How to prepare for gastroscopy of the stomach in the morning
When prescribing FGDS for the first half of the day, especially careful preparation begins in the evening.
Before this, the patient is recommended to follow a standard diet before gastroscopy (it will be discussed a little later), and on the eve of the procedure it is necessary to switch to the lightest possible diet. Breakfast and lunch the day before the examination should consist of light dishes, and for dinner, the diet before FGDS prescribes eating only light, quickly digestible dishes: cottage cheese casserole, pureed vegetables or stew. Standard preparation for gastroscopy in the first half of the day contains only one point: you should not have breakfast before the procedure. Even coffee and tea are banned. You can only drink 100-150 ml of water 2-3 hours before the diagnosis. If you plan to conduct an examination under anesthesia, you should not drink at all.
How you feel during gastroscopy and the degree of likelihood of complications directly depends on the accuracy of your preparation in the morning. If the patient prepares, ignoring the listed conditions, there is a possibility of strengthening the gag reflex. This is fraught not only with discomfort for the patient himself, but also entails the danger of vomit getting into the respiratory tract. In addition, the presence of food and liquid debris in the stomach makes visualization of the mucous membranes difficult
That is why such close attention is paid to preparation on the day of the study.
Local procedures
In addition to general recommendations, there is a list of local procedures that can increase the information content and safety of fibrogastroduodenoscopy. These include:
Examinations for the presence of diseases of the upper respiratory system (tonsillitis, ARVI, etc.), as well as the oral cavity (caries). They can lead to an increased risk of infection of the esophagus and stomach during the procedure due to mechanical introduction of infection. In this regard, all such diseases, if detected, must be treated appropriately.
>Doctor examines throat
- Gastric emptying. The endoscopic procedure can be scheduled for the morning, or for the second half of the day. In the first case, the meal should be completed the evening before, and if endoscopy is carried out in the afternoon and late afternoon (from 13:00 to 18:00), then the patient can have a light snack in the morning. But before the study, his stomach may be pumped out. As a rule, such measures allow FGDS to be performed on an empty stomach, which significantly improves visibility during examination, and therefore increases information content and reduces the number of possible diagnostic errors.
- The use of local anesthetics (lidocaine-based sprays, etc.) before the procedure reduces the sensitivity of the oral mucosa to the inserted endoscope and reduces the urge to vomit. This allows you to achieve psychological comfort for the patient during the study.
It is important to note that all of these recommendations are mandatory for patients. Moreover, if a person takes any medications, he should consult about them with his doctor.
There are also a number of features in preparing for gastroscopy in people with somatic diseases. For example, all patients with diabetes should be tested at the earliest possible time of day, since prolonged fasting can lead to a significant decrease in blood glucose levels.
Diet before FGDS
On the eve of FGS, preference in eating is given to easily digestible foods. The optimal time between the last meal and the endoscopic examination is 7-8 hours. Moreover, even during the last day before gastroscopy, the patient is recommended to exclude the following foods from his diet:
- Spicy dishes with a lot of spices or seasonings.
- Whole grains and pasta from durum wheat.
- Flour and confectionery products.
- Fatty meats or fish.
- Salted and smoked products.
- Alcohol.
It is also important to stop smoking on the day of the study. All of these products and tobacco contribute to irritation of the mucous membrane of the esophagus and stomach, and the production of large amounts of mucus
This will complicate the study and may lead to a picture of gastritis, which in fact will be temporary, as it will go away on its own within 24 hours.
Meals on the day before gastroscopy should consist of small portions and contain only “light” dishes. The food temperature should be comfortable, close to room temperature, the amount of salt or other flavoring additives should be minimal or completely absent. The patient can consume milk and milk-based products, lean meats and fish, boiled eggs, vegetable and chicken broths, etc.
Foods you shouldn't eat
Preparation for gastroscopy of the stomach necessarily includes a number of restrictions regarding diet. Three days before gastroscopy, do not consume foods that can damage the mucous layer of the stomach - spicy, hot dishes with spices and seasonings. For the same reason, it is prohibited to drink alcoholic beverages that can lead to the appearance of gastritis during the examination.
What can’t you eat besides “aggressive” foods? In the period two days before the procedure, it is necessary to exclude from the diet:
- Meat and fish with high fat content.
- Any fast food products (they can be eaten 2-4 days before the examination).
- Products that have been smoked, pickled or salted.
- Any type of mushroom, regardless of cooking method.
- Before FGDS, the patient should not eat any types of sauces or ketchups.
- Many drinks cannot be drunk before the study, primarily strong coffee, soda, etc.
