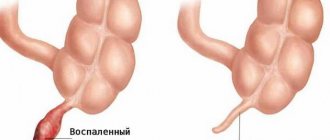
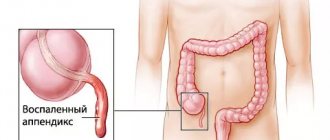
Symptoms of inflammation of the appendix of the cecum have distinctive features for different ages. Appendicitis is a dangerous disease; if medical care is not provided in a timely manner, it can result in rupture of the appendix and infection of internal organs. This often leads to death.
In a child, inflammation occurs in a short time (2-3 days from the beginning of the process to peritonitis), so if parents doubt the nature of abdominal pain, it is necessary to contact a surgeon to confirm or deny the disease.
Causes of appendicitis in children
Inflammation in the appendix occurs due to blockage of the lumen or the presence in the organ of favorable conditions for the appearance of tissue suppuration.
The development of appendicitis can be caused by several reasons:
| What causes a passage to be blocked? | What causes inflammation | Notes |
| Ingestion of husks from seeds, fish bones, berry or fruit seeds into the appendix. And also low-quality products. | A foreign body blocks the lumen and with sharp ends can damage the mucous membrane and cause inflammation of the organ | You can avoid appendicitis if you watch what your child eats. |
| Fecal stones, dysbiosis and constipation | The presence of fecal stagnation, disruption of intestinal microflora, also causes an inflammatory process | Eliminating constipation and having regular bowel movements will help prevent appendicitis |
| Deformations of the organ and disruption of its functioning. As well as congenital pathologies in the development of the appendix associated with a strong narrowing of the lumen | Due to blockage, the lining of the appendix begins to become inflamed. | It is impossible to prevent the disease, but timely detection will avoid complications |
| Swelling due to infection | In infectious diseases (otitis, measles, tonsillitis), pathogens enter the appendix with the help of blood and cause inflammation | Timely treatment of diseases and a strong immune system will prevent appendicitis from developing |
| Inflammation of the lymphoid tissue of the appendix can greatly narrow the lumen | Hypothermia, overeating and sweets contribute to the development of appendicitis, as a favorable environment is created for the inflammatory process | To prevent illness, you need to lead a healthy lifestyle and monitor your temperature. |
| Worm infestations and other parasites | Helminths clog the lumen and in the process of vital activity, toxins are released, they irritate the walls of the organ and provoke the onset of inflammation | Timely control of parasites will prevent the development of the disease |
In children under 2 years of age, inflammation of the appendix is rare. This is due to nutrition (children eat under the supervision of adults), the organ itself is still in a thickened state and shorter, so blocking the passage is difficult. In the process of growing up, the organ stretches and the lumen narrows, which leads to an increased risk of developing the disease.
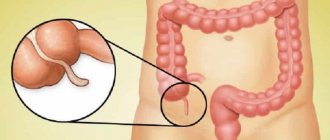
Description and features of the disease in childhood
Appendicitis is an acute inflammation of the worm-shaped organ (appendix) extending from the cecum. Due to the immaturity of the gastrointestinal tract in infants, this pathology is extremely rare, but starting from the age of 2 years, the risk of the disease increases. About 5% of cases occur in kindergarten children, 13% in preschool age, and more than 80% in schoolchildren. It has been observed that boys are affected by this condition more often than girls.
If patients 4-6 years old can tell what worries them, then it is difficult or impossible to obtain a verbal description of symptoms from children under 3 years old. This is the first feature of the disease in childhood and, accordingly, the main difficulty in diagnostic matters.
The second feature of appendicitis in children is its transience. The pathology develops quickly, often involving the peritoneum: necrosis of the cecum, development of peritonitis.
Inflammation of the appendix is a rather insidious disease, skillfully “masquerading” as ordinary food poisoning, flatulence and other types of gastrointestinal dyspepsia. Parents are not always able to assess the danger of symptoms: the thought of serious, health- and life-threatening pathologies often does not even appear.
Factors that increase the risk of developing appendicitis
Symptoms of appendicitis in a child occur at the onset of the inflammatory process. Children with reduced immunity and impaired blood supply are more susceptible to this disease. Their body is not able to fight even the slightest disruptions in the body.
The likelihood of developing appendicitis is increased in children with a hereditary predisposition. That is, the organ initially has weak protection from external influences or is incorrectly located.
Impaired functioning of the digestive tract, as well as deviations in the development of the appendix, increases the likelihood of the formation of an inflammatory process. The risk of developing the disease increases in a child with a severe infectious disease and prone to frequent allergic reactions.
