Where is?
The iliac region is located inside the abdominal cavity of men and women. This part of the human body is conventionally divided into right and left sides. In each part of the ileum there are internal organs that have their own functional purpose.
In the right cavity are concentrated:
- cecum;
- appendix;
- ileum.
The cecum, which has no pathological changes and is not in a painful state, is closed in front by loop-shaped tissues of the small intestine.
If the cecum is completely filled with gases, it covers the entire cavity. The left side of the iliac fossa contains loops of the jejunum. The sigmoid colon is also located in this part of the abdominal cavity, but it runs from the 3rd sacral vertebra to the iliac crest.
If the cavity of the bladder and rectum is completely filled with biological contents, the loops of the S-shaped intestine smoothly move to the left side of the ileum.
The ileum also contains the following organs of the reproductive system of men and women:
- the ureter connecting the renal pelvis to the bladder;
- round ligament of the female reproductive organ - the uterus;
- The male reproductive organ is the vas deferens.
All of the above organs receive stable blood supply through the main blood vessels. The ileum is one of the least capacious parts of the abdominal cavity.
Diseases of the ileum
Intestinal diseases have relatively similar symptoms; most often they are provoked by disturbances in the absorption of substances, the amount of excretion, and digestion. If you have frequent stomach rumbling, upset, frequent and regular pain, you need to undergo examinations in order to diagnose a possible disease in the early stages.
If you ignore the above symptoms, then after 2-4 years the disease will reach the final stages and begin to actively progress. In this case, complications will arise: amyloidosis, obstruction, bleeding, fistulas.
Crohn's disease
This disease is statistically quite common. In this case, inflammation occurs precisely at the end of the intestine, namely in the last 20 centimeters. For a disease, the moment of timely detection of the disease and, accordingly, treatment is very important.
Characteristic symptoms:
- pain on the right (often confused with appendicitis);
- fever;
- nausea, vomiting (observed very often);
- anemia;
- bleeding (blood is observed in the stool);
- the appearance of scars (if there are a large number of them, intestinal obstruction appears);
- frequent diarrhea, constipation;
- pain (they most often occur 3-4 hours after eating).
Lymphoid hyperplasia
The disease occurs due to changes in the intestine itself. Most often, these disorders disappear and do not cause any harm to the body. There are cases when everything does not go so smoothly; the reason for this may be relapses and deviations of intestinal tissue.
Symptoms:
- sudden loss of body weight that is difficult to regain;
- diarrhea;
- decreased immunity (the body does not resist, which allows infections to easily enter it);
- blood in feces;
- pain (abdominal);
- bloating;
- excessive gas formation.
Malignant formations
Ileal cancer itself is not very common; metastasis from other organs is more often diagnosed. Nutrition plays an important factor in this disease. It is fatty and smoked food, or rather its excessive consumption, that is a provoking factor. As mentioned above, if the disease is ignored for a long time, the tumor can spread and infect neighboring organs. The following symptoms may appear:
- nausea;
- colic;
- bloating;
- heaviness;
- weight loss;
- obstruction;
- bleeding in the intestine.
Ulcer
In case of chronic intestinal disease and untimely, neglectful attitude to treatment, defects - ulcers - can form. According to statistics, more than 70% of the disease occurs in men.
The main reasons may be disturbances in the functioning of blood vessels, taking medications that are not suitable, injuries to the intestinal lining, and excessive amounts of hydrochloric acid.
In the first stages, the characteristic symptoms are pain, which worsens when eating fatty and spicy foods, most often on the right side. In the final stages, pus and blood appear in the stool. If treatment is not started in time, complications may occur:
- perforation;
- cancer;
- narrowing of the intestine;
- internal bleeding.
Atresia
A characteristic symptom is that substances do not pass through the last part of the intestine. The peculiarity of this disease is that it is congenital.
Symptoms:
- bloating;
- lack of meconium;
- vomiting, nausea (typical already in the first days of life);
- anxiety;
- the child’s appetite disappears;
- insufficient feces.