You should stop drinking carbonated water
The list of foods that you need to give up in a shorter period of time (24 hours) is as follows:
- Various types of cereals and legumes.
- Dairy products, including cottage cheese, butter, etc.
- Eating confectionery and flour products, including pasta, is not allowed.
- The patient should not eat a number of vegetables and fruits: citrus fruits, quince, tomatoes.
What does improper preparation and standard complications lead to?
If the patient’s preparation for fibrogastroduodenoscopy was incorrect, the result may be erroneous. In addition, nausea and vomiting, belching and bloating may occur. In case of low visibility, due to improper preparation, injuries to the mucous membranes of the esophagus and stomach are possible.
The most severe and rare complications include asphyxia, but this occurs mainly if the patient took drugs that, together with anesthesia, caused a severe allergic reaction.
Standard complications include:
- Pain in the larynx. This occurs due to mechanical damage to the organs by the tube, especially when breathing improperly and ignoring doctor’s advice. Unpleasant sensations may occur during swallowing for several days. To speed up healing, it is better to avoid irritating foods.
- Bleeding in the esophagus, stomach, intestines in places of injury to the walls.
- Perforation. Occurs rarely.
- Laryngotracheitis, hoarseness.
- Allergic reactions.
- Jaw injuries are a very rare occurrence.
- Pain at the biopsy site.
- Injury to the gastrointestinal tract. May occur with sudden movements of the patient.
Moral preparation for the procedure
It is very important to learn to control your emotions before and during the procedure. The calmer the patient, the easier it is for the doctor to work
In addition, if the patient is relaxed, the probe advances easier and the pain of the manipulation is reduced.
Those who go for examination for the first time experience many fears, including for their lives. There is an opinion that you can suffocate while the endoscope is in the digestive tract. This is a completely incorrect and baseless judgment.
The tube does not border the respiratory tract at all, and therefore FGDS does not pose any danger.
Discomfort is largely associated with the process of pumping air to straighten the walls and obtain a clear picture. There is no way to avoid this, but understanding these simple truths, you can go through the procedure with confidence and without a grain of doubt.
Some patients are advised to administer local anesthesia to quell panic. In fact, the procedure is completely painless and there is no need to use the drug. On the contrary, after using it, it is difficult for the patient to swallow and breathe, as the treated surface becomes numb.
Preparation for FGDS: the essence of the examination, contraindications and general rules
To make the correct diagnosis of diseases of the stomach and duodenum, various instrumental diagnostic methods are used. One of the most accurate and informative research methods is fibrogastroduodenoscopy (FGDS) or gastroscopy. This procedure is carried out using an endoscope, which allows the specialist to literally look into the internal organs of a person.
The endoscopic technique is not hazardous to health, but may cause discomfort to the patient. To minimize psychological discomfort, you should prepare for FGDS in advance. In addition to the patient’s psychological mood, there is a whole list of requirements for preparing for the study. Provided you follow all the doctor’s recommendations, the procedure will be quick, painless and successful.
The essence of the examination
An endoscopic examination is performed if there is a suspicion of peptic ulcer of the stomach, duodenum, gastritis, duodenitis and a number of other pathologies of the digestive organs. A routine examination using FGDS is carried out in the process of preparing a patient for a long-term surgical intervention, as well as in the presence of serious pathologies in the liver, gall bladder or pancreas.
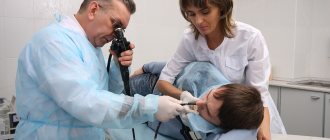
The procedure is performed using special equipment. An endoscope is a flexible tube about ten millimeters thick. The end of the tube is illuminated. During the examination, it is inserted into the patient’s digestive tract, and the specialist can see the organs in detail. The procedure lasts on average ten minutes.
FGDS is carried out only after preparing the patient for the study. The presence of food or water in the digestive organs will make the procedure impossible. In addition, there are a number of contraindications to gastroscopy, so such a study is not suitable for every person.
Contraindications
For a number of diseases, FGDS is strictly prohibited. Patients with the following pathologies are not allowed to undergo the procedure:
- severe curvature of the spinal column;
- aortic aneurysm, tumor and other diseases that displace the esophagus;
- blood clotting disorder;
- esophageal stenosis;
- severe conditions after a myocardial infarction or stroke;
- bronchial asthma in the acute stage;
- enlarged thyroid gland;
- during and after a hypertensive crisis.
The procedure is performed in extreme cases if the patient has:
- enlarged cervical lymph nodes;
- angina pectoris;
- mental disorders;
- third stage hypertension;
- acute inflammation in the pharynx or larynx.
