Acute purulent paraproctitis is an infectious pathology of fatty tissue located near the rectum. The disease has an acute and chronic course, as well as varying levels of spread. A chronic disease can be aggravated by the presence of fistulas. The acute form is characterized by the base of a purulent focus in the middle of the adipose tissue, which will require serious surgical treatment.
About the disease
Purulent paraproctitis is a dangerous disease that is a complication of hemorrhoids. If appropriate measures are not taken in time, an abscess will immediately develop, threatening a person’s life. When adipose tissue rots, hospitalization of the patient is necessary. Specialists determine the severity and select the appropriate method of surgical treatment of acute paraproctitis.
Paraproctitis accounts for 15-35% of all pathologies in this part of the intestine. The disease ranks 4th after colitis, hemorrhoids, and anal fissures. In men, inflammation appears much more often than in women, this is due to the anatomical structure of the cellular lumen near the rectum. The disease is usually observed in patients 30-50 years old; paraproctitis practically does not occur in children.
Clinics for treatment with the best prices
Price
Total: 189in 15 cities
| Selected clinics | Phones | City (metro) | Rating | Price of services |
| Clinic named after Peter the Great | +7(812) 303..show+7(812) 303-50-60+7(812) 303-50-00 | St. Petersburg (m. Akademicheskaya) | — | 4525ք (90%*) |
| Clinic named after E.E. Eichwald | +7(812) 303..show+7(812) 303-50-50+7(812) 303-50-00 | St. Petersburg (metro Chernyshevskaya) | — | 4525ք (90%*) |
| Medical unit No. 165 | +7(499) 506..show+7(499) 506-69-69+7(499) 611-11-79+7(499) 611-11-97+7(499) 506-69-66 | Moscow (metro station Kashirskaya) | — | 4910ք (90%*) |
| St. Andrew's Hospitals in Varshavka | +7(499) 323..show+7(499) 323-98-33+7(499) 323-98-00 | Moscow (metro station Varshavskaya) | — | 4960ք (90%*) |
| Federal State Budgetary Institution Scientific Center of Neurology | +7(495) 490..show+7(495) 490-20-09+7(495) 374-77-76 | Moscow (metro station Shchukinskaya) | — | 5025ք (90%*) |
| KB No. 122 named after. L.G. Sokolova | +7(812) 363..show+7(812) 363-11-22+7(812) 559-95-95 | St. Petersburg (m. Ozerki) | — | 5730ք (90%*) |
| Clinic of St. Petersburg State Pediatric Medical University | +7(812) 542..show+7(812) 542-93-57+7(812) 248-18-40+7(812) 295-46-23+7(812) 295-40-31 | St. Petersburg (metro station Vyborgskaya) | — | 6250ք (90%*) |
| MEDSI in Butovo | +7(495) 023..show+7(495) 023-60-84 | Moscow (metro Dmitry Donskoy Boulevard) | — | 7200ք (90%*) |
| MEDSI on Prechistenka | +7(495) 739..show+7(495) 739-53-67+7(495) 152-55-46 | Moscow (metro Park Kultury) | — | 7200ք (90%*) |
| MEDSI on Polyanka | +7(495) 730..show+7(495) 730-57-23+7(495) 152-55-46 | Moscow (m. Polyanka) | — | 7200ք (90%*) |
| * — the clinic does not provide 100% of the selected services. More details by clicking on the price. | ||||
Source
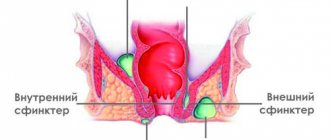
Paraproctitis
(perirectal abscess) - acute or chronic inflammation of the adirectal tissue. Paraproctitis is one of the most common proctological diseases (20-40% of all rectal diseases). Paraproctitis is in 4th place in frequency after hemorrhoids, anal fissures and colitis. Men suffer from paraproctitis more often than women. This ratio ranges from 1.5:1 to 4.7:1. Paraproctitis is a disease of adults: descriptions of rectal fistulas in children are rare.
Causes
The main cause of paraproctitis is the penetration of pathogenic microflora into the pararectal area. The provocateurs of the disease are staphylococcus, E. coli, and less commonly, chlamydia, viruses, etc.
Ways microbes enter the rectum:
- cracks, tears in the mucous membrane - injury occurs due to too dense stool during childbirth;
- anal glands - the infection enters through their lumen, located at the bottom of the rectal canal, causing inflammation;
- Morgagni's crypts are folds of intestinal tissue, often one of the crypts is caused by an abscess;
- hemorrhoids - bleeding from cones is associated with damage to the mucosa, which causes infection.
