Causes and treatment of pain in the pit of the stomach
There are different types of stomach diseases. The most common among them are:
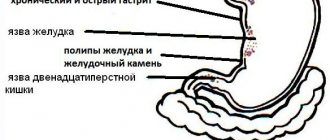
Peptic ulcer
The ulcer is indicated by a sharp pain, similar to a stab with a knife (dagger). It becomes unbearable if the ulcerations are perforated and intensifies with inhalation and sudden movements. The localization of the pain syndrome changes from the center above the navel and right hypochondrium to the entire abdominal area, to the back and right shoulder. At the same time, the stomach itself hardens and becomes “wooden”.
You cannot hesitate in such situations. Internal bleeding can be fatal. He is recognized by low blood pressure, severe pallor, sudden weakness, and an ambulance is urgently called. The severity of a stomach ulcer and its location affect the severity of the discomfort. In case of a perforated ulcer, urgent surgical intervention is indicated.
Gastritis
You can distinguish gastritis from an ulcer on your own. There is a connection between the acidity of gastric juice and the time of onset of discomfort. In the hypoacid form, a dull aching pain appears after eating and does not bother you on an empty stomach. With hyperacid it is the opposite. The pain may be barely noticeable or unbearably severe. It can be triggered by smoked foods, rough, spicy foods.
Chronic gastritis is characterized by:
- heartburn;
- rumbling in the stomach;
- nausea;
- belching;
- unpleasant taste in the mouth.
The type A form of gastric inflammation is characterized by: diarrhea, intolerance to fatty and dairy products. Over time, B12 deficiency anemia may develop.
Often, pathology in the stomach involves the pancreas, duodenum, and bile ducts, which complements the clinical picture with symptoms characteristic of pancreatitis, as well as cholecystitis.
The reasons for the feeling of heaviness in the pit of the stomach may be associated with duodenitis or peptic ulcer. In such cases, there is a complete lack of appetite as the body refuses to digest food.
Causes of pain in the pit of the stomach after eating
Pain at night from 10 pm to 4 am worries patients with stomach or duodenal ulcers. May occur on an empty stomach or be associated with meals. May be a reaction to spicy, fatty foods. In case of diseases of the duodenum, discomfort occurs on an empty stomach, and in case of stomach pathologies, for example, peptic ulcer, after eating. Sometimes relief comes after sour vomiting.
Soreness is called early if it appears an hour after eating and disappears after 1.5 hours when the food leaves the stomach. It may be late, it bothers you 2-3 hours after eating. It is due to the fact that gastric juice entering the duodenum irritates its mucous membrane. Hunger pains appear 5-7 hours after eating and are relieved while eating.
Pain in the pit of the stomach and physical activity
An important point is the connection between discomfort in the epigastric region and body position and physical activity. When diagnosed with adhesions, it occurs if the patient lifts weights or changes body position. When diagnosed with “prolapse of the stomach”, it is the other way around if the person assumes a horizontal position.
Burning in the pit of the stomach
A burning sensation accompanies the course of acute gastritis. The disease develops very quickly. The clinical picture is complemented by vomiting, diarrhea, bloating, and an unpleasant taste in the mouth. Fever and herpes rashes are also possible.
A burning sensation in the middle of the stomach is most likely a sign of functional dyspepsia. It is characterized by impaired motor activity of the stomach and duodenum. Provocateurs of the condition are considered to be smoking, drinking alcohol, certain medications, in particular aspirin, hypersensitivity of the stomach and disorders of the nervous system.
Pain in the pit of the stomach in different locations
If you are worried about pain in the right hypochondrium, it may indicate problems in various organs, including:
- heart and blood vessels;
- liver and pancreas;
- esophagus, stomach, duodenum;
- lungs.
Pain in the left side of the epigastric region may be associated with:
- pyelonephritis;
- gastritis;
- pancreatitis;
- hiatal hernia.
Pain in the pit of the stomach that radiates to the back can be a symptom of chronic or acute pancreatitis. The cause is often related to stones stuck in the bile ducts. They arise due to errors in nutrition, nervous and physical stress. When the gallbladder becomes infected, acute noncalculous (stoneless) cholecystitis may develop.
The pain can radiate to the base of the neck, shoulder blade, and collarbone. It can be paroxysmal or constant. Accompanied by fever, nausea, vomiting. The patient is forced to constantly change body position in search of a less painful position.
Where is it located and why should it hurt?
In medical language, this place on the body is called the epigastric region - the point of connection of the anterior ribs. Why is it called a spoon? Yes, because this depression under the urinary process is shaped like a teaspoon. True, if we look at ourselves in the mirror, we won’t see any spoon. It is only visible on the human skeleton, but it is not difficult to determine exactly where the above-mentioned area is located.
The importance of this place lies in the fact that it is a projection of the internal organs. An experienced doctor can make a preliminary diagnosis based on how severe the pain in the pit of the stomach is: dull or aching, whether it is felt on the right or left. In other words, discomfort in the pit of the stomach is evidence of problems with internal organs. The main thing is not to panic, but to quickly find out the causes of the symptom and begin treatment.
What measures to take
If the listed symptoms and manifestations occur rarely and disappear quickly, you should reconsider your diet. Perhaps the reason for the pain is that you overeat, are in a hurry, abuse fast food, or eat dry food.
A balanced diet will help you get rid of unpleasant symptoms in a short time. Try to normalize your diet: eat small portions, do not skip meals. It is recommended to limit the consumption of heavy and fatty foods and carbonated drinks.
