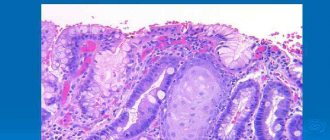
A disease in which cells from different organs of the gastrointestinal tract, such as the small or large intestine, gradually form in the gastric epithelium is called gastric metaplasia. The problem occurs against the background of another disease in which healthy epithelial cells die. As a result, the newly formed tissues perform the physiological function of the intestines with the loss of basic gastric properties.
Failure in the formation of stomach cells is a transitional disease.
Description
Gastric metaplasia characterizes a transitional state and not an independent disease. Gradual modification of stomach tissue occurs with constant exposure to unfavorable factors, such as nutritional disruptions, drug or alcohol abuse.
The gastric mucosa reacts to the irritant with an inflammatory process, which without treatment becomes chronic. An atrophic change occurs in cells that gradually lose their functional ability . At this stage, gastric metaplasia begins in most cases. If appropriate measures are not taken, transformation into dysplasia occurs, characterized by changes in cell nuclei and cytoplasm, and this leads to cancer. Metaplasia is also called the benign course of tissue atrophy. This process is considered reversible if proper therapy is prescribed and all recommendations are followed.
Features and risks
Intestinal metaplasia occurs:
- complete small intestine;
- incomplete colon.
The forms differ from each other in their tendency to malignancy. The first focal type is not precancer, since the altered cells retain their functions. The second type tends to become malignant due to impaired cellular differentiation, which is similar to dysplasia.
The danger of metaplasia lies in the difficulty of differentiating the disease due to the lack of specific signs. The clinical picture is fully consistent with the symptoms of focal pathology that caused cell atrophy. For example:
- In the chronic stage of gastritis with high acidity, “hunger” pains, increased heartburn, and “night hunger” appear.
- With an ulcer - clearly localized pain on an empty stomach. Symptoms will worsen in spring and autumn.
- With reflux syndrome with the reflux of intestinal contents into the stomach - a bitter taste in the mouth, widespread pain, vomiting.
- When a bolus of food is expelled from the stomach back into the esophagus, there is a strong burning sensation in the digestive tract, sour belching.
The only reliable method for diagnosing focal disease is fibroesogastroduodenoscopy, performed simultaneously with a biopsy. With its help, the stomach and intestines are carefully examined and the type of irritant, the localization of the tumor, the prevalence of the focal form are determined, and the malignancy of the process is confirmed or refuted.
Kinds
General typical classification of metaplasia:
- I - complete, small intestine, mature;
- II - incomplete, colonic, immature.
Based on the degree of distribution and area of areas with modified epithelium, they are distinguished:
- mild - damage to 5% of the organ surface;
- moderate -20%;
- pronounced - over 20%.
Based on the severity of the atrophic process in the gland, the following types are distinguished:
- A - insignificant;
- B - intermediate;
- C - complete.
By the nature of the lesion:
- Pyloric or antral form of development, which can be: focal with the replacement of part of the glands of the fundus against the background of inflammation and disruption of the process of cell renewal; diffuse with the distribution of atrophy from the pyloric to the fundus of the stomach, the antrum can be captured; the process takes place without destruction or death of cells.
- Ciliated shape. The appearance of cells of this type in the stomach indicates the development of adenocarcinoma.
- Pancreatic form with the appearance of small-grained cells with acidophilic and basophilic endings.
Complete metaplasia
Foci of mature metaplasia are formed from all cellular structures of the intestine, which contain sialomucins, sulfamucins, enterocytes (goblet, borderless, bordered). When filling the epithelium of the stomach lining, goblet nuclei alternate with bordered ones. A special feature of this type is the presence of Paneth nuclei with apical granulation in the deep pits of the wall. In most cases, small intestinal metaplasia occurs with underlying chronic gastritis. Another name for the problem is enterolization.
Small intestinal is sometimes combined with incomplete metaplasia. They can be located in the same gland or in different parts of the gastric wall. Enterolization is considered to progress to colonic metaplasia. In chronic inflammation, the focus of complete metaplasia turns into incomplete metaplasia in 11% of cases.
Incomplete metaplasia
The immature form of the pathology is characterized by the replacement of gastric nuclei with alternating goblet-shaped and prismatic ones. No other names are found. The epithelium becomes polymorphic with a tendency to increase nuclear-cytoplasmic influences. There is a disruption in the process of maturation and differentiation of the glands, which is characterized by the uniformity of the upper and lower layers.
