General rules
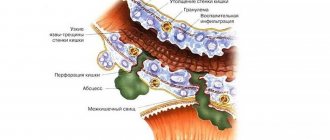
Crohn's disease is a chronic disease that causes transmural granulomatous inflammation of the intestine, which can be localized in any part of the tract - from the mouth to the anus. However, damage to the distal small intestine is more common. The main causes of the disease are considered to be genetic predisposition and an inadequate immune response, which leads to chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, tissue damage and the appearance of deep ulcers. The disease progresses in waves with alternating remissions and exacerbations. Patients are concerned about diarrhea (sometimes with blood), nausea, abdominal pain, loss of appetite, weakness and fatigue, and weight loss.
Deep (transmural) damage to the intestine leads to serious complications - fistulas and strictures . The resulting abscesses in the intestinal wall lead to the formation of fistulous tracts between the intestine and other organs or intestinal loops. The condition of the patients is serious: they are worried about constant pain, diarrhea , anorexia , weight loss and periodically rising temperature. If the ulcers heal, fibrous strictures remain and symptoms of obstruction appear. In such cases, intestinal resection is recommended. Drainage of formed abscesses and creation of anastomoses to bypass fistulas are also carried out.
Treatment consists of prescribing anti-inflammatory ( aminosalicylates ) and hormonal ( budesonide , prednisolone ) agents. In moderate forms of the disease, glucocorticoids are administered intravenously and then orally. The treatment plan includes a diet with complete exclusion or limitation of milk and raw fiber (vegetables, nuts, seeds). It helps eliminate inflammation, promotes healing of ulcerated mucosa and replenishes nutrients.
There is no special diet for Crohn's disease, but the most suitable is Diet No. 4 , which is prescribed differentially at different stages of the disease. It involves the exclusion of foods that cause peristalsis, fermentation and putrefaction in the intestines. Nutrition for this disease is prescribed mechanically and chemically gentle with a high content of vitamins and protein. Strict adherence to the diet is important for malabsorption syndrome . Sometimes a minor diet violation can cause the condition to worsen.
In the acute stage, all vegetables and fruits are excluded. Decoctions and jelly from blueberries, bird cherry, black currant, chokeberry and pomegranate juice are widely used. Pomegranate peels are used in decoctions as an astringent.
Most patients have protein deficiency due to protein loss, anorexia and malabsorption, which leads to weight loss. In this regard, during any phase of the disease, nutrition should be as high in calories as possible due to protein.
It is also important to exclude additional sensitization by food allergens, so the diet should be hypoallergenic, excluding extractives, chocolate, cocoa, eggs, coffee, citrus fruits, red apples, strawberries, wild strawberries, baked goods, and industrial canned food. When remission is achieved, the diet is less strict.
Basic nutrition rules:
- Exclusion of products containing fiber (rye bread, vegetables, fruits, bran bread, whole grain). Fiber causes increased fermentation, and this increases the frequency of bowel movements. In the acute period of the disease with increased diarrhea, fiber is excluded, and then foods with low fiber content are introduced (potatoes, cauliflower, zucchini, pumpkin, semolina, rice). The fiber content is reduced by boiling, grinding and rubbing through a sieve, which allows you to include the necessary vegetables and fruits without compromising your health.
- Six meals a day, which are based on pureed, slimy soups, mushy, pureed and semi-liquid dishes.
- Boiled (steam) method of preparation.
- Increased protein content (on average 120-130 g, more precisely 1.3-2 g per kg of weight).
- Reducing fats that are poorly absorbed and have a laxative effect. They are limited at the beginning of treatment, and after the process subsides, the amount of fat is increased and evenly distributed over all meals.
- Small and frequent meals.
- Prohibition of eating hard and thick foods.
- Implementation of the water regime (1.5-2 l).
- Limit salt (8-10 g), as it causes irritation of the intestinal mucosa and loosening of stools.
During an exacerbation, the diet includes liquid and pureed porridges (rice, semolina) with water, since milk and broths are excluded. It is convenient to use porridge for baby food, but it must be diluted with water. It should be taken into account that buckwheat porridge enhances motor skills, so it is not recommended during an exacerbation.
