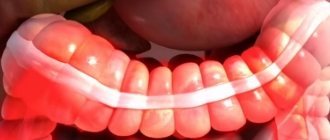
What it is
Chronic intestinal colitis is an inflammatory process that affects the mucous membrane and submucosal layer of this organ. The disorder is equally common in both women and men, but in the latter it manifests itself at a later age.
The chronic form of colitis involves phases of exacerbation and remission phases, when there are no signs. Symptoms with this form are less pronounced than with acute colitis. The pathology is diagnosed simply and treated comprehensively.
Risk factors
Risk factors for the occurrence of colitis are as follows:
- reduced immunity;
- poor nutrition;
- frequent stress;
- alcohol abuse;
- a history of autoimmune diseases;
- abnormal structure of blood vessels in the intestine.
Manifestation of colic in children, their causes
In an infant, intestinal colic is a widespread phenomenon. It often occurs in 1-4 months of a baby’s life. A child reacts to the appearance of colic as follows:
The baby's tummy is tense. Its palpation brings painful sensations to the little patient. The attacks occur at certain hours at night and recur within a week or two.
p, blockquote 17,0,0,0,0 —>
In children under 4 months of age, colic is not a pathology, but a consequence of enzymatic disorders. Its symptoms are observed in children, both bottle-fed and natural-fed.
The cause of discomfort in the intestinal area may be:
p, blockquote 19,0,0,0,0 —>
- Infection.
- Allergy to dairy products or breast milk.
- Inflammation.
- Psychogenic factor (tense family situation, mother's depression).
Intestinal colic in newborns - video
Causes
In approximately 30% of patients, intestinal inflammation is a consequence of intestinal infections (dysentery, salmonellosis). Less commonly, the reason is long-term treatment with antibiotics, which disrupt the normal balance of intestinal microflora.
Causes may also be related to alcohol abuse and poor diet, which contribute to inflammation. In some cases, chronic colitis is a complication of other gastrointestinal diseases, such as chronic gastritis , hepatitis, pancreatitis, as well as a consequence of abnormalities in the development or functional insufficiency of the intestine.
What causes intestinal colic?
Colic is a consequence of irritation of the intestinal walls by a provoking factor. Smooth muscles respond to this with a strong contraction (spasm). Intense physical activity can trigger colic. During this, tension in the mesentery occurs, which leads to stabbing pain in the left side of the abdomen.
p, blockquote 12,0,0,0,0 —>
Colic occurs due to:
p, blockquote 13,0,0,0,0 —>
- Immaturity of gastrointestinal tract structures, flora insufficiency (in children).
- Eating heavy foods that contribute to the formation of gases (flour products, fried foods, soda).
- Exposure to large amounts of air when eating. This can happen if you talk during a meal or eat on the go.
- Constipation.
- Entry of a foreign body into the gastrointestinal tract.
- Food allergy (to lactose).
- Allergic reactions.
- Disorders of blood supply to various parts of the intestine. This occurs due to ulcerative formations and diverticulosis.
- Intestinal obstruction.
Forms of chronic colitis
The disease comes in several types:
- Spastic. It manifests itself as severe pain that occurs in various parts of the intestine, so the dislocation of pain sensations changes.
- Nonspecific ulcerative colitis. This disease is characterized by the spread of pain throughout the intestines. Ulcers and bleeding are also possible.
Depending on the cause, chronic colitis can be allergic, infectious, ischemic, radiation, toxic, or combined. In the latter case, several etiological factors are combined.
According to the prevalence of the lesion, colitis is:
- segmental - when only a specific part of the intestine is involved in the pathological process;
- total - the entire colon is affected.
By severity:
- mild degree - when it is easy to achieve remission;
- moderate severity - to ensure long-term relief of symptoms, medications and diet are needed;
- severe degree - exacerbation prevails over remission, and it is difficult to achieve the latter.
Symptoms of colic in adults
The pathological condition is characterized by pain in the abdomen with tingling. The localization of painful sensations is different, because spasms gradually move from one part of the intestine to another. Pain syndrome is accompanied by:
- Nausea.
- The urge to vomit.
- Increased gas formation.
- Bloating.
To ease the attack, the person takes a position that helps reduce pain - leaning forward with the body.