Stage of disease progression
In the absence of timely medical care, acute gangrenous or phlegmonous forms of the disease develop. This stage of disease progression is the most dangerous.
Symptoms of appendicitis in children in this case are associated with infection of the internal organs of the abdominal cavity. The cells of the appendix die, so the pain syndrome may subside. In this case, intoxication of the body occurs, which is accompanied by a deterioration in the child’s well-being. He begins to delirium. If left untreated, blood poisoning occurs.
Types of inflammation of the appendix
The inflammatory process in the appendix can occur in several stages (they will be described below), as well as according to different classifications. Before prescribing treatment, the surgeon must determine the classification and stage of appendicitis.
Types of classifications:
1. According to the nature of the disease:
- acute form . In this case, inflammation develops rapidly with vivid symptoms and requires urgent surgical intervention;
- chronic _ Sometimes, in an acute form, the symptoms may subside without medical assistance, and the process enters the chronic stage. If the disease is detected in a chronic form, surgery is also required.
2. From the location of the appendix in the abdominal cavity:
- traditional , when the appendix is in the right place. In this case, it is not difficult to find out whether the pain is caused by appendicitis or another disease;
- atypical _ Sometimes the process can go around the kidney, small intestine, or be located on the left side. Then diagnosing the disease becomes difficult. The pain radiates to different organs or to the opposite side.
3. From the cause of the inflammatory process:
- vascular _ The infection has entered the appendix through the circulatory system or there are disturbances in the blood supply, which complicates the outflow of processed materials from the organ;
- infectious . Inflammation of the appendix is caused by the development of an infectious disease in the body, the presence of parasites or pathologies of the digestive tract;
- mechanical _ Inflammation is a consequence of blockage of the passage, which occurs due to the entry of foreign objects or narrowing of the lumen due to the development of tumor processes.
After confirming the development of appendicitis, identifying the location of the organ and the cause of the disease, the surgeon needs to find out at what stage the inflammatory process is.
The stages are as follows:
- Uncomplicated appendicitis.
- Developed inflammatory processes.
- Acute inflammation.
Depending on this, the urgency of surgical intervention will be determined.
How to prevent
Proper nutrition and regular bowel movements are of great preventive importance. It is important to treat inflammatory diseases in a timely manner. Appendicitis develops rapidly and can often have an atypical course. If you feel unwell, consult your doctor, be it fever, dyspeptic disorders or abdominal pain.
The appendix is an important organ of the human body. If it becomes inflamed in teenagers, do not hesitate: take action already when the first signs of appendicitis appear. The disease develops rapidly, with characteristic manifestations and can cause severe complications. To prevent this from happening, a quick examination in a hospital and surgery if the diagnosis is confirmed are necessary.
When a teenager voices a complaint such as a stomach ache, parents should find out the nature of the pain, since the syndrome is one of the signs of appendicitis. The difficulties of self-diagnosis of inflammation of the appendix are that the clinical picture of this condition resembles overeating, poisoning and gastrointestinal diseases. Appendicitis is a serious pathology. Delayed medical intervention is dangerous due to the development of intestinal obstruction, infection of the peritoneum and death if the appendix ruptures.
The main causes of inflammation of the cecum are:
- Chronic constipation.
- Helminthic infestations.
- Oncological neoplasms.
- Blockage of the intestinal lumen caused by the activity of pathogenic microflora or the entry of a foreign object.
Uncomplicated appendicitis
Symptoms of appendicitis in a child at this stage are poorly identified. Painful sensations are similar to the development of pathology in the digestive tract. Initially, they concentrate in the center of the abdomen, then move to the right side, to the lower part. The pain is dull, paroxysmal in nature. But over time it begins to intensify.
Sometimes at this stage of the development of the disease, one-time vomiting occurs, loose stools appear and the temperature rises to 37.5-38 degrees. Urination becomes more frequent. You may experience dry mouth and increased heart rate. The tongue at the root becomes covered with a white coating. The condition of the abdomen is not modified, but when pressure is applied to the appendix area, painful sensations occur.
With uncomplicated appendicitis, only thickening of the walls of the organ and a slight inflammatory process develop.
No tissue destruction or necrosis is observed. If the disease is recognized at this stage, the operation proceeds without complications and has a quick recovery period. Simple appendicitis takes 6-20 hours to develop.
What can appendicitis be confused with?
Pain from appendicitis occurs suddenly . It is localized in the area of the reproductive organs, so suspicion often falls on gynecological problems in girls and urological problems in young people.