The presence of contraindications does not always prevent the procedure from being performed
FGS is done in cases where the importance of the examination outweighs the risks to the patients’ health. In this case, general anesthesia may be used to minimize the risk of accidental injury.
How to prepare for the examination
Fibrogastroduodenoscopy is prescribed in advance so that the patient has time to prepare for it. The doctor explains in detail to the patient how this needs to be done correctly and talks about the procedure itself. Preparation for the FGDS includes general and private events. General measures are aimed at the doctor identifying all possible complications that may arise during the procedure, and local measures concern the patient himself.
General preparation:
The doctor identifies contraindications and corrects conditions that are dangerous for performing FGDS. If there is a need to conduct a study, despite contraindications, the patient is sent to a hospital, where the procedure is performed under general anesthesia. If there is inflammation in the esophagus or upper respiratory tract, the infection will need to be treated first and then tested. When interviewing the patient, the doctor identifies possible allergies to anesthetics and other medications that may be used during the procedure. The patient must be informed about all allergic reactions to medications. Preparation for FGDS includes the patient’s psychological attitude towards the procedure
Many people are afraid of it, so the doctor talks in detail about how this will happen and explains the importance of the study. If the anxiety state cannot be eliminated, the patient is prescribed sedatives.
Local preparation consists of following the doctor’s recommendations:
- rules for taking medications;
- rules for eating a few days before and the evening before the procedure;
- what you need to take with you to the study;
- what can and cannot be done directly on the day of the FGS.
What not to eat after FGDS
After fibrogastroduodenoscopy has been done, patients should not eat food seasoned with any spices, fatty, smoked, fried foods, any sauces and gravies, as well as foods that contain small seeds and a lot of acid. Such food irritates the mucous membranes and can provoke severe discomfort and exacerbation of the disease for which FGDS was performed.
The list of foods prohibited for consumption includes those that take a long time to digest, cause gas formation, and place a heavy burden on the gastrointestinal tract:
- mushrooms;
- White cabbage;
- cucumbers;
- baked goods, fresh baked goods;
- marinades and pickles;
- coffee, strong tea;
- carbonated drinks;
- rich broths from meat and fish;
- sausage.
The minimum period when you can eat the listed products without risk to health is at least 2 weeks, and if there are problems during the FGDS, you should refrain from consuming them for 1-2 months.
How to prepare for gastroscopy of the stomach
In consultation with a doctor before performing an FGDS, you must inform about:
- all chronic and other diseases;
- temporary ailments;
- medications taken.
The health worker, in turn, must:
- find out if there are any contraindications to the procedure;
- carry out tests for allergic reactions to anesthetics;
- tell in detail about the stages, algorithm and features of the manipulation;
- if necessary, review the patient’s medical history and tests.
The “Stomach Hurts” channel has prepared a video that offers a list of indications and contraindications for performing an FGDS.
For gastroscopy to be painless and quick, you need to properly prepare for the procedure in the morning, which is often scheduled for the first half of the day.
In this case you cannot:
- brush your teeth;
- use chewing gum;
- do an ultrasound or other examination.
It is advisable to do light exercises or yoga the day before. According to indications, preparation for FGDS in the morning may include taking enzymatic preparations to activate the stomach and eliminate flatulence.
Proper diet
Preparation for FGDS is, first of all, dietary nutrition.
Two days before the test you need to stop eating spicy, smoked and fried foods. These foods irritate the stomach lining and increase acidity levels. A complete list of foods that should be excluded from the diet in a few days in order to properly prepare for fibrogastroscopy:
- alcohol;
- seeds;
- chocolate;
- oatmeal;
- carbonated drinks.
To calculate how many hours before FGDS you are not allowed to eat, you need to consider that:
- products (except those contraindicated) are completely processed by absolutely healthy organs of the digestive system within 8 hours;
- if a person is diagnosed with problems with the gastrointestinal tract, at least 10-12 hours must pass between the last meal and the procedure;
- when such an examination is scheduled for the morning, it is rational to take the last meal at about 8 o’clock in the evening the day before;
- In the evening you need to eat at least 4 hours before bedtime.
FGDS is effective only if the patient has no food residues in the stomach and on the walls of the esophagus.
What can you eat?
A light dinner may include:
- buckwheat or rice porridge with water;
- boiled chicken meat;
- lean fish;
- stewed or boiled vegetables;
- fruits;
- fruit drinks from berries.
What can't you eat?
12 hours before the examination, the doctor will strictly prohibit:
- legumes;
- dairy products;
- bread;
- mushrooms;
- fat meat;
- fish;
- nuts;
- fresh vegetables.