Symptoms
Since in a chronic course the phase of retreat of symptoms and exacerbation alternate, most often patients turn to the doctor precisely when the symptoms acutely make themselves felt. During remission, they are absent altogether or are expressed very weakly.
The main symptoms of chronic colitis are as follows:
- pain that manifests itself in the lateral parts of the abdomen (the nature of the pain can be either acute or aching);
- rumbling in the intestines;
- belching, often with an unpleasant odor;
- measuring the abdomen in size;
- increased gas formation;
- false urge to defecate, which can occur every few days;
- nausea and weakness;
- unpleasant taste in the mouth;
- increased fatigue;
- sleep disorder;
- pale skin;
- brittle nails and hair loss;
- change in eating habits.
With nonspecific ulcerative colitis, the following symptoms are possible:
- impurities of pus or blood in the stool;
- frequent diarrhea;
- mild tingling pain in the lower abdomen;
- loss of appetite;
- inflammation of the organs of vision (extremely rare);
- pain in the joints;
- muscle weakness.
With an exacerbation of the symptoms of this form, changes in the intestinal mucosa are possible, such as swelling, bleeding, the appearance of small ulcers and formations similar to polyps.
Chronic colitis of a spastic nature manifests itself as follows:
- painful spasms that worsen with hunger or at night;
- bloating;
- flatulence;
- alternating diarrhea and constipation;
- insomnia and, as a result, constant fatigue;
- headache of varying intensity;
- complete bowel movement is often possible only the second or third time, and the process of excreting feces occurs only once a few days;
- rumbling in the stomach.
To reduce the symptoms, a constant diet is needed, but it must be taken into account that certain foods can cause constipation.
Intestinal colic: symptoms and treatment in adults
Intestinal colic is a complex of intestinal disorders that appear as a result of disturbances in its motor functions and are accompanied by severe pain in the stomach. Colic is a symptom of gastrointestinal disorders, and not a separate disease.
According to ICD-10, intestinal colic is classified as a major pathology, so the diagnosis may have the following options:
- Irritable bowel syndrome, code K58, if there are no organic disorders.
- Other functional intestinal disorders, code K59, if there are disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract.
The last category has sub-items:
- Constipation – K59.0;
- Diarrhea – K59.1;
- Neurogenic excitability of the intestine – K59.2;
- Megacolon – K59.3;
- Sphincter spasm – K59.4.
Intestinal colic may indicate the presence of various diseases, which can only be identified by a qualified doctor.
Causes
The symptom can be caused by a number of factors of different origins. Severe, sharp pain in the stomach occurs for the following reasons:
Human infection with helminths
- Worm infestations. Infection with helminths irritates the nerve endings of the intestinal walls, resulting in colic. In addition to pain, the disease will be accompanied by nausea, loss of appetite, and weight loss. This pathology is more often observed in children. A child becomes infected with helminths through dirty hands.
- Intoxication. Toxins affect the intestinal muscles, leading to cramping. Intoxications include poisoning: mushrooms, food, plant and animal poisons, synthetic substances, salts of heavy metals. Intestinal colic can occur in women during toxicosis.
- Viruses. ARVI, influenza, and other viral diseases cause inflammation of the lymph nodes of the abdominal cavity, which can provoke spasms and stomach pain.
- Infections. Intestinal infections (salmonellosis, dysentery, cholera, typhus) can also cause intestinal colic. When microbes come into contact with food, they multiply and produce toxins. When consuming such products, food toxicosis develops.
- Diseases of the digestive tract. Colitis, gastritis, ulcers, pathologies of the liver, pancreas provoke digestive disorders. Poorly digested food enters the small intestine in large quantities, causing cramping pain in the abdomen.
- Poor nutrition. Eating cold, stale foods; abuse of fried, fatty foods; dry food - all this can cause intestinal spasms. The result is bloating and acute pain.
- Obstruction in the intestines occurs when there are obstacles in the path of feces, the walls contract, and colic occurs in the intestines. Tumors and gallstones are the causes of the pathology.
- Stress. In stressful situations, nervous excitability spreads to the intestines, which causes a cramping attack of pain.
- Consequence of surgery. Performing an operation in the abdominal cavity often causes intestinal cramps and colic. People over 40 years of age who have undergone surgery and have adhesions on their abdomen are susceptible to this pathology.
