Optimal timing of hyperthermia
The temperature after surgical treatment of appendicitis persists for 3-4 days , but sometimes for 10-12 days. The early postoperative period is accompanied by a temperature of 38.5°C, but every day it decreases and stabilizes within 37-37.5°C.
Prolonged persistent hyperthermia is a sign of trouble, indicating the development of an infectious process and the addition of complications.
Possible reasons
Surgery is a huge stress for the body ; during the operation, the functionality of internal organs is disrupted and cells are destroyed. One of the natural reactions in response to a stress factor is an increase in temperature. After the operation, the production of a huge number of leukocytes is activated for the timely neutralization of pathogenic microorganisms, viruses and fungi.
There are other reasons for rising temperatures:
- reaction to certain medications;
- the body’s reaction to drainage installations for removing exudate;
- postoperative complications associated with tissue damage to internal organs;
- massive bleeding during the intervention, excessive blood loss;
- accession of infections;
- respiratory infections in the early postoperative period.
Fever after appendicitis surgery can occur if the diet and rest regime are not followed.
Note! Doctors consider an increase in temperature after appendectomy as normal, but constant monitoring of the qualitative and quantitative composition of blood and urine is required for timely detection of the inflammatory process.
Temperature after removal of appendicitis: how long does it last, norms
The body’s reaction in the form of an increase in temperature after any surgical intervention is normal in most cases.
After treatment of acute appendicitis or after appendectomy, hyperthermia is often an immune response of the body and indicates the correct recovery stage.
How long does the temperature last after surgery to remove appendicitis, what are the reasons for its appearance, normal and pathological variants - is discussed in the article.
Reasons for rising temperature
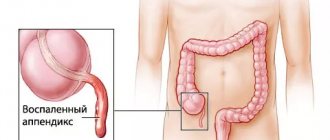
Treatment of acute appendicitis is always a surgical operation to remove the appendix. Intervention in the body, its integrity, is an unnatural process that disrupts the functioning of organs and cells. The body reacts by increasing its temperature.
In most cases, such a reaction is a variant of the norm, since the immune system after surgery for appendicitis begins to produce a large number of leukocytes to neutralize possible viruses and pathological conditions.
As a rule, when damaged tissues heal, a reaction in the form of an increase in temperature is considered normal.
It is not recommended to lower the temperature below 38C, so as not to disrupt the body’s healing process. Moreover, doctors are concerned when a person’s body temperature does not increase.
This indicates that the immune system is very weak, which means that adverse reactions, complications, and inflammatory diseases are possible.
The absence of hyperthermia after abdominal surgery can especially lead to serious health problems.
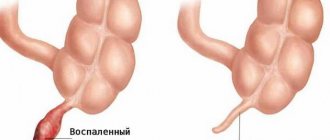
Experts note that overheating in the human body begins at the stage of the inflammatory process in the appendix of the cecum. This is a symptom indicating an inflammatory process, acute appendicitis. Therefore, after removal, the symptom persists for several days.
But in some cases, long-term persistence of fever indicates pathology.
- A strong temperature jump over a short period of time for no apparent reason. Sometimes such a reaction indicates an allergic reaction when introducing certain drugs or the ingress of pathogenic microflora that is actively reproducing.
- Hyperthermia as an immune response to the introduction of a drainage system after surgery. If it goes beyond a certain time, it is considered a pathology and requires drug treatment.
- Complications during surgery resulting in damage to internal organs.
- Excessive blood loss during surgery.
- Infection during surgery.
- A patient with ARVI during the postoperative period. The patient's body's defenses after removal of the appendix are aimed at recovery. Against the background of reduced immunity, any ARVI is tolerated more severely by the patient, longer, and longer treatment is required.
- The patient does not follow a diet after the appendix has been excised. If you ignore the diet prescribed by the doctor, disturbances in the functioning of the intestines, and even inflammatory processes, are possible.
An increase in temperature after removal of the appendix lasts about a week and is considered normal and part of the recovery phase.
But if the time frame is not met and the fever persists after a week, additional blood, urine and other tests are necessary, at the discretion of the specialist.
Tests are necessary to establish the exact cause of fever, diagnosis, and timely treatment.
Diagnosis
When diagnosing the causes of hyperthermia after removal of the appendix, a blood test is prescribed to determine the presence of an inflammatory process. In this case, the number of leukocytes matters. But a blood test is not the only diagnostic method. Medical professionals often use:
- Diagnosis using an ultrasound machine. The procedure allows you to surgically examine the abdominal cavity without additional penetration and examine whether there is any damage to the internal organs. In the absence of damage, the site of the former attachment of the process of the cecum is examined. The area is examined for the presence of an inflammatory process.