The incidence of detection of this type of metaplasia is increased in benign diseases of the stomach. Almost all cases of cancer developed precisely because of metaplasia of tissue damage. Therefore, the immature form is a precancerous condition, characterized by a high mortality rate when detected late.
In gastric cancer, colonic metaplasia is found in 94% of cases. Due to the high frequency of coincidences of malignant transformations, pathology of this type requires a differentiated assessment when diagnosing intestinal metaplasia.
Causes
The causal factors influencing the development of gastric pathological processes have not been fully studied. To date, a group of the most significant provoking criteria has been identified, leading to the onset of intestinal metaplasia in 100% of cases. The group includes:
- constant irritation of the stomach walls;
- chronic inflammation of the epithelial membrane;
- prolonged depression or constant psycho-emotional overload;
- inflammatory processes in the esophagus;
- ulceration of the epithelial membrane;
- intestinal dysfunctions, manifested by frequent reflux of gastric and duodenal contents into the esophagus.
Foci of metaplasia are often diagnosed with low acidity of digestive juice in the stomach. Lack of acid leads to selective changes in healthy microflora in the digestive organ. The process is accompanied by the destruction of gastric bacteria with abundant contamination of intestinal microorganisms.
Infection of the mucous membrane with Helicobacter is considered a dangerous phenomenon that provokes many pathologies in the gastrointestinal tract, including metaplasia. The microbe secretes proenzymes that add salts of nitric and nitrous acids to form carcinogenic products - nitrous substances. These substances combine with other carcinogens from ingested foods. Serious damage to gastric tissue occurs, which rapidly progresses, provoking the development of a malignant tumor. The pathological process intensifies when the rules of a healthy diet are not followed, for example, due to the abuse of salted food and strong alcohol.
Reasons for the development of pathology
The main cause of gastric metaplasia is considered to be Helicobacter pylori, a pathogenic microbe that causes the development of ulcers and chronic gastritis with damage to the organ mucosa. The danger of this microorganism lies in its ability to transform glandular epithelial cells into atypical (cancerous) ones. Enhanced regeneration of the damaged epithelial layer of the stomach leads to disruption of cell differentiation and their degeneration into intestinal cells.
The pathological process occurs gradually in several stages.
- infection of the stomach with the pathogenic microbe Helicobacter pylori;
- progressive inflammation of the mucous membrane, turning into a chronic form (gastritis);
- death of mucosal epithelial cells, atrophy;
- deregulation of cell division and formation processes;
- intestinal metaplasia;
- the beginning of carcinogenesis – the appearance of atypical cancer cells.
Prerequisites that support inflammation and irritation of the gastric mucosa include:
- The presence of duodenogastric reflux is the reflux of bile from the duodenum into the stomach due to insufficiency of the duodenal sphincter.
- The damaging effect of many medications: anti-inflammatory drugs ( diclofenac, ibuprofen ), cardiac glycosides, steroid hormones.
- Irritating effects of alcoholic drinks, poor-quality food, toxic substances.
- Rejection of gastric contents into the esophagus.
- Diseases of other organs involved in digestion (pancreas, liver, gall bladder).
- Prolonged stress, depression.
- Hormonal imbalance in the body.
- Age-related changes.
Symptoms
Intestinal metaplasia, which affects the gastric mucosa, does not have specific symptoms. The clinical picture of the problem corresponds to the causative factors that provoked the atrophy of the glands. In pathologies with an imbalance in the acidity of the digestive juice, the patient will complain of the following sensations:
- constant burning in the gastrointestinal tract;
- "hunger" pains;
- severe hunger during sleep.
With reflux pathology with constant reflux of bile into the stomach, the patient will complain of symptoms such as:
- diffuse pain;
- vomiting;
- bitter taste in the mouth.
During diagnosis, a disorder in the muscular activity of the sphincter in the antral zone of the stomach will be detected, and reverse peristalsis will appear. Histological analysis will reveal focal metaplasia located in the antrum of the organ. If the provoking factor is an ulcer, the following are noted:
- local pain with high intensity;
- “hunger” pains that subside after eating;
- periodic exacerbation of pain, mainly in spring and autumn.
During an endoscopic examination, characteristic complications such as scars, perforations, and bleeding will be revealed.
