea of any origin. On the first day, especially if dehydrated, it is advisable to refuse food completely. Next, the dishes are introduced into the diet in small quantities.
Diet rules:
- reception is carried out 5-7 times a day;
- portions are small;
- food temperature – warm;
- food is steamed or boiled;
- Fried and baked foods are prohibited.
Preferred Products:
- oat and rice porridges;
- low-fat fish (pollock, perch, etc.);
- dietary meat – rabbit, chicken fillet, veal;
- fruits with a binding effect - quince, banana, pomegranate;
- vegetable broths and soups;
- drinks - tea, jelly.
What to eat and drink is not recommended:
- fatty meat and fish;
- fermented milk products, milk (with the exception of natural yoghurts);
- rich pastries, fresh wheat bread;
- sweets;
- beans;
- fruits;
- spices;
- coffee;
- carbonated drinks and alcohol;
- raw vegetables;
- mushrooms;
- canned food;
- semi-finished products, fast food.
Treatment of chronic diarrhea
Therapy begins even before the causes of the pathology are identified, since some measures do not require delay. At the initial stage, they usually resort to adsorbents, antibiotics, astringents and anti-inflammatory drugs, enzymes, pro- and prebiotics.
Features of treatment depend on the cause of chronic diarrhea. In any case, symptomatic therapy is carried out. It involves the use of antidiarrheal agents, represented by:
- synthetic drugs;
- adsorbent medications;
- dentals;
- herbal preparations with tannins.
Among the synthetic drugs, Loperamide is often used. It is used for diarrhea caused by gastroenteritis or inflammatory bowel disease. This drug is also known under other trade names, among which Imodium is the most popular.
Among the adsorbent medications, activated carbon, Enterosgel, and Smecta are usually used. Among the toothbiotics, the most effective are Bifidumbacterin, Lactobacterin, and Colibacterin. An effective herbal preparation is the fruit of bird cherry.
Treatment also includes drugs that have an astringent effect. These include Tannacomp, which also has anti-inflammatory properties.
If chronic diarrhea has developed due to infection, then antibiotics must be included in treatment. There are several groups of such drugs - the choice of a suitable drug should be made by a specialist after determining the exact cause (causative agent) of the disease.
After antibiotic therapy, normalization of the intestinal microflora is required. To do this, they resort to Linex, Bifiform, Bifidumbacterin, Hilak Forte, Acylact, Lactobacterin.
If absorption is impaired, they resort to Somatostatin or Sandostatin. These drugs have a strong antidiarrheal effect.
If chronic diarrhea is caused by gastrointestinal pathology, then it is often necessary to include enzymes in treatment. Among such drugs they resort to Creon, Mezim, Festal.
Prolonged diarrhea leads to dehydration, electrolyte metabolism and acid-base balance are disrupted. In this case, rehydration is carried out. It can be done intravenously. For this, Trisol, Chlosol, Kvartasol, Acesol are used. The rate of administration of the electrolyte solution and its volume depend on the severity of the pathology.
Rehydration can be achieved through oral administration. In this case, use Regidron, Glucosolan.
Prevention
To avoid prolonged diarrhea, follow the rules for preventing the condition:
- maintain personal hygiene to prevent infection;
- wash vegetables and fruits thoroughly;
- follow the rules for heat treatment of eggs, meat and fish;
- treat chronic diseases in a timely manner;
- try exotic dishes with caution;
- avoid allergens;
- when treating with antibiotics, take additional medications that eliminate dysbacteriosis;
- do not eat spoiled foods, follow storage rules;
- Always pay attention to expiration dates when purchasing products.
Prolonged diarrhea in adults does not occur out of nowhere, so it is important to promptly detect the root cause of the unpleasant symptom, which will avoid dangerous complications. Diarrhea should not be ignored; it can be fatal.
Previous entry Causes and treatment of diarrhea at 39 weeks of pregnancy
Next entry What to do if you have diarrhea at 40 weeks of pregnancy?
Causes of constant diarrhea in men
Often, failure of the gastrointestinal tract functions leads to diarrhea in adults.
The reasons may be different:
- overeating or starvation;
- intestinal dysbiosis in case of damage by pathogenic microorganisms, viral infection, helminthic infestations;
- stress;
- excessive use of antibiotics;
- sudden change in weather conditions;
- non-compliance with diet;
- food poisoning from low-quality, stale products;
- development of an inflammatory process in the stomach or intestines, gastritis, ulcers, intestinal flu;
- toxic damage to the large intestine in case of poisoning with mercury, mushrooms, berries
Often, in addition to diarrhea, the temperature is elevated, which can cause the formation of tumors and polyps in the intestines. Sometimes black diarrhea mixed with blood and pus comes out, which happens after a resection of the stomach or cancer.
For intestinal ulcers:
- in addition to diarrhea, nausea is observed;
- vomit;
- bloating;
- pain and colic;
- dry skin and mucous membranes in the mouth and lips.
In case of intoxication of the body:
- passing dark urine with blood.
It happens that the cause of diarrhea is a severe course of another disease in the body. In some cases, you need to call an ambulance immediately.