Legumes, nuts and seeds take several days to digest, and fresh vegetables cause increased gas formation. These factors make research difficult, often making it impossible.
Rules for eating
General nutritional recommendations include:
- consume foods only in small portions;
- the number of meals per day should be at least 5 times;
- exclude foods that cause flatulence from the menu;
- In case of increased gas formation in the stomach, take enzyme medications for 3 days as prescribed by your doctor.
The last meal should be 4 hours before bedtime and consist of dishes that are quickly absorbed in the stomach.
A light dinner in the evening on such a diet usually consists of the following dishes:
- fish with stewed vegetables;
- chicken breast with buckwheat porridge;
- oatmeal;
- baked apples and white bread crackers.
It is important to know that FGS diagnostics are carried out only on an empty stomach, so you should never have breakfast on the day of the procedure. In addition, it is not recommended to brush your teeth in the morning after waking up, as this can lead to the production of mucus in the stomach.
In the morning, 3-4 hours before the diagnosis, you are allowed to drink a glass of mineral water without gases or strong tea, to which you can add a little milk. The amount of liquid you drink in the morning should not exceed 150 ml.
After the end of FGDS, unpleasant sensations arise in the throat, such as burning and discomfort, and the incoming parts of the esophagus ache. And the question immediately arises - how long can you not eat after gastroscopy? Experts note that eating food right away is strictly prohibited. In addition, only a doctor can assess the situation.
But usually, depending on the condition, the patient is allowed to eat after about 1 hour or 30 minutes. after the procedure. The food consumed should be soft and light, and not overload the stomach. Such products include:
- light soups;
- yoghurts and kefir;
- porridge;
- puree.
You can drink water after FGDS; it will not cause any harm to the body.
How to prepare for fibrogastroscopy?
The preparatory process for FGDS is not particularly complicated, but it does require careful implementation of all of the above points. Firstly, checking the mucous membranes of the organs should be carried out strictly on an empty stomach - even a small amount of food will cause a copious secretion of gastric juice. This will not only prevent you from getting informative results, but can also cause nausea and even vomiting.
Therefore, the patient needs to check in advance with the doctor or in the diagnostic office how long before the examination he should not eat or drink. As a rule, you need to abstain from food for at least 10–12 hours and from drinking liquids for at least 2 hours. Optimally, if FGS is scheduled for the morning, then the last meal should be no later than 18.00, and in the morning you can drink a glass of still water or weak tea. When preparing for FGS, you should not eat slowly digestible foods - nuts, seeds, chocolate
Dinner on the eve of a gastroscopic examination should be light and quickly digestible, and for 1-2 days before the scheduled examination, you should avoid foods that are slowly digested - chocolate, nuts, seeds. The second important point for a certain group of patients will be an absolute cessation of smoking at least 4–5 hours before FGDS. This is due to an increase in the secretory function of the gastric glands when smoking just one cigarette.
On the day of the examination, in the morning, in addition to the above, you should not brush your teeth or chew gum, as these actions also lead to an increase in the secretion of gastric juice. If the person being examined is taking a course of vital medications, then you must first consult with a doctor about the possibility of stopping them for several hours.
If you have an allergic reaction to the anesthetic used, be sure to report it in advance so that the diagnostician can offer an alternative option. It is also worth warning about possible difficulties with swallowing the endoscope - in such cases, the procedure is carried out under anesthesia.
There are several types of anesthetic drugs used, differing in properties and effects on the body. Familiarize yourself in detail with the options and features of performing FDGS under anesthesia
Here.
Preparation for FGDS of the stomach: recommendations, diet
ass=”align-left”>How to properly prepare for FGDS and in what cases is it possible to conduct research?
For the procedure to be successful, the patient must:
- receive referrals from a doctor, medical insurance and passport;
- wear loose clothing with a loose collar and belt;
- take a towel to remove saliva;
- give written consent to the procedure;
- carry out the necessary preparation before the FGS;
- notify the doctor about the presence of allergies to medications (preparation before FGDS involves irrigating the throat with anesthetics that reduce the gag reflex).
If, for good reasons, the doctor decides to perform gastroscopy under anesthesia, then FGS preparation is carried out according to an individual plan and the doctor’s prescriptions.
When an FGDS is prescribed, how to prepare so that food residues in the stomach do not distort the examination results? Preparation for FGDS of the stomach does not involve a special menu. During normal digestion, the stomach takes 8 hours to digest food without leaving any residue. But some foods take longer to digest.