Also, inflammation of the appendix can resemble renal colic, inflammation of the bladder, urolithiasis, pyelonephritis, enterocolitis and other intestinal diseases.
Girls may experience pain in the right side for the following reasons :
- the beginning of menstruation;
- dysmenorrhea;
- inflammation of the appendages;
- endometriosis;
- ovarian cyst or rupture.
An examination by a gynecologist is mandatory..
In young men, appendicitis can be confused with orchitis, urethritis, inguinal hernia, cysts, and prostatitis. The difference between inflammation of the appendix is the absence of problems with urination.
Developed inflammatory processes
After the end of the phase of uncomplicated appendicitis, usually after 24 hours, the disease enters the 2nd phase, which can occur in 2 ways.
They are:
- phlegmonous. It is characterized by increased pain, rapid breathing and a temperature of 38 degrees. On external examination, tension in the right side of the abdomen is noticeable. The tongue is completely covered with a white coating. At this time, the appendage itself begins to fill with purulent contents, and ulcers appear on the outside of the organ. It is possible that the vessels of the appendix may be blocked by blood clots. Determining the disease at this stage is not difficult;
- gangrenous . There may be either a continuation of the phlegmonous or uncomplicated stage of development of appendicitis. During this phase, necrosis of the tissues and nerve endings of the appendix occurs. As a result, the patient notes a decrease in the pain symptom, but when palpating the appendix, an unbearable pain occurs. The stomach itself is in a bloated state. Temperatures can drop to 36 degrees. Severe intoxication is observed, accompanied by vomiting and increased heart rate. The phase is dangerous due to wall rupture due to cell necrosis.
Signs of the disease
The key symptom of any inflammation is pain. In some cases, with appendicitis in the initial stages, it may be unclear and mildly expressed, so the child eats, plays, and attends educational institutions quite calmly. And his parents attribute his condition to eating problems, constipation, or even a deliberate lie.
Pain is one of the main signs of appendicitis
However, after 1-2 days the picture changes dramatically: the sick child becomes indifferent to toys and favorite activities, refuses to eat, stops jumping, running, and tries to lie down. In this case, complaints of abdominal pain become the main symptom of the disease; possible fever, nausea.
Another scenario is characterized by the sudden development of pathology. Sharp pain behind the peritoneum on the right, radiating to the legs when walking, dizziness, intense nausea, fever, is accompanied by a violent reaction of the child to an attempt by adults to touch the stomach.
Both clinical pictures allow parents to suspect acute appendicitis and go to the doctors as quickly as possible.
Once again, general signs of inflammation of the appendix:
- Pain in the right side of the abdomen, near the navel, sometimes radiating to other parts of the body.
- Nausea.
- Disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract, manifested by stool disorders.
- Fever.
Signs of appendicitis in children under three years of age
Children under 3 years of age are mostly unable to tell their parents about specific causes of concern. Malaise and pain are expressed in the only available way - crying, especially in babies under one year old. It's time to sound the alarm if your child:
- cries for no obvious reason (fed, dressed, watered, etc.);
- intensely presses the legs to the stomach;
- refuses food and favorite treats;
- does not allow touching the skin of the abdomen;
- tries not to move;
- sits or lies in an unusual and uncomfortable position for him;
- if he crawls or walks, then slowly, without sudden movements.
In addition to behavioral signs, symptoms of appendicitis in young children include:
- fever up to 38-39, sometimes up to 40 degrees, appearing suddenly;
- frequent swallowing of saliva;
- loose stools;
- skin rashes;
- swollen lymph nodes;
- dry mucous membranes.
If you notice such symptoms, you must contact the emergency room of the nearest hospital or the ambulance service! And as quickly as possible.
Signs of appendicitis in preschool and school children
The main symptom, pain, makes itself felt in the vast majority of cases acutely and in the navel area. After a few hours, it gradually moves to the area of the right iliac region and intensifies slightly. The child complains of aching, monotonous pain and nausea. One-time vomiting is possible, most often occurring even before the onset of discomfort in the umbilical area. The temperature rarely rises to 38 degrees, preferring to remain between 37.3-37.8. There are frequent cases of appendicitis in children 8-13 years old without fever.
As the disease progresses, the child’s condition worsens:
- general intoxication increases;
- the skin turns pale;
- mucous membranes become dry;
- nausea and pain increase;
- loose stool appears.
When appendicitis is combined with other infections, for example, viral hepatitis or measles, a sharp rise in temperature to 39-40 degrees and the addition of additional symptoms uncharacteristic of inflammation of the appendix are possible.