Structure
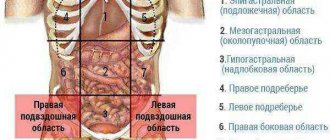
The iliac region is located in the lower part of the abdominal cavity, covering its sides, as well as the lower abdomen. In order to ensure high-quality diagnosis and control over the health of the internal organs of the digestive and genitourinary systems, the ileum is divided into 2 main structural segments. This part of the body has the following structure.
The iliac region consists of the left and right parts
| Name of the structural part of the iliac region | Location in the abdominal cavity |
| Left | This part of the iliac region is located inside the abdominal cavity in the space between the lower left row of ribs and the ilium. |
| Right | The right iliac fossa covers the abdominal cavity from the right side from the lower ribs to the ilium. |
If we look at the anatomical structure of this part of the peritoneum in the pictures, we get the visual impression that the left and right iliac regions are located directly above the lateral part of the pelvic bones or directly above the hip joints.
Both parts of the ileum are located opposite each other and perform a single physiological function as a reservoir for the internal organs of the digestive and genitourinary systems.
What is the ilium
If you study human anatomy, it is necessary to clarify that this is one of the largest bones of the human skeleton - the hip joint. By its design, the ilium is paired, massive, and symmetrical. The relief of this skeletal element is determined by the muscles; structurally there are several characteristic sections of various sizes and densities.
What organs are located in the iliac region?
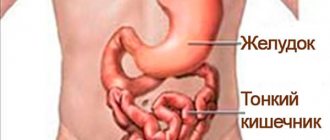
The iliac region is located in the lower part of the abdominal cavity. It contains the following internal organs, which are vital for maintaining the stable functioning of all systems of the human body:
- cecum;
- appendix;
- sigmoid colon;
- ureter (this organ is localized in this part of the abdominal cavity, in both men and women);
- loop-shaped tissues of the jejunum;
- small intestine;
- ileum;
- vas deferens in men;
- round ligament of the female internal reproductive organ - the uterus.
This part of the abdominal cavity contains a nerve plexus that connects tissues and muscle fibers to the lumbar spine. Thanks to them, nervation of the above internal organs, as well as other elements of the digestive and genitourinary systems, is carried out.
Groin pain during pregnancy
The situation when women have pain in the right groin is especially relevant for those who are preparing to become a mother.
Some pregnant women experience pain in the lower abdomen
But such a symptom does not always signal the development of some kind of ailment in a pregnant woman. It often happens that this feeling accompanies the entire pregnancy. During this period, the female body experiences enormous physiological and hormonal changes.
The longer the pregnancy, the more the woman listens to herself and discovers a variety of painful sensations, including in the groin area. And this is all understandable: the fetus grows, the uterus enlarges and causes sprains.
A slight restlessness in the groin may be the cause of increased levels of the hormone progesterone, which reduces intestinal motility, causing constipation in a pregnant woman.
This is accompanied by a feeling of discomfort and painful sensations in the rectum and abdomen. Or maybe, on the contrary, groin pain indicates the appearance of flatulence.
We cannot exclude diseases that are sometimes detected in women during pregnancy.
Here are some of them:
- Symphysitis. The cause of this pathology may be swelling of the symphysis pubis and excessive divergence of the frontal bones. This mother’s illness, as a rule, does not affect the baby’s health. And in the expectant mother, this disease most often disappears after childbirth. But during the birth itself, this pathology can cause serious problems.
- Infectious and inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary organs. They are also characterized by pain in the groin area. This symptom may indicate: colpitis, cervitis, cystitis, etc.
- Ectopic pregnancy. Very often, the attachment of a fertilized cell in the fallopian tube is not immediately diagnosed and pregnancy in the first stages proceeds as traditional.
The appearance of pain in the groin area and lower abdomen, accompanied by bloody discharge and weakness, should cause concern that there is pain in the groin on the right. In women, this pathology is associated with a great threat to life and should be eliminated as quickly as possible.
Read the new article in the section: Gallstone disease: treatment without surgery and diet
What diseases are localized within this area?
