Heartburn, as well as its accompanying symptoms: nausea, belching, pain, heaviness and bloating in the abdomen, bother people quite often throughout their lives. However, not everyone knows that discomfort in the stomach and esophagus can indicate serious illnesses, and not just be the cause of overeating or eating low-quality foods. Therefore, patients with regular heartburn and heaviness in the stomach are advised to self-medicate less and buy pharmaceutical drugs without doctor’s recommendations; the best option would be to undergo a diagnostic examination and begin treatment prescribed by a specialist.
Heartburn and heaviness in the stomach
Causes of heartburn and heaviness in the stomach
Discomfort and burning behind the sternum are often accompanied by other symptoms. People complain of pain in the throat, stomach and esophagus, bloating, belching, nausea and constipation. They occur an hour after eating food or during intense physical exertion. The reasons for this are various:
- Poor nutrition. Abuse of fatty, fried, salted and peppered foods, alcohol.
- Diet. As a result of frequent overeating, the stomach cannot cope with large amounts of food and a person begins to feel heaviness and pain in the stomach, he is bothered by belching air and heartburn. Nutritionists recommend eating five to six small meals a day.
- Physical exercise. If you immediately start exercising after eating, you will hardly be able to avoid heartburn, pain in the abdomen and other unpleasant sensations.
- Use of certain types of medications.
- Improper fluid intake. Few people know, but water, as well as fresh vegetables and fruits, must be consumed half an hour after a meal or before it.
The reasons for this are as follows:
- Carbonated drinks along with meals or immediately after meals have a negative effect on the gastric mucosa, causing irritation. This leads to nausea, heaviness, heartburn and belching.
- Drinking water during meals increases the volume of food eaten, which reduces the ability of the digestive system to process it.
- If you immediately drink food with water, then hydrochloric acid begins to reduce its bactericidal effects.
Feeling of a lump in the stomach
Gastritis
33355 August 21
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Feeling of a lump in the stomach: causes of occurrence, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods.
The feeling of a coma in the stomach is described when one experiences a feeling of heaviness, discomfort and fullness in the stomach, even when it is only slightly filled. Sometimes patients find it difficult to determine the exact location of the coma and point to the lower third of the sternum or solar plexus. In some cases, a feeling of a lump and cramps in the stomach may occur on an empty stomach.
Types of feeling of a coma in the stomach
A feeling of heaviness or coma in the stomach can be an independent symptom, but may be accompanied by other unpleasant sensations. Sometimes it is heartburn, sour belching, bloating, constipation.
In some cases, a feeling of a lump appears when swallowing
, making it difficult for chewed food to pass through.
In addition, patients may complain that food did not enter the stomach, but stopped in the esophagus.
In such patients, vomiting of unchanged food is possible. When describing symptoms, you should pay attention to the time of onset of discomfort - before
or
after eating
.
The patient may feel heaviness in the stomach with pain or heartburn, on an empty stomach or after eating, and night pain also occurs.
Sometimes the sensation of a lump in the stomach occurs
regardless of food intake
.
In such cases, they complain of stomach spasms
, sometimes accompanied by a feeling of a lump in the throat.
What diseases cause a sensation of a lump in the stomach?
Eating more than your usual amount of food
, accompanied by a feeling of fullness and heaviness in the stomach. This condition is not a manifestation of the disease and goes away on its own after some time.
It should be noted that stomach capacity varies depending on eating habits.
People who are small or
have undergone gastric resection
can eat a small portion, otherwise they will not only experience a feeling of heaviness or fullness in the stomach, but also vomiting.
A sensation of coma may occur when consuming foods that cause excess gas.
, as well as
food that is difficult to digest
(salads with mayonnaise, fatty, fried and smoked dishes) and
highly carbonated drinks
.
When eating dry and hastily,
an unpleasant sensation in the epigastric region is caused by poor processing of the food bolus with saliva and insufficient secretion of gastric juice.
However, a feeling of coma or discomfort in the stomach, or more precisely, in the epigastric region, may appear after eating even a small amount of food
.
This condition can be caused by diseases of the gastrointestinal tract or other reasons.
First of all, they assume indigestion, or functional dyspepsia. Its symptoms most often include pain and discomfort immediately after eating, a feeling of heaviness and fullness in the stomach, heartburn, belching, nausea, sometimes vomiting, reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus, bloating and bowel dysfunction.