Atypical picture
Unfortunately, according to the “standard scheme”, appendicitis develops only in 30% of children, the remaining 70% undergo an atypical course of the disease. In these cases, the pain is not localized in the right iliac region or near the navel, but at other points. For example, when the inflamed appendix is located in the liver area, the pain initially appears in the stomach area, and only then moves to the right and down. When the process is localized in the pelvic area, urination becomes more frequent, and the process of urine outflow is accompanied by pain radiating to the abdomen. Also, with atypical appendicitis, pain often appears in the back, in the lower back, behind the sternum, and sometimes in the rectum.
If there is doubt about the diagnosis, the child is prescribed additional examinations: urine analysis, blood analysis, ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
Only a specialist can make a final diagnosis, since the signs of appendicitis fit well into the picture of other diseases. Doctors have at their disposal methods of laboratory and instrumental examination that allow them not only to determine the disease, but also to clarify the form of the disease, the location of the inflamed area, and the severity of the condition.
Acute inflammation
Symptoms of acute appendicitis in a child are observed in cases of severe progression of the disease. The stage is characterized by rupture of the appendix and leakage of contents onto nearby organs.
In this case, the patient experiences continuous severe pain, which intensifies further. Nausea with vomiting becomes more frequent, heartbeat is rapid. The abdominal muscles are tense to the limit. The tongue is completely covered with a white coating and appears dry.
Most often this condition is observed after 72 hours. Depending on the state of immunity, the time may decrease. In rare cases, children experienced attenuation of pain and a decrease in the inflammatory process; in this case, the disease enters the chronic stage. In this case, the body will continue to be poisoned by toxins.
Symptoms
At the initial stage, signs of appendicitis in children can manifest themselves in different ways. The nature of the attacks depends on the location of the appendix.
The most obvious and first symptom is the appearance of pain in the umbilical region.
As the inflammatory process progresses, the pain gradually shifts to the area where the appendix is located.
The nature of the pain depending on the location of the process:
- Classic location. The pain syndrome shifts to the lower region of the peritoneum on the right.
- Pelvic location. Severe pain is felt in the area above the pubis, accompanied by frequent urination, diarrhea with mucus.
- Subhepatic location. Severe pain appears under the right rib.
- Retrocyclic location. Pain appears in the lumbar region.
In any area of localization of the appendix, small patients refuse to eat.
Signs of intoxication
In any form, the signs of appendicitis in children are very similar to poisoning. Young patients feel nausea, gagging, and vomiting.
The distinguishing feature of this disease from intoxication is the lack of relief after vomiting. In young children, vomiting occurs only once.
At school age, it can be one-time or take place in two stages.
Temperature
Raising body temperature is one of the main symptoms of the disease. How it manifests itself:
- In babies, body temperature rises to critical levels - 40°C.
- In children aged 3-5 years, the thermometer registers 38-39°C.
- In schoolchildren and high school students, a rise in body temperature to 38°C is noted.
Chair
One of the important signs of the disease is bowel dysfunction:
- Young children experience loose stools (diarrhea).
- At the age of 3-5 years, children experience stool retention, which should not be confused with constipation.
- In adolescence, as in adults, symptoms of constipation are noted.
Language
When examining a patient, regardless of age, the surgeon always pays attention to examining the tongue. Based on his condition, the doctor is able to determine the developing stage of the disease.
How is it shown:
- Simple or catarrhal appendicitis. The specialist notes the wet surface of the tongue, which is covered with a white coating at the root.
- Destructive stage. Often at the phlegmonous stage, the surface of the tongue is moist, completely covered with a white coating.
- Gangrenous stage. It is the most dangerous, the surface of the tongue is dry, completely white.
You should be careful about this sign, especially in children.
Signs of appendicitis in children
Depending on age, the symptoms of appendicitis in children vary. This is influenced by the state of the immune system (in babies it is still developing), and the appendage itself becomes longer every year, and the lumen narrows.