Meat and fish dishes are included (in the form of boiled minced meat, steamed cutlets, quenelles and pates). Drinks include compotes and jelly, herbal infusions, chokeberry juice. A special place is given to products that reduce intestinal motility (jelly from blueberries, pears, quince, bird cherry, dogwood, strong black and green tea). You can eat baked apples. During an exacerbation, even boiled vegetables and all dairy products (sour cream, cheeses, cottage cheese) are excluded. For a month after an exacerbation, you need to strictly adhere to the diet, gradually moving to Table 4B and 4B .
Table 4B is assigned upon improvement. The diet remains the same, but the list of permitted foods is expanding. You can try introducing thin noodles, potatoes, boiled grated carrots, zucchini and cauliflower into your diet, but in limited quantities. Sour cream and kefir are carefully introduced, as well as a small amount of sweet berries. The diet is prescribed for 1.5 months until stool is completely normalized, then Diet No. 4B .
Table 4B is recommended during the recovery period. It includes vegetable fats and new products: cabbage and green peas, small quantities of beets, watermelon, raspberries, strawberries. The amount of butter is also increased to 15 g. Dishes are prepared boiled or steamed, and also baked in the oven; food is served mainly in unchopped form.
During the period of stable remission, you can eat boiled vegetables that do not contain a large amount of fiber: broccoli, carrots, cauliflower, zucchini, onions in dishes. Multivitamin supplements can help fill nutritional deficiencies.
This diet is used for several months, and when the condition improves, undiluted boiled vegetables, lump boiled meat and crumbly porridges can be introduced into the diet. Unprocessed dishes should gradually replace pureed ones. A zigzag transition to a new diet is possible: new dishes are consumed 2 days a week, and the usual diet on the remaining days.
Selecting nutrition for this disease is not an easy task and depends a lot on the person’s endurance and observation. At first, to select foods, it is advisable to keep a food diary, in which all the foods consumed during the day and the intestinal reaction to them are recorded. In this way, you can create an individual diet with dishes and products that are well tolerated.
In severe cases of the disease, persistent diarrhea and exhaustion of patients, parenteral nutrition and enteral tube feeding are prescribed: alvesin , aminopeptide , aminosol , cosylate , vamin , casein hydrolysate , nutrichim , isocal . This diet is indicated in the presence of intestinal fistulas.
Product tolerance
Patients are often interested in what diet is recommended for Crohn's disease and is best tolerated by the body? Often the method of cooking affects food tolerance:
- Vegetables should be steamed for as long as possible
- Fruits must be peeled and washed. The peel of the fruit is difficult to digest and has a laxative effect,
- Low-fat yogurt is better tolerated than yogurts made from cream or containing sweet fruits,
- Eggs help provide the body with an adequate supply of protein. Soft boiled eggs are better tolerated than hard-boiled eggs.
Eggs
Tolerance to different foods varies from person to person. Therefore, it is recommended that people with CD keep a diet diary and note which foods caused discomfort and which did not, in order to create a personalized nutrition plan in the long term.
Authorized Products
Diet No. 4B is suitable for constant nutrition of patients. The basis of her diet:
- Soups in a weak broth with cereals (except millet), vegetables and noodles. Of the vegetables, carrots, zucchini, pumpkin, potatoes and cauliflower are most often well tolerated, and if tolerated well, white cabbage and green peas are allowed, but in boiled form.
- Stale wheat bread, you can eat dry biscuits and biscuits.
- Choose lean meat (veal, beef, chicken, turkey) and prepare steam cutlets, meatballs and meat in pieces. Fish is also low-fat boiled, stewed or baked in foil without a crust.
- For side dishes you can try carrots, potatoes, pumpkin, zucchini and cauliflower. Prepare them boiled or steamed in the form of purees and casseroles. Some patients tolerate ripe tomatoes without skin well.
- Dishes from cereals (except pearl barley and millet) are prepared well boiled, first pureed, and then switched to crumbly porridges; boiled vermicelli is allowed. You can use instant water-based porridge for children, which is beneficial in its composition because it is enriched with vitamins and minerals. A specialized mixture for patients with IBD ( Nutrilon Pepti TSC ) is added to the finished porridge.
- Egg dishes (1-2 per day) - steam omelettes and soft-boiled eggs.
- Dairy products are excluded, but if well tolerated, you can drink kefir on a limited basis and add freshly prepared cottage cheese and butter to dishes up to 10 g per meal.