Therefore, when preparing for gastroscopy, it is undesirable to consume the following products:
- chocolate, sweets;
- alcoholic drinks;
- seeds, nuts;
- salads;
- spicy dishes.
During the period when preparation is underway (FGDS is prescribed in advance), eat low-fat foods, steamed or boiled foods.
Photo: Blok B., Shahshal G., Schmidt G. Gastroscopy. - M.: MedPress-Inform, 2015. - 216 p.: UGC
write that endoscopic methods practically eliminate diagnostic errors. Therefore, study the recommendations for preparing for the procedure and calmly conduct meaningful research. Be healthy!
Attention! The material is for informational purposes only. You should not resort to the methods described herein without first consulting your doctor.
- Emma Swerden. Acute upper gastrointestinal bleeding // BMJ. — 2018. — 25 October. - Access mode:
Reviewer: Candidate of Medical Sciences, Professor Ivan Georgievich Maksakov
00:47
2020-09-25
Features of table No. 1
In general, nutrition after FGDS corresponds to dietary table No. 1, which is used for diseases of the stomach and duodenum. This diet, in addition to restrictions on the choice of foods, has a number of features that take into account the calorie content of food, portion size, and diet. She prescribes following a special regimen after gastroscopy:
- You can only cook boiled, stewed and steamed dishes;
- for the first 2-5 days, food should be well ground or pureed until smooth;
- the dishes contain a minimum of salt and are completely free of spices;
- Dishes should not contain refined sugars or a lot of fat.
The daily diet should contain 1500-2800 kcal, divided into 5-7 meals. The serving size per serving is 200-250 ml. Food should be slightly warm, not hot or cold. In addition, you should pay attention to your drinking regime. You can drink at least 2 liters of liquid per day: tea, juices, plain water, mineral water without gases.
Important! In the first days after FGDS, you should carefully listen to the sensations in the stomach and intestines. If some dishes provoke discomfort, you should not eat them. It is also worth adjusting the portion size depending on individual characteristics: you can eat a little more or less.
Why is an endoscopic examination of the gastrointestinal tract performed?
A diagnostic study of the digestive system using a gastroscope is used to study the condition of the mucous membranes - this makes it possible to identify various ulcerations, inflammations and tumor-like formations. Examination methods such as computed or magnetic resonance imaging, radiography and ultrasound are not able to provide a clear picture of the ongoing pathological processes. Gastroscopy allows the attending physician to literally “look” into the patient’s internal organs.
Indications for its implementation are:
- esophagitis – inflammation of the esophageal mucosa;
- gastroesophageal reflux pathology is a recurrent disease that is caused by the “reflux” of gastric contents into the esophagus;
- some types of hernia (protrusion of internal organs through a defect in the peritoneum);
- gastrointestinal bleeding;
- study of changes in mucous membranes that can lead to the development of cancer;
- diagnosing a pathological process in which loss of appetite, flatulence, pain in the upper gastrointestinal tract, problems with swallowing food, and weight loss are observed;
- disruption of the movement of food to the intestines;
- monitoring the course of peptic ulcers and cancer;
- monitoring the patient's condition after surgical interventions on visceral organs.
Preparing for gastroscopy - how much you should not eat and drink before endoscopic examination
Table of contents
Gastroscopy is a modern instrumental method for studying the upper gastrointestinal tract (gastrointestinal tract): stomach, esophagus, pyloric sphincter, duodenum. Diagnostics have been carried out for many years and make it possible to identify a wide range of different diseases and pathological conditions. Until recently, research was very unpleasant and even painful. Today, the procedure is carried out using a flexible fiber gastroscope, which follows all the bends of the esophagus, which reduces discomfort. During the examination, miniature instruments (optics and LEDs) are also used. This also reduces any discomfort for the patient. It is also important that gastroscopy can be performed under anesthesia. This completely eliminates all risks of any discomfort.
The information content of the procedure largely depends on proper preparation.
That is why the patient must be informed in advance about certain rules. We recommend that you read them and strictly follow them.
Preparing for the procedure in the morning
If the test is carried out in the morning, the patient will have to refuse food in the evening. It is forbidden to consume even easily digestible foods, as they can cause a decrease in diagnostic information.
Also, preparing for gastroscopy of the stomach almost completely eliminates drinking.
The patient is allowed to drink no more than 100 ml of water 3-4 hours before the examination.
Local anesthesia during fibrogastroduodenoscopy
Gastric endoscopy was previously performed without anesthesia. However, at the moment, before the study, all patients are given local anesthesia. After all, the most unpleasant part of fibrogastroscopy is the insertion of an endoscope into the stomach, which has a rather large diameter.