Signs of appendicitis depending on age:
| Symptoms | Up to 3 years | From 3 to 10 | Over 10 years old |
| When they appear | The child's condition quickly deteriorates from the first hours of inflammation. | Appear in the evening of the first day. Pronounced | The first symptoms appear in the evening or at night |
| Digestive system disorder | Nausea, possible vomiting, refusal to eat. The stool becomes loose and frequent, with mucus | Nausea accompanied by vomiting, partial refusal to eat. Disturbance in the process of defecation (stool retention occurs) | Complete refusal to eat, occasional vomiting. A white coating appears on the tongue. A feeling of thirst appears. There may be no stool at all. |
| Urination | Painful, frequent | More often than usual | Sometimes it may be more often than usual |
| Temperature, degrees | 40 | 39 | 38 accompanied by chills |
| Heartbeat | Increased frequency, in older children the frequency does not correspond to the temperature. | ||
| Child behavior | Moody, inactive, restless. Bends his legs under himself, especially the right one. Does not allow himself to be laid on his side, where the appendix is located | Rapid fatigue, apathy. When walking, it is impossible to fully lean on the right leg due to pain | Lethargy, fatigue. |
| Dream | Anxious, absent on the first day | Restless, intermittent | Drowsiness, but no normal sleep |
| Abdominal pain | They are present, but the child cannot show where it hurts. Doesn't let you touch your stomach | Complaints of pain throughout the abdominal area | Initially, the pain is localized throughout the peritoneum, but in the evening it moves to the appendix area. The child cannot lie on his right side due to pain. When positioned on the left side, a feeling of discomfort arises, and nagging pain intensifies in the opposite side. |
| Abdominal condition | During the period of inflammation of the appendix, gases stop passing, this leads to bloating and muscle tension occurs. | ||
Parents should be alerted to the appearance of a fever without cold symptoms, with pain in the abdomen. The sensation intensifies when sneezing, walking (especially when leaning on the right leg). They can radiate to the lumbar region. There is practically no appetite. After the vomit is released, the child does not feel any improvement.
It is not recommended to carry out diagnostics at home by pressing on the area of appendicitis. Since this can provoke organ rupture and the development of peritonitis. If there are prerequisites, even doubtful ones, it is necessary to call emergency help.
https://youtu.be/oapw5NCG4pY
Symptoms
Most often, the acute form of the disease occurs in childhood. Its signs appear 12 hours after the development of the pathological process.
Appendicitis (symptoms in children 10 years of age and older usually coincide with signs of pathology in adults) can manifest itself:
- stomach pain. Most often, discomfort is localized in the lower right. But since in children the appendix is often located in an atypical place, discomfort can cover the entire abdomen, and sometimes radiate to the lower back. The child tries to move less, takes a position in which the pain is felt less - on the right side with his legs tucked in or on his back. Pain increases when walking, coughing, or changing body position. The inflammatory process is characterized by constant pain; it can only change its intensity, but does not go away completely. Depending on the location of the appendix, the nature of the pain may change:
- when the organ is located low, aching pain occurs in the pubic area;
- if the appendix is located behind the cecum, discomfort is localized in the lumbar region, in the right lower abdomen;
- when the organ is located behind the peritoneum, pain is observed in the lower back, radiating to the genitals or thigh;
- lethargy, fever. In most cases, the disease manifests itself with a sharp increase in temperature to 38°C. With the rapid development of pathology with complications, the thermometer readings can rise to 40°C. If the destruction of organ tissue begins, the temperature decreases, the pressure drops and the pulse quickens;
- rapid deterioration of the condition. If purulent inflammation occurs, the baby's skin may turn pale, and he suffers from thirst. With the development of peritonitis, intense pain occurs.
As the pathological process develops, the child's pain may intensify. But it also happens that the pain subsides.
This is not a sign of recovery; on the contrary, such a symptom should alert you, as it indicates the transition of the pathology to a gangrenous form. In this case, the nerve endings of the organ die, which leads to a feeling of relief and reduction of pain.
But the discomfort in the abdomen is replaced by signs of general intoxication: the child becomes weak, vomiting appears, which does not bring relief, but the temperature may remain normal. A characteristic sign of the development of the inflammatory process is a white coating on the root of the tongue.
Diagnostic methods
Symptoms of appendicitis in a child, especially pronounced ones, require urgent treatment in the surgical department. Only a complete examination will confirm or refute the diagnosis.
If the attack occurs at night or in the evening, you should not delay visiting the hospital until the morning; you must immediately call an ambulance.
To confirm the diagnosis, a specialist conducts a visual examination of the child, takes tests and, if necessary, prescribes a hardware examination. If the diagnosis is confirmed, then surgery is performed to remove the appendix.
In-person examination of the child
When going to the hospital with symptoms similar to appendicitis, the surgeon examines the child and collects verbal information.
The specialist needs to know:
- when did the pain occur and where is it located;
- whether there was any food intake that could provoke irritation of the digestive tract;
- did the temperature rise;
- general condition of the patient;
- whether there was vomiting and how many times;
- Are there any stool abnormalities?