With a weakened immune system, hematogenous spread of inflammation can occur when pathogenic bacteria enter the bloodstream.
The causes of acute paraproctitis are as follows:
- diabetes;
- atherosclerosis;
- intestinal disorder (constipation, diarrhea);
- ulcerative colitis;
- anal fissures, hemorrhoids;
- Crohn's disease;
- exhaustion of the body;
- kidney disease;
- immunodeficiency;
- prostatitis, cystitis, urethritis.
Purulent paraproctitis is a secondary process that appears against the background of another disease. Treatment without eliminating the root cause will not have a lasting effect. Initially, it is important to establish the cause of paraproctitis and eliminate it.
Types of suppositories for paraproctitis
There are many different suppositories used to treat paraproctitis. Some of them contain only medications, others contain substances of plant origin. The choice of a specific drug depends on the presence of certain indications. It should be remembered that suppositories must be used under the supervision of a physician.
Suppositories for symptomatic treatment
These drugs eliminate local pain, reduce tissue inflammation, and have a regenerative and some bactericidal effect.
| Drug name | Active substance | Pharmacological effect | Dosage |
| Ichthyol candles | Ichthammol (ichthyol) | Local anesthetic, regenerating, antiseptic; increases the tone of the vascular wall in the area of inflammation, improves blood circulation. | One piece at a time 2 times a day; course of treatment – 1-2 weeks. |
| Suppositories with propolis | Propolis | Bactericidal, local anesthetic, reparation, anti-inflammatory, antitoxic, phagocytic; enhances the effect of antibacterial drugs. | 1 piece each twice a day for 10 days; It is recommended to take the second course with a break of 2 months. |
| Anuzol | Xeroform, zinc sulfate, belladonna (belladonna) leaf extract. | Antiseptic, astringent (denaturing proteins, forms a protective film on the affected area, preventing the entry of pathogenic microorganisms), drying (reduces inflammation, preventing tissue exudation). | Depending on the severity of the disease, from 1 to 3 suppositories per day for a course of 10-14 days. |
| Suppositories with methyluracil | Methyluracil (dioxomethyltetrahydropyrimidine) | Regenerating (provides rapid granulation and epithelization of tissues), anabolic (accelerates the growth of new cells), immunostimulating. | Adults 2-8 suppositories per day, children – one piece. course 1-16 weeks. |
| Posterisan | Inactivated E. Coli (Escherichia coli) cells | Reparation, immunostimulating; increases the resistance (stability) of tissues to the effects of pathogenic microorganisms. | 1 piece each twice a day, and also after each act of defecation; Possible combined use with ointment. |
| Ultraproct | Fluocortolone, cinchocaine. | Anti-inflammatory, antipruritic, analgesic, antihistamine. | One suppository 1 time per day at night; course of treatment is 7-10 days. |
Any suppositories used for paraproctitis are inserted into the rectum after a cleansing enema or natural bowel movement; Before insertion, it is recommended to perform anal hygiene.
Antibacterial
Suppositories containing antimicrobial substances are prescribed in the preoperative period to patients suffering from chronic paraproctitis, as well as to patients after surgical treatment when their general condition worsens (fever, signs of intoxication of the body). Antibacterial suppositories fight this disease quite effectively, but they are used only as complex therapy with mandatory surgical intervention.
The most common suppositories for the treatment of paraproctitis are:
- Olestesin. The antibacterial effect is achieved with the help of the sulfonamide included in the composition - sodium etazol. The medicinal substance anesthesin has an analgesic effect, and sea buckthorn oil has an anti-inflammatory and hemostatic effect. Apply rectally 2 times a day.
- Proctosedyl. This drug is a combination drug, the components of which have an anti-inflammatory (reduction of swelling, itching, hyperemia), local analgesic effect. This product also improves microcirculation of affected tissues. The antibacterial effect is achieved due to the framycetin included in its composition. Suppositories are administered into the rectum 2 times a day for no more than one week.
- The destruction of infection in paraproctitis can be achieved by introducing tampons soaked in antibacterial ointments, such as Gentamicin, Levomekol.
If symptoms of paraproctitis are detected, you should immediately consult a specialist. Untimely and irrational treatment of this disease can lead to a number of serious complications.
Types and symptoms
Acute paraproctitis occurs for the first time and is associated with a feeling of pain during bowel movements, high body temperature, malaise, headache, and lethargy. The contents of the abscess can break into the rectum or into the pelvic area.
The chronic form of paraproctitis is no better, since it can cause purulent-inflammatory formation.