- Jelly and decoctions of blueberries, bird cherry, dogwood, quince, black currant, compotes with pureed fruits, jelly, soufflé of sweet berries, baked and mashed apples and pears are allowed, but it all depends on individual tolerance.
- You can drink herbal teas, rosehip infusion, weak tea, and still water up to 1.5 liters per day. You can add diluted fresh juices.
Table of permitted products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Fruits | ||||
| quince | 0,6 | 0,5 | 9,8 | 40 |
| pears | 0,4 | 0,3 | 10,9 | 42 |
| dogwood | 1,0 | 0,0 | 10,5 | 44 |
| apples | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 47 |
Berries | ||||
| blackberry | 2,0 | 0,0 | 6,4 | 31 |
| blueberry | 1,1 | 0,4 | 7,6 | 44 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| dried pears | 2,3 | 0,6 | 62,6 | 249 |
| dried blueberries | 0,9 | 0,7 | 72,3 | 309 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| buckwheat (kernel) | 12,6 | 3,3 | 62,1 | 313 |
| semolina | 10,3 | 1,0 | 73,3 | 328 |
| oat groats | 12,3 | 6,1 | 59,5 | 342 |
| cereals | 11,9 | 7,2 | 69,3 | 366 |
| white rice | 6,7 | 0,7 | 78,9 | 344 |
Bakery products | ||||
| white bread crackers | 11,2 | 1,4 | 72,2 | 331 |
Confectionery | ||||
| Maria cookies | 8,7 | 8,8 | 70,9 | 400 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| dried bird cherry | 8,4 | 0,0 | 16,8 | 101 |
Dairy | ||||
| acidophilus | 2,8 | 3,2 | 3,8 | 57 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cottage cheese 0.6% (low fat) | 18,0 | 0,6 | 1,8 | 88 |
Meat products | ||||
| boiled beef | 25,8 | 16,8 | 0,0 | 254 |
| boiled veal | 30,7 | 0,9 | 0,0 | 131 |
| rabbit | 21,0 | 8,0 | 0,0 | 156 |
Bird | ||||
| boiled chicken | 25,2 | 7,4 | 0,0 | 170 |
| turkey | 19,2 | 0,7 | 0,0 | 84 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| butter | 0,5 | 82,5 | 0,8 | 748 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| mineral water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| green tea | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| black tea | 20,0 | 5,1 | 6,9 | 152 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Diet features
Diet for Crohn's disease (terminal ileitis) is carried out according to generally accepted rules. However, recommendations may vary for different patients. In clinical practice, doctors most often rely on data from ESPEN/ESPGHN (European Association for Clinical Nutrition).
It should be remembered that there are no uniform recommendations that would be completely suitable for all patients..
The disease progresses in waves, which leads to different approaches to treatment. The exacerbation phase requires adherence to a diet, primarily to alleviate the patient’s condition and prevent relapse. It is believed that during the period of remission there is no need to follow strict restrictions.
The diet for Crohn's disease in the acute stage is based on the following approaches:
- A gentle approach - food should not irritate the intestinal mucosa. Dishes must be prepared by boiling, baking or steaming. In severe cases, they are consumed exclusively in the form of purees, grated porridges and soups;
- The daily intake of fats and carbohydrates is somewhat reduced, and protein foods, on the contrary, are welcomed;
- In Crohn's disease, the diet is followed in fractional meals. It is necessary to eat at the same time, in small portions, at least 5 times a day;
- In addition to eating properly, it is important to drink a sufficient amount of free liquid - 1.5-2 liters per day;
- Dishes should not be excessively cold or hot, maintain the optimum within the limits of human body temperature;
- No more than 10 g of salt per day is allowed;
- They somewhat limit the intake of plant fiber, which can irritate the intestinal mucosa, ultimately stimulating peristalsis.
Despite extensive assurances that Crohn's disease can be cured solely by diet, this cannot be believed. This pathology remains poorly understood to this day; it is prone to inevitable progression, reducing a person’s quality of life. Therefore, nutritional correction should be carried out in parallel with standard therapy regimens.
Fully or partially limited products
- In therapeutic nutrition, cereal products (popcorn, cereal breads), bread with added seeds, bran, rye and whole grain are completely excluded, since they injure the mucous membrane and cause bloating.
- Fresh bread and pastries that cause fermentation in the intestines.
- Radishes, onions, garlic, sorrel, turnips, radishes, spinach, and mushrooms are excluded.