After this, a visual inspection and palpation will be performed. The surgeon determines the condition of the skin and abdomen (whether there is tension or bloating). The type of tongue is assessed, and the amount of plaque can determine what stage the inflammatory process is already at. The relationship between pulse and temperature is checked.
Next, the surgeon checks the response to the tests:
- a T-shirt is pulled on the child and a light stroking is carried out with the hand; if appendicitis is present, pain appears in the right side;
- the surgeon applies pressure in the area of the appendix and sharply removes his fingers, in this case the child should experience severe pain.
If the symptoms of appendicitis in a child are confirmed, you should immediately consult a doctor who can confirm or refute the diagnosis.
In some cases, rectal palpation may be necessary. This is done to exclude intestinal obstruction and determine pain in the wall of the (anterior) rectum. Often, these symptoms may correspond to pancreatitis; to exclude this disease and accurately determine the condition of the appendix, the surgeon may order further examination.
Hardware diagnostics
The symptoms of appendicitis in a child described above can be confirmed by hardware examination.
To identify the inflammatory process in the appendix, the surgeon prescribes:
- Ultrasound . Using an ultrasound examination, the specialist not only confirms the diagnosis, but also determines what stage the disease is at, whether there is fluid in the abdominal cavity and how urgently surgical intervention is needed.
- X-ray . The procedure allows you to identify inflammation in the appendix, as well as the cause. If there are already complications from the disease, they can also be determined using an X-ray machine.
- CT scan Tomography is necessary to exclude diseases with similar symptoms and located in the pelvic region.
- Laparoscopy . The procedure is indicated for children over 7 years of age. Using a tube (inserted by puncturing the abdomen) with a camera, the condition of the appendix and nearby organs is assessed.
Sometimes for a complete diagnosis it is necessary to combine 2 or 3 types of hardware diagnostics. In this case, the necessary operation will be performed with high precision and fewer complications.
Analyzes
A more complete picture can be established after urine and blood tests, which are taken immediately after the initial examination. With their help, the presence of an inflammatory process in the body, as well as the condition of the body, will be revealed. Using urine, it is determined whether there is a pathology in the bladder.
For girls of childbearing age (over 13 years of age), a pregnancy test is performed.
An examination and consultation with a gynecologist may be required. In rare cases, a stool test is necessary to identify an inflammatory process in the rectum.
Symptoms by age
At each age, the symptoms of appendicitis can manifest themselves differently. It is very important for parents to learn to recognize the disease at the first signs.
Up to 3 years
At the age of three, the pathological process manifests itself instantly, its development proceeds very quickly.
The appearance of the first such symptoms should be a cause for concern and prompt consultation with a doctor.
Diagnosis is best done when the child is sleeping.
The most alarming symptoms characteristic of the pathology are:
- Loss of appetite, refusal even of your favorite food;
- Motor activity decreases;
- Moodiness, tearfulness;
- Restless state;
- Sleep disturbances, insomnia on the first night of the attack;
- Nausea, vomiting;
- Temperature rises to 40°C, and with breastfeeding up to 37.5°C;
- Frequent bowel movements or diarrhea;
- Pain when urinating;
- Rapid pulse;
- It is impossible to examine the baby; he bends his right leg under him while squatting;
- When bending to the right or when moving, the pain increases. Feelings of severe pain when lying on the right side;
- Diarrhea with mucus, especially with diarrheal appendicitis.
The danger of the disease lies not only in the transition from a simple stage to a destructive one. With frequent diarrhea, the child is at risk of dehydration.
In what cases should you immediately call an ambulance:
- When the body temperature rises, which has nothing to do with colds;
- For several hours the child suffers from pain in the abdominal area;
- Pain in the abdominal cavity is disturbing when walking, intensifies when sneezing, coughing;
- Reducing pain when pressing on the affected area. When you suddenly release your hand, the pain intensifies.
3-5 years
Appendicitis in children 5 years old is easier to recognize. At this age, the child is able to show a painful place and complain about additional signs.
When diagnosing, this greatly simplifies the study and allows you to quickly make the correct diagnosis.
At this age, children can tolerate mild pain without complaining to their parents about the illness.
7 years
Symptoms of appendicitis in children 7 years old are similar to those of adults. But it is still quite difficult to make a diagnosis at this age.
The child may be very frightened, cry constantly, and be capricious. Because they are afraid to tell their parents about their pain, children may hide dangerous signs of illness.
The most common symptoms in children 7 years old:
- Nausea;
- Vomit;
- Pain in the abdominal cavity;
- The stool is broken;
- Increased body temperature;
- Deterioration of general condition.