Dyspepsia can be a symptom of both functional disorders of the gastrointestinal tract and organic diseases.
Functional causes of dyspepsia are often caused by errors in diet and medications.
Iron ions have an irritating effect on the gastric mucosa, which is most pronounced when taking medications based on ferrous iron. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, which are systematically taken for rheumatic and non-rheumatic diseases of the musculoskeletal system, also cause undesirable effects: heaviness and discomfort in the stomach, nausea, vomiting, and dyspeptic disorders.
Neurological disorders
(neuroses, depression), psychological trauma almost always affects the state of the gastrointestinal tract, leading to impaired motility.
Functional dyspepsia is not accompanied by erosive or ulcerative lesions of the stomach; its symptoms disappear when the general state of health is normalized.
One of the common causes of discomfort in the stomach immediately after eating is
gastritis
. It is accompanied by functional and inflammatory processes that have a negative effect on the gastric mucosa. Symptoms of gastritis include heaviness and pain in the stomach, indigestion, nausea, heartburn, sour belching and bloating when eating any food. The inflammatory process leads to atrophy of the mucous membrane and disruption of the glands that secrete gastric juice.
Insufficient gastric juice and weak peristalsis of the stomach and intestines make it difficult to digest food.
Gastritis is often accompanied by dyspepsia. In addition to a feeling of heaviness and aching pain in the epigastric region after eating, poor appetite, weakness, fatigue, and irritability are noted. When pressing on the abdomen, a dull pain appears in the projection of the stomach.
Impaired motor-evacuation functions
upper digestive tract is always accompanied by a feeling of coma or a feeling of heaviness in the stomach. Disorders of esophageal motility are usually caused by incoordination of the esophageal sphincters. Uncoordinated work of the esophageal muscles can lead to a delay in the bolus of food on the way to the stomach, the reflux of food particles into the respiratory tract, and reflux (return of stomach contents into the esophagus). Impaired gastric motility leads to slow emptying, which is accompanied by a feeling of heaviness and fullness even with a small amount of food consumed, pain in the epigastric region, heartburn, nausea and vomiting.
Motility disorders of the esophagus and stomach may be associated with gastroesophageal reflux disease, gastritis, tumors and stenoses (narrowings), metabolic disorders (hyperkalemia, hypercalcemia), postoperative complications of gastrectomy, taking certain medications (opiates, antidepressants, hormones), alcohol and nicotine .
Peristalsis worsens with a sedentary lifestyle and with age.
Stomach cancer can also cause symptoms such as a feeling of heaviness or a lump in the stomach. Moreover, depending on the location of the tumor, its manifestations vary. If the tumor is located closer to the esophagus, problems with swallowing food occur. This is accompanied by increased salivation, nausea, vomiting, and pain in the epigastric region. When the tumor is localized in the lower parts of the stomach, closer to the duodenum, a prolonged feeling of heaviness after eating and bloating is characteristic. When burping, a putrid odor may be felt.
Which doctors should you contact if you feel a lump in your stomach?
If there is a constant feeling of a lump in the stomach or a feeling of heaviness, it is necessary to contact or to make a preliminary diagnosis. The gastroenterologist may also refer the patient to an oncologist. A consultation may also be required.
Diagnosis and examination if you feel a lump in the stomach
First of all, clinical blood and stool tests are necessary for differential diagnosis.
What diseases occur?
Various diseases of the digestive system can provoke heaviness in the stomach and heartburn:
- Duodenitis. Symptoms of this disease are regular and aching pain.
- Gastritis. Discomfort in the stomach and esophagus is characterized by intense pain and heartburn that occurs half an hour to an hour after a meal.
- Cholecystitis. There is a burning sensation in the esophagus and discomfort in the stomach immediately after eating fatty, heavy foods.
- Food allergies.
- Ulcerative lesions of the stomach and small intestine.
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease. Painful sensations spread to the esophagus and cause discomfort and burning.
- Diaphragm hernia. This disease is characterized by pain symptoms and heartburn when the patient is in a horizontal position and when the body bends sharply.
- Chronic intoxication.