- The postoperative suture is examined. Sometimes there may be inflammation at the edges of the suture, which can cause prolonged fever.
- It is possible to biopsy the material through an open wound after removal of the appendix.
- Taking urine for analysis. The analysis provides information on the presence of leukocytes and possible problems with the genitourinary system.
The indicated diagnostic methods are sufficient to establish the exact cause of prolonged hyperthermia; additional studies are required in rare cases.
It should be understood that the values in the analyzes for men, women and children have different ranges and different variants of the norm.
Women, due to the way their bodies work, have a wider range of leukocytes than men. This is associated with a specific day of the menstrual cycle. In this regard, after 21 years of age, test results are divided based on gender.
When testing blood in children, the level of leukocytes is higher than normal not only in pathological conditions such as acute appendicitis, but also in other cases. The immune system of a child, in comparison with an adult’s body, is not as perfect. At the same time, infections and pathogenic environments more often enter the child’s body, which requires the immune system to increase the level of leukocytes.
Leukocytes in human blood
This is necessary to protect the body. If a child has appendicitis, the doctor must take blood for analysis not only before the operation, but also after it. The procedure is necessary to monitor your well-being and the proper healing process.
Treatment for pathological processes
If pathological processes are detected that serve to maintain body temperature for a long time after surgery for the appendage of the cecum, adequate therapy is necessary. Doctors use medication to treat pathological conditions:
- Antibiotic drugs. Often used when a bacterial infection is detected in a wound after surgery. During diagnosis, the degree of sensitivity of the body to a particular drug is also revealed, after which antibacterial therapy is prescribed.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. The main ones: Nurofen, Ketonal, Ibuprofen.
- Antipyretic drugs. Analgin, Aspirin, Paracetamol.
The patient must remember that if the temperature rises after discharge from the hospital, one should not self-medicate! You should immediately seek help from a doctor, because hyperthermia may indicate a serious pathological course that poses a threat to the health and life of the patient.
Elevated body temperature after excision of the appendix of the cecum lasts above 37C for 7-10 days, which is normal. By day 10, most patients are normally afebrile. No doctor will discharge a patient if hyperthermia remains above normal.
If fever persists beyond the specified time, even 2 weeks after surgery, a course of antibiotic treatment brings the patient’s state of health back to normal.
But if there is no effect from antibacterial therapy, the doctor prescribes repeated surgery. The operation is indicated to study the abdominal cavity to accurately determine the cause.
Often, ultrasound machines do not allow us to see the cause of the inflammatory process in the abdominal cavity, which causes the fever to persist.
It is important for the patient to monitor the condition after appendicitis, monitor recovery and well-being, and report the slightest deviation to the doctor in a timely manner. Correct treatment, proper diagnosis, and adequate response to the complication will allow you to feel normal after surgery and maintain health without compromising your quality of life.
It is important after discharge from the hospital to follow some rules for a speedy recovery and recovery after surgery. Be sure to follow a diet. Violations in the form of eating spicy, fried, heavy foods in large quantities put a strain on the intestines, contribute to the formation of constipation and inflammation.
Physical activity should be feasible. You can’t immediately play sports or start heavy physical labor. Muscles and tissues must recover properly.
You need to monitor your daily routine and ensure adequate sleep and rest.
Source: https://GastroTract.ru/appenditsit/temperatura-posle-udaleniya-appenditsita.html
Classification of fever
The classification is intended to identify hyperthermia relative to pathology or normality. There are two key criteria : the level of rise and temperature fluctuations.
By lift level
The following types of temperature are distinguished according to the level of rise::
- subfebrile - numbers vary from 37 to 37.5°C, are typical for the early postoperative period, refer to the normal variant, hyperthermia does not require relief;
- febrile - indicators exceed 39°C, indicating the onset of secondary inflammation, the body’s reaction is aimed at preventing the generalization of the infectious focus;
- pyretic (or fever) - values exceed 39°C, indicating the onset of active local or generalized inflammation, the condition requires repeated surgery or antibiotic therapy;
- hyperpyretic - temperature above 40°C requires urgent intervention, poses a danger to life, indicates a generalized infection, sepsis.
To monitor the patient’s condition after surgery to remove appendicitis, hospitalization is indicated for 5-7 days.
