Causes of bleeding from the anus
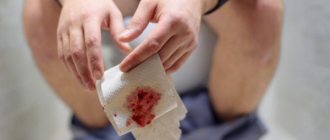
If you notice blood on toilet paper after bowel movements, even if the process of bowel movement occurs without pain, you should definitely consult a proctologist for advice in order to establish the cause of the bleeding, start treatment in a timely manner and avoid possible complications.
Why does blood appear from the anus after stool in both men and women:
- A fairly common factor is hemorrhoids (enlargement of the veins of the rectum). Scarlet blood appears from the anus during defecation.
- Anal fissure is the second most common cause of rectal bleeding. The disease is characterized by a burning sensation during bowel movements, sometimes accompanied by acute pain (patients describe it as cutting and then squeezing). Bloody discharge appears in both small and copious portions.
- Inflammatory diseases of the colon.
- The presence of benign formations (polyps). A characteristic symptom is the discharge of blood from the rectum after defecation. The blood is darker, often with mucus.
- The presence of a malignant tumor of the rectum. Blood of different colors may be released. Quite often, the blood released does not differ in any way from the blood that is released, for example, from hemorrhoidal tissue. And if the presence of hemorrhoidal disease only worsens the quality of life (hemorrhoidal tissue never degenerates into a malignant tumor), then the presence of a benign formation or a malignant tumor can be harmful to health and life-threatening, which is why you should not try to independently determine the source.
Only a coloproctologist can determine the true cause of bleeding from the anus and select the appropriate treatment. Timely diagnosis allows for effective conservative and minimally invasive treatment.
Most common reasons
Haemorrhoids
Main article: Hemorrhoids: symptoms and treatment About 10% of people in the middle age group suffer from hemorrhoids, men are susceptible to the disease 4 times more often.
Its development is facilitated by a sedentary lifestyle, heavy physical labor, and pregnancy.
At the beginning of the disease, there is discomfort and a sensation of a foreign body in the anus. Recurrent rectal bleeding then appears. They occur during defecation or immediately after it. The blood has a bright red color; it does not mix with the feces, but covers it on top. Traces of blood may be found on toilet paper and underwear. The volume of blood released varies from a few drops to a puddle. Frequent intense bleeding leads to the development of anemia.
Be sure to read:
Staphylococcus aureus in a child’s stool: is treatment needed and when?
When inflammation occurs, pain occurs during defecation and persists for some time after it.
Mucus discharge irritates the skin around the anus, causing an itchy sensation, and contributes to the development of eczema.
Anal fissure
Main article: Rectal fissure
It is a linear ulcer located in the lower part of the anal canal.
Its main symptoms are bleeding and pain that occurs during bowel movements. The pain is quite intense, burning, stabbing in nature, radiating to the perineum, sacrum, and rectum. It lasts from several minutes to several hours.
Bleeding is usually minor. In this case, the blood is on the surface of the stool in the form of stripes and does not mix with it. Sometimes blood comes out in drops at the end of a bowel movement, leaving marks on paper or underwear.
Polyposis of the colon
Polyps are benign neoplasms of epithelial nature.
They can be single or multiple, localized in any part of the colon, and are prone to degeneration into malignant tumors. The main complaints of patients with polyposis are:
- discomfort;
- abdominal pain that does not have a clear localization;
- bowel dysfunction in the form of alternating constipation with diarrhea;
- stool mixed with mucus and blood.
Bleeding with polyposis is not intense. The blood is dark, mixed with mucus and feces, however, the closer to the anus the polyp is located, the brighter the blood. Bleeding can also be hidden, and quickly leads to anemia in the patient.
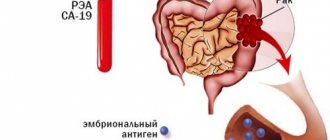
Colorectal cancer
Main article: Colorectal cancer: symptoms and treatment
Tumors of the large intestine begin to manifest themselves only after 1.5-2 years from the moment of their occurrence. Bleeding is a delayed symptom and develops at the stage of tumor disintegration.
The first signs of rectosigmoid cancer are spastic constipation, the stool becomes ribbon-shaped, and later mucus and blood appear on its surface. Often with intestinal cancer, hemorrhoids develop, which are extremely difficult to treat. Pain is not typical for this location and appears only with the development of intestinal obstruction. The tumor may not be detected by palpation even in the late stages of the disease.
When a tumor affects the right parts of the colon, the first symptoms appear very late and are nonspecific. Signs of intoxication increase (fever, accelerated ESR), lack of appetite, rapid loss of body weight. Pathological impurities appear in the stool: mucus, blood (usually hidden), pus, and sometimes the stool takes on the appearance of “raspberry jelly.” Later, pain appears in the right half of the abdomen, and the tumor is often detected by palpation.
Be sure to read:
Stool color in newborns: where is the norm and where is the pathology?
Rectal cancer is characterized by nagging, burning pain in the rectum, frequent urge to defecate, followed by the release of mucus and blood. Blood does not mix with feces, but unlike hemorrhoids, it is released at the beginning of defecation. Feces may include pus and tumor breakdown products.