Symptoms
Signs of pathology are as follows:
- Acute pain in the intestinal area, which has a paroxysmal character. Painful sensations are concentrated in the navel area. The pain lasts for several days and radiates to the genitals. The temperature does not rise.
- In the acute form of gastritis, colic is accompanied by bloating, nausea, belching, and vomiting.
- When defecating, mucus appears in the feces.
- There is stool disorder.
- When palpating the abdomen, a sharp pain is felt.
- The patient experiences a change in appetite, weakness, and a worsening general condition.
Types of intestinal colic
There are four types of intestinal colic:
- Rectal. This type of colic occurs in the rectum. Characterized by sharp pain, false and painful urge to defecate.
- Appendicular. It is the first symptom of acute appendicitis. Accompanied by increasing pain in the iliac region.
- Hepatic. Occurs with the development of cholelithiasis, cholecystitis. With hepatic colic, the patient feels severe pain in the right hypochondrium, radiating to the arm. A bitter taste appears in the mouth, vomiting, nausea.
- Lead. Is a sign of lead poisoning. The victim has severe stomach pain, gums bleed, abdominal muscles tense, temperature rises, and a gray coating forms on the tongue. In this case, the help of a qualified specialist is necessary.
- Pancreatic. Develops in diseases of the pancreas. Characterized by vomiting, diarrhea, bloating, cramping pain in the upper abdomen.
- Renal. Occurs with urolithiasis, tumors, pyelonephritis. The patient complains of sharp pain radiating to the lower back. The temperature rises, urination is impaired, and blood pressure drops. With pain, loss of consciousness is possible.
Diagnostics
When diagnosing this pathology, the following measures are taken:
- Anamnesis. By interviewing the patient, the doctor finds out the place of work and the presence of chronic diseases of loved ones. The first is to eliminate contact with harmful substances, the second method eliminates the presence of infectious diseases.
- Inspection. By palpation, the specialist determines the pathological cause of the disease.
- Taking tests. A general analysis of blood, urine, and feces is prescribed. In this way, infection with helminths, the development of an inflammatory process, and disturbances in the functioning of the kidneys and liver are excluded.
- Radiography. Helps identify obstruction, intestinal damage, the presence of fluid and foreign bodies in the peritoneum.
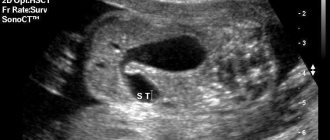
- Ultrasound. The method allows you to identify the root cause of colic formation.
- CT. Used when other examinations are ineffective. Allows you to identify tumors and neoplasms in the intestines.
- Colonoscopy. The procedure allows you to examine the surface of the colon.
- Sigmoidoscopy. This method is used to study the small intestine.
Treatment
When the diagnosis is made, the cause of the pathology is determined, comprehensive treatment begins. Intestinal colic in adults can be treated in the following ways.
Conservative methods
For intestinal colic, the doctor prescribes the following tablets:
- Antispasmodics eliminate pain;
- Sedatives;
- Anti-inflammatory;
- Antacids reduce hydrochloric acid;
- Preparations for normalizing stool.
In case of severe infectious diseases of the intestines, the patient is hospitalized. It is not recommended to make compresses with a warm heating pad, as this provokes an inflammatory process.
Traditional medicine recipes
Treatment for colic caused by parasitic infections is recommended using traditional methods:
- Dill. Prepare a decoction from a spoon of dried dill and a glass of milk. Take once, after meals.
- Motherwort. Will help get rid of intestinal cramps. The medicine is prepared from one teaspoon of juice and a glass of warm water.
- Pomegranate. You will need pomegranate peels. Grind a teaspoon of crusts, pour boiling water over them, and cook for 30 minutes. Decant and cool. Take two tablespoons three times a day.
- Pumpkin. Grind pumpkin seeds, pour a glass of boiling water, leave, add sugar. The course of treatment is five days.
- Tansy. Pour boiling water over a tablespoon of dried herb and let it brew. Drink the infusion throughout the day.
- Lavender. Lavender oil helps relieve spasms and pain. A few drops of lavender are added to the drink.
- Ginger. Pour half a teaspoon of ginger root into a glass of boiling water. They insist and persist. Drink the infusion three times a day.
- Sagebrush. You will need 100 grams of grass. It is poured with boiled water and left for two days. Then cook over low heat for an hour. Decant, add honey, simmer in a steam bath until the mixture thickens.