The right and left iliac regions can be subject to inflammatory and infectious diseases that are caused by mechanical damage to tissue, an autoimmune reaction of the body, or due to bacterial infection of tissues of internal organs. The following types of diseases can be localized within this area of the body.
| Type of disease | Characteristics of clinical manifestations and their localization |
| Appendicitis | This disease is also found under the medical term - inflammation of the vermiform appendix. The disease is characterized by acute symptoms with the occurrence of cutting pain in the right iliac region. A person with this diagnosis cannot independently stand in an upright position, as severe pain forces him to bend over or lie on his back. During palpation of the cavity, the pain intensifies. An increase in body temperature and the occurrence of fever are also recorded. Lack of timely surgical treatment can lead to the formation of a purulent abscess, rupture of the appendix and peritonitis. |
| Volvulus of the sigmoid colon | This is a pathological condition of the digestive system, which is localized in the ileal region. Occurs as a result of increased pressure inside the abdominal cavity. It can develop after strangulation of an inguinal hernia, prolonged fasting, prolonged constipation, or lifting heavy objects. Volvulus of the sigmoid colon is accompanied by sharp or cutting pain in the lower abdomen. The change in the position of the organ as a result of torsion can reach 90 degrees. In medical practice, there are clinical cases when, as a result of too active intestinal peristalsis, the sigmoid colon undergoes 2 to 3 twists. A patient who has had a sigmoid colon volvulus in the ileal region requires emergency surgical intervention. Otherwise, acute inflammation of the mucous membrane of the organ occurs, the blood supply to its tissues is disrupted, vascular thrombosis develops and the process of necrosis begins. |
| Helminthiasis | Infection of the intestines and other parts of the digestive system by parasites can also cause a painful condition of the organs located in the ileum. In the lower abdomen, pathological symptoms are felt in the form of cutting pain, increased gas formation and bloating, and the presence of atypical lumps. In addition to these signs of helminthiasis, which are localized in the intestines of the ileum, there is a feeling of nausea, loss of appetite, physical weakness and fatigue. |
| Acute prostatitis | A complication of this urological disease, which is diagnosed exclusively in men, can cause inflammatory damage to the vas deferens. This pathology develops when a bacterial infection localized in the tissues of the prostate gland spreads to other parts of the male reproductive system. The vas deferens is located in the ileum, and its damage causes acute pain, which intensifies during intense walking, squatting, heavy physical labor, and prolonged sitting. |
| Intestinal dysbiosis | This is a disease that is associated with an imbalance of beneficial and pathogenic microflora living in the intestines. The disease is characterized by cutting or aching pain in the intestines located in the ileum on the left and right sides. A person suffers from increased gas formation, lack of appetite, and nausea. Constipation or diarrhea cannot be ruled out. The disease develops as a result of prolonged antibacterial therapy, poor-quality or unbalanced nutrition, and alcohol abuse. |
| Endometritis | This disease is a gynecological pathology, the symptoms of which appear after inflammation of the inner epithelial layer lining the cavity of the female reproductive organ. The disease can be acute or chronic. Pain in the iliac fossa is also cutting or aching in nature. |
| Abscess of the iliopsoas muscle | This is a dangerous disease of the musculoskeletal system, which is characterized by an acute inflammatory process and the formation of a purulent abscess. The disease affects the muscle fibers of the iliopsoas muscle, which are destroyed as a result of an infectious-inflammatory process. The disease develops as a result of mechanical trauma to tissue due to blows, falls, lifting heavy objects, and the consequences of surgical intervention on the organs of the iliac fossa. The main symptoms of this disease are acute pain, an increase in local and general body temperature, a change in the color of the skin in the area where the purulent abscess is localized (it becomes red, purple or even bluish). |
| Inflammation of the appendages | Diseases associated with the development of acute or chronic inflammation in the uterine appendages can also cause pain in the iliac region. The pathology may be associated with inflammation of the ovaries, the formation of benign or cancerous tumors in their tissues. |