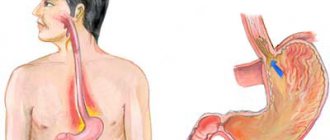
The mechanism of heartburn
When the cardiac (gastroesophageal) sphincter between the esophagus and stomach is weakened, heartburn appears. The return (reflux) of acidic food back into the esophagus causes a neutralization reaction to begin, releasing heat. The mucous membrane of the esophagus cannot protect its walls from the effects of heat and aggressive gastric juice - a burning sensation occurs behind the sternum. Reflux of food is accompanied by the movement of air from the stomach back to the esophagus - belching occurs. First of all, when such symptoms appear, you need to find out what is causing the heartburn.
Mechanical causes of reflux
The return of food from the stomach can occur with increased pressure on the stomach, which is facilitated by:
- tight clothing, tight belt or corset;
- bending forward, lifting weights immediately after eating;
- horizontal position of the body after eating, making it difficult for the food bolus to move downwards;
- overeating and fullness of the stomach with food;
- hasty snacks, swallowing air while eating (aerophagia).
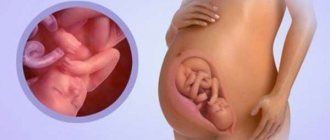
In women, carrying a child, especially in the 3rd trimester, is accompanied by frequent bloating and heartburn, as the fetus puts pressure on the stomach and interferes with digestion.
Medicines that cause heartburn
A side effect of many medications is a burning sensation in the chest:
- products containing theophylline (for the treatment of asthma);
- adrenaline blockers (for blood pressure);
- nitrates (for heart failure);
- hormonal drugs (Progestin, Thyroxine);
- tricyclics - drugs against depression;
- sedatives;
- nonsteroidal analgesics and antispasmodics (Nimesulide, Diclofenac).
All these drugs relax the sphincter muscle ring, which poorly prevents the reverse reflux of food from the stomach.
Products that provoke reflux esophagitis
Heartburn is caused by the abuse of certain foods: some promote the secretion of large amounts of gastric juice, others relax the gastroesophageal sphincter. Eating acidic foods leads to esophagitis, which develops with regular consumption:
- alcohol;
- coffee, tea;
- fatty and spicy foods, fast food;
- bakery and confectionery products, chocolate;
- Coca-Cola, sparkling water.
If, after eliminating these factors, the burning sensation in the esophagus after eating does not stop, then you should consult a doctor and find the cause of the pathology.
Other states
Heartburn and accompanying manifestations may occur not only due to poor diet and the presence of gastric diseases, but also in the following cases:
- Excess weight. In people with large body weights, the pressure inside the stomach increases, pushing digestive juices into part of the digestive canal. Eating small portions of food can help get rid of discomfort.
- Pregnancy. In women in this position, heartburn, nausea and other manifestations are observed quite often. This is due to changes in hormonal levels or the large size of the uterus, which displaces organs, including the stomach.
- Surgical intervention. After operations to remove malignant tumors on or near the stomach, patients often complain of a burning sensation in the esophagus and stomach heaviness.
Features of treatment
Considering that increased accumulation of gases in the intestines and heartburn appear in various pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, only a doctor can select effective drugs for treatment, since these are narrow-spectrum drugs, which are strictly prohibited to be used independently due to many side effects.
Medications
To alleviate the patient’s condition with pain, painful bloating and heartburn (especially if this is a one-time digestive disorder), the following drugs can be used:
Mezim Forte - stimulates the production of substances for the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, reduces the level of acidity in the stomach, relieves the feeling of heaviness and fullness after eating. Enterosgel is an absorbent that removes toxic substances from the body. Used for poisoning, intestinal infections, bloating. Espumisan - quickly eliminates the accumulation of gases in the intestines. Hilak Forte is a prebiotic that normalizes the quantitative and qualitative composition of intestinal microflora, improving the process of food digestion. Hydrolycite is a drug that neutralizes hydrochloric acid in the stomach. Quickly relieves heartburn and can be used in the treatment of acid-related gastrointestinal diseases. Rennie is a drug that normalizes the functioning of the digestive tract, reduces high acidity in the stomach, and eliminates heartburn. Effective for eliminating painful symptoms, not intended for the treatment of diseases and disorders of the gastrointestinal tract.
Folk remedies
In folk medicine there are also several effective ways to help cope with heartburn and bloating:
mint tea - brew 1 tsp. chopped dry herbs in 1 tbsp. boiling water Useful for digestive disorders caused by stress, depression, nervous exhaustion; soda solution - for high acidity, drink 250 ml of water with ¼ tsp of soda dissolved in it; ginger tincture - to normalize the intestinal microflora and improve the functioning of the digestive tract, drink 1 tsp. tinctures after meals. To prepare it, use fresh ginger root. 50 g of the product is cut into pieces and poured into 1 liter of vodka, you can add 100 g of honey. All infuse in a dark, warm place for 2 weeks.