In addition to the basic rules, you must adhere to additional ones, such as:
- transition to fractional meals, its essence is to eat food in small portions, several times a day;
- You can’t not eat anything, if you don’t have an appetite, drink a cup of tea and a cracker or a piece of cheese;
- dinner no later than three hours before bedtime;
- high-quality and fresh dishes should come first and not their quantity;
- you need to give up processed foods and fast food;
- dishes that are difficult to digest should be consumed in small quantities and in the first half of the day;
- It is very useful to take a walk;
- alcohol only in small quantities, and in case of exacerbation it must be completely forgotten;
- You need to constantly drink water, at least one and a half liters per day, but drink water only between meals, on an empty stomach.
Health care
Treatment of stomach pain is associated with neutralizing the effects of gastric and hydrochloric acid. But according to doctors, such a folk remedy as soda should not be used, and there is a possibility of ulcers appearing on the lining of the stomach. In most cases, painkillers are used, such as Nosh-Pa, Almagel, Gastal, antacid suspensions for high acidity.
If your stomach always hurts after eating, then you need to make an appointment with a gastroenterologist or therapist. The doctor will prescribe an examination which consists of:
- general blood test;
- esophagogastroduodenofibroscopy (EFGDS);
- ultrasound examination;
- colonoscopy;
- coprogram (stool examination) and urine test for amylase;
Based on the results obtained, the doctor will prescribe appropriate medications to eliminate this or that pathology.
Pain syndrome, which has a regular acute nature, accompanied by high fever and digestive problems, is a serious signal from the body. Contact your doctor and get examined. Tell your doctor all associated clinical manifestations: vomiting, nausea, flatulence, belching, heartburn, diarrhea, constipation, headaches, weakness and fever. Self-medication and the use of any medications without the knowledge of a doctor are prohibited.
Diagnostics
Only a doctor can say exactly what caused the pain in the epigastric region based on test results. Pain in the pit of the stomach is a multivariate symptom. To find out its true cause, the doctor collects data on the history of the disease, finds out how the pain syndrome manifests itself, what kind of lifestyle the patient leads, what medications he takes.
A number of priority studies will be required using laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- ECG;
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy;
- probing method;
- stool analysis to detect occult blood;
- general urine and blood tests.
Treatment can be symptomatic or aimed at eliminating the underlying cause of the condition. If acute appendicitis, oncology, or rupture of an internal organ is detected, surgery is indicated. Drug treatment and supportive therapy are prescribed by a specialist in the appropriate field. The patient can only strictly follow the medical recommendations of the gastroenterologist, including those related to nutrition.
Why does your stomach hurt in early pregnancy?
Both before and after pregnancy is definitely established, a woman may have a stomach ache. The nature of the unpleasant sensations can be pulling, pressing, bursting, sharp, cutting. Manifestations occur temporarily (depending on the influence of external factors) or are constantly present.
If your stomach feels tight after conception, then for your own peace of mind you need to consult a gynecologist. Having ruled out possible problems and determined that the pregnancy is intrauterine, the patient will receive a list of approved medications to relieve discomfort. Every second expectant mother who seeks medical help due to abdominal pain in the early stages is diagnosed with pathology. The sooner it is eliminated, the greater the chance of a favorable prognosis.
Aching pain, as during menstruation
Nagging pain in the lower abdomen after conception indicates increased uterine tone. Temporary sensations not accompanied by bleeding may occur due to physical activity, fatigue, or nervous tension. Almost all expectant mothers encounter such manifestations.
It’s worse when your stomach hurts constantly after conception. Additionally, the patient complains of lower back pain and bleeding. These symptoms indicate hypertonicity and require mandatory ultrasound monitoring. During the scan, the sonologist discovers a hematoma formed between the fertilized egg and the uterine wall. When it opens, it comes out in the form of brown bloody discharge. The appearance of scarlet blood is an even more dangerous sign.
Pulling in the lower abdomen due to hypertonicity may be due to insufficient synthesis of progesterone. This condition can be determined using a blood test to determine the level of this hormone. If pain occurs, as during menstruation, the patient is prescribed maintenance therapy. Treatment involves eliminating the cause of hypertension and replenishing the deficiency of the corpus luteum hormone. Such abdominal pain should not be taken as a sign of pregnancy. A disturbing symptom is a dangerous condition and can lead to termination of pregnancy.
Sharp pain in the groin area
Cramping abdominal pain can be a symptom of an ectopic pregnancy. This condition is dangerous for a woman’s life, so it cannot be delayed. An ectopic pregnancy is characterized by the attachment of an embryo in an unintended place. Most of these cases are found in the area of the fallopian tubes. Less commonly, the fertilized egg is attached to the ovary or peritoneum.
It is necessary to understand that it will not be possible to maintain such a pregnancy. The growth of the fertilized egg will continue for up to 5-8 weeks, after which it will stop. In this case, a fallopian tube or ovary may rupture, which can lead to complete removal of the reproductive organs and even death. If severe pain appears in one or the other side of the abdomen, you should consult a gynecologist to rule out a pathological condition.
Acute abdominal pain can be a sign of inflammation of the appendix. Statistics show that about 10% of expectant mothers experience this condition. The pathology is accompanied by fever, nausea, and stool disturbances. To rule it out, you need to consult a surgeon and take a blood and urine test.