| Oncology of the ilium | This is bone tissue that is located in close proximity to the iliac space. Its defeat by a malignant neoplasm causes a large number of unpleasant symptoms associated with impaired motor activity of the lumbar spine, hip joint and lower limb. One of the first signs of the disease is prolonged and persistent pain in the iliac fossa, which cannot be eliminated by taking potent analgesics. |
| Inguinal or femoral hernia | The appearance of an inguinal or femoral hernia disrupts the functioning of internal organs and tissues located in the iliac region. A characteristic sign of the disease is the formation of a round lump that rises above the general level of the skin surface of the abdomen. This is a hernial sac that is soft to the touch. The main danger of this disease is the high risk of strangulation of the hernia, which will lead to the development of necrosis of the tissues from which it was formed. The disease is treated by surgical removal of the hernial formation. |
| Urolithiasis disease | Symptoms of this disease manifest themselves in the form of burning or aching pain if foreign stones or sand enter the cavity of the ureter from the kidney. The pain syndrome appears periodically or bothers the person constantly. The pathological condition of the organs of the excretory system can cover the right, left side of the iliac fossa, or both sides at once, if the patient suffers from bilateral kidney damage from stones. The disease is treated with medication or surgery. |
Men diagnosed with inflammation of the seminal vesicles may also experience a feeling of discomfort and nagging pain, which is localized in the iliac fossa. In medical practice, there are cases when the painful condition of this part of the body was associated with pathological changes in the tissues of the ilium.
Causes of pain in the anterolateral part of the peritoneum
Pain in the iliac region is mostly caused by injuries and pathologies of the internal organs of the digestive tract and genitourinary system.
- varicose veins of the pelvis caused by a sedentary lifestyle;
- acute or chronic inflammation of the uterine appendages, lymphadenitis of the iliac lymph nodes, abscesses of the iliopsoas muscle;
- postoperative adhesions;
- benign and malignant tumors of the gynecological area;
- urolithiasis, inflammatory processes in the kidneys, prolapse of the ureter;
- hydrocele (dropsy of the testicle);
- inguinal or femoral hernia, elongation and torsion of the sigmoid colon, causing obstruction;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- colitis, dysbacteriosis, prolapse of intestinal loops, chronic constipation, overflow of feces, helminthic infestation;
- poisoning and infectious diseases accompanied by diarrhea.
What does pain in the iliac region mean?
The iliac region is located on the sides of the lower abdomen. The occurrence of discomfort, a feeling of acute or aching pain on the left or right side may indicate the development of an inflammatory or other pathological condition of the internal organs.
Left
The occurrence of pain on the left side of the iliac region may be associated with inflammation of the mucous membrane of the sigmoid colon, volvulus, intestinal obstruction, constipation or dysbacteriosis. The pain syndrome is characterized by frequent cramping attacks, which intensify as the inflammatory process worsens.
On right
Pain on the right side of the iliac region most often indicates inflammation of the appendix, which is also known as appendicitis.
In men, similar symptoms may be associated with inflammation of the seminal vesicles and hyperplasia of prostate tissue. In women, acute or aching pain in the right side of the iliac region occurs due to pathologies of the uterine appendages.
The most common causes of pain
There are ailments due to which pain in the iliac region manifests itself most often. Moreover, this does not depend on the gender and age of the patient.
Irritable bowel syndrome. A frequently recorded pathological deviation, due to which the intestinal muscles remain in a convulsive state for a long period. The patient experiences torment from strong contractions on both sides and in the center of the abdomen, becomes irritable, and experiences anxiety. The motor functioning of the intestine is impaired.
Obstruction of the intestinal tract. Painful manifestations of a cramping type in the left part of the iliac zone occur regardless of food intake. It is often accompanied by heaviness, belching, nausea, vomiting, bloating of the abdominal cavity, and the person suffers from constipation.
Infection with helminths. Clusters of helminths provoke obstruction. The activity of worms in the small intestine can cause dull pain on the left side of the lower abdomen.