If the provocateur is a hormonal imbalance, the course of the pathology will be asymptomatic. The problem is discovered accidentally during a blood test for another reason.
With helicobacteriosis, the symptoms will be typical of chronic gastritis. Along with general symptoms, when examining a biopsy taken from the mucous membrane, waste products of Helicobacter will be detected. The data will be confirmed by a respiratory test, which involves analyzing the patient’s exhaled air, as well as by examining stool. General symptoms of metaplasia, characteristic of all patients:
- the appearance of constant or periodic pain in the epigastric region;
- belching sour or bitter;
- periodic attacks of nausea and vomiting;
- loss of appetite.
Clinical picture
The process of replacing normal gastric epithelial cells with intestinal ones takes a long time and necessarily against the background of some kind of stomach disease. There are no characteristic symptoms in the initial stages. The clinical picture corresponds to the underlying disease.
Discomfort and periodic pain in the stomach associated with eating.
When bile is thrown up - bitterness in the mouth, nausea, vomiting, burning in the epigastric region, indigestion - belching, bloating, diarrhea.
As metaplasia progresses and the number of hydrochloric acid-producing cells decreases, the acidity of gastric juice decreases and atrophic gastritis develops. The leading symptoms are those caused by a decrease in the digestive capacity of the stomach: a feeling of heaviness and fullness in the stomach after eating, cramping pain, increased flatulence, general weakness, loss of appetite, weight loss.
If metaplasia is provoked by a stomach ulcer with hypersecretion, severe “hunger” pain, seasonal exacerbations. If therapy is ineffective, complications such as gastric bleeding, penetrations, and perforations are possible.
Diagnostics
Detection of the problem is possible with fibrogastroduodenoscopy, an endoscopic method for examining the internal cavity of the stomach. The procedure is carried out using an endoscope with a camera and a probe for collecting biological material for histological analysis.
With metaplasia, the biopsy specimen reveals characteristic tissue changes at the cellular level. The presence of sulfamucin, a substance capable of absorbing carcinogens, is detected. The formed compound is the main provocateur of the development of oncology.
At the same time, changes in the composition of self-antigens in cells are detected. A carcinoembryonic antigen appears due to decreased differentiation of cell nuclei. This can be confirmed by blood test results. An additional method for detecting pathology is the method of chromatic endoscopy. During the procedure, the condition of the affected tissues stained with methylene blue is assessed. Changed tissues as a result of exposure to the dye acquire a specific color. The method determines the degree of metaplasia. When conducting a comprehensive diagnosis, the size and location of metaplasia is clarified.
Methods for diagnosing pathology
Metaplasia is often discovered incidentally during endoscopy for other gastrointestinal diseases. The main method for confirming the diagnosis will be an FGDS with a biopsy; during the examination, the histologist will determine the presence of foreign cells in the mucosa that produce sulfamucin.
This secretion actively absorbs carcinogens, which subsequently provoke the development of a cancerous tumor. In addition, the content of carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) increases in the patient’s blood.
To determine the extent of the lesion, the chromoendoscopy method is used. A special dye tints diseased cells so that they can be seen under a microscope. Thus, when making a diagnosis, the type, size and location of abnormal changes are also noted.
Medicines
Directions of drug therapy:
- Preventing the return of a bolus of food from the stomach into the esophagus. This will prevent focal or diffuse inflammation in the lower esophagus, causing gastroesophageal reflux disease.
- Destruction of infection that has developed due to the contamination of the gastric and intestinal mucosa with Helicobacter.
- Prevention of cancer development.
The treatment regimen is developed by the attending physician based on the diagnostic results obtained. In order to restore beneficial gastric microflora, drugs like Linex are prescribed. It is recommended to take synthetic and natural immunomodulators and herbal medicine recipes. Appointed:
- proton inhibitors to stabilize the acidity of the digestive tract in conditions of its increase: “Rabeprozole”, “Omeprozole”, “Pantoprazole”;
- antacids to neutralize hydrochloric acid: Maalox, Phosphalugel;
- H2-blockers of histamines to suppress secretory activity: Cimetidine, Ranitidine;
- gastroprotectors to regulate gastric acidity and prevent mucosal destruction.
Drug therapy is carried out with dynamic monitoring of the patient’s condition and recovery processes in the stomach. If the conservative method is ineffective and metaplasia progresses, surgery is prescribed.