In accordance with the distribution of foci of infection, the disease is divided into several types, which have their own symptoms of acute paraproctitis:
- Subcutaneous – located in the fatty tissue under the skin near the anus. It is easy to notice and is a red swelling. When a person sits down or touches the pathological area, pain occurs, in addition, the symptom is of a pulsating nature. Weakness, fever, and headache are also noted. Due to swelling, defecation is difficult.
- Submucosal - the location of the abscess under the intestinal mucosa. It is not difficult to identify the disease. The patient suffers from pain in the anus and noticeable swelling. Often the contents break into the intestine, suppuration flows out, after which recovery occurs.
- Pelviorectal - based in the pelvic-rectal space, adjacent to the abdominal cavity. Paraproctitis manifests itself as chills, fatigue, and body aches. If its size is significant, there are symptoms of intoxication.
- Ischiorectal - inflammation is located in the ischiorectal cavity. There is pain when coughing or sneezing. Then the temperature increases and the anus swells.
- Retrorectal - the abscess is located behind the rectum, there are no signs for a long time, only symptoms of intoxication are possible. Sciatic nerve pain and neurological manifestations are sometimes observed.
It happens that acute paraproctitis turns into chronic, due to the fact that the first one was not completely treated. The pathology is protracted and characterized by the presence of fistulas. The disease is expressed by the separation of pus with blood into the perineum, where the formation mainly opens, and itching is felt.
This fistula usually does not cause pain because its contents flow out. If pain occurs during bowel movements, this indicates the presence of an internal fistula, where there is a violation of the outflow of pus.
Symptoms
Acute paraproctitis is manifested by symptoms characteristic of local purulent inflammation, pain, hyperemia, hyperthermia and tissue swelling, suppuration. Chronic paraproctitis is the result of untreated acute paraproctitis, so its symptoms most often repeat those of acute paraproctitis, but their severity is usually less. With chronic paraproctitis, a pararectal fistula often develops, which is manifested by discharge of ichor or pus into the perineal area. Constant discharge contributes to irritation of the perineal skin and itching. A well-drained (having a free outlet for pus) perirectal fistula usually does not bother the patient with pain or discomfort. The pain symptom is characteristic of an incomplete internal fistula. In this case, the pain intensifies during defecation and subsides after it (this is due to improved drainage of the fistula at the time of stretching of the anal valve). Pain in the coccyx. Constipation. Constipation in children. Leukocytosis. Neutrophilia. Chills. Diarrhea (diarrhea).
Diagnostics
A coloproctologist can determine the exact disease. The specialist conducts a palpation examination of the rectum.
Diagnostics to determine the location of the abscess involves:
- radiography with contrast;
- Ultrasound examination.
In addition to the nature of the formation itself, the presence of fistulas, as well as additional inflammatory areas, is established.
In case of severe pain, examination is carried out using local anesthesia. Having made a diagnosis, the doctor establishes a method for opening the abscess.
Treatment
Purulent paraproctitis should be treated immediately; only an autopsy will help. Many patients do not seek help immediately and use various methods, leading to the point where the pain becomes simply unbearable.
If the disease is detected at the initial stage of development, it will be possible to manage with conservative methods. Antibiotic therapy, UHF, and various sitz baths are used.
Surgery
Treatment of purulent paraproctitis is performed surgically. Manipulation involves opening the abscess and cleaning out the abscess. Next, rinsing is done with the prepared solution containing an antiseptic and antibiotic. During surgery, drainage is performed by making a small incision over the abscess and removing the edges of the skin.
The best treatment for chronic paraproctitis is considered to be complete resection of pathological tissues and fistulas.
Fistulas must be subdivided before the operation is performed, because the crucial point for correct intervention is the precise stopping of the path of the fistula. For example, treatment of subcutaneous or submucosal abscesses is carried out using a special probe.
Postoperative therapy
The operation does not provide a full guarantee of cure. The pathological process can recur even in the case of a favorable outcome.
After paraproctitis during the rehabilitation period you should:
- follow a diet that helps restore the functioning of the digestive system and prevent constipation;
- carry out careful personal hygiene after each bowel movement;
- use sitz baths recommended by your doctor;
- a little later it is good to perform certain gymnastics that improve blood supply.
If complications or secondary inflammation occur, repeated intervention is performed to open the abscess and clean it. The doctor will then prescribe immunomodulatory treatment.
Traditional therapy is used for chronic illness only at the time of preparation for surgery. Effective recipes with medicinal plants help relieve inflammation.
Signs and symptoms of chronic paraproctitis
Chronic paraproctitis often occurs due to spontaneous opening of an abscess or improper treatment (opening) of acute paraproctitis.