Lengthening of the sigmoid colon. It can lead to the formation of an additional intestinal loop and provoke painful manifestations of the cutting type. Additional symptoms include lack of bowel movements and difficulty breathing.
Colitis. If the wall tissues of the large intestine become inflamed, the stomach aches, bloating occurs, diarrhea with mucus occurs, and you always want to go to the toilet. These symptoms last from several days to a month or more. If this is a nonspecific ulcerative type of the disease, colic in the left side intensifies after eating and is accompanied by frequent bowel movements and hemorrhages from the anus.
Enteritis. A person experiences pain in the lower peritoneum on the right. Diarrhea, nausea begins, and undigested food remains come out.
Appendicitis. Pain syndromes during inflammation of the appendix are of various types and in the first phase are practically not disturbing. Gradually they increase and become local with a concentration in the right abdominal region, unbearable when pressed. Pulsating attacks are accompanied by nausea and a rise in temperature.
Bowel cancer. Painful manifestations in the lower abdomen with such a disease are usually quite mild. Neoplasms obstruct the movement of excrement, which leads to persistent defecation delays and swelling of the peritoneal region. After the release of excrement plugs and gases, the pain subsides for a while.
Urolithiasis and urinary duct prolapse. They report themselves by painful manifestations in this area. Often acute pain, similar to renal colic, indicates blockage of the urinary canals with a stone or dysfunction of urinary diversion.
Cystitis. In addition to pain, the patient suffers from constant unsuccessful attempts to release the bladder, burning and stinging, if this is still possible. If the unpleasant feelings increased in intensity and spread to the posterior hypochondrium, the inflammation probably spread to the kidneys and caused pyelonephritis.
Cholecystitis and cholelithiasis. When exacerbating, they provoke the appearance of burning pain on the right side, especially when inhaling, when straightening the body, and walking.
Varicose veins The development of pathology is possible in the abdominal area. Incompetence of the venous vessels in the pelvic area often occurs in those who have to stand for long periods of time at work. The disease is characterized by aching pain in the legs and abdominal area, especially at night.
Inguinal or femoral hernia. Aching pain manifestations can appear in the left and right zones of the peritoneum from below - depending on the location of the problem area.
Osteochondrosis. It provokes aching pain in the direction of the affected nerve fiber, which radiates to the iliac region and to the hip joint.
Sometimes painful sensations are provoked not by pathological abnormalities and ailments, but by excessive physical exertion and mental fatigue. In the first variant, the muscle structures become tense, a burning sensation and tingling sensation appear. During nervous stress, pain occurs on the sides of the peritoneum and in the middle.
Fracture of the ilium
The ilium is the largest part of the 3 paired bones that form the pelvis. With its help, the bone tissue of the pelvis is connected to the spine. An ilium fracture is a high-energy pelvic injury that can occur as a result of an accident, a fall from a great height, a gunshot wound, or a mine explosion.
This pathology is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- acute pain in the lumbar spine, which intensifies when pressing on the pubic bone;
- formation of a subcutaneous hematoma in the scrotum in men and perineum in women;
- urinary incontinence or involuntary urination if bone tissue has been displaced with damage to the excretory organs;
- vaginal bleeding in women;
- violation of the position of the prostate gland and the inability to palpate it in men;
- presence of blood inside the urethra;
- persistent pain in the lower abdomen on the left or right;
- anal bleeding;
- weak or complete absence of sensitivity in the perineum, pubis, anus, inner thigh or entire lower limb (this symptom is characteristic of ilium fractures with damage to the nerve plexus of the lumbar spine).
Diagnosis of an iliac bone fracture involves the use of radiography and CT scan of the pelvis. If the diagnosis is confirmed, the traumatologist or surgeon takes measures for external or internal fixation of the bone tissue that has undergone a fracture.
During the treatment period, the patient is bedridden and requires constant care. The duration of therapy ranges from 1 to 6 months. depending on the severity of the fracture and the possible presence of complications.