Despite the ease of using folk recipes and the simple ingredients they contain, it is advisable to consult a doctor before using them. In addition, these methods help to temporarily get rid of painful symptoms, and do not cure the underlying cause of their occurrence.
How to avoid unpleasant sensations?
When you are concerned about regular stomach pain and a burning sensation in the chest, the first thing you should notice is what happens after that. When provoking factors have been identified, you should simply avoid them. If this is due to acute or chronic illnesses, then you should not self-medicate and delay visiting a doctor.
To avoid discomfort in the stomach and esophagus, you should take care of this in advance. Every person's morning should begin with exercise 15 minutes before breakfast. The first meal should be complete in order to give the body a charge of energy and strength for the whole day. It is important to lead an active lifestyle and take more walks, which is especially welcome after meals. Stress and conflict situations negatively affect the digestive system, so you should try to avoid them. Smoking often provokes heartburn, nausea and other associated symptoms; nicotine is especially dangerous on an empty stomach.
Why does bloating occur?
Gases move through the gastrointestinal tract along with food - this is a normal physiological process.
Movement of gases through the gastrointestinal tract
Air is present in the upper part of the stomach in the form of a bubble. Hurrying, talking, laughing while eating, we are able to swallow up to 1 liter of air, which then comes back in the form of belching or hiccups, which can carry food away from the stomach and provoke heartburn.
In the small intestine, acidic food from the stomach interacts with the alkaline environment of bile and pancreatic enzymes. The reactions are accompanied by the formation of intestinal gases: some of them are absorbed into the blood, and the other part moves into the colon. Painless gurgling in the abdomen is a manifestation of reactions in the small intestine.
The processing of the food bolus in the colon is completed. Here, beneficial saprophytic bacteria feed on food residues, mainly fiber. Their waste products (hydrogen, methane, carbon dioxide) are excreted along with feces. Normally, gas is released from the body up to 15 times a day, approximately 200 ml of gases are released, which do not have a pronounced stench.
When poorly digested food enters the rectum, pathological flora begins to develop, which causes increased gas formation - flatulence. Products of pathogenic microbes (sulfur dioxide, ammonia, indole, skatole) in the form of foam overwhelm the intestines, indigestion is accompanied by constipation or diarrhea. Sometimes up to 3000 ml of gases accumulate in the intestines, this causes the stomach to swell and hurt, gas separation is accompanied by a stench, and its frequency increases tens of times.
Causes of flatulence in healthy people
With healthy digestion, increased gas formation can occur for several reasons.
Binge eating
The gastrointestinal tract is capable of processing a certain amount of food at one time. If more of it is supplied, food is retained first in the stomach, the small intestine lacks bile and enzymes to process it, and as a result, poorly digested rotting food enters the small intestine - a breeding ground for pathogenic bacteria. Eating before bed has the same effect.
Consumption of products that cause gas formation
- All types of cruciferous vegetables (cabbage, radishes, radishes) are rich in healthy fiber, but contain sulfur. It inhibits saprophytes - bacteria that provoke flatulence develop instead.
- Legumes (peas, beans, lentils) contain vegetable protein, which is difficult to break down and enters the rectum insufficiently processed, which leads to flatulence.
- Products with coarse fiber (raw vegetables and fruits) - consuming them immediately after meals speeds up the movement of the main food through the digestive tract; it enters the large intestine poorly digested.
- Individual intolerance to dairy products: due to a lack of lactose, milk is not digested and causes flatulence.
Other reasons
Taking antibiotics and other medications for a long time disrupts the balance of microflora in the intestines; pathogenic flora suppresses beneficial bacteria and causes flatulence. Its cause may be stress: nervous overload is accompanied by the release of adrenaline, which accelerates intestinal motility, so food does not have time to be digested well. Flatulence is one of the signs of irritable bowel syndrome.
The nutritional factor - overeating, irrational diet, abuse of certain foods - causes irritation of the esophagus at the very beginning of food digestion and flatulence at the end of this process. If the causes of heartburn and bloating are not addressed in a timely manner, they will become symptoms of diseases of the digestive tract.