The anesthetic is sprayed onto the root of the tongue, which effectively suppresses the gag reflex that appears when the device is advanced. Under the influence of the drug, there is a strong decrease in sensitivity and numbness of the tissues. The procedure is easy and painless.
The advantage of local anesthesia is its accessibility to the general public. It can be performed on an outpatient basis as it does not require special equipment.
Before administering the drug, the patient is tested for individual intolerance. Indeed, in the presence of an allergic reaction, there is a high risk of developing Quincke's edema, since the medicine is sprayed onto the mucous membrane of the throat and the root of the tongue.
The test is mandatory for patients who have predisposing factors to the development of a hypersensitivity reaction:
- tendency to allergies of various etiologies;
- history of atopic dermatitis or vasomotor rhinitis, bronchial asthma;
- registered allergic reaction to any drug.
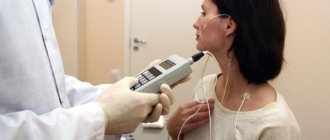
How are ultrasound and FGDS studies carried out?
Ultrasound is classified as a non-invasive method for examining an organ, that is, diagnosis takes place without penetrating the internal environment of the body.
Transabdominal method - through the anterior abdominal wall.
The patient removes clothing from the upper part of the body and lies with his back on the couch. The doctor lubricates the skin of the epigastric area with a special gel for better skin contact with the sensor. Using smooth pressing movements, the piezoelectric sensor is moved along the projection zones of the stomach (epigastric, left hypochondrium).
Ultrasound with a water-siphon test is performed to study the motor function of the stomach. The patient drinks 0.5 liters of water through a straw to prevent air from being swallowed into the stomach. The sensor is installed in the area of the projection of the pylorus (the transition of the stomach to the duodenum) and muscle contractions of the sphincter are recorded for 15-20 minutes. The data obtained allow us to assess the degree of preservation of gastric motor function.
Fibrogastroduodenoscopy (FGDS) is a method of obtaining information about the condition of the initial parts of the gastrointestinal tract (stomach, duodenum) using a fiber-optic system. A probe is inserted into the patient through the esophagus into the stomach, at the end of which a video camera is mounted, which transmits to the monitor a real picture of the organs being examined. The video recording is saved, which makes it possible to conduct a comparative analysis of the results.
The study is carried out under local anesthesia with solutions of lidocaine and dicaine.
During endoscopy, the patient is positioned on the left side. After anesthesia of the oropharynx, a plastic ring is inserted into the mouth to prevent damage to the probe as a result of closing the jaws
The doctor, under visual control, carefully moves the probe to the esophagus and asks the patient to take a deep breath, while the mouth of the esophagus reflexively opens. As the endoscope moves, small portions of air are introduced to straighten the folds
According to a special scheme, all parts of the stomach are sequentially studied.
If no therapeutic manipulations are performed during the procedure, it is completed in 10–15 minutes, then the probe is smoothly removed from the digestive tract.
Both procedures are performed on an empty stomach. Preliminary preparation significantly increases the diagnostic capabilities of the methods. The main goal of preparation is the absence of food masses and gas in the stomach.
The patient is prescribed a diet for 2-3 days with the elimination of fried, fatty, spicy foods. Exclude from the diet foods that contribute to increased gas formation: fresh vegetables, fruits, legumes, nuts, seeds. Limit the consumption of sweets, brown bread, baked goods, juices, dairy products, carbonated drinks, and alcohol.
Before the procedure, you should not smoke, as toxic combustion products of tobacco irritate the gastric mucosa, causing increased mucus production. Chewing gum is also not recommended - it can trigger the production of gastric juice as a reflex.
What pathologies can be seen during ultrasound?
Previously, before the introduction of ultrasound into medical practice, fluoroscopy was used to diagnose stomach diseases. Doctors are often asked the question: which is better at detecting pathology, an X-ray of the stomach or an ultrasound? Fluoroscopy is prescribed for contraindications to FGS, and although X-ray with contrast is an informative diagnostic method, it is unsafe, since its use exposes the patient to radiation.
The use of ultrasound is completely safe, but its diagnostic capabilities are limited, so it is combined with some other method of identifying gastric pathologies.
Ultrasound examination is a diagnostic method based on such a physical phenomenon as echolocation. Ultrasound is reflected differently by body tissues. An ultrasound machine detects sound vibrations reflected from tissues and transforms them into a graphic image on the monitor screen.