Diet
Diet is a mandatory component of treatment, regardless of the nature of the pathology. Nutrition should be balanced. It is necessary to exclude fatty, fried, salty, smoked foods from the diet. It is not recommended to consume baked goods, carbonated water, sweets, and canned food. It is necessary to completely give up alcohol. Don't overeat on meat dishes.
You can eat lean fish and porridge. It is recommended to consume more fresh vegetables, fruits, and dairy products. You should drink fresh juices and herbal teas.
Surgery
In cases of appendicitis and severe disorders, surgical intervention is required. Then the basis of treatment will be taking medications and diet.
Preventive measures
It is important to follow preventive measures that will help avoid this problem:
- Get preventive examinations on time.
- Get rid of bad habits.
- Introduce regular physical activity into your daily routine.
- Eat right.
- Lead an active lifestyle.
- Don't skip meals.
- Don't eat dry food.
- Avoid stressful situations.
- Cleanse your body of toxins weekly. To do this, you need to brew flax seeds.
- Don't eat at night.
- Ensure yourself a good night's sleep.
- Treat colds promptly.
Source: https://GastroTract.ru/simptom/kolika/kishechnaya-kolika.html
Diagnostics
To diagnose chronic colitis, you will need to consult a therapist and gastroenterologist. Its measures are as follows:
a conversation with the patient, during which he must talk about all the symptoms he has;- examination of the patient: palpation of the abdomen and eye examination. In the presence of inflammation of the latter, diagnosis is also carried out by an ophthalmologist;
- blood test (acute and biochemical);
- immunological analysis;
- stool analysis;
- colonoscopy (helps distinguish exacerbation from remission);
- X-ray using a contrast agent;
- Ultrasound.
Treatment of chronic colitis
Treatment for chronic colitis differs depending on the phase of the disease. At the remission stage, following a diet is sufficient; in case of exacerbation, drug therapy is needed. Treatment should be individualized, taking into account the type of disorder, severity of symptoms and general condition of the patient
Drug treatment
Typically, the following groups of medications are used for chronic colitis:
antibiotics;- probiotics - aimed at restoring the number of beneficial microorganisms in the intestinal microflora;
- antispasmodics - reduce pain;
- laxatives or fastening agents depending on the symptoms (diarrhea or constipation);
- medications containing enzymes;
- corticosteroids, immunosuppressants (for nonspecific ulcerative colitis);
- enveloping medications and sedatives (for spastic colitis).
Non-drug treatments
Among non-drug methods for chronic colitis, sanatorium-resort treatment may be indicated. Mineral waters, baths, microenemas, and intestinal lavage are useful.
Sometimes doctors recommend courses of physiotherapeutic procedures, such as magnetic therapy, acupuncture, and mud applications. Surgical intervention may be required if there are urgent indications in case of complicated colitis.
Some folk recipes can also be used:
- A decoction of sage, St. John's wort, caraway, and mint helps to cope with inflammation.
- For increased gas formation, mint, motherwort, and nettle are useful.
- To eliminate spasms in the intestines, microenemas with a decoction of calendula or chamomile can be performed.
- For ulcerative colitis, a microenema with sea buckthorn oil at night is useful.
Additional treatment methods are carried out in courses. It is recommended to consult a doctor before using them.
Diet for chronic colitis
Therapy will not be effective if the patient does not comply with a special diet. The rules of the diet for chronic colitis are as follows:
- The diet should contain a lot of fiber. It is found in vegetables, cereals, and bread.
- Food should be consumed 4-6 times a day.
- Lean fish and meat are consumed boiled. You can also eat boiled eggs.
- The diet should include many first courses cooked in vegetable broths.
- Seafood is healthy.
- Fruits and vegetables must be peeled.
- Foods that irritate the intestines should be eliminated from the diet. These include dairy and fermented milk products, legumes, spicy and salty foods, nuts, and alcohol.
Nutrition should be high in calories and include a large amount of substances needed by the body: vitamins, proteins, etc.
Diet for colitis is one of the measures included in the complex treatment of the disease
Intestinal colic: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
Intestinal colic, ICD code 10 - K59 , belongs to diseases of the digestive system. It is characterized by paroxysmal pain in the abdominal area, which can go away on its own. Despite the wave-like nature of the attacks, colic can signal serious diseases of the digestive tract (gastritis, ulcers).