Feeling of pressure and fullness in the perineum
The stomach may hurt after conception due to sprained ligaments. The rapid growth of the uterus forces the pelvic floor muscles to work. The ligaments holding the reproductive organ are stretched, causing lumbago and a feeling of pressure in the perineum. This often happens during advanced stages of pregnancy, when the uterus extends beyond the pelvis.
Pressure and bloating can be caused by bowel movements. As you know, progesterone affects the functioning of the digestive tract. Consuming a large number of incompatible foods (which is not uncommon in the early stages) causes a bursting feeling in the stomach.
It is not always possible to differentiate your sensations and distinguish physiological from pathological discomfort on your own. To dispel doubts and get rid of worries, you need to consult a gynecologist.
https://www.e-motherhood.ru/priznaki-v-pervuyu-nedelyu-beremennosti/https://nogostop.ru/zhivot/mozet-li-bolet-zivot-posle-zacatia.htmlhttps://myzachatie. ru/planirovanie/oshhushheniya-v-zhivote-na-rannih-srokah-beremennosti.html
Why does my stomach hurt?
When a person mentions pain in the pit of the stomach, the epigastric triangle, which includes many internal organs, appears in the mind. Pain in the pit of the stomach is one of the important reasons that requires immediate consultation with a specialist, since epigastric pain can give rise to various diseases.
Pneumonia
Often, pressing pain in the pit of the stomach occurs due to pneumonia or, as this disease is popularly called, pneumonia.
Streptococcus pneumoniae – the causative agent of pneumonia © shutterstock
Pneumonia is a dangerous disease of an infectious nature. Until modern medicine took invented medications to a higher level, almost 80% of patients died from pneumonia. Today, these figures have decreased by half. However, pneumonia is considered one of the most dangerous diseases.
November 12 is World Pneumonia Day.
Experts have identified a number of factors and ailments that contribute to the development of pneumonia:
- Common cold or flu;
- Bronchitis;
- Past infectious diseases;
- Reduced immunity.
Pneumonia can be unilateral, bilateral, lobar, lobar and focal forms. Each form requires appropriate and immediate treatment.
Signs of illness
A common trigger for pneumonia is severe hypothermia, after which a person develops the following symptoms:
- Chest pain in the pit of the stomach when breathing or coughing;
- Wet cough;
- Fatigue;
- Fever, chills and sweating.
Under no circumstances should such symptoms be neglected . When the first pain in the pit of the stomach appears, you should immediately go to see a specialist. The doctor will conduct a thorough examination and give directions for tests and fluorography.
Treatment options
Treatment for pneumonia depends on the type of pneumonia you have, the germ causing your infection, and how severe your pneumonia is. The doctor takes into account the degree and severity of the illness that causes pain in the pit of the stomach, the age of the victim, and the presence of any complications.
“Pneumonia can be prevented through immunization, adequate nutrition and addressing environmental factors.” – WHO
Bacterial pneumonia is treated with medications called antibiotics.
Antibiotics don't work when pneumonia is caused by a virus. If you have viral pneumonia , your doctor may prescribe an antiviral medicine to treat it.
Hiatal hernia
When asked why there is pain in the pit of the stomach, doctors often answer – hiatal hernia. A hernia is a protrusion of abdominal organs, often the esophagus, stomach, or, less commonly, other organs.
The photo on the right shows a hiatal hernia © shutterstock
Hiatal hernia is divided into sliding or axial, paraesophageal, and combined forms of flow. The disease also has several degrees of severity, each of which manifests itself with its own symptoms and requires appropriate treatment.
Experts have identified some reasons that provoke the development of the disease:
- Changes in the diaphragm associated with age;
- Injuries;
- Birth defect;
- Pressure on nearby muscles when lifting heavy objects.
“The risk of getting a hernia hernia increases with age, and they often occur in people over 50.” – US National Institutes of Health
Pancreatitis
Pain in the pit of the stomach may be due to pancreatitis, an inflammatory disease of the pancreas. The disease is divided into acute and chronic forms, each of which manifests itself with its own symptoms and requires appropriate therapy.
© shutterstock
Women, men and even children are not immune from pancreatitis. Men suffer more often due to neglect of the symptoms that appear. They prefer to visit the hospital when the disease has almost completely consumed the organ, which entails long-term treatment.
“The most common cause of chronic pancreatitis is alcohol consumption.” – US National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
Experts have been able to identify a number of causes causing pancreatitis:
- Alcohol abuse;
- Eating fatty foods;
- Cholelithiasis;
- Long-term use of medications;
- Hereditary predisposition;
- Viruses or parasites.
Urolithiasis disease
Oddly enough, severe pain in the pit of the stomach may indicate urolithiasis.
© shutterstock
The population at risk is in the age category from 21 to 60 years . Men are more likely to develop kidney stones than women.
According to scientists, urolithiasis, which leaves pain in the pit of the stomach, is a consequence of an imbalance in the human body. Because there is no single reason that causes this disease.
You are more likely to develop kidney stones if you have certain conditions, including:
- blockage of the urinary tract;
- inflammation in the intestines;
- cystic kidney diseases;
- digestive problems;
- gout;
- obesity;
- taking diuretics.
People at risk should be attentive to the signs that their body gives them. Hence, visit hospital facilities on time.
Myocardial infarction
The causes of pain in the pit of the stomach may lie in the development of myocardial infarction - a well-known emergency condition in which the flow of blood to the heart is blocked by a blockage. Interruption of blood flow can damage or destroy part of the heart muscle.
© shutterstock
According to statistical studies, myocardial infarction, which causes pain in the pit of the stomach, is diagnosed more often in men than in women.