Previously, ultrasound of the stomach was rarely used in medical practice, since the stomach is a hollow organ filled with air, which almost completely reflects sound waves, and it was almost impossible to obtain information about the internal structure. High-resolution instruments are now used, which have many additional functions compared to standard models.
Diagnostic capabilities of gastric ultrasound:
- neoplasms: benign, malignant;
- diaphragmatic hernia;
- pyloric stenosis or incompetence;
- erosions and ulcers of the mucous membrane;
- swelling and thickening of the gastric walls;
- foreign bodies;
- changes in regional lymph nodes and blood vessels.
What does improper preparation and standard complications lead to?
If the patient’s preparation for fibrogastroduodenoscopy was incorrect, the result may be erroneous. In addition, nausea and vomiting, belching and bloating may occur. In case of low visibility, due to improper preparation, injuries to the mucous membranes of the esophagus and stomach are possible.
The most severe and rare complications include asphyxia, but this occurs mainly if the patient took drugs that, together with anesthesia, caused a severe allergic reaction.
Standard complications include:
- Pain in the larynx. This occurs due to mechanical damage to the organs by the tube, especially when breathing improperly and ignoring doctor’s advice. Unpleasant sensations may occur during swallowing for several days. To speed up healing, it is better to avoid irritating foods.
- Bleeding in the esophagus, stomach, intestines in places of injury to the walls.
- Perforation. Occurs rarely.
- Laryngotracheitis, hoarseness.
- Allergic reactions.
- Jaw injuries are a very rare occurrence.
- Pain at the biopsy site.
- Injury to the gastrointestinal tract. May occur with sudden movements of the patient.
How to easily undergo a gastroscopy
Not all people tolerate the study well. Statistics show that painful sensations rarely occur, because modern endoscopes are small and thin. But often a gag reflex occurs, interfering with the normal procedure. In order for gastroscopy to be as comfortable as possible, experts advise you to behave correctly. They make the following recommendations:
- Choose comfortable clothing for the procedure that will not restrict movement.
- Relax. Fear contributes to excessive tension in the muscles of the esophagus. This interferes with the free passage of the gastroscope. People with increased nervousness may be offered sedatives.
- Breathe correctly (through your nose only). If you breathe through your mouth, saliva can enter your respiratory tract and cause a cough. Breathing should be deep and even, inhalation and exhalation should be slow. This eliminates the gag reflex. The patient experiences only unpleasant sensations from a foreign body in the esophagus and stomach. The procedure is easiest for people who do breathing exercises.
Nowadays, medical equipment is constantly being improved, so a modern endoscope causes minimal inconvenience. To prevent the probe from biting, the doctor uses a plastic mouthpiece.
Gastroscopy is a popular and informative diagnostic method that allows you to detect pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract even at an early stage of development. The method has been successfully used in gastroenterology for many years.
This article is posted for educational purposes only, does not replace an appointment with a doctor and cannot be used for self-diagnosis.
April 19, 2019
Additional recommendations
Conversation with a doctor
Be sure to warn your doctor about the following factors:
- Before inserting the probe, the doctor sometimes treats the mucous membrane of the larynx with a special anesthetic. The active substance of the anesthetic may vary. Therefore, you should warn the diagnostician about existing allergic reactions to one or another component.
- Before gastroscopy, it is necessary to tell the doctor about chronic diseases, despite the fact that concomitant diseases are not a contraindication for examination of the organ. If gastroscopy is performed with a biopsy, exacerbations and relapses may occur, depending on the type of disease.
- If a woman carrying a child is undergoing gastric endoscopy, the doctor should be warned about this, especially in the first months of pregnancy. In this case, the doctor selects safer anesthetics.
- Be sure to tell the specialist if you had a gastric biopsy or any surgical intervention less than a month ago. This factor can become a serious contraindication for gastroscopy, since after a biopsy the mucous membrane of the organ is very vulnerable, and the examination will harm the patient.
Examination of the stomach if you feel unwell
Sore throat, runny nose, cough and other cold symptoms are not a contraindication to endoscopic examination.
However, during gastroscopy, the patient feels insecure and constrained, and experiences fear. Debilitating symptoms of the disease can significantly worsen the situation
If you are not feeling well or even in a bad mood, experts advise postponing preparation for gastroscopy until you have fully recovered.
Moral preparation
When examining the stomach, mental preparation for manipulation is necessary. This is due to the fact that when the patient is in a calm state, the procedure is much faster and is considered more informative.
Worries about whether the examination is painful, whether the procedure can provoke vomiting, how to properly prepare for gastroscopy and other important aspects can put pressure on the patient’s psyche, which is why many refuse the examination. To set a person up, the doctor needs to tell him how gastric endoscopy is performed, why it is needed and what consequences are possible.