Drug treatment
Before you begin treatment for heartburn and its additional symptoms, you must visit a doctor and undergo a diagnostic examination. Based on the results obtained, the gastroenterologist will make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe an appropriate course of therapy. The following medications can cure heaviness in the stomach and burning sensation in the esophagus, which can be easily purchased in pharmacy chains:
- "Allohol." This medicine is intended to normalize the flow of bile and prevent its stagnation in the esophagus. The medication should be taken after or during meals, one or two tablets three times a day.
- "Renny." The drug contains magnesium and calcium carbonates, which, when interacting with stomach acid, form water-soluble salts and water. The medicine is intended to reduce the level of acidity in the digestive system.
- "Panzinorm." The medicine is taken strictly according to the doctor’s recommendation, and it should be taken during meals or immediately after meals.
- "Omez." This medication is able to normalize the production of hydrochloric acid in digestive juice.
- "Motilak". Improves peristalsis of the stomach and small intestine, speeds up the process of food passage. The drug can be used to prevent vomiting, as it increases the tone of the muscles that separate the stomach from the esophagus.
- "Festal". The medication is taken during meals or after meals. one tablet at a time. Take the dragees with water without chewing. If necessary, you can take two tablets at a time.
- "Motilium". After consuming the medicine, gastric emptying is accelerated and there is an antiemetic effect, which is due to the ability of the medication to tone the esophagogastric sphincter.
- "Gastal." This drug is prescribed to reduce acidity and is prescribed for diseases associated with increased production of hydrochloric acid.
- "De-nol." It has an antimicrobial effect and protects the stomach from the formation of pathogenic microflora.
- "Mezim." The medication is taken one to three tablets in the morning, lunch and evening. The duration of treatment is indicated by the doctor individually for each patient.
- "Ranitidine". The drug is used to reduce the total amount of substances that cause irritation of the mucous layer of the stomach and small intestine.
Treatment
The choice of methods to get rid of these dyspeptic manifestations depends on the cause of the pathology.
If they arise due to eating disorders, then it is easiest to cope with. It is enough to optimize your diet and diet. Avoid hard-to-digest foods, overeating, and eating at night. It is recommended to drink before or after meals at intervals of 25-30 minutes.
It is much more serious if heaviness in the abdomen, heartburn and belching are manifestations of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (gastrointestinal tract).
At an appointment with a gastroenterologist
If the manifestations often recur, then you should seek medical help from a therapist or gastroenterologist. The specialist will diagnose the pathology that led to the complaints and prescribe treatment. Various gastrointestinal pathologies, the manifestations of which are heaviness in the stomach, heartburn, belching, have only some identical areas of treatment. Others have a specific focus.
- Diet. It is mandatory for any gastrointestinal pathology. It is somewhat different for different pathologies. Fatty, spicy, fried, smoked foods are definitely excluded. Food intake is carried out in small portions, 5-6 times a day. The last meal should be 2-3 hours before bedtime.
- Antacid drugs.
- Proton pump blockers.
- Antibiotic therapy. Depends on the cause of the pathology. For gastritis and ulcerative changes, it is aimed at destroying Helicobacter pylori.
- Enzymatic preparations. They are prescribed for replacement purposes in case of enzyme deficiency (Festal, Panzinorm, Mezim).
- Drugs that promote the excretion of bile and eliminate its stagnation (Allohol).
- Prokinetics. Strengthening the motility of the stomach and intestines (Motilak, Metoclopramide, Motilium).
- Antacids. They reduce the aggressiveness of already produced hydrochloric acid (Rennie, Ranitidine, Almagel).
Unconventional methods of therapy
In the fight against burning in the esophagus and heaviness in the stomach, alternative medicine advocates and offers the following folk recipes:
- Millet infusion. The main component is poured with boiling water for 15 minutes and during this time kneaded with your hands. It is necessary to knead the millet until the liquid takes on a milky tint. The medicinal infusion is drunk several times a day.
- Freshly squeezed potato juice. Peel the potatoes and put them through a juicer; you can also grate them and squeeze the juice into a glass. You should drink the liquid in small sips after waking up on an empty stomach. The course of treatment is ten days, after which the same break is taken and, if necessary, therapy is resumed.
- Infusion of dill, fennel and anise. The seeds are crushed and three tablespoons of all ingredients are poured into a glass of boiling water. The liquid is drunk symptomatically during an attack.