By the nature of the jumps and frequency
Another important criterion is temperature fluctuation. The following types of hyperthermia are distinguished :
- constant - characteristic of low-grade fever and febrile temperature, with a long course it indicates chronic inflammation;
- remitting - indicators constantly vary within two degrees, do not decrease to normal values, characterize abscesses;
- hectic - constant fluctuations from normal to critical values, characterize a generalized infection, sepsis;
- intermittent - characterizes the interval of increase within 3-4 days from normal to febrile and higher, not typical for the recovery period.
The patient during the recovery period requires special attention from medical personnel . Even the most successful operation can lead to unforeseen complications. When answering the question of how long the temperature lasts after surgery, it is important to take into account the patient’s immune status, general clinical history, severity of the condition, complications and other aspects.
Signs of the development of pathological hyper- and hypothermia
Main signs of pathological temperature fluctuations:
- a sharp change in the qualitative and quantitative composition of the blood against the background of heavy bleeding;
- malaise;
- sweating (cold, sticky sweat covers the forehead, feet and hands);
- blood pressure disorders;
- heart rate instability;
- symptoms of intoxication: nausea, vomiting, upset stool.
Dangerous signs include depression of consciousness, sharp abdominal pain, constipation, profuse indomitable vomiting, and persistence of a high temperature for more than 10-12 days.
Symptoms to watch out for
The difficulty in diagnosing appendicitis lies in the fact that it is well disguised as other diseases with a related clinical picture, for example, influenza, inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, female and male genital organs, and others. Symptoms more characteristic of this disease begin to appear as it progresses. So, at the initial stage of its development one can observe:
- pain in the umbilical region;
- slight increase in temperature;
- nausea, possibly vomiting;
- weakness in the body;
- cardiopalmus;
- bowel dysfunction;
- dizziness.
Over the next few days from the moment the first symptom appears, the clinical picture changes, and the person’s general condition noticeably worsens. As a rule, people seek medical help precisely during this period, when they no longer have the strength to endure the painful condition. Doctors note the temperature for acute appendicitis from 38 degrees and above. In this case, a number of other symptoms are observed:
- severe pain in the right side;
- nausea, frequent vomiting;
- severe tachycardia;
- bloating;
- stopping the gastrointestinal tract.
In this state, a person practically cannot move, since changing posture provokes increased pain. If you do not call an ambulance at this stage, complications that are incompatible with life may occur.
Potential Risks and Complications
A common complication after appendectomy is the addition of a secondary infection in the absence of adequate antiseptics of the sutures during dressings, as well as incomplete removal of purulent exudate.
There are other types of infectious complications after surgery for appendicitis :
- Urogenital infections . Pathogenic microorganisms can penetrate the urinary tract and kidneys, and inflammation can occur even before the appendix is removed, complicating the subsequent recovery period. People with kidney pathologies and chronic inflammation of the bladder are at risk. The most common are secondary pyelonephritis, nephritis, glomerulonephritis, cystitis, urolithiasis, and urethritis.
- Respiratory infections . A weakened body increases the risk of developing ARVI with or without severe respiratory symptoms (cough, shortness of breath, lacrimation, rhinitis). In the absence of normal immune defense, other complications may occur: bronchitis, pneumonia, nasopharyngitis.
Important! A weakened body is susceptible to nosocomial infections caused by staphylococci, streptococci, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli, Klebsiella, Escherichia, etc.
Causes
Doctors still cannot determine all the reasons why inflammation of the appendix occurs. The only thing we can say for sure is that it is caused by an infection. This may be the entry of E. coli, staphylococcus and other strains of pyogenic bacteria into the shoot. Of course, they cannot develop there on their own. Factors that cause the appearance of pathogenic microflora in appendicitis:
- blockage of the appendix exit;
- blood stagnation caused by vascular dysfunction;
- slowing down bowel function.
In addition, there are risk factors that significantly increase the chance of appendicitis. These include:
- frequent constipation;
- abundant consumption of protein foods;
- bad habits;
- disruption of the cardiovascular system;
- infectious diseases.
It is noted that in some cases, hidden pelvic infections lead to the appearance of appendicitis in men, and gynecological inflammatory diseases in women. Some experts talk about the chronic form of the disease, when after an acute condition a decrease in inflammation of the appendix and the manifestation of symptoms was noticed. But such cases are rather the exception. Most often, the process is removed to avoid complications and subsequent relapses.
Which doctor will help?