Among the causes include:
- Increased cholesterol in the blood;
- High blood pressure;
- High blood sugar due to diabetes;
- Overweight and obesity;
- Tobacco smoking;
- Hereditary predisposition;
- Advanced age;
- Constant stress.
“Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death worldwide.” – WHO
Signs of a heart attack
Periodic pain in the pit of the stomach in the chest area is a consequence of coronary heart disease, which leads to a heart attack. Many people know that they have heart problems, so they take medications to help relieve pain in the pit of the stomach in the sternum area. But it is important to use only medications prescribed by your doctor.
Myocardial infarction manifests itself:
- Pain in the pit of the stomach on the left side;
- Chest pain or discomfort;
- Pain or discomfort in one or both arms;
- Hesitant breathing;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Sudden dizziness;
- Cold sweat;
- Fatigue.
No person should ignore pain in the pit of the stomach and the symptoms described above, as the disease can be fatal.
Gastritis
Often, pain in the pit of the stomach occurs due to gastritis, a pathology that causes inflammation of the mucous membranes of the stomach.
Illustration of inflammation due to gastritis © shutterstock
Among the causes that provoke gastritis are::
- H. pylori infection;
- Stress;
- Alcohol abuse;
- Regular use of painkillers;
- Bile reflux;
- Autoimmune response.
Signs of gastritis
Clinical manifestations of the disease include:
- Pain and burning in the pit of the stomach;
- Discomfort in the upper abdomen;
- Nausea;
- Vomit;
- Shortness of breath;
- Dizziness or weakness;
- Red blood in vomit;
- Black, tarry stool;
- Red blood in stool;
- Weakness;
- Pallor.
Doctors treating stomach pain
The causes and treatment of pain in the pit of the stomach can only be identified by a qualified specialist. A person must visit a therapist who will conduct an examination, survey and necessary diagnostics, then refer him to one of the specialized specialists:
- Gastroenterologist;
- Urologist;
- Cardiologist;
- Surgeon;
- Oncologist.
Less popular causes of pain in the pit of the stomach
When a person has a stomach ache in the pit of his stomach, the causes are::
- Ulcer;
- Peritonitis;
- Pneumothorax;
- Pleurisy;
- Stenosis;
- Food poisoning;
- Gastrointestinal disorders.
Summarizing
If a person feels severe pain in the pit of the stomach, you should not wait for complications; you should immediately go to see a doctor. Only a specialist will be able to identify the true cause of pain in the pit of the stomach and prescribe a course of necessary therapy. It is important to remember that timely treatment is the key to a quick recovery.
information revision
: June 4, 2021.
Source: https://PrichinyBolej.ru/2244-bolit-pod-lozhechkoj.html
Contraindications
An incorrect diagnosis can lead to the fact that treatment will not only be useless, but will provoke serious complications. After all, many medications and physiotherapeutic techniques that are effective for some diseases accompanied by abdominal pain are strict contraindications for other diseases with similar symptoms.
For example, if a number of medications prescribed for pancreatitis are given to patients with hepatic colic, the reaction may be unpredictable. And treating a number of stomach diseases with antibiotics can cause serious dysbiosis.
And absolute contraindications for pain in the abdomen or stomach are self-medication - especially independent decision-making to take a painkiller or antispasmodic. If, for example, such drugs are used by a person whose appendix is inflamed, relief will follow for a while. But this will not be help, but false help to yourself. There are often cases when patients who did not get to the surgeon in a timely manner to remove appendicitis began to experience necrosis of the tissues of neighboring organs.
Under no circumstances should you resort to even seemingly “harmless” means to combat high acidity without making a diagnosis. What seems to be simply a release of excess hydrochloric acid and inflammation of the stomach may turn out to be a symptom of a completely different disease, such as a heart attack.
Also, for abdominal pain with an unclear diagnosis, you should not apply a heating pad with hot water. In a number of pathologies, heat only accelerates the inflammatory process and activates bleeding.
Treatment of gastritis of the stomach
Treatment of inflammation of the gastric wall requires eliminating the cause of the pathology. Helicobacter eradication is carried out with antibiotics (clarithromycin, oxacillin). An increase in intragastric secretion is eliminated by antisecretory drugs of the h2-histamine blocker group, Na/K-ATPase inhibitors (omez, esomeprazole, ranitidine). Along with pharmaceuticals, diet therapy is prescribed with the limitation of spicy, fatty, fried foods. If you have gastritis, you should not eat:
- Canned food;
- Sparkling water;
- Spicy foods;
- Alcohol;
- Cold or hot food.
Types of diseases
Almost every pathology that occurs is accompanied by pain and discomfort. The most common of them include:
- Gastritis, erosion. Severe pain occurs during an exacerbation of a chronic disease, intensifies after eating and is localized in the upper abdomen. In addition to pain, exacerbation is accompanied by a feeling of fullness and discomfort; attacks of nausea, heartburn, frequent belching, and halitosis (bad breath) may be present. The pain is dull and aching in nature. When a peptic ulcer is complicated, attacks of pain are described as a burning sensation and intensify after eating due to gastric juice entering the affected stomach wall. Exacerbations are seasonal and occur mainly in spring and autumn.
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease. Often detected during esophagogastroscopy. The development of pathology occurs due to the reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus. The pain is concentrated directly under the sternum and can spread along the flow of fluid containing gastric juice. Acidic foods, carbonated drinks, strong tea or coffee, fried and spicy foods increase pain and contribute to muscle weakening of the esophagus. This significantly aggravates the patient's condition.