- Sour berries and fruits, since they contain organic acids in large quantities, which enhance intestinal motility (cranberries, gooseberries, lemons, red currants, sour apples, cherries).
- The consumption of strong meat and fish broths is limited.
- Fatty meats, fatty fish and canned food, and any sausages are excluded. During the period of exacerbation, barley, millet, pearl barley, legumes and pasta are excluded.
- Milk and its products, since patients with inflammatory bowel disease often have intolerance. In addition, many authors believe that dairy products can cause Crohn's disease.
- Chocolate, jam, dried fruits, honey, sugar, carbonated drinks, kvass, alcohol (especially sparkling, champagne, beer). Kvass, cocoa and coffee with milk increase intestinal motility, and all drinks with gas cause bloating. It is necessary to limit the consumption of caffeine , which has a laxative effect.
Table of prohibited products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| vegetables legumes | 9,1 | 1,6 | 27,0 | 168 |
| canned vegetables | 1,5 | 0,2 | 5,5 | 30 |
| cabbage | 1,8 | 0,1 | 4,7 | 27 |
| radish | 1,2 | 0,1 | 3,4 | 19 |
| turnip | 1,5 | 0,1 | 6,2 | 30 |
| beet | 1,5 | 0,1 | 8,8 | 40 |
| horseradish | 3,2 | 0,4 | 10,5 | 56 |
| garlic | 6,5 | 0,5 | 29,9 | 143 |
| spinach | 2,9 | 0,3 | 2,0 | 22 |
| sorrel | 1,5 | 0,3 | 2,9 | 19 |
Fruits | ||||
| bananas | 1,5 | 0,2 | 21,8 | 95 |
| melon | 0,6 | 0,3 | 7,4 | 33 |
| kiwi | 1,0 | 0,6 | 10,3 | 48 |
Berries | ||||
| grape | 0,6 | 0,2 | 16,8 | 65 |
Mushrooms | ||||
| mushrooms | 3,5 | 2,0 | 2,5 | 30 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| nuts | 15,0 | 40,0 | 20,0 | 500 |
| dried fruits | 2,3 | 0,6 | 68,2 | 286 |
| sunflower seeds | 20,7 | 52,9 | 3,4 | 578 |
| pumpkin seeds | 24,5 | 45,8 | 4,7 | 556 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| corn grits | 8,3 | 1,2 | 75,0 | 337 |
| pearl barley | 9,3 | 1,1 | 73,7 | 320 |
| Wheat groats | 11,5 | 1,3 | 62,0 | 316 |
| millet cereal | 11,5 | 3,3 | 69,3 | 348 |
| barley grits | 10,4 | 1,3 | 66,3 | 324 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| pasta | 10,4 | 1,1 | 69,7 | 337 |
Confectionery | ||||
| jam | 0,3 | 0,2 | 63,0 | 263 |
| jam | 0,3 | 0,1 | 56,0 | 238 |
| candies | 4,3 | 19,8 | 67,5 | 453 |
| pastry cream | 0,2 | 26,0 | 16,5 | 300 |
| cookie | 7,5 | 11,8 | 74,9 | 417 |
| shortbread dough | 6,5 | 21,6 | 49,9 | 403 |
Ice cream | ||||
| ice cream | 3,7 | 6,9 | 22,1 | 189 |
Cakes | ||||
| cake | 4,4 | 23,4 | 45,2 | 407 |
Chocolate | ||||
| chocolate | 5,4 | 35,3 | 56,5 | 544 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| seasonings | 7,0 | 1,9 | 26,0 | 149 |
| mustard | 5,7 | 6,4 | 22,0 | 162 |
| ketchup | 1,8 | 1,0 | 22,2 | 93 |
| mayonnaise | 2,4 | 67,0 | 3,9 | 627 |
Dairy | ||||
| milk | 3,2 | 3,6 | 4,8 | 64 |
| kefir | 3,4 | 2,0 | 4,7 | 51 |
| sour cream | 2,8 | 20,0 | 3,2 | 206 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cheese | 24,1 | 29,5 | 0,3 | 363 |
Meat products | ||||
| pork | 16,0 | 21,6 | 0,0 | 259 |
| ham | 22,6 | 20,9 | 0,0 | 279 |
Sausages | ||||
| dry-cured sausage | 24,1 | 38,3 | 1,0 | 455 |
| sausages | 10,1 | 31,6 | 1,9 | 332 |
| sausages | 12,3 | 25,3 | 0,0 | 277 |
Bird | ||||
| duck | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
| goose | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| dried fish | 17,5 | 4,6 | 0,0 | 139 |
| smoked fish | 26,8 | 9,9 | 0,0 | 196 |
| canned fish | 17,5 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 88 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| vegetable oil | 0,0 | 99,0 | 0,0 | 899 |
| animal fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| cooking fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
Alcoholic drinks | ||||
| whiskey | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,4 | 235 |
| vodka | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,1 | 235 |