Coding of intestinal colic according to ICD 10
Intestinal colic is not an independent pathology, but a symptom of indigestion. Therefore, its designation according to international standards has several variations:
ICD 10 codeName of pathologySpecificity of the disease
| K 58 | Irritable bowel syndrome | Functional disorders without changes in organs. |
| K 59 | Other functional intestinal disorders | In addition to colic, acute intestinal obstruction and diarrhea are observed. |
| K 59.0 | Constipation | Inability to have a bowel movement for several hours or days. |
| K 59.1 | Functional diarrhea | Frequent bowel movements with loose stools. |
| K 59.2 | Neurogenic excitability of the intestine | Due to damage to the nervous system, the evacuation of intestinal contents occurs uncontrollably. |
| K 59.3 | Megacolon | Increase in the size of the large intestine. |
| K 59.4 | Anal sphincter spasm | Involuntary contraction of the anal muscles. |
| K 59.5 | Other functional disorders of a specified nature | Atony of the esophagus, dyskinesia of the digestive tract. |
| K 59.9 | Functional bowel disorder, unspecified | Requires additional diagnostics. |
In accordance with ICD 10, intestinal colic is considered as an addition to the main pathology; when writing a diagnosis, the encoding of intestinal colic and the name of the main disease are used.
Functional gastrointestinal disorder
By “functional disorder of the stomach and intestines” we mean a number of disorders of the gastrointestinal tract that are not associated with changes in the structure of the digestive organs. FGIT (functional disorder of the gastrointestinal tract) is characterized by the presence of:
- Functional bloating.
- Functional constipation.
- Diarrhea.
- Irritable colon or small intestine syndrome (gastrointestinal dysfunction).
FRF appears due to:
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Mental instability (severe stress, constant worries).
- Heavy physical work.
- Infectious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
FGIT is spoken of when its symptoms have bothered the patient for 6 months or more. Moreover, symptoms must actively manifest within 3 months.
What causes intestinal colic?
Colic is a consequence of irritation of the intestinal walls by a provoking factor. Smooth muscles respond to this with a strong contraction (spasm). Intense physical activity can trigger colic. During this, tension in the mesentery occurs, which leads to stabbing pain in the left side of the abdomen.
Colic occurs due to:
- Immaturity of gastrointestinal tract structures, flora insufficiency (in children).
- Eating heavy foods that contribute to the formation of gases (flour products, fried foods, soda).
- Exposure to large amounts of air when eating. This can happen if you talk during a meal or eat on the go.
- Constipation.
- Entry of a foreign body into the gastrointestinal tract.
- Food allergy (to lactose).
- Allergic reactions.
- Disorders of blood supply to various parts of the intestine. This occurs due to ulcerative formations and diverticulosis.
- Intestinal obstruction.
Symptoms of colic in adults
The pathological condition is characterized by pain in the abdomen with tingling. The localization of painful sensations is different, because spasms gradually move from one part of the intestine to another. Pain syndrome is accompanied by:
- Nausea.
- The urge to vomit.
- Increased gas formation.
- Bloating.
To ease the attack, the person takes a position that helps reduce pain - leaning forward with the body.
Manifestation of colic in children, their causes
In an infant, intestinal colic is a widespread phenomenon. It often occurs in 1-4 months of a baby’s life. A child reacts to the appearance of colic as follows:
- Facial hyperemia.
- Constant screaming and anxiety.
- Pressing your knees towards your stomach.
The baby's tummy is tense. Its palpation brings painful sensations to the little patient. The attacks occur at certain hours at night and recur within a week or two.
In children under 4 months of age, colic is not a pathology, but a consequence of enzymatic disorders. Its symptoms are observed in children, both bottle-fed and natural-fed.
The cause of discomfort in the intestinal area may be:
- Infection.
- Allergy to dairy products or breast milk.
- Inflammation.
- Psychogenic factor (tense family situation, mother's depression).
How to eliminate intestinal colic?
Intestinal colic, despite its pain, is a temporary phenomenon. However, patients always have a desire to get rid of unpleasant attacks once and for all. What can help relieve colic symptoms?
Effective methods are:
- Abdominal and back massage. It is done using smooth circular movements.