Those who have undergone this procedure claim that gastroscopy is absolutely painless. On average, the procedure lasts 5-20 minutes. To reduce the sensitivity of the root of the tongue, doctors in some cases use anesthetic agents. This is necessary to suppress the urge to vomit.
The main task of the specialist is to calm the patient. The patient's anxious state can lead to involuntary compression of the esophagus, and, as a result, to difficulties during the examination.
Don't be afraid and don't worry. FGDS, although unpleasant, is an absolutely painless study, which an experienced specialist does quickly and efficiently. Remember that this is the only way to examine the stomach and duodenum and not miss complications that threaten not only health, but also life!
What is gastroscopy of the stomach and how is it done?
This is an endoscopic method for examining the stomach and duodenum. Diagnosis is carried out using an endoscope - a flexible tube with a diameter of up to 10 mm with a video camera at the end.
The procedure is performed in a specialized diagnostic room.
If necessary, anesthesia is used, but the procedure can be performed without it. Preparation for gastroscopy and sequence of actions:
- The patient lies on his left side, bending his knees to his chest.
- A special mouth guard is inserted into the mouth so that when the jaw reflexively clenches, it does not spoil (swallow) the endoscope.
- The patient takes a deep breath to widen the esophagus tube, where an endoscope (probe) is slowly inserted.
- During diagnosis, a person breathes deeply, evenly, and tries to relax emotionally.
- The probe is moved for a detailed examination of all areas of the gastric mucosa, causing the patient discomfort and causing vomiting.
- Images of the intestinal cavity and video are recorded.
- After the examination, the endoscope is carefully removed.
- After 5 days, they provide a transcript of the gastroscopy in hand.
Gastroscopy of the stomach is prescribed for the following patient complaints:
- feeling of heaviness, fullness in the stomach after eating and without;
- pain in the epigastrium, which bothers you on an empty stomach and on a full stomach;
- bitterness, taste of a “copper coin” in the mouth;
- sour belching, heartburn;
- nausea, frequent bouts of vomiting;
- vomit containing blood and particles of undigested food.
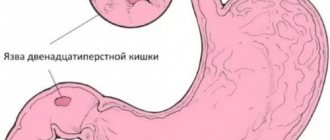
Diagnostics is necessary to establish and clarify the diagnosis. Possible diseases of the gastrointestinal tract:
- atrophic gastritis;
- stomach bleeding;
- peptic ulcer;
- polyps, malignant tumors;
- stenosis of the gastric lumen.
What can you eat the day before the examination?
It is recommended to bake food in the oven or steam. To prepare for the procedure and get accurate results, you need to normalize your diet. It should be steamed, boiled or stewed. The most useful food is pureed or finely chopped. The meat can be eaten in the form of cutlets cooked in the oven. Do not use oils or animal fat. The dietary diet for 2-3 days before FGDS should contain the following foods that do not cause irritation to the gastric mucosa, which are presented in the table:
| Group | Healthy food |
| Fish | Carp |
| Zander | |
| Cod | |
| Hake | |
| Flounder | |
| Meat | Beef |
| Chicken | |
| Turkey | |
| Rabbit | |
| Eggs | Boiled |
| Soups | Vegetables |
| With added cereals | |
| Fermented milk products | Low-fat cottage cheese |
| Whole milk | |
| Low fat sour cream | |
| Porridge | Oatmeal |
| Buckwheat | |
| Fruits | Banana |
| Figs | |
| Raisin | |
| Dried apricots |
What can you eat after gastroscopy?
Doctors recommend eating soft foods after FGDS that do not contain solid particles. The list of foods that are allowed to be consumed after gastroscopy includes:
- soft puree from boiled vegetables - pumpkin, carrots, potatoes, zucchini and cauliflower;
- milk semi-liquid porridge with semolina or buckwheat, millet (it is advisable to grind millet and buckwheat groats in a blender or grind them);
- meat soufflé, steam cutlets made from dietary meat or fish;
- steam omelette or soft-boiled eggs;
- pasta.
The list of foods allowed after FGDS of the stomach includes fresh fermented milk drinks, as well as pureed cottage cheese, freshly squeezed juices slightly diluted with water (do not take citrus), and herbal teas. Bakery products can be included in the diet, but you should choose dried white bread, dry biscuits and biscuits.
Important! When choosing what to eat for the first time after gastroscopy, you should give preference to foods and dishes with a neutral taste, without pronounced sourness or sweetness.