| cognac | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,1 | 239 |
| liquor | 0,3 | 1,1 | 17,2 | 242 |
| beer | 0,3 | 0,0 | 4,6 | 42 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| bread kvass | 0,2 | 0,0 | 5,2 | 27 |
| coffee with milk and sugar | 0,7 | 1,0 | 11,2 | 58 |
| Pepsi | 0,0 | 0,0 | 8,7 | 38 |
| sprite | 0,1 | 0,0 | 7,0 | 29 |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| apricot juice | 0,9 | 0,1 | 9,0 | 38 |
| grape juice | 0,3 | 0,0 | 14,0 | 54 |
| plum juice | 0,8 | 0,0 | 9,6 | 39 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Diet for chronic pancreatitis: nutritional rules during exacerbation
Diet for a pancreatic disease such as pancreatitis is no less important than drug therapy
. It is thanks to constant proper nutrition that patients manage to avoid exacerbations of pathology. A balanced diet also makes it possible to eliminate a number of unpleasant symptoms of the disease (severe pain, nausea and vomiting, fever, etc.).
Factors of occurrence and symptoms of pancreatitis
The pathology is characterized by inflammatory relapses, as a result of which the normal functioning of the pancreas and the release of sufficient amounts of enzymes and hormones are disrupted. The disease is dangerous due to its progression. With the development of pancreatitis, organ tissues are destroyed, which leads to irreversible consequences for the entire body.
Important! Inflammatory phenomena can be a consequence of the acute stage of the disease or an independent manifestation if the patient suffered from jaundice, liver cirrhosis, atherosclerosis, or abuses alcohol or fatty, unhealthy foods.
The main symptoms of pancreatitis include
:
- Heaviness in the stomach (mainly after eating)
- Severe pain on the right side in the navel area
- Belching
- Heartburn
- Bloating
- Acute feeling of hunger
- Sweetish taste in the mouth
- Bad breath
- Nausea
- Frequent, oily and liquid stools
- Swelling of the eyelids
- Dry lips
- Skin redness
The disease is also characterized by the accumulation of toxic substances in the patient’s body and impaired insulin production.
Features of a special diet
A diet for pancreatitis
should contain a large amount of protein, but a minimal amount of fat
. Such components should be eliminated from the diet during exacerbations completely or reduced to a minimum. This will improve the condition of the pancreas and gallbladder.
In some cases, it is allowed to use a small amount of vegetable oil. The need for protein is due to the fact that it allows you to quickly renew injured areas of the pancreas. Patients can also consume carbohydrates, but provided there is no predisposition to diabetes.
If such a predisposition exists, you should avoid foods that contain sugar.
The diet for chronic pancreatitis (during exacerbations) also involves reducing salt intake. The complete exclusion of salty foods for just 2-3 weeks will help reduce the swelling of the gland.
If during severe exacerbations the patient suffers from severe symptoms of the disease, he is prescribed only liquid and pureed food. Any food should be eaten warm.
You need to avoid too hot and cold drinks and food.
Food for the patient should be prepared without seasonings and spices. It is important to carefully monitor the freshness of the products used. If the patient eats porridge, it should be cooked exclusively with water. Vegetable purees, low-fat cottage cheese, tea (without sugar and weak), and pureed soups will be useful.
Gradually, egg whites, lean meat and fish, slightly dried bread, and jelly can be introduced into the diet. Portions should be small, but food should be eaten often enough to prevent the feeling of hunger, during which many patients complain of severe discomfort in the organ area. It is best to switch to six meals a day.
When is a diet prescribed for pancreatitis?
Typically, patients' diets are adjusted immediately after diagnosis.