Intestinal metaplasia of the stomach: causes, symptoms and consequences
- In focal - some tubular glands are replaced due to inflammation, damage to cell renewal of the gastrointestinal tract.
- The diet must include fresh vegetables and fruits.
- As a result, the normal absorption of vitamin B12 is disrupted, which leads to anemia and neurological disorders.
- In this regard, there is an opinion that to treat metaplasia it is necessary to use drugs that suppress the secretion of acid that affects the stomach.
Removal of modified cells by endoscopic method. Elimination of gastroesophageal reflux disease - a disease in which the acidic contents of the stomach are regularly thrown into the esophagus. What is characteristic is that both of these diseases are extremely common among the population, while the patients themselves treat them extremely negligently. I want to try to get rid of enteritis as quickly as possible, and most importantly, somehow simpler and painless.
So I’m thinking, maybe I should also advise him to order?
Intestinal metaplasia - what is it? Comprehensive diagnostics gives a more accurate picture of the disease. In addition, the pathology occurs with a malignant tumor - adenocarcinoma. Treatment of intestinal metaplasia can be either medical or surgical. It is better not to drink coffee, strong tea, and completely avoid carbonated drinks. I love him, I would give my life for him, but I can’t ease his suffering. I love him, I would give my life for him, but I can’t ease his suffering.
This happens during endoscopy. Preventive measures to help prevent the development of intestinal metaplasia include reducing fatty foods, canned foods, and alcohol in the diet. Various variants of mucin formation. I decided to buy it on the Internet. Russian Journal of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, Coloproctology. From tomorrow everything will be different for me!
This stomach tea is a super remedy! This disease is quite dangerous, as it is considered a precancerous stage. This is a disease in which tissue from the stomach lining is replaced by intestinal cells. This makes it difficult to make a timely diagnosis. This also applies to other products. This leads to the fact that the stomach cannot cope with its functions, since the detected cells perform new functions.
- Some medications (calcium antagonists, nitrates) relax the sphincter.
- My husband is 19 years older than me, but after therapy he will give a head start to any young man!
- Observations over the past two decades have confirmed that tissue changes in intestinal metaplasia and intestinal type gastric cancer (Lauren classification) are completely identical.
- With the pyloric type of disorder, focal and diffuse lesions are distinguished.
From tomorrow everything will be different for me! Intestinal metaplasia of the gastric mucosa itself does not cause any special manifestations. The tea itself is specific, but pleasant. Today we will talk about the healing effects of teas.
Late tumor progression and invasion [8]. Complete intestinal metaplasia is similar to the small intestine not only structurally, but also functionally and morphologically. Try it yourself and you will understand me. The last meal should be at least 2 hours before bedtime. An accurate diagnosis can be made against the background of the manifestation of specific cells that synthesize sulfamucin, as well as new antigens on cell surfaces.
And when the rate of cell renewal reaches its maximum, a malfunction occurs in the genetic apparatus of these cells. And it was called the paradigm of gastric carcinogenesis (Fig. This is what I recommend to all patients of the clinic. The intense impact of negative factors on the mucous membrane causes an increase in the rate of their formation. Information is provided for informational purposes only.
He will tell you about all the intricacies of a therapeutic diet and help you customize it for yourself. Not only will it not be beneficial, but it can also harm your health. The danger is that there are no specific symptoms for this disease. Very often, patients at our clinic ask the question: how to treat gastritis at home? Pancreatic – quite rare.
Over time, cells are formed at this site that are specific to another organ of the gastrointestinal tract (large, small intestine). As for the severity of atrophy of the glandular layer, there are such varieties as: complete (C), intermediate (B), minor (A). To determine the extent of damage to the gastrointestinal tract, an additional study is carried out using endoscopic equipment.
This happens because this organ contains a huge number of nerve fibers. I ordered tea for my husband on February 23rd. I received the tea 4 days later, it came in a closed envelope, without identification marks. The ulcer was receding by leaps and bounds!
It all depends on the cause of the disease and its manifestations. All those who have metaplasia are registered. This type of metaplasia occurs quite often.
Drug treatment is carried out under conditions of dynamic monitoring of the patient’s condition and the progress of the recovery process in the stomach. The method of collecting cells or epithelium is called a biopsy. Microscopic description Fragments of the superficial parts of the gastric mucosa of reduced height, in the lamina propria there is lymphoplasmacytic and eosinophilic infiltration with an admixture of granulocytes, leukodiapedesis, crypt abscesses.