- Gastrointestinal ulcers and their complications (bleeding, penetration, perforation). These conditions are characterized by acute stabbing pain, which is first concentrated in the gastric region and then spreads beyond it. These complications require emergency medical care and subsequent treatment in a hospital setting, since there is a high probability of developing peritonitis (inflammation of the peritoneum). Without timely treatment, sepsis or shock develops, then death occurs.
- Appendicitis. This disease is common and occurs due to inflammation of the tissue of the appendage of the cecum. It does not depend on age or gender, but women are most vulnerable to it. The development of pathology is characterized by paroxysmal pain in the abdomen, especially in its upper part. Then the source of pain moves to the right side under the lower ribs. Acute pain increases significantly as the disease progresses. If left untreated, the next stage of the disease becomes peritonitis. The pain subsides slightly, which is explained by the death of tissue and nerve endings of the appendix. This condition requires emergency medical care in the form of transporting the patient to a hospital and subsequent surgery to remove the appendix of the cecum (appendectomy).
- Narrowing of the pylorus. This pathology is characterized by pain that occurs after eating. The condition is accompanied by a feeling of fullness and heaviness in the abdomen. Compensated pyloric stenosis does not involve electrolyte abnormalities or vomiting. While its decompensation significantly worsens the patient's condition. Frequent bouts of vomiting and intense, ongoing pain appear. The amount of food entering the duodenum from the stomach is significantly reduced. Regular bouts of vomiting lead to disruption of electrolyte metabolism, which often has negative consequences.
There are cases when pain in the epigastric region (epigastric region) is not associated with the occurrence of any pathologies of the digestive system. For example, sometimes myocardial infarction can be accompanied by aching pain in the epigastric region. This happens due to a peculiar reaction of the nerve fibers located in the solar plexus.
Some pulmonary diseases (pneumothorax, pleurisy, lower lobe pneumonia) may also be accompanied by epigastric pain. Accompanied by cough with sputum and shortness of breath. To exclude a disease or confirm a diagnosis, a person undergoes X-ray examinations.
If there is pain in the epigastric region, the causes of its occurrence may be cholecystitis due to cholelithiasis, or renal colic. These pathologies have a paroxysmal nature of pain, at the peak of which there is an outpouring of vomit. Antispasmodics are used to relieve symptoms.
Pain in the mesogastric region can also be caused by such reasons as: acute infections, enlarged liver, pancreatitis, tumor diseases of internal organs
Therefore, it is very important to undergo a full examination to exclude serious pathologies or receive appropriate treatment.
Gastric ulcer: symptoms and treatment
Gastric ulcer is characterized by a violation of the structural integrity of the mucous membrane of the organ, leading to destruction of the wall. The main difference between an ulcer and erosive gastritis is damage to the deep part of the mucous membrane, which results in alternating remissions and exacerbations.
A stomach ulcer is accompanied by severe pain in the pit of the stomach, which is in some way associated with eating. Night pain in the stomach is a typical symptom of a duodenal ulcer. High severity of the nosology leads to belching, heartburn, and decreased motor function of the stomach. Manifestations of the disease intensify with the following complications:
- Bleeding;
- Penetration – perforation into surrounding organs;
- Perforation is a rupture of the wall with the release of free gas.
Symptoms of pain after eating in irritable bowel syndrome
Symptoms of pain include cramps in the intestines, excessive gas formation, which provokes severe distension of the intestinal walls.
Characteristic signs of irritable bowel syndrome are:
- a painful sensation around the navel after eating, which goes away after bowel movement;
- constipation and flatulence;
- diarrhea (often in the morning);
- belching, heaviness in the stomach;
- nausea.
Such symptoms usually appear after prolonged nervous tension, stress, and also after physical exertion. Frequent intestinal disorders are accompanied by tinnitus, dry mouth, headache, weakness in the body muscles and insomnia.
Diagnosis of pain after eating in the lower abdomen
In order to accurately determine the cause of pain after eating in the lower abdomen, the doctor prescribes the following types of examinations:
- coprogram (stool analysis);
- blood chemistry;
- sigmoidoscopy - examination using a rectoscope of the rectum and sigmoid colon;
- irrigoscopy - examination of the intestines using x-rays. In this study, the intestines are filled with a special contrast agent during analysis;
- colonoscopy - examination of a section of the intestine up to one meter in length.
To effectively treat pain in the lower abdomen after eating, you should follow a diet that includes eating vegetables, fruits and dairy products; It is useful to eat dishes made from meat and fish products, either steamed or boiled. It is necessary to exclude spicy, smoked foods, chocolate, coffee and alcohol, as well as cabbage and flour products from the diet, as they contribute to excessive gas formation.
In addition to this diet, the doctor may prescribe medications to relieve spasms, as well as to improve food digestion; laxatives or, conversely, fixative medications. If necessary, treatment of dysbiosis in the intestines is carried out.
[], [], [], [], []
My stomach hurts in the pit of my stomach, it burns, what medicine will help?
An attack of appendicitis occurs with a sharp, constant type of pain in the pit of the stomach and spreads to the umbilical area. Further, the pain is localized in the iliac region with significant muscle tension.
Pain in the pit of the stomach of a girdle type is a consequence of acute pancreatitis. Worsening occurs after taking fatty foods and alcohol. There is frequent vomiting of bile, which does not alleviate the condition.
In the gastralgic form of myocardial infarction, quite acute pain initially manifests itself in the epigastric zone, covering the cardiac region and scapula. There is a decrease in pressure, rapid and arrhythmic pulse. The patient remains sedentary to reduce pain.