It is especially important to pay attention to the diet during an exacerbation. With severe symptoms of pancreatitis, experts advise adhering to the principle of “cold, hunger and rest.”
In the first 2-3 days after an attack, you are allowed to drink weak and unsweetened tea, still mineral water and rosehip decoction. When you come out of fasting, you gradually include in your diet dishes that have a good effect on the condition of the inflamed organ.
These include oat decoction and vegetable broths.
During exacerbations, special gentle fractional meals are recommended for at least 6-12 months. During this period, the organ can fully recover. At the same time, the patient himself will have time to get used to healthy nutrition.
A diet for pancreatitis will not become too strict for him and require a high level of self-control. At the same time, it will be the key to recovery.
Thanks to it, you can avoid not only surgical intervention, but also long and often tedious conservative therapy.
Important! Both treatment and diet for pancreatitis of the pancreas in men and women, regardless of symptoms, should be prescribed exclusively by a doctor. Only a gastroenterologist has accurate information about the condition of the pancreas, and also has special professional skills and knowledge.
Products that are recommended and not recommended for illness
For pancreatitis, you should eat foods such as
:
- Lean meat: lean pork, veal, chicken, rabbit, turkey
- Lean fish: pike, flounder, pollock and cod
- Cereals: oatmeal, semolina and rice
- Pasta made from durum wheat
- Fermented milk products
- Vegetables: potatoes, zucchini, beets, carrots
Milk is allowed to be consumed only in porridges, milk soups and jelly. If your condition improves, you can supplement your diet with mild and low-fat varieties of cheese. When preparing steam omelettes, you can use eggs. As for fruits, it is better to give preference to non-acidic apples. They can be baked and eaten as a puree.
Strictly prohibited
:
- Onion
- Sorrel and spinach
- Radish, radish, horseradish and rhubarb
- bell pepper
- Seasonings and hot spices
- Alcohol products
- Coffee and cocoa
- Carbonated drinks
During a diet for chronic pancreatitis, you should try to exclude goose and duck meat, lamb and lard. You cannot eat fried meat, kebabs, sausage products and deli meats.
All types of canned fish and meat, rich meat broths, and jellied meat are also prohibited for patients.
Fatty cottage cheese and sour sour cream, sharp and smoked cheeses, legumes, tomatoes, cakes and pastries, ice cream and chocolates should be removed from the diet.
It is not recommended to use margarine, as well as beef and pork fat when preparing dishes. At least during exacerbations, you should avoid oils in any form.
Advantages of treatment at MEDSI
- Experienced gastroenterologists.
Our doctors have the necessary knowledge and skills for the comprehensive management of patients with chronic pancreatitis (including exacerbations). Gastroenterologists can choose a suitable diet that takes into account all the features of the patient’s lifestyle and his current condition - Modern diagnostic methods
. Laboratory and instrumental techniques are used for examinations. We have the necessary expert-level equipment, which allows us to quickly make a diagnosis and prescribe adequate therapy in any situation (including if complications arise) - Modern methods of treatment
. We use both proven methods and our own proprietary developments, which allow us to treat chronic pancreatitis during exacerbation quickly and competently, with minimal discomfort for the patient, using effective and safe medications. Particular attention is paid to proper nutrition - Involvement of other specialists in working with the patient
. If necessary, patients can be observed not only by gastroenterologists, but also by nutritionists, endocrinologists, etc.
If you want our gastroenterologist to carry out the necessary treatment and select the optimal diet for you, call +.
Menu (Power Mode)
It must be remembered that the diet must be followed for a long time and new foods must be introduced carefully. With six meals a day, the menu should be varied and include alternating dishes from chicken, fish, beef and, with normal tolerance, cottage cheese, as well as various cereal dishes. You can include eggs daily. When the process subsides, add pureed vegetables with low fiber content (pumpkin, zucchini, potatoes).
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
Sample menu for the week
In the acute phase of the disease, a two-day therapeutic fast is first suggested, which is aimed at calming the intestines.
These days you need to drink at least two liters of liquid, which should include currant and blueberry juice diluted with water. Multivitamin complexes and lactose-free protein drinks are taken.
After a couple of days, when the pain subsides, the second stage of nutrition begins, which includes porridge with water, pureed soups, and slimy broths. Meatballs or meatballs made from lean meat and fish are also allowed. They can be steamed.