Diverticular disease
Diverticulosis in most cases affects the large intestine, mainly its left sections. The incidence of the disease increases with age, affecting more than 60% of the population after 70 years of age.
Uncomplicated colonic diverticulosis is usually asymptomatic. Inflammation of the diverticulum manifests itself:
- pain predominantly in the left abdomen;
- unstable stool;
- decreased appetite;
- nausea;
- increased temperature;
- leukocytosis.
Diverticulitis is complicated by bleeding in 3-5% of patients. It is often profuse and develops suddenly. Signs of acute blood loss increase (weakness, pale skin, dizziness, tachycardia), and little changed blood appears in the stool.
Nonspecific ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease
Main articles: Ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease
Inflammatory bowel diseases with similar intestinal manifestations. They are characterized by an undulating course with periods of exacerbation and remission.
The main symptoms of the disease are:
- bloody diarrhea;
- abdominal pain;
- fever during exacerbations.
With nonspecific ulcerative colitis, diarrhea with blood can be the only symptom of the disease for a long time. With Crohn's disease, bleeding occurs less frequently; depending on the level of damage, blood in the stool may be detected in the form of dark clots or bright red streaks.
In addition to intestinal damage, there are systemic symptoms (erythema nodosum, arthritis, skin and eye damage, sclerosing cholangitis, etc.)
Intestinal and other infections
Main article: Intestinal infections: symptoms and treatment
Anal bleeding is sometimes a symptom of certain infectious diseases (dysentery, typhoid fever, amoebiasis, hemorrhagic fevers).
Infectious diseases are characterized by:
- acute onset;
- febrile fever;
- weakness;
- headache, muscle pain;
- and other manifestations of intoxication: vomiting, diarrhea, severe abdominal pain.
In this case, abdominal pain always precedes bleeding. The blood is usually dark and mixed with stool and mucus.
Pseudomembranous colitis
Main article: Pseudomembranous colitis
One of the dangerous complications of antibiotic therapy. Most often it develops while taking sulfonamides, clindamycin, ampicillin, lincomycin, and cephalosporin drugs.
The disease manifests itself as cramping abdominal pain, intoxication syndrome, and severe diarrhea. The stool is copious, watery, and in severe forms it takes on the appearance of “rice water.” The stool contains pathological impurities - mucus, blood.
Discharge color and disease
- bright red, scarlet blood from the anus on toilet paper or underwear, drops at the end of a bowel movement (stool) - hemorrhoids or anal fissure;
- red color of blood during anal bleeding - cancerous tumor, intestinal polyp;
- dark blood clots - tumors of the distal colon, diverticulosis;
- cherry-colored blood from the anus - pathology of the colon;
- black, tarry stools - diseases of the stomach, duodenum and small intestine.
IMPORTANT!
Bleeding is a serious symptom, after the appearance of which you cannot postpone a visit to the doctor. Unfortunately, blood from the anus can cause diseases such as a tumor of the rectum or colon. And in the worst case, this tumor may turn out to be malignant. Blood can also occur as a result of injury to a polyp - a benign tumor. Long-term polyposis can be a sign of colon cancer.
Principles of treatment
At the first signs of blood from the anus, before the ambulance team arrives, the patient should be laid sideways and ice placed in the perineum. Cooling causes vascular spasm and stops the flow of blood. A cold compress is applied for 10-15 minutes, then removed for 5 minutes and done again. Cooling manipulations must be continued for 1 hour. Walking or sitting increases blood circulation in the pelvic veins and increases blood loss.
Surgical intervention
The main therapy must be carried out inpatiently. The treatment regimen is determined based on the reason that caused the blood to leak and can combine various methods of therapy: medication, surgery, non-drug, physiotherapy, herbal medicine and traditional health recipes:
- Drug therapy is applicable for infectious rectal bleeding and helminthiasis.
- Surgical intervention is prescribed: to remove hemorrhoids, polyps and various tumors, excision of fissures in the anus, stopping internal bleeding, blockage of arteries and veins or intestinal obstruction, etc.
- Contact treatment is prescribed for ulcerative pathologies of the stomach and duodenum (cauterization of the ulcer).
- Combination therapy is the combined use of several types of treatment. For example, after surgery, antibacterial drugs are used. When the patient weakens, immunomodulators, vitamin-mineral complexes, and agents for restoring microflora and intestinal activity are prescribed.
- Rectal therapy in the form of medicinal suppositories is usually prescribed for hemorrhoids and anal fissures. The therapeutic effect of such suppositories can be of different directions: painkillers, antiseptic, anti-inflammatory, wound healing, laxatives, immunomodulatory.
Thus, it is important to know that traces of blood on toilet paper after bowel movements are very often alarming signals of serious pathological processes occurring in the human body and threatening healthy life. This requires a mandatory visit to the doctor.