- Applying warm objects (heating pad or compress) to the abdomen.
- Taking warm baths. They have a beneficial effect on the abdominal walls, relaxing them.
Medications that are suitable for patients include:
- Preparations based on simethicone. Thanks to the action of the latter, bloating disappears and excess gases are eliminated.
- Medicines containing trimebutine. This substance improves intestinal function. It also controls the tension and relaxation of its walls.
Herbal infusions help reduce pain. They are prepared from chamomile and mint.
For children with colic it is recommended:
- Light abdominal massage.
- Place on tummy.
- Give fennel teas.
Options for preventing intestinal colic
How to make sure that intestinal colic does not interfere with everyday life and does not bother you? There are several options for preventing colic:
- Stick to a healthy diet. You need to give up fatty and fried foods. You should remove cabbage, beans, and plums from the menu, that is, those foods that cause increased gas formation.
- Use food additives such as ginger, mint for cooking. They improve digestion.
- Eat regularly. You need to eat 5-6 times a day, but in small portions.
- Eating should be done in a calm environment. You need to chew your food thoroughly.
- Exercise. However, remember that physical activity after eating is not permissible.
- Prevent the development of constipation. To do this, you need to drink at least 2 liters of water per day and eat foods rich in fiber.
For preventive purposes, it is recommended to take probiotics and prebiotics. The former, due to the content of natural bacteria in them, help improve the condition of the natural intestinal flora, complementing it. The latter support the development of flora and the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Prevention of colic in children
The following ways help prevent colic in infants:
- It is necessary to feed the baby in an upright position, having previously removed all possible irritating factors from the room.
- Make sure your baby is getting food and not air when bottle feeding.
- After eating, it is important to hold the baby in an upright position (carry in your arms for 10 minutes).
- Organize the menu of a nursing mother so that it does not contain fatty foods, as well as foods that can cause a hyperreaction in the child (citrus fruits, chocolate).
It is important for the patient not to self-medicate, but to seek help from a qualified specialist if symptoms similar to colic begin to bother him.
Source: https://netgastritu.com/kishechnik/kolika/
Possible complications and consequences
If the disease is not treated, it can cause a number of complications. This mainly concerns ulcerative colitis. The consequences may be as follows:
- Perforation of the ulcer, which often results in peritonitis. In this case, the symptoms will be manifested by severe bloating and tension in the abdominal muscles, high fever, chills, a coating on the tongue, and general weakness.
- Gangrene of the colon and affected areas of the intestine. In this case, you may feel weakness, high temperature, and decreased blood pressure.
- Blood poisoning or spread of infection to other organs.
- Bleeding in the intestines (with chronic ulcerative colitis).
- The appearance of an oncological tumor is also possible.
Video - Chronic intestinal colitis: causes, symptoms, treatment of colitis.
Constipation ICD-10
ICD-10 constipation is included in a separate group with code K59.0. The regulatory document prescribes the classification of the disease, its symptoms, and treatment methods. When diagnosing a patient, doctors are guided by the International Classification of Diseases. The use of generally accepted measures helps to achieve maximum effectiveness in diagnosing and combating constipation.
The disease in the global classification
Based on the worldwide classification, which has been in effect since the beginning of 2007, the diagnosis of Constipation, ICD 10 code K59.0, belongs to the block of Other intestinal diseases of the Digestive Organ Diseases class. The document assumes that the disease is chronic constipation. The ICD-10 code is further divided into two subtypes, differing in the symptoms of the disease and the cause of its manifestation.
The code K59.0.0 classifies hyponic and atonic constipation caused by weakening of the intestinal muscles. As a rule, the main reasons are poor nutrition and poor mobility during the day. Code 59.0.1 is assigned for the diagnosis of spastic constipation. This type of disease is caused by disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system. Spastic constipation is characterized by spasms in the intestinal area, but no organic changes occur inside it.
Constipation according to ICD-10 and methods of its treatment
In addition to diagnoses, the global classifier indicates methods of treating diseases of a certain type. Chronic constipation was no exception; ICD-10 suggests the use of three treatment options used at different stages of the disease. Each method involves the use of special methods. There are three types of treatment for constipation:
- integral therapy;
- rehabilitation;
- prevention.
The table shows the methods used at different stages and for different treatments of chronic constipation.