New foods can be introduced every three days. Let's look at a sample menu for the week.
Monday:
- Breakfast: pureed buckwheat porridge.
- Second breakfast: apples, baked without peel.
- Lunch: soup cooked in a second meat broth.
Tuesday:
- Breakfast: pureed rice porridge.
- Second breakfast: grated carrot salad.
- Lunch: soup based on fish broth.
- Afternoon snack: cocoa on water.
- Dinner: stewed vegetables.
Wednesday:
- Breakfast: semolina porridge on water.
- Second breakfast: a couple of pieces of low-fat cheese.
- Lunch: soup made with vegetable broth.
- Afternoon snack: white bread crackers, kefir.
- Dinner: boiled lamb and buckwheat.
Thursday:
- Breakfast: pureed oatmeal porridge;
- Second breakfast: rice pudding.
- Lunch: mushroom soup.
- Afternoon snack: milk.
- Dinner: seafood without adding spices.
Friday:
- Breakfast: pureed oatmeal.
- Afternoon snack: bread and butter.
- Lunch: pureed cereal soup.
- Afternoon snack: mashed cottage cheese with added butter.
- Dinner: steamed fish meatballs.
Saturday:
- Breakfast: steamed omelette.
- Afternoon snack: pear, which needs to be peeled.
- Lunch: soup with chicken broth.
- Afternoon snack: weak coffee with milk.
- Dinner: boiled chicken.
Sunday:
- Breakfast: pureed maize porridge.
- Afternoon snack: corn flakes.
- Lunch: vermicelli soup.
- Afternoon snack: fruit and tea.
- Dinner: boiled meatballs with rice.
During the day you are allowed to drink weak tea, rosehip decoction, acidophilus milk, and kefir. It is also important to drink enough plain water.
Getting used to a new diet is quite difficult, so in order not to think every time what to cook, nutritionists recommend creating a rough menu for the whole week. Thus, for breakfast you can serve:
- cornflakes;
- baked apple or other permitted fruit;
- buttered toast;
- puffed rice;
- nutrient mixtures of liquid consistency.
Lunch for Crohn's disease can consist of vegetarian soup with parsley, a boiled piece of lean meat, baked river fish, a slice of white bread and compote. For dietary meals for chronic gastrointestinal diseases, vegetables are steamed, rice and pasta are boiled, and nutritional mixtures, fruits, jelly or pudding are also served.
Diet recipes for Crohn's disease
When starting to prepare different dishes, you need to know some rules and technological techniques. For dietary nutrition, boiled meat is passed through a meat grinder, and vegetables are pureed. Pureed soups are recommended, in which cereals are boiled until soft, pureed and boiled again. Porridges take longer to cook than usual, and to reduce the cooking time, you can use ground cereal or cereal flour and cereal resins in a coffee grinder.
Vegetables and chopped dishes are simmered in a saucepan under a lid, with 1/3 of the liquid added. Juicy fruits are simmered without liquid (in their own juice). Steam cooking is used with the lid closed, which reduces the loss of nutrients. You can use a wire rack or sieve for this.
To reduce the content of extractives and protein, digestion is recommended. When cooking a large piece of meat, extractive substances and proteins are preserved, and the broth turns out to be unsaturated. When baking, the food is cooked until half cooked and then baked until a light crust forms. When baking, you can add sauce, eggs, and sour cream to meat and vegetable dishes.
First meal
Clear soup with meatballs
The soup is prepared in water. Place finely chopped potatoes and carrots into boiling water. Bring them to half-cookedness, add salt and add beef (minced chicken) meatballs, add bay leaf and bring to readiness.
Potato, cauliflower and carrot soup
Boil all the vegetables and onions, drain the broth, and blend the vegetables in a blender, leaving a few whole cabbage inflorescences. Dilute the vegetable puree with a decoction of vegetables, add salt and boil. Dip whole cabbage inflorescences into the finished soup, add butter and croutons.
Second courses
Liver soufflé
Remove the films from the liver and grind it into a paste in a blender, add chopped onion and a piece of soft butter. Beat the yolks and whites separately (until strong foam). Add one at a time to the liver mass, lightly salt. Place into molds, or into one large mold. Bake for 30 minutes at 200 degrees. Garnish: steamed grated carrots with unrefined sunflower oil.