Pneumonia of the basal type (location of the focus is the lower segments of the lungs) and pleurisy occur with acute pain, which intensifies with breathing and coughing. The disease is described by rapid pulse, noise and wheezing in the sternum, abdominal tension and fever up to 40°C.
Symptoms of pain in the pit of the stomach with spontaneous pneumothorax are localized in the chest on the left or right.
An attack of “dagger” pain in the epigastric zone describes purulent peritonitis, which occurs when there is a through defect in the intestinal or gastric wall (ulcer perforation). The disease is accompanied by muscle tension. Over time, the pain subsides.
The condition of perforation of an ulcer of the posterior gastric wall is characterized by cutting pain if effusion occurs into the peritoneal cavity. Filling the omental bursa is less painful.
Pain in the epigastrium during palpation, along with nausea, vomiting, and severe weakness are symptoms of exacerbation of duodenitis (inflammation of the duodenum).
A cramping, acute pain in the pit of the stomach, radiating to the hypochondrium on the right side, subsiding after taking antispasmodics, accompanies hepatic colic.
Symptoms of intoxication:
- headaches, dizziness, general weakened state;
- high temperature, chills;
- state of nausea, vomiting;
- diarrhea;
- fainting, convulsions.
Infection with Crimean hemorrhagic fever is fraught with a gag reflex, moderate febrile symptoms and pain in the epigastric area.
Pain in the stomach after eating
The most common diseases such as gastritis, stomach and duodenal ulcers are indicated by pain in the pit of the stomach after eating.
Symptoms of diseases with high acidity are pain, heartburn, “sour” belching. Patients with low acidity note a feeling of heaviness, fullness in the stomach, nausea, and belching.
Pain syndrome can also appear on an empty stomach, which is more typical for problems with the duodenum.
Cutting pain in the epigastric zone after eating is a sure sign of exacerbation of pancreatitis. The pain is constant, up to several hours, sometimes days. The degree of intensity of pain depends on the stage of the disease, often radiating to the back area, hypochondrium. The pain is girdling in nature.
Increased pain in the pit of the stomach is observed if you take a horizontal position on your back, and bending forward, on the contrary, reduces the pain. The disease occurs with dry mouth, nausea, accompanied by hiccups, belching, vomiting, and diarrhea. The patient often loses his appetite and loses a lot of weight.
In a critical condition, the blood pressure drops, the pulse quickens, there is an increase in temperature and shortness of breath.
Aching pain in the pit of the stomach
A “sucking” feeling in the pit of the stomach is a reminder from the body of the need to eat. This feeling often accompanies a state of increased excitement, a nervous experience. A nagging pain in the pit of the stomach, especially after a meal, is a clear sign of gastritis.
The disease occurs if:
- there was an unpleasant odor from the mouth, belching appeared;
- there is a decrease or loss of appetite;
- whines/sucks in the epigastrium.
An insidious disease - stomach cancer may not manifest itself for a long time. The symptoms of the early stages of the disease are similar to chronic gastritis, gastric and duodenal ulcers, pancreatitis or cholecystitis. Many patients self-medicate and seek help only at the acute stage, when treatment is difficult or impossible.
Stomach cancer is characterized by pain in the pit of the stomach, often aching and very severe. Soreness can be associated with food intake: it occurs after eating or on an empty stomach.
Some patients experience a change in eating habits or a complete loss of appetite. Vomiting contents like coffee grounds and black stools are dangerous signs that may indicate stomach bleeding.
Patients' complaints reveal general weakness and fatigue.
A hernia of the linea alba also provokes aching pain that is not associated with eating. When the abdomen tenses, a tubercle appears, which disappears with relaxation.
Severe pain in the pit of the stomach
A signal from the body that should never be ignored is severe pain in the pit of the stomach.
Acute pain syndrome can strike you both at rest and during periods of maximum physical or mental activity. Such pain may indicate myocardial infarction.
Conditions of dizziness, active sweating, and unreasonable fear of death are indicative symptoms. The pain often affects the arm, jaw and back.
Acute, sometimes shingles, pain indicates an exacerbation of pancreatitis. It should be noted that the nature of the disease can be judged by the location of pain. If severe pain is localized on the left, then the cause of discomfort is the tail of the pancreas. Girdle pain indicates damage to the entire organ.
Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum occurs with sharp, acute, burning, stabbing pain. Studies have shown that men suffer from this disease twice as often as the female population.
Dull pain in the pit of the stomach
The process of acute gastric atony is a rare disease in which the muscle tone of the stomach is disrupted and it is stretched.
The disease can be reflexive in nature or appear as a result of myocardial infarction, peritonitis, pneumonia, thrombosis of gastric vessels and a number of infectious lesions.
Surgical intervention and recovery from anesthesia can lead to gastric atony.
Source: https://menchov.ru/bolit-zhivot-pod-lozhechkoj-zhzhet-kakoe-lekarstvo-pomozhet/
Diagnosis and consequences
In order to make a correct diagnosis, the doctor prescribes an examination.
What procedures need to be completed during the examination:
- Gastroscopy.
- X-ray of the stomach.
- Examination of blood for the presence of excess organisms.
- Analysis of gastric juice acidity.
- Less often - checking for worms and E. coli.
If you do not consult a doctor in time, then seemingly harmless symptoms of burning in the esophagus and stomach can develop into serious illnesses, such as:
- Ulcer.
- Chronic gastritis.