Surgery
Surgery is a radical method of eliminating the problem. The goal of surgical intervention is to prevent the development of a malignant tumor. There are:
- Abdominal intervention, in which the affected area is completely removed. The advantage of this method is that it minimizes the risk of carcinogenic formations.
- Laparoscopy is a minimally invasive intervention that involves a small depth of the lesion. It is carried out using an endoscope.
Advantages:
- short rehabilitation period;
- minimum complications;
- low degree of epithelial injury;
- visual aesthetics of seams.
Treatment methods
Depending on the degree of damage to the mucous membrane and the patient’s health condition, the doctor prescribes a course of treatment. As a rule, metaplasia therapy requires an integrated approach. It includes taking pharmaceutical medications, following a special diet and using proven traditional medicine. In rare cases, doctors resort to surgery. Let's consider each of these methods separately.
Treatment of metaplasia
Medicines
Once a diagnosis is made, the patient is prescribed a course of drug treatment, the main objective of which is to:
- normalization of gastric juice secretion;
- destruction of pathogenic microorganisms, including Helicobacter pylori;
- prevention of the development of malignant formation;
- preventing damage to the mucous membrane of the esophagus as a result of stomach acid entering it.
"Clarithromycin"
As an addition to basic medications, doctors may prescribe some types of first-line antibacterial drugs. The most effective of them include Clarithromycin and Amoxicillin. The duration of the antibacterial course is 1-1.5 weeks, but if this does not give the desired result, the doctor will prescribe the use of second-line antibacterial agents. As a rule, second-line antibiotics are prescribed when the patient’s body exhibits low sensitivity to drugs.
"Amoxicillin"
Diet
Treatment of all gastroenterological diseases must be accompanied by adherence to a special diet prescribed by a doctor. This will not only speed up the recovery process, but also prevent possible relapses of the pathology. In this case, the diet consists of eliminating from the patient’s diet all harmful foods that have an irritating effect on the digestive system. First of all, this applies to sour, smoked, salty, spicy or fatty foods. It is also recommended to limit the amount of pickled and canned foods, white bread and dairy products.
Nutrition rules
It is recommended to eat small portions, but often. This is called fractional nutrition. It is also advisable to avoid night or late snacks, as this overloads the digestive system - at night, the affected mucous membrane should be restored, and not fully functioning. All dishes must be steamed or boiled. Make sure that food is sufficiently cooked during cooking, especially fish and meat.
Important! If you have diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, it is not recommended to eat too hot or cold food. This leads to irritation of the mucous membrane of the internal organs, which only intensifies the symptoms of the pathology. The temperature of all dishes should be moderate.
You can't eat food that's too hot
Folk remedies
Traditional therapy can be supplemented with proven traditional medicine. But we must not forget that the use of even the most effective and proven folk remedies is not a reason to refuse drug treatment. Traditional therapy serves only as a supplement. Otherwise, you risk triggering the disease, provoking the development of additional symptoms or intensification of old ones.
Treatment with folk remedies
Alternative medicine offers many effective methods to combat and prevent the onset of formation of foci of metaplasia. Treatment with folk remedies is carried out by consuming decoctions and tinctures of medicinal plants and herbal preparations, which reduce the manifestations of inflammation and relieve pain . Recipes:
- Collection with chamomile, yarrow, calendula, marshmallow root. You need to take 5 g of each herb, mix it, pour 500 ml of boiling water. The product is infused in a thermos for 1 hour. The drink is taken after filtering 4 times a day, half an hour before meals. Quantity of 1 dose - 20 ml.
- A decoction of flaxseeds. You need to take 25 g of seeds, pour boiling water, cook for 5 minutes. After settling for 2 hours, the drink is drunk before each snack. Dosage - 30 ml.
- Tincture with St. John's wort. 15 g of crushed herb is poured into 250 ml of boiling water and infused in a thermos for 12 hours. The drink should be consumed after filtering, bringing the volume to 250 ml half an hour before meals. Dosage - 50 ml. The course is 2 weeks, repeated after a 7-day break.
What treatment is prescribed
Therapy is carried out comprehensively, based on how severely the epithelium is affected. In addition, the patient is registered with a gastroenterologist.
Drugs
Treatment trends are as follows:
- Eliminate the problem of backflow of stomach contents into the esophagus. This prevents the inflammatory process in the latter.
- Elimination of infection caused by Helicobacter.