Minced chicken casserole with zucchini
You can use ground chicken or turkey. Peel the zucchini, remove the seeds, peel the onion and pass everything through a meat grinder. Mix with prepared minced meat. Add eggs, salt. Place the mixture into a baking dish. Bake for 40 minutes at 180 degrees. If desired, you can supplement the casserole with boiled carrots chopped in a blender and chopped herbs.
Snacks
Eggplant (zucchini) caviar
Bake the eggplants in the oven, pass through a meat grinder, first removing the skin. Add lightly sautéed onions and tomatoes (tomato paste). Beat in a blender, add salt and simmer a little.
What kind of illness is this?
Crohn's disease is a chronic inflammation of the walls of the gastrointestinal tract. Most often, the lesion is localized in the ileum, but in some cases it spreads to other parts.
As a result of the disease, the intestinal walls are damaged, ulcers, scars and swelling form on them. Of course, digestive disorders are also observed. The disease goes hand in hand with an ulcer and can develop in the body in parallel with gastritis, pancreatitis and other inflammatory processes. It is believed that this is a hereditary disease, which is very difficult to get rid of.
Reviews and results
Looking through the reviews, we can conclude that selecting food products for this disease is not an easy task and depends a lot on the person’s endurance and observation. At first, to select foods, many kept a food diary, in which they recorded all the foods consumed during the day and the intestinal reaction to them. Thus, an individual diet was compiled with dishes and products that were well tolerated.
Of course, therapeutic nutrition has a positive effect on the condition of the gastrointestinal tract. By eliminating forbidden foods from the diet, patients achieved a reduction in pain and frequency of bowel movements, bloating and rumbling in the intestines. Many always strictly follow the diet and only slightly expand it if their health allows.
- “... I have been sick for a long time, and I came to the conclusion that it is necessary to exclude those foods that can cause deterioration or exacerbation. For me it is: whole milk (but I can tolerate goat milk well), ice cream, fresh pineapple, chocolate, Snickers and other sweets. Otherwise, during the period of remission I hardly follow a diet. The only thing that remains constant is oatmeal with water in the morning. I try to eat natural products: I bake my own bread, I make kefir and cottage cheese from goat’s milk myself, I eat homemade butter, and vegetables from my garden. Proper nutrition is very important for this diagnosis, but restrictions must be selected individually”;
- “... I try to exclude inherently dangerous products. I think everyone has foods that make them worse, but it's individual. I don't eat anything fried. My usual foods are rice, potatoes, buckwheat, lean meat (usually beef) and liver (I ate a lot when there was not enough iron), I rarely eat wheat and corn porridge. Low-fat sea fish is easier to tolerate, but salmon is difficult to digest. I make an omelette in the microwave. Once a week I allow low-fat cottage cheese with sour cream - I also tolerate it well. Sometimes there are deviations in the form of boiled sausage and sausages, but rarely. I only drink tea without sugar. This power supply scheme is quite satisfactory”;
- “... I made up my own diet, going through exacerbations and excluding intolerable foods. Of course, I don’t eat fried, smoked, cold or spicy. Only boiled meat and stewed fish. I buy veal and chicken. The porridge is mostly rice and buckwheat, for breakfast it’s oatmeal, I boil everything for a long time and add a piece of butter. There was a long “torment” with fruits and vegetables. It was not possible to introduce either an apple or a banana, in any form - immediately gas formation and diarrhea the next morning. With potatoes, bloating is also guaranteed, so I refused it altogether. Boiled carrots pass fine and just a little cabbage. I also had to exclude coffee and chocolate, which caused an exacerbation with bleeding. From dairy products I allow cottage cheese (I make it myself) and butter. I had to give up sweets, removed sugar altogether and gas formation became significantly less. I try to eat separately and drink filtered water.”
What can you eat during CD remission?
During remission, CD patients must be careful about the amount of nutrients and fluids they have lost during the ongoing acute phase of diarrhea. To replenish lost nutrients, it is recommended to consume foods rich in fiber. These include:
- Finely ground whole grains
- Dried and fresh fruits and vegetables,
- Rice,
- Oats,
- Potato.
Wheat, milk, corn and yeast are less tolerated by patients with CD. Many people with CD suffer from lactose or fructose intolerance. It is necessary to undergo a special medical examination to exclude such a problem. If you are lactose intolerant, you will have to remove dairy and fermented milk products from your daily menu.