Treatment of diseases that cause abdominal pain
Treatment for each disease that causes abdominal pain is individual. For example, appendicitis can only be treated surgically, i.e. removal of the inflamed appendix (appendectomy). Treatment of gastritis involves taking antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, painkillers and following a strict diet.
Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum cannot be avoided without taking antibacterial agents, drugs that reduce stomach acidity, and medications with an enveloping effect. Gastroesophageal reflux can be cured with partial nutrition, antacids, and proton pump inhibitors.
If conservative treatment does not produce positive results, surgical intervention is indicated. Therapy for Crohn's disease directly depends on the severity of the disease and location. In case of narrowing of the intestine, purulent inflammation and ineffectiveness of drug treatment, surgery is indicated.
Therapy is selected individually
Urinary tract infections are treated with antibiotics, after culture has been carried out to identify microorganisms and their sensitivity to certain drugs. Getting rid of diseases of the female genital organs is also not possible without antibiotics; in addition, it is worth paying attention to the cause of the disease and its location.
In some cases, surgical intervention is not necessary. Mandatory conditions on the path to recovery are stopping smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages, following a strict diet prescribed by a gastroenterologist or other specialist.
Ilial bone cancer: causes and signs
The first symptoms of a malignant tumor of the ilium are the following sensations experienced by a sick person:
- feeling of aching pain in the perineum or lumbar region;
- body temperature in the area where the affected bone is located is 1-2 degrees higher;
- the skin surface on the inner side of the thigh, scrotum, perineum becomes swollen and red;
- the sensitivity of the skin on the back of the thigh is impaired;
- While walking, you feel a sharp pain in your thigh or lower abdomen.
The main reasons for the development of oncology are hereditary predisposition, daily contact with carcinogenic and toxic substances, bad habits, a sedentary lifestyle, previous pelvic injuries, chronic inflammation of bone tissue.
Pain in the right side of the lower abdomen in women
Pain in the lower abdomen in women can appear due to various gynecological diseases, for example: endometriosis, fibroids, adnexitis. In this case, the woman is bothered by unpleasant pulling sensations in the lower lateral parts of the abdomen or in the perineum, which intensify when walking. In addition, the pain may be accompanied by discharge from the genitourinary system. Such manifestations are characteristic of inflammatory changes in the right fallopian tube: chronic or acute andexitis, in which a nagging or acute and severe pain appears in the lower anterior abdominal wall on the right. The pain can spread to the perineum, lower back and inner thigh, body temperature rises, mucopurulent discharge appears.
Sharp and sudden pain in the lower abdomen on the right may be a sign of cyst torsion, tumor of the fallopian tube or right ovary, which requires urgent surgical treatment. Ovarian apoplexy usually occurs in the middle of the menstrual cycle. If a sharp and severe pain appears on the right or left above the groin, radiating to the anus, and accompanied by dizziness, weakness, loss of consciousness, this condition may be a manifestation of a rupture of an ovarian cyst after sexual intercourse or an ectopic pregnancy with 1-2 weeks of delay in menstruation.
Trephine biopsy of the iliac bone
Trepanobiopsy of the iliac bone is a type of diagnostic examination, the conduct of which involves the selection of bone marrow particles, as well as tissues.
The main purpose of the procedure is their histological examination, aimed at determining the health of the bone tissue structure. Doctors receive comprehensive information about the quality of the cellular composition of the bone marrow, the percentage of adipose and hematopoietic tissue, the condition of blood vessels and stroma.
Histological analysis makes it possible to determine the presence of a benign or cancerous neoplasm if signs of a tumor process are found in the structure of the ilium. Biological material is collected using a needle puncture. The patient is under general anesthesia, and the diagnostic procedure itself is a simple surgical operation.
Ilium bone hurts
Since the structure is subject to systematic compression and is open to direct blows, doctors do not deny the frequent clinical pictures of fractures in patients of different age categories. If the characteristic lumpiness begins to hurt, you need to immediately consult a specialist to promptly determine the etiology of the pathological process. Acute pain syndrome occurs not only due to fractures of bone structures; doctors also focus on other pathogenic factors. Restoring the integrity of damaged tissues is a long process.