The manifestation of symptoms of appendicitis is a reason to visit a medical facility. To find out whether a deterioration in well-being is associated with the onset of a disease, you need to consult with doctors such as:
These specialists can give a competent assessment of the patient’s health status and determine the stage of development of the disease. If he exhibits the above symptoms, and the results of the examination revealed a swollen, hard abdomen and a white coating on the tongue, then acute appendicitis is diagnosed. This means that the disease can be life-threatening, so consultation with a surgeon and immediate surgery to remove the appendix are indicated. To obtain more accurate data about the patient’s well-being, the doctor may ask:
- How many days ago did your stomach first hurt?
- Where exactly and what kind of pain was it?
- Have you had an elevated body temperature?
- How often did you vomit?
- Where is the pain located now?
- Is there slow gastrointestinal function?
- What other symptoms are you worried about now?
If no complications are found that would prevent surgery, the patient will undergo an appendectomy in the near future.
Diagnosis in the postoperative period
Diagnosis of complications in the postoperative period regarding removal of an inflamed appendix is not difficult and rarely leaves doubt.
Basic methods for identifying pathological conditions:
- general and detailed blood tests;
- general urine test (if necessary, daily, according to Nechiporenko);
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs (for example, to detect free fluid in the peritoneum);
- daily palpation of the peritoneum and abdominal organs during a medical examination.
Be sure to respond to the patient's complaints about any changes in well-being . Timely diagnosis of complications often allows for conservative treatment.
Relationship between the type of appendectomy and hyperthermia
It is very difficult to predict in advance exactly how a person will react to removal of the appendix, and how long the temperature will last after the intervention. It is important to understand that hyperthermia after surgery is an expected phenomenon.
The indicators are also influenced to some extent by the method the surgeon chose to remove the inflamed appendix:
- Laparoscopic. A more modern and less traumatic method. The inflamed appendix is removed through several small holes in the abdomen. The duration of the rehabilitation period is significantly reduced, since during the intervention the tissue was damaged minimally. Typically, the temperature after surgery persists for 2-3 days, and then disappears without a trace and on its own. Increases to subfebrile levels.
- Abdominal surgery. This method is used mainly in complex clinical cases (for example, peritonitis, perforation of the appendix or purulent exudate). Removal of the affected process is carried out through a classic incision in the abdomen, which is then sutured. The rehabilitation period is longer. The temperature can be either low-grade or relatively high – 38-38.5°C. Lasts up to 10 days.
Prolonged and persistent hyperthermia is the first sign that indicates the progression of an infectious or inflammatory process, as well as the development of complications after the intervention.
Treatment tactics for complications
The addition of secondary infectious processes after removal of the appendix is treated with antibiotics from the group of cephalosporins and penicillins. As symptomatic therapy, drugs based on ibuprofen, ketoprofen, paracetamol, and aspirin are prescribed.
Repeated surgery is often required. If local inflammation is diagnosed, intensive antiseptic treatment of suture fragments is carried out.
Note! If necessary, drain the wound surface, and additionally sanitize the abdominal cavity to avoid sepsis, peritonitis, other acute septic complications, and abscess.
Diagnosis
When diagnosing the causes of hyperthermia after removal of the appendix, a blood test is prescribed to determine the presence of an inflammatory process. In this case, the number of leukocytes matters. But a blood test is not the only diagnostic method. Medical professionals often use:
- Diagnosis using an ultrasound machine. The procedure allows you to surgically examine the abdominal cavity without additional penetration and examine whether there is any damage to the internal organs. In the absence of damage, the site of the former attachment of the process of the cecum is examined. The area is examined for the presence of an inflammatory process.
- The postoperative suture is examined. Sometimes there may be inflammation at the edges of the suture, which can cause prolonged fever.
- It is possible to biopsy the material through an open wound after removal of the appendix.
- Taking urine for analysis. The analysis provides information on the presence of leukocytes and possible problems with the genitourinary system.
Preventive actions
There is no specific prevention of fever in the early postoperative period . In no case should the temperature be lowered than 38.5°C in order to objectively assess the patient’s current status. Its premature reduction can distort the true clinical picture and complicate the early diagnosis of postoperative complications.
It is important to adhere to the following recommendations:
- organization of an adequate diet, sleep and wakefulness;
- timely dressing and antiseptic treatment of the suture and wound surface;
- regular collection of blood and urine tests, monitoring of laboratory parameters;
- antibiotic therapy as indicated.
General preventive measures involve avoiding contact with infections , especially during periods of high epidemiological risks, as well as maintaining quarantine in the department.