- Nuts. Almonds can relieve burning in the esophagus and discomfort in the stomach. The nut is chewed during an attack, and its active substances at this time neutralize hydrochloric acid and thereby remove discomfort.
Treatment using traditional methods
Traditional methods of treating heartburn and heaviness in the stomach are aimed at restoring intestinal motility and artificially replenishing enzymes.
Potato juice. You need to take potatoes in small sips. It helps eliminate heartburn and pain.
But there is one important rule: you need to take potato juice only 3 minutes after preparation, but no later than 10 minutes. Otherwise, it will lose all its healing properties.
Millet infusion. You need to take 3 tablespoons of millet and pour hot boiled water over it for 30 minutes. Treatment consists of drinking liquid. It helps eliminate the presence of seizures.
The appearance of unpleasant symptoms is a reason to pay attention to the condition of your body, undergo the necessary diagnostics, and also undergo a course of treatment. The very first thing you need to do is stop frequent overeating.
Prevention and diet therapy
To prevent stomach discomfort and heartburn, the following preventive measures should be followed:
- do not take a horizontal position immediately after eating and do not go to bed;
- eat food often and in small portions;
- It is not recommended to drink liquids during and after meals, especially coffee and carbonated drinks;
- Do not eat too hot or cold food;
- You should eat slowly and do not talk during the meal, as this leads to the accumulation of gases in the stomach.
Diet plays an important role in the treatment of heartburn and related symptoms. The patient should avoid drinking alcoholic beverages, smoking, excessively eating fatty and fried foods, sour and too sweet foods. Dishes should be steamed, baked or boiled. It is necessary to give preference to low-fat varieties of fish and meat, exclude canned food, smoked meats and semi-finished products from the menu. The patient's diet must include cereals, potatoes, durum pasta, dairy and fermented milk products. In order not to provoke heartburn and heaviness in the stomach, you should eat exclusively light foods that do not cause irritation to the gastric mucosa.
List of main reasons
Heartburn and the accompanying heaviness in the stomach can occur due to problems with the stomach and other organs of the gastrointestinal tract.
Bad habits and poor nutrition affect the appearance of symptoms. Heartburn often appears simultaneously with a feeling of heaviness in pregnant women, and can also be caused by stress.
Gastrointestinal diseases
The list of main problems begins with common diseases:
- A hiatal hernia in the muscle that separates the abdominal and thoracic cavities - the diaphragm. Its increase to a certain size leads to protrusion of part of the stomach beyond its usual location. Because of this, heartburn often appears - especially during sleep, after exercise and eating.
- Chronic gastritis with high acidity. The reason for the increased pH level can be an unhealthy diet (including fatty, salty or fried foods), and heartburn in this case usually appears after eating.
- Ulcers of the stomach or duodenum. Due to these diseases, food enters the intestines later than usual. Distension of the stomach leads to increased pressure inside it and the appearance of additional digestive problems. One of the signs of pathology is heartburn.
The causes of symptoms are also considered to be achlorhydria and achylia. Due to these pathologies, not only the acidity in the gastric juice decreases, but also the content of a special enzyme for breaking down the proteins eaten - pepsin. And heartburn is caused by the reflux of lactic and butyric acids into the esophagus, formed during the fermentation of digested food.
Errors in nutrition
Patients who do not follow basic nutritional rules also suffer from heartburn:
- those who abuse food that is unsuitable for their health – high in fat, salt and spices, as well as food prepared by frying or smoking;
- those who violate the diet - first of all, overeating or eating rarely, but in large volumes (whereas it would be correct to eat more often, but in small portions);
- those who incorrectly consume fresh fruits or vegetables, which it is advisable to consume no earlier than half an hour after a meal.
Carbonated water, especially sweet water, can also cause heaviness in the stomach with a burning sensation. Lively conversations while eating and poor chewing of food are not recommended for people suffering from stomach problems. It has an adverse effect on the stomach, leading to heartburn and a stressful state for the patient. Due to stress, the digestion process is disrupted, and the likelihood of unpleasant symptoms increases.
Pregnancy
Heartburn and heaviness in the gastrointestinal tract often accompany pregnancy, especially in the later stages. One of the main reasons is increased levels of a hormone called progesterone, which causes poor gastric motility. Food is digested more slowly and unpleasant symptoms occur.