- Prevention of cancer tumor formation.
After studying all the tests, the gastroenterologist determines an individual treatment regimen. To normalize the microflora, the drug “Linex” or its analogue is prescribed. Additionally, synthetic and natural immunomodulators and herbal treatment are often prescribed.
The most commonly used medications are:
- Inhibitors. Restores acid levels in gastric juice. These are Omeprazole, Rabeprazole, Pantoprazole and others.
- Antacids. Neutralize hydrochloric acid. This is Phosphalugel, Maalox.
- H2 blockers, which neutralize the activity of secretions. These include Ranitidine, Cimetidine.
- Gastroprotectors. They normalize acid levels and block the process of cell replacement.
- Micropreparations for chronic gastritis, erosion of the gastric mucosa, ulcers, adenocarcinoma.
Surgical intervention
Surgery is prescribed only in extreme cases when other treatment methods are ineffective. The procedure is performed with special endoscopic equipment. This is the so-called minimally invasive surgery.
In more advanced cases, complete removal of the changed zone is required. Carrying out such manipulation minimizes the risk of the formation of carcinogenic formations.
Home methods
The disease cannot be cured using folk remedies alone. They are used as additional ones to eliminate inflammation and reduce symptoms.
- Flax decoction: pour 25 grams of seeds into 200 ml of boiling water, simmer in a water bath for 60 minutes, cool, strain. Take 2 tbsp. spoons before meals.
- Take 5 grams of chamomile, yarrow and marshmallow, pour 0.5 liters of boiling water, leave for 60 minutes. Drink every time before meals.
Nutrition for illness
For more effective therapy, it is necessary to follow a healthy diet. A special diet has been developed for this:
- Remove dairy and fermented milk products from the menu.
- Avoid spicy, salty, fried foods, as they irritate the gastric mucosa.
- During treatment, avoid drinking alcohol, coffee and soda.
- Eat small portions, but at least 6 times a day.
- Do not eat 2 hours before bedtime.
- Increase your consumption of vegetables and fruits.
- Be sure to include various cereals in the menu.
- Avoid eating too hot or too cold foods and drinks.
Diet for metaplasia of the gastric mucosa
Effective treatment of foci of metaplasia on the mucosa is made by following the correct regimen and diet. Important Recommendations:
- Exclusion from the diet: dairy products, foods that irritate the gastric mucosa, such as fried, spicy, over-salted foods.
- Refusal to drink alcohol in any form, coffee, carbonated drinks.
- Fractional meals - up to 6 times a day. In this case, the last meal should be 2.5 hours before bedtime.
- Including salads from fresh vegetables and fruits in the daily menu.
- Consumption of all available types of cereals and cereals.
- Food should be warm, since hot food irritates and burns the mucous membrane, and cold food can provoke vasospasm and increase the production of hydrochloric acid due to long digestion.
General rules
Resection of the stomach or part of it in a number of cases is the only possible method of treating and saving the patient’s life. Stomach surgery is a radical method of treating extensive malignant neoplasms ( stomach cancer ), stomach ulcers , polyps, and gastric bleeding that are not amenable to conservative treatment. Despite the progress of medicine, gastric removal remains one of the most difficult surgical operations, and even if it is successful and there are no significant complications, rehabilitation takes a long period of time, and nutrition after gastric surgery is the most important component of this process.
Diet after gastrectomy or after removal of part of the stomach
Parenteral nutrition after gastrectomy begins with Diets No. 0A , 0B , 0B ( 1A , 1B , 1B surgical) prescribed sequentially. Their intended purpose is to provide the patient’s body with a minimum amount of basic food nutrients, unload and spare the stomach, and prevent intestinal bloating and flatulence . The diet contains easily digestible foods containing complete proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and macro/microelements and an increased amount of free fluid. Salt consumption is sharply limited.
On the first postoperative day, the patient is shown to be hungry; on day 2 - the diet includes 250 ml of warm sweet tea and rosehip infusion (50 ml), which are given after 15-20 minutes in a teaspoon; on days 4-5, in the absence of abdominal bloating and normal peristalsis, Diet No. 0A and 2 soft-boiled eggs are prescribed; on days 6-8 Diet No. 0B ; on days 9-11 - Diet No. 0B .