- Pancreatitis.
- Stomach bleeding.
One of the most serious diseases that can be caused by exposure of the gastric mucosa to constant large amounts of acid or bile is malignant neoplasm. If you consult a doctor in a timely manner, the tumor can be cured, but if the disease is advanced, then surgery will no longer be possible.
Therefore, if you have a burning sensation in your stomach, you should immediately pay attention to it and go to the doctor.
Others
The stomach often burns due to heart disease, angina pectoris, pleurisy, myocardial infarction, and also with increased blood pressure.
If the disease is caused by heart disease, its symptoms are relieved by taking nitroglycerin. But after this, it is better to contact a cardiologist and tell about the alarming symptoms.
A burning sensation in the esophagus often appears due to stress and nervous conditions. In the modern rhythm of life, a person is constantly faced with problems and nervous shocks, which provokes a burning sensation in the esophagus and stomach. Only careful treatment of your nerves will help you cope with this problem.
When taking medications, you need to be careful, as some of them can cause unpleasant symptoms and discomfort. When a doctor prescribes medications that cause hormonal changes, he also prescribes antacid therapy.
Sometimes the burning sensation can be caused by bacterial infections. Once bacteria enter the body, they weaken its barrier functions. Due to such infections, changes occur in the mucous membrane, and ulcers and gastritis appear.
Pregnant women quite often encounter discomfort, as hormonal disruption occurs, the uterus enlarges, and the woman feels pain and heaviness after eating.
The main enemy of the body is alcohol and smoking. They have a bad effect on the entire body, and with stomach diseases, the patient’s condition only worsens. Therefore, you need to give up bad habits.
Diagnostic methods
Since the causes of pain in the epigastric region can be different, treatment methods depend on the disease that provoked the appearance of the symptom. In addition to general recommendations, such as a balanced diet and giving up bad habits, each disease will have its own specific treatment recommendations.
First of all, when pain appears in the pit of the stomach, it is necessary to establish an accurate diagnosis. To do this you will need to do a full examination:
- abdominal organs;
- pancreas;
- liver and kidneys;
- gallbladder.
If pancreatitis and gastroesophageal reflux are suspected, an additional endoscopic examination and ultrasound of the pancreas may be required.
Prevention
Doctors at the 5th Hospital will not only select the optimal diagnostic and treatment option for each patient, but will also advise on how to prevent relapses.
Diet occupies a special place among measures to prevent intestinal and stomach diseases.
It is important to learn to maintain balance in nutrition. You should not overeat, chew food thoroughly and slowly
At the same time, when choosing a diet, experienced doctors take into account all factors:
- functional state of the intestines, liver, pancreas
- secretory function of the stomach,
- intestinal motility,
- the presence of other concomitant diseases.
In addition to your diet, it is important to reconsider how you store and process food. Do not leave food open in the sun
Avoid damp food storage areas. Otherwise, they may begin to mold and rot. Avoid contact between raw foods and cooked foods.
Exercise therapy is also of great importance in the complex of preventive measures. Instructors-methodologists select their own loads and exercises for each patient.
Cramping pain in the epigastrium and diarrhea
When both the small and large intestines, and sometimes the stomach, are involved in the pathological process, total damage to the entire gastrointestinal tract develops - gastroenterocolitis.
Nausea, vomiting, severe pain in the epigastrium, worsening after eating, diarrhea may be a sign of infectious diseases
Chills, increased body temperature, nausea, repeated vomiting, and cramping pain in the epigastric region, mainly in the iliac and periumbilical regions, are noted. Then comes frequent loose stools, sometimes mixed with mucus.
With gastroenterocolitis or enterocolitis, diarrhea is of a mixed nature - feces can be copious, but mixed with mucus, less often blood or pus. A typical example of gastroenterocolitis is food poisoning.
An attack of appendicitis occurs with pain and diarrhea. The onset is sudden. In half of the cases of the classic course, pain appears in the epigastric region or throughout the abdomen, after a few hours it is localized in the iliac region on the right.
In people with chronic gastritis, the disease progresses in waves. Exacerbations occur when the diet is violated or when there is anxiety. Epigastric pain appears, which is described as “stomach cramps,” and stool disturbances. Dyspeptic disorders can take the form of both diarrhea and constipation. With diarrhea, the frequency of stools is no more than 2-3 times a day. Some patients report improvement in pain after bowel movements.
Nausea, vomiting, severe pain in the epigastrium, worsening after eating, diarrhea may be a sign of infectious diseases. Among them there are diseases that are life-threatening. If these symptoms appear suddenly and occur or worsen after each meal, you should consult a specialist.
Symptoms of common stomach diseases
Gastritis is inflammation of the gastric mucosa. The damage does not penetrate deeply. According to morphological features, the following categories of disease are distinguished: catarrhal, superficial, atrophic, erosive varieties of nosology.
The superficial (catarrhal) form is formed in people with a prolonged increase in intragastric secretion. The disease is provoked by irritation of the epithelium with hydrochloric acid.
The cause of the erosive form is poor quality nutrition, intake of toxic substances, consumption of rough food, and insufficient chewing of food. Americans often experience nosologies associated with long-term consumption of hot dogs, hamburgers, and cheeseburgers.
Symptoms of erosive gastritis:
- Nausea;
- Dull pain in the upper abdomen;
- Unpleasant taste;
- Heartburn;
- The presence of occult blood in the stool.