Bleeding pattern and disease
- Regular heavy bleeding not associated with bowel movements - diverticulosis, polyposis, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, rectal or colon cancer;
- Blood mixed with feces - cancer of the rectum and colon;
- Bleeding with diarrhea - dysbiosis, irritable bowel syndrome;
- Discharge of blood with mucus or pus - internal hemorrhoids, rectal prolapse or polyp;
- Severe bleeding with mucus - proctitis, colitis, rectal cancer.
Make an appointment
Causes
Bleeding while going to the toilet is by and large an integral part of the onset of the development of pathology of the intestinal tract.
Most often, bleeding in an adult or child appears due to the development of a certain disease.
Defecation may be accompanied by bleeding in the following cases:
- colon cancer;
- formation of polyps;
- hemorrhoids, especially in the acute stage;
- cracks in the anus and rectum;
- diverticulosis (protrusion of the intestinal walls);
- intestinal ulcer;
- nonspecific ulcerative colitis;
- tumor growth in any part of the intestine (most often the large intestine, sigmoid and rectum);
- irritable bowel syndrome;
- phlebectasia;
- endometrosis of the large intestine, does not occur in men, only in women;
- ischemic colitis;
- Crohn's disease;
- intestinal damage by helminthic infestation (men are less susceptible than women, but the main risk group is children);
- infectious intestinal diseases (dysentery, salmonellosis and others);
- chronic constipation can cause the rectum to bleed;
- girls may notice drops of blood on toilet paper when they are in an interesting position - being pregnant, this is due to a change in the location of some organs and their pressure on the intestines;
- Intestinal tuberculosis can in rare cases cause bloody stools.
Blood on toilet paper
If, during bowel movements or after visiting the toilet, you notice blood on paper or on your underwear, then you should not ignore this symptom. The same applies to blood in the stool.
All of the above diseases and conditions, if untreated, have a lot of complications, so it is better to establish the reason that the anus is bleeding and bloody feces are coming out as early as possible.
Video
Diagnosis and treatment
When faced with an intimate problem, especially such as bleeding from the anus during bowel movements, you can get confused, especially if you don’t know about the methods of diagnosing and treating such ailments or don’t understand which doctor to contact.
A proctologist or coloproctologist is a doctor who diagnoses and treats diseases of the colon, rectum and anus, as well as problems of the sacrum, coccyx and perineum. You should not postpone a visit to this specialist if there is blood from the anus after stool.
A proctologist will listen to complaints and the history of their occurrence, and to determine the cause of the appearance of blood from the rectum, he may perform the following procedures:
Digital examination of the rectum: a primary research method that makes it possible to assess the condition of the anus and identify possible pathologies in the form of neoplasms, anal fissures, uncharacteristic discharge, and bleeding.
After a digital examination, the coloproctologist, if necessary, prescribes further diagnostic methods using special equipment:
- Anoscopy. This is an examination of the last 3-7 cm of the rectum; it is in this area that almost half of the sources of visible bleeding are located. There are several types of anoscopes (straight, conical, with and without a cutout, transparent and not transparent), each of them is used strictly according to indications, but any of these types allows you to perform a full examination of the anal canal and lower ampullary rectum. Anoscopy is used when performing minimally invasive methods of treating hemorrhoids (ligation, sclerotherapy), as well as performing a number of surgical interventions (bipolar coagulation). As a rule, no preparation is required to perform diagnostic anoscopy; preparation is required for anoscopy for therapeutic purposes.
- Sigmoidoscopy or rectoscopy (RRS or RRS) is a diagnostic procedure using a special device with a camera. It makes it possible at the initial appointment to quickly and painlessly visually assess the condition of the rectal mucosa, identify the presence of mucosal formations and compression of the intestine. During rectoscopy, up to 20 cm of the intestine is examined (the entire rectum and the place of its transition to the sigmoid). Preparation is required for rectoscopy.
- Colonoscopy is the most informative method of examining the large intestine compared to others. It is carried out using a flexible fiber colonoscope equipped with a high-resolution camera that will show even the smallest sources of bleeding. The procedure is also prescribed for the purpose of endoscopic removal of colon formations. A colonoscopy is performed by an endoscopist.
The appropriate method of treating the disease is determined and prescribed by the doctor. You should not engage in self-treatment and neglect contacting a coloproctologist.
How to prepare for the examination?
The own research of specialists from the proctology department of the Altermed clinic made it possible to make a visit to a proctologist as easy and comfortable as possible. There is no longer any need to fast the day before and plan the procedure for the morning. In the proctology departments of Altermed, a way has been found to successfully cope with all these difficulties. This is Microlax bowel preparation.
The use of Microlax microenemas makes fasting unnecessary, does not require special equipment or premises, and saves a lot of time. The laxative effect occurs 5-15 minutes after administration of the drug. The quality of bowel cleansing is such that treatment can begin immediately after rectoscopy and anoscopy. If it is necessary to use during pregnancy and lactation, Microlax does not require special precautions.
The Proctology Clinic provides diagnostics using the most modern equipment. The best doctors in St. Petersburg - both men and women - and a delicate approach are at your service.
Other articles by the author
- Blood from the anus
- Prolapse of the rectum (rectal prolapse)
- Pain in the anus
- Anal fringes
- Treatment of anal fissure