What symptoms in 7-year-old children should prompt parents to call a doctor:
- Decreased appetite;
- Nausea with single or repeated vomiting;
- High temperature, chills;
- Constipation or diarrhea;
- Dryness of the tongue, the surface of which is coated.
If symptoms of appendicitis in children 7 years of age appear separately or all together, they should be shown to the doctor no later than 2-3 hours after the onset of the attack.
10 years
In children 10 years of age, the following symptoms of the disease are observed:
- The child is frightened and may hide pain from his parents due to fear of surgery;
- Completely refuses to eat food;
- Feeling weak;
- There is pain throughout the entire abdominal cavity, passing after 2-3 hours to the right iliac region. When bending over, the pain effect intensifies;
- Chills, increased body temperature up to 38°C;
- Dryness of the tongue, the appearance of a white coating on its surface;
- Vomiting once or twice;
- Thirst;
- Constipation;
- Rapid pulse;
- Weak condition.
Adolescence
Signs of appendicitis in a teenager over 12 years of age are manifested in a discrepancy between the pulse rate and body temperature.
The pulse is increased and the body temperature is low. Only a specialist should diagnose the disease and check these symptoms.
Symptoms of appendicitis in adolescents aged 14-19 years are very similar to signs of the disease in adult patients.
At this age, pathology occurs most often. If signs of the disease appear in a girl, she must be referred to the gynecological department for examination by a gynecologist.
This measure is necessary to exclude pregnancy or diseases of the female genital organs.
Treatment of appendicitis
The method of treating appendicitis depends on the stage of the inflammatory process and existing contraindications (serious condition of the patient, impaired blood clotting). Before surgery, especially if there are the listed contraindications, preparation for the operation is necessary.
If appendicitis is clearly expressed, but without rupture, the child is prescribed antibiotics and drugs that reduce intoxication of the body. If necessary, antipyretic and immunostimulating.
The duration of preparation, depending on the patient’s condition (sometimes it is necessary to stabilize him) and the condition of the appendix, can range from 2 to 12 hours. Additionally, medications that improve blood clotting can be prescribed. If the child’s inflammatory process is at an uncomplicated stage, then it can be removed laparoscopically.
It is done under general anesthesia. 3 punctures are made in the abdomen (for insertion of the camera and for instruments). The duration of the operation can be from 20 minutes. The method is safer, with a minimum of possible complications and a quick recovery period.
If there is a rupture or a state close to rupture, abdominal surgery is performed. It is also performed under general anesthesia. An incision is made in the area of the appendix, then the inflamed appendix is removed. If there was a rupture, then pus and mucus are removed from the abdominal cavity. This type of operation is dangerous due to complications and has a long recovery process.
For any type of surgical intervention, the child spends 7 days under the supervision of specialists. During this time, the sutures are processed and the child’s recovery is checked. If the suture does not heal well, or the child experiences pain, this is immediately reported to the attending surgeon. Perhaps complications have begun to develop.
After discharge, the child is freed from physical activity and needs to follow a diet.
It is also necessary to take antibiotics; the duration and dosage are prescribed by the surgeon. The duration of recovery can be from 30 days. If there was an organ rupture, the postoperative period takes up to 6 months.
Causes
The appendix is a kind of “dead end” of the large intestine, and its inflammation is caused by blockage or narrowing of the “outlet” under the influence of a number of factors:
- abnormalities in the anatomical structure of the intestine;
- torsion of the colon;
- clogging with fecal stones;
- parasitic infections.
As a result, the cavity of the appendix is unable to empty itself, the outflow of mucus is hampered, pressure on the walls of the organ increases, and swelling increases. The consequence of these phenomena is disruption of blood flow, activation of opportunistic microorganisms, and stagnation of venous blood. 10-12 hours after the onset of obstruction, inflammation begins. In some cases, it is eliminated by the forces of the body itself, but most often it develops further.
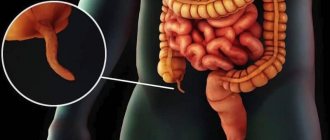
Inflamed appendix
The next stage of the disease is the rupture of the inflamed process and the entry of pus and feces into the free abdominal cavity. This process is rapid and can take from 1 to 3 days.
Another reason for infection of the appendix is the proliferation of opportunistic microorganisms living in the intestines. Under favorable circumstances, which include drug abuse, disruption of peristalsis, they cause inflammation. Microbes can also enter the cavity of the appendix from the outside: through blood or lymph from other affected organs. For example, a relationship has been proven between acute appendicitis and a history of recent nasopharyngeal diseases.