- Diet No. 0A . Contains 5-10 g of proteins, 15-20 g of fats and 180-200 g of carbohydrates. The volume of free liquid is 1.8-2.2 l, sodium chloride is no more than 1-2 g. The energy value of the daily diet varies between 760-1020 Kcal. Food is served in liquid form. Fractional diet - up to 7-8 times a day and the amount of food per meal is no more than 250 g. The diet includes mucous decoctions with cream, light low-fat meat broth, fruit and berry jelly/jelly, sweet rosehip decoction, fruit and berry juices . Dishes with a pureed and dense consistency, drinks containing carbon dioxide, and whole milk are completely prohibited.
- Diet No. 0B . Contains 40-50 g of protein, 50 g of fat and 250 g of carbohydrates. The volume of free liquid is up to 2 l/day, sodium chloride is no more than 4-5 g. The energy value of the daily diet is 1580-1650 Kcal. Food is prepared in liquid/puree form. Diet - up to 6 times a day, portion size should not exceed 400 g. In addition to the permitted products of Diet No. 0A , the diet is expanded by adding mucous cereal soups cooked in vegetable broth, soft-boiled eggs, liquid pureed rice and buckwheat porridges cereals, protein steamed omelettes, pureed dietary meat and fish, sweet berry jelly.
- Diet 0B . It is a diet of a transitional stage to subsequent physiologically complete nutrition. Contains 80-90 g of protein, 70 g of fat and 320 g of carbohydrates. The volume of free fluid is 1.5 l/day. Sodium chloride no more than 6-7 g. The energy value of the daily diet is 2100-2400 Kcal. Food is served in puree form. Diet: 5-6 times a day. The diet additionally includes cream/mashed soups, pureed steamed meat and fish, pureed cottage cheese with cream, fermented milk drinks, baked apples, pureed fruit/vegetable puree and 50-75 g of white crackers.
The duration of each surgical diet is 2-4 days, but, if necessary, the time spent on them can be lengthened or shortened. That is, approximately, after 9-12 days, the surgical diet after the operation ends, and the patient is transferred to the standard Diet No. 1 according to Pevzner (mashed version), which limits the amount of food consumed at one time: no more than 250 g of the first pureed dish or a glass of liquid (250 g), and for lunch - only two dishes. Meals are fractional, 5-6 times a day.
The diet contains an increased amount of protein (100-110 g), which includes dishes from boiled minced meat, boiled fish, fresh mashed/calcined cottage cheese, and egg white omelettes. The amount of fat in the diet is at the level of physiological norms or several times higher (80-90 g). If the patient does not tolerate fats well (and in their pure form too), which is manifested by bitterness in the mouth, regurgitation, diarrhea, their quantity is limited to 60-70 g. The carbohydrate content is reduced to 300-320 g due to easily digestible carbohydrates.
In some cases, in particular with dumping syndrome , manifested by dizziness , weakness, palpitations , chills, a feeling of heat, abdominal pain and bloating, diarrhea that appears after eating, it is necessary to completely eliminate foods containing sugar, since the consumption of easily digestible carbohydrates is one of the reasons for its appearance.
To slow down the evacuation of food from the gastric stump, it is recommended to consume viscous and jelly-like foods. You can practice separate meals of dense and liquid consistency, starting with dense ones, as well as eating in a lying position. Eat food in even small portions 6-7 times a day. After eating, you need to lie/recline in bed for 30-40 minutes. You can also practice eating butter before eating carbohydrate foods, which inhibits the removal of food from the gastric stump. If whole milk is poorly tolerated, it is excluded from the diet and replaced with other products.
Strong broths based on meat, mushrooms and fish, fatty red meat and fish, some types of birds (duck, goose) and products based on them (sausages, canned food, ham, smoked meats), fried foods, dough products are completely excluded from the diet. , fresh bread, savory snacks, salted fish and vegetables, solid animal fats, undiluted raw vegetables and fruits.
If the patient feels well, 3-4 months after the operation, he is gradually transferred to the unprocessed version of Diet No. 1 . The diet is physiologically complete, contains an increased amount of proteins and an almost normal amount of fats and complex carbohydrates. The restriction applies to simple carbohydrates in order to prevent the development of dumping syndrome. Culinary methods of processing products are preserved: the products are boiled or steamed, and after boiling, baked or stewed. In terms of the range of products, the diet of this diet option is more extensive, but the rules and restrictions are the same.