The disease progresses in waves: periods of well-being are followed by periods of exacerbation. When the fistula tract closes, pus again accumulates in large quantities. The patient's condition worsens. After another opening and discharge of pus, the patient’s general condition improves. Gradually the fistula begins to close, but the disease continues to exist.
During periods of exacerbation, the following signs and symptoms are recorded:
- Discharge from the fistula tract (pus, mucus, gases, feces) is scanty.
- The pain syndrome is not clearly expressed.
- The general condition suffers. The patient develops insomnia, irritability, headache, and decreased performance.
With chronic paraproctitis, the following types of fistulas are formed:
- Full. They have two outlets: on the skin and the rectal mucosa.
- Incomplete. They have two holes: one ends blindly in the form of a “bag”, and the other is functioning.
- External. The hole goes out and is located on the skin.
- Internal. The hole comes out inside the rectum on the mucous membrane.
There are complex fistulas that connect the rectum to nearby organs - the vagina (rectovaginal fistulas) and the bladder (entero-urinary).
Rectal fistulas
Rectal fistula is a chronic inflammation in the anal crypt, pararectal tissue or intersphincteric space with the formation of a fistula tract. Fistulas, as a rule, form against the background of improper treatment or spontaneous opening of an abscess during acute paraproctitis.
How the disease develops
A fistula that spontaneously opens inside the rectum often heals on its own, but with a fragile scar, which can reopen due to injury - cycling, constipation, etc. During the next healing, pus accumulates again, and an abscess can form in another place. The same thing happens when an abscess is opened incorrectly, when the fistula opening, which is constantly infected with intestinal flora, is not eliminated. Over time, connective tissue forms around the fistula tract, and in the fatty tissue, with insufficient drainage, purulent infiltrates and cavities form.
Only 1/3 of patients seek medical help in a timely manner, another third of patients turn to doctors only after self-opening of the abscess, the remaining third - after opening of the abscess and the formation of chronic paraproctitis.
Rice. 11. Breakthrough of the abscess outward during paraproctitis.
Signs and symptoms of the disease
- Discharge from the rectum of ichor, pus and particles of feces, which is why patients have to use pads and wash frequently.
- When the fistula tract is blocked by granulation tissue or purulent-necrotic masses, pus again accumulates in the perirectal tissue or intersphincteric space. The appearance of new abscesses occurs against the background of a deterioration in the general condition of the patient. Patients are worried about headaches, weakness, decreased performance and potency, and mental health problems. Pain appears in the perineal area. There is stool retention and difficulty urinating, and tenesmus occurs.
Complications
- With the long-term existence of chronic paraproctitis, against the background of the development of scar tissue, severe local changes are formed in the form of deformation of the lumen of the rectum and perineum, which causes insufficient retention of feces and gases.
- Malignancy of fistula tracts.
- Development of amyloidosis of internal organs.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of the disease is not difficult. First of all, the internal opening of the fistula tract and its direction to the fibers of the anal sphincter are identified. However, with unsuccessful operations in the past, this procedure turns out to be complex and requires qualified diagnostics.
Rice. 12. Fistulas in chronic paraproctitis.
Rice. 13 and 14. In the photo on the left is an external fistula opening in chronic paraproctitis, on the right is deformation of the anal canal and multiple fistulas.
Forecast
The prognosis will depend on the stage of development of paraproctitis and the location of the abscess in the anal canal. With timely and correct treatment of the early stage, the result is positive.
Chronic, complicated acute purulent paraproctitis can reappear, especially when treating fistulas formed after an illness. A severe illness requires enormous efforts for the recovery to be final. Such therapy can last for several years and result in a cure.
We recommend: What is the difference between enterovirus and rotavirus: list of main differences
Medicines for the treatment of paraproctitis in adults
Ointments for paraproctitis in adults have a complex effect: wound healing, immunomodulatory, analgesic, anti-inflammatory. Highly effective medical products: Balsamic liniment according to Vishnevsky, Proctosedyl, Locacorten-N (Lorinden).
Vishnevsky ointment
Vishnevsky ointment for paraproctitis is a combination medicine. Has several effects at once: disinfects, relieves inflammation, regenerates damaged areas
It must be used carefully, as there is another property - it promotes the purulent process.
Vishnevsky ointment for paraproctitis is used according to the instructions. Apply to a gauze bandage and apply to the diseased area, with a piece of cellophane placed on top. This will enhance the impact effect. This warming compress is worn for up to 12 hours. Then the skin is removed and treated with an antiseptic; it will help get rid of the very unpleasant odor of the ointment.
The duration of treatment depends on the healing process.