The atrophic form is characterized by complete degeneration of the epithelium, in which the functional tissue loses its properties. The nosology is considered a precancerous disease, so it needs to be treated from an early stage. The disease is often combined with secondary pathology: cholecystitis, colitis, pancreatitis, appendicitis.
Etiology
Pain in the epigastric region is caused by various ailments that affect many internal organs. Among the ailments, the most common causes of this symptom are:
- a wide range of diseases of the stomach, duodenum, esophagus and other gastrointestinal organs. In particular, chronic gastritis of various origins, pancreatitis and pyelonephritis;
- acute course of appendicitis. At the beginning of development, aching pain is noted in the navel area, then in the epigastrium, after which it spreads to the entire right side of the abdomen;
- myocardial infarction - can often be accompanied by painful spasms in this place. The pain is expressed quite acutely, and is also accompanied by a decrease in blood pressure and an increase in heart rate;
- pleurisy and pneumonia - with such disorders, pain in the upper abdomen sharply intensifies with strong coughing and inhalation, often the pain can radiate to the back;
- acute duodenitis – a slight pain syndrome appears, the sensitivity of this area increases, and signs of intoxication of the body are also observed;
- pyloroduodenal stenosis - characterized by the fact that pain is expressed after eating, accompanied by heartburn and frequent vomiting;
- various infectious disorders that cause sudden abdominal pain;
- hemorrhagic syndrome;
- typhus – differs in that it involves the solar plexus in the pathological process, thereby causing intense pain in this area.
But not only diseases can become a factor in the manifestation of unpleasant sensations in the epigastric region. Often the source of pain can be damage to other internal organs, in particular:
- stomach – there are severe and paroxysmal pains, often accompanied by other symptoms. Can occur both after meals and on an empty stomach;
- heart - in addition to the appearance of painful spasms in the epigastric region, pain spreads to the right shoulder and lower jaw;
- lungs - the intensity of pain varies depending on the breathing rate;
- pancreas - provokes constant and colicky pain, which can radiate to the back or left shoulder;
- intestines - almost always causes pain in the epigastrium, which is accompanied by many other signs;
- spleen – causes intense pain, often spreading along the left side of the body and neck;
- gallbladder - diseases associated with this organ often cause unbearable pain in the epigastric region, pain radiating to the back is often observed;
- kidney - sharp pain, spreading to the perineum and lower back;
- diaphragm - spasms in this area are greatly intensified during food consumption or deep breaths.
Another reason why epigastric pain may occur is oncology of one of the gastrointestinal organs or cancer metastasis.
Provoking factors and causes of pain
Why does discomfort occur, and in what ways can it be eliminated? The principles of treatment depend on the factors that provoked the appearance of the pathological symptom.
Among the most common causes of discomfort in the pit of the stomach, doctors include the following:
Developing stomach ulcer
A very likely and dangerous cause of aching pain in the pit of the stomach may be an ulcer on the gastric mucosa. Here you need to pay attention to the following clinical manifestations:
- frequent pain and belching;
- nausea immediately after eating;
- lack of appetite;
- problems with stool (diarrhea, constipation);
- flatulence;
- bloating;
- sour taste in the mouth.
If such factors occur, then it is better to go to the hospital and do an endoscopic analysis of the stomach. Or, as people say, swallow a tube. Alas, this is the only way to identify a stomach ulcer and begin treatment at a more or less early stage.
There is a general principle that allows you to understand even before going to the doctor whether your stomach is bothering you or not. If discomfort occurs immediately after eating, this is a stomach problem. If it hurts before eating, on an empty stomach, and after eating, on the contrary, it goes away, then this is a lesion of the duodenum.
Duodenal ulcer
Aching pain on the right, which radiates to the back, may signal the appearance of an ulcer in the duodenum. The disease is caused by the bacterium Helicobacter Pylori, as in the case of stomach ulcers, but not only it. Additional causes of the disease:
- endocrine disorders;
- unbalanced diet;
- alcohol abuse;
- increased acidity in the gastrointestinal tract;
- too frequent use of antipyretics (Aspirin, Ibuprofen, Nurofen).
The development of ulcers is facilitated by a lack of microelements and vitamins in the body. They take part in redox reactions, the disruption of which can lead to destruction of the duodenal mucosa;
Pancreatitis
Acute constant pain in the epigastrium on the left side is a characteristic symptom of the development of pancreatitis. In the case of an acute course of the disease, it may also be of a shingles nature. Pancreatitis is essentially a malfunction of the pancreas. That is, enzymes for digesting food are not produced, which leads to decay of the duodenal contents. Food is not digested or absorbed by the intestines, which causes nausea and profuse vomiting.
Factors that cause pancreatitis include:
- a large amount of fried, fatty and smoked foods in the diet;
- alcohol abuse;
- long-term use of medications (especially hormonal ones).
Pancreatitis, alas, can be not only an independent disease. Very often it is preceded by the development of a stomach ulcer.
Appendicitis
With appendicitis, pain is first felt in the pit of the stomach, then in the navel, and then moves to the right side. The disease is accompanied by nausea and pain in the right side, which can intensify with deep breathing. As you know, appendicitis cannot be treated with medication; you will need the help of a surgeon.
Lesions of the esophagus
If discomfort in the pit of the stomach on the right is episodic, most likely the symptom is caused by damage to the esophagus, in particular, gastroesophageal reflux. When swallowing, pain radiates to the throat. Factors that provoke diseases of the esophagus are chemical or mechanical damage, inflammation of the ENT organs, and excessive physical activity. If you have such symptoms, you should contact a gastroenterologist.