Left
If the left segment hurts in the absence of a fracture, it is possible that the indicated area is subject to increased physical activity. Such an uneven distribution of “heaviness” over time can lead to a dislocation or fracture and cause disability for the patient. Other, no less dangerous causes of a characteristic disorder of the human skeleton may be as follows:
- malignant tumors;
- osteomyelitis;
- tuberculosis;
- metabolic bone diseases;
- congenital disorder of collagen synthesis;
- age-related changes in the body;
- Paget's disease;
- long bed rest;
- chronic blood diseases.
On right
With sharp pain on the right side of the iliac bone, we are also talking about an extensive pathology, which can cause other symptoms, for example, decreased mobility of the limbs, displacement of the bone structures of the hip joint with further discomfort, and the patient’s confident progress towards disability. The reasons why the once strong right structure can hurt are the following:
- blood diseases, for example, leukemia, bone marrow damage, multiple myeloma;
- deficiency of minerals, possibly vitamin D;
- consequence of injury;
- long-term use of medications - synthetic hormones;
- excessive secretion of cortisol;
- advanced age of the patient;
- professional sports;
- herniated intervertebral discs;
- osteochondrosis;
- oncology.
Treatment
Treatment of diseases of the iliac region is symptomatic. In the case of the development of dysbacteriosis, colitis with infectious inflammation of the mucous membrane of the sigmoid colon, antibacterial agents are used, the active components of which are effective against microorganisms of specific strains. The type of antibiotic is selected based on the results of laboratory diagnostics.
Appendicitis, volvulus of the sigmoid colon, malignant and cancerous neoplasms, blockage of the ureter with stones, acute inflammation of the prostate gland with impaired urine outflow require surgical intervention.
Most operations performed on the organs of the iliac region are not complicated. If you consult a doctor in a timely manner, the prognosis for a full recovery is positive.
The iliac region is a depression in the lower abdomen that is divided into the right and left sides. Its cavity contains the cecum, sigmoid colon, ureter, uterine appendages in women, vermiform appendix, and vas deferens in men.
The depression is located between the ilium and the lower ribs. Diseases of this part of the body are associated with dysfunctions of the digestive and genitourinary systems. Treatment of pathologies is symptomatic. Includes the use of anti-inflammatory, antibacterial agents, as well as surgical intervention.
Article design: Vladimir the Great
Diagnosis of abdominal pain
If you experience pain in the lower abdomen, navel area or side of an unknown etiology, you should immediately consult a doctor or call an ambulance. The doctor needs to carefully and carefully palpate all parts of the abdomen in order to more accurately understand what pathology a given patient may have.
After examination, a specialist will identify the places of highest sensitivity in a certain area. In addition, the medical professional collects anamnesis:
- when did the first signs of the disease appear;
- whether this is the first time the patient experiences such symptoms;
- in what case does pain appear and when does it begin to intensify;
- what additional signs appeared or were present, for example, stool upset, vomiting, hyperthermia, etc.
Important! In a child, diagnosing the disease can be difficult.
This is due to the fact that the baby cannot independently point to the place where the pain is localized and name other symptoms of the pathology (except for those that the parents themselves can personally observe).
In order to timely and correctly diagnose the pathology, you can undergo the following measures: radiography of the abdominal organs, ultrasound of the abdomen, clinical and biochemical blood tests, laparoscopy (for diagnostic purposes during surgical treatment).
The photo shows areas of the man’s abdomen, upon palpation of which one or another pathology can be assumed. They are also used to diagnose problem areas not only in adults, but also in children.
With palpation, the doctor can mentally make a diagnosis, which is further confirmed by a comprehensive examination
Pain in pregnant women
Any pain in the abdomen during gestation in the iliac region can indicate both physiological changes and some trouble in the body.
Most often, such pain can be caused by the rapidly increasing size of the uterus, in which the fetus develops. As a rule, such pain is mild, appears suddenly and passes rather quickly, without causing much discomfort to the pregnant woman.