It is allowed to eat low-fat meat soups, borscht, cabbage soup (once a week), dried wheat bread, low-fat fish and beef, chicken dishes, and savory cookies. It is allowed to eat boiled and raw vegetables, garden herbs, fermented milk products, dishes based on buckwheat and rice, potatoes, mild low-fat cheese, dietary varieties of sausages, fresh fruits and berries.
In the absence of complications and satisfactory gastrointestinal function, 6 months after surgery, the patient can switch to a normal diet, but taking into account the diet and the characteristics of the chemical composition of the diet. It is possible to independently adjust the set of food products in the diet, taking into account individually intolerant foods. With a significant loss of body weight (by 10-15%) after gastrectomy, especially for cancer, the calorie content of the daily diet should be increased compared to the physiological norm by increasing the content of basic nutritional nutrients recommended for the diet.
peptic ulcer occur, a pureed version of Diet No. 1 , and in case of exacerbation - sequentially No. 1A and 1B with changes made to them taking into account intolerance to certain foods. In general, the nutrition of patients with diseases of the operated stomach must be individualized.
It is advisable to include specially developed dietary nutritional mixtures in the diet after gastric surgery - “ Nutrizon ”, “ Nutridrink ”, “ Berlamin Modular ”, which should be administered in small portions, possibly diluted with water, with constant assessment of their tolerability.
Dietary nutrition must necessarily include taking vitamin-mineral complex tablets, drugs that normalize the motor-evacuation function of various parts of the gastrointestinal tract and drugs containing enzymes to improve digestion processes ( Creon , Mezim-Forte ). Complete rehabilitation of patients is long-term and usually occurs by the end of the first year after surgery.
Diet
Proper nutrition allows you to avoid most gastrointestinal pathologies and, accordingly, prevent the development of foci of intestinal metaplasia. Nutrition and diet are considered correct if the following conditions are met:
- reducing the amount of carbonated drinks, spicy and smoked foods, salty and refined foods that negatively affect the condition of the mucous membranes;
- increasing the amount of cereals, bread, vegetables, fruits consumed;
- consumption of boiled lean meat.
Diet
Patients with this disease are recommended to follow a diet for metaplasia. Nutrition should be healthy and balanced. It is necessary to exclude all unhealthy foods, including fried, fatty, spicy and sweet. You should also avoid dairy products because... they are not processed properly in the stomach, and then wander in the intestines with consequences. Your daily diet must include cereals, fresh fruits and vegetables.
A split diet is recommended, including 5-6 meals per day. The serving size should be small: approximately the size of one glass. The last meal should be no later than two hours before bedtime: night snacks put a lot of stress on the gastrointestinal tract.
A mandatory rule for patients with intestinal metaplasia of the stomach is a complete cessation of alcohol and smoking. Bad habits can provoke and accelerate the development of various pathological processes in the human body.
Thus, intestinal metaplasia is a truly dangerous pathology, which brings a lot of discomfort and, as it progresses, leads to the development of oncopathology. Therefore, it is necessary to consult a doctor as quickly as possible, diagnose the pathology in order to begin timely comprehensive treatment under the supervision of a qualified specialist.
Successful eradication reduces the rate of progression of intestinal metaplasia, but, unfortunately, does not lead to its reverse development.
Limiting the consumption of harmful substances
Reducing the amount of alcohol consumed will reduce the negative impact on the stomach and avoid damage to the epithelium in the membrane. If abused, gastritis will be a mild problem, and the most dangerous will be a malignant tumor.
If you do not follow basic rules, a gentle nutritious diet, and refuse to lead a healthy lifestyle, you can provoke the development of serious pathologies. If any suspicious signal occurs indicating a malfunction of the stomach, intestines or the entire gastrointestinal tract, you should consult a specialist for advice.
Forecast and preventive measures
Surgery may be required in advanced forms of the disease.
Eliminating pathological manifestations in the gastrointestinal tract forever is problematic. With early diagnosis and the required therapy, it is possible to stop metaplasia and relieve painful symptoms. The advanced form of the disease requires surgical intervention, otherwise the prognosis is unfavorable. In severe cases of the disease, cancer develops.
Regular prevention helps prevent metaplasia from occurring. It is recommended to limit the consumption of fatty and unhealthy foods and give up alcohol. Stress factors predispose to the progression of pathology, so they should be avoided. By following the rules of hygiene, it is possible to reduce the risk of infection with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, which serves as a trigger for the development of gastric abnormalities.