There are also infections directly related to inflammation of the appendix. These include:
- tuberculosis;
- typhoid fever;
- amoebiasis.
There are certain factors that increase the risk of developing appendicitis in children. It is advisable to warn in a timely manner:
- constipation;
- helminthic infestations;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- excessive zeal in nutrition;
- abuse of sweets with low physical activity;
- lack of fiber-rich foods in the diet.
Keeping the child's lifestyle as healthy as possible, proper age-appropriate nutrition and regular medical examinations greatly reduce the risk of appendicitis.
Forecast
The success of treatment depends on the stage at which the operation was performed. If there was no rupture of the appendix, the child will fully recover within a month after surgery. If the contents of the appendix enter the abdominal cavity, the child can recover and be under the supervision of a pediatrician for more than 3 months, sometimes up to 6.
Symptoms of appendicitis cannot be ignored in both adults and children. Timely detection of inflammation and subsequent treatment help avoid complications. It also guarantees a complete and rapid recovery of the patient.
Author of the article: Kotlyachkova Svetlana
Article design: Oleg Lozinsky
Features of the flow
The disease in adolescents has its own characteristics: there are differences in clinical manifestations and course, and the risk of complications increases.
What is the main danger
Appendicitis in a child appears suddenly and in most cases develops rapidly , within 12 hours.
Rarely, symptoms may persist for 5-7 days. If the disease is not recognized in time, complications are likely that are difficult to eliminate.
If the inflamed appendix is not removed, its walls perforate . The inflammatory process quickly spreads to the peritoneum, resulting in peritonitis. This is the most dangerous consequence; the disease poses a threat to the child’s life.
Note. In adults, complications develop within 2-3 days; in a child, they can occur within 2-3 hours.
Complications
In addition to peritonitis, other, no less dangerous consequences are likely.:
- appendicular infiltrate, abscess;
- intestinal obstruction;
- sepsis.
Catarrhal (uncomplicated) appendicitis can turn into phlegmonous (accompanied by vascular thrombosis) or gangrenous (characterized by tissue necrosis) within 12-24 hours.
Features of surgical intervention
Conservative treatment of appendicitis in adolescents is prescribed only for appendiceal infiltrate - fusion of the appendix with neighboring organs. But after about a month, the patient still undergoes a planned appendectomy. In other cases, the operation is performed immediately.
Instead of a long incision, the surgeon makes a hole with a diameter of 5 mm and inserts an endoscope. The smart device completely replaces manual intervention, minimizes blood loss and does not affect surrounding tissues. Already 2 hours after the operation, the teenager can walk freely around the ward, and after 2 days he goes home.
- It is important to follow a diet for several weeks after surgery. From the 4th day, the teenager can eat steamed cutlets, liquid porridges, and low-fat soups. Meals are fractional, up to 6 times a day. Drinking regimen – about 2 liters of clean water. You can't drink soda. Products that provoke increased gas formation are excluded from the diet.
- Despite the illness, the child is recommended to lead an active lifestyle. Of course, excessive physical activity is unacceptable, but walking, quiet games or simple housework will not hurt to restore the body.
Remember that a ruptured appendix can cause blood poisoning. Bacteria will fill the circulatory system and affect the functioning of important organs and systems. With timely surgery on a teenager, the prognosis for appendicitis is favorable.
To begin timely treatment, you need to know the signs of appendicitis in a teenager. Such knowledge will never be superfluous. By knowing the first symptoms you can avoid complications. Let's take a closer look at the signs of appendicitis in adolescence.
Diagnostics
If the symptoms of appendicitis in adolescents are easier to find out through a survey, then diagnosing appendicitis in young children is difficult because the child cannot describe his feelings.
To make a diagnosis, the patient should be placed on a hard surface and the right iliac region should be felt. When the appendix is inflamed, its compaction is easily felt. If this compaction is pressed for a while, the pain subsides, and after the hand is removed, it intensifies - this may indicate local peritonitis.
In this regard, first of all, girls are referred for examination to a gynecologist. Unfortunately, given adolescence, the child does not always complain of minor pain, and sometimes even deliberately hides it for fear of ending up in the hospital. The parent must pay attention to unnatural posture or other changes in behavior.
One of the non-obvious signs is a tilt to the right, a slight lameness on the right leg, the patient prefers to sit down carefully, as if sparing the right side.
The main sign is a depressed state - the teenager wants to lie on his left side and lie with his legs tucked. Possible tearfulness and isolation.