Sometimes the pain syndrome is caused by digestive disorders, which are very common among pregnant women. Women who suffer from constipation during pregnancy regularly feel pain in the left iliac region. To get rid of such pain, it is enough to adjust your diet and normalize your daily routine.
Excessive activity of the baby in late pregnancy also leads to pain in the lower abdomen. An already grown and strengthened baby can rest against the abdominal organs, which results in the appearance of pain.
Women “in an interesting position” should remember that any pain in the left or right iliac region during pregnancy requires consultation with a doctor.
Diagnostic measures
If your stomach hurts on the right or left, primary care will be provided by your local physician. If necessary, he will refer you for consultation to a specialist practicing in the field of:
- proctology;
- urology;
- gynecology;
- traumatology;
- surgery;
- gastroenterology.
After the doctor examines the medical history and analyzes the symptoms of illness, he will refer you for laboratory tests and hardware diagnostics: intestinal sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy, ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity and pelvic organs, fibrogastroscopy. Endoscopy with biopsy and diagnostic laparoscopy are possible.
Even mild discomfort in the iliac zone can be an alarming signal of hidden pathology. You shouldn't ignore them. If pain and associated dysfunctions occur, you need to undergo a medical examination.
Principles of treatment and prevention
Treatment depends on the cause of the disease, so diagnosis is important. In the complex therapy of many types of ileitis, the following are used:
- dietary nutrition;
- enzymes to improve digestion;
- drugs to reduce gas formation.
The possibility of using this or that remedy should be checked with a specialist, but do not self-medicate.
Prevention of ileitis is a healthy lifestyle without bad habits and a balanced diet.
Pain syndrome in women
Representatives of the fair sex are often tormented by pain in the right or left side. Usually their occurrence is provoked by ailments in the field of gynecology.
Menstrual irregularities due to hormonal imbalances. Painful sensations can appear at any stage of the cycle. They are often accompanied by dysfunctional uterine hemorrhages. With such deviations, women complain of acute, paroxysmal or aching pain in the iliac zone and in the lower abdominal regions.
Bacterial and viral infections. With an inflammatory process in the ovaries or appendages, the pain is localized on the right or left side. This is due to damage to one of the paired organs. Synchronous inflammation of both ovaries and appendages provokes the appearance of unpleasant feelings on both sides at once. During an exacerbation, the painful sensations are extremely severe and are accompanied by chills, fever, headaches, and unusual discharge. Chronic inflammatory diseases cause aching pain and a feeling of fullness in the iliac zone.
Ectopic pregnancy. Pain can occur on both the right and left, depending on the location of the improperly implanted fertilized egg. At first it causes almost no discomfort, but as the disease progresses it intensifies. The condition is dangerous due to internal and external bleeding; with rapid development, death is possible.
Ovarian cyst. Depending on the location of the formation, it will hurt on one side. The patient feels as if there is a stabbing or pressing sensation in her side. If a cystic formation causes sharp, excruciating pain, its stem may be twisted. This condition requires immediate surgical intervention.
Neoplasms of internal reproductive organs. Due to tumors, pain in the iliac region occurs infrequently. Typically, women suffer from mild pain after menopause.
Ovulation. Sometimes this natural process is accompanied by sharp pain manifestations in the lower peritoneum, reflected in the subcostal area. It is not difficult to predict that it is caused by the release of an egg from the follicle - the discomfort recurs every month in the middle of the menstrual cycle. Specific therapy in this situation is not required; an antispasmodic tablet is sufficient.
Features of ailments during pregnancy
Pain in the iliac region while expecting a baby is often not considered a pathological abnormality. What can cause it:
- rapidly growing uterus;
- excessive energy of the baby in late pregnancy;
- digestive problems.
Pain in the left iliac region in pregnant women is often caused by constipation, which occurs due to pressure on the esophagus and a change in diet. You can cope with discomfort without taking pharmaceuticals, which are not recommended in the later stages. It is necessary to balance the diet and normalize the daily routine. If this does not help, the doctor will recommend enterosorbents that will not harm the health of the fetus.