Vaginal tablets are prescribed for adults. The Trichopolum tablet is removed from the packaging by cutting the film along the contour of the tablet, moistened with boiled cooled water and inserted deep into the vagina. Trichopolum therapy lasts no more than 10 days and is repeated no more than 2-3 times a year. The dose and duration of use depends on the disease:
- for trichomonas vaginitis, one vaginal tablet per day is used for 7-10 days in combination with taking trichopolum tablets orally
for nonspecific vaginitis and bacterial vaginosis, one vaginal tablet per day for 7 days, if necessary in combination with oral trichopolum tablets
Use of Trichopolum during pregnancy and breastfeeding
Trichopolum is contraindicated in the first trimester of pregnancy; in the second and third trimesters it should be taken with caution only if the benefit to the pregnant woman outweighs the risk to the unborn child, given that metronidazole crosses the placenta. FDA category of effect on the fetus is B.
Trichopolum (metronidazole) is excreted into breast milk, creating concentrations similar to those in blood plasma. May impart a bitter taste to breast milk. To exclude the effect of Trichopolum on the child, breastfeeding while taking Trichopolum and for another 2 days after the end is not recommended.
general information
According to the pharmacological index, trichopolum belongs to the groups “Other synthetic antibacterial agents” and “Medicines for the correction of disorders in alcoholism, toxic and drug addiction”, according to the ATC - to the subgroup “J01XD01 metronidazole” of the group “Imidazole derivatives”, as well as to the subgroup “A01AB17 metronidazole "Group "A01AB Antimicrobials for local treatment of diseases of the oral cavity."
Trichopolum has contraindications, side effects and application features; consultation with a specialist is necessary.
The manufacturer of trichopolum is Polpharma, Poland (JSC Akrikhin).
On the website gastroscan.ru in the literature catalog there is a section “Antibiotics used in the treatment of gastrointestinal diseases”, containing articles on the use of antimicrobial agents in the treatment of diseases of the digestive tract.
Instructions for medical use of trichopolum
Instructions for medical use of various dosage forms of Trichopolum from the manufacturer (pdf):
- "Trichopol", tablets containing 250 mg of metronidazole
- "Trichopol", solution for infusion containing 5 mg of metronidazole in 1 ml
- "Trichopol", vaginal tablets containing 500 mg of metronidazole
Other medicines containing the active ingredient metronidazole
Bacimex, Deflamon, Klion, Metrovagin, Metrogyl, Metroxan, Metrolacare, Metron, Metronidazole, Metronidazole IV Brown, Metronidazole Nycomed, Metronidazole-AKOS, Metronidazole-UBF, Metronidazole tablets 0.25 g, Metronidal, Metroseptol, Orvagil, Rosamet, Rozeks, Siptrogil, Tricho-PIN, Trichobrol, Trichosept, Flagyl. Efloran.
≫ More information on the topic: https://www.gastroscan.ru/handbook/145/4432
How to use
One Trichopolum tablet contains 250 mg of metronidazole (active substance), potato starch, magnesium stearate, gelatin, and starch syrup. How to take Trichopolum for gastritis? The most common regimens include taking the drug 250 mg four times a day or 500 mg twice a day during and after meals. The maximum duration of treatment is fourteen days. Patients diagnosed with liver or kidney failure require an individually selected treatment regimen. High concentrations of the active substance in the liver can lead to coma. In elderly patients, the dose of metronidazole should be reduced. During treatment with the drug, you should not drink alcohol. After taking Trichopolum, candidiasis of the digestive tract sometimes develops. In this case, the doctor prescribes antifungal agents. The medicine causes weakness, dizziness, psychomotor reactions decrease, confusion occurs, and convulsions appear.
Causes
Doctors often prescribe Trichopolum for gastritis. The product is proven, inexpensive and actively used in the fight against the disease. Doctors list the main causes of acute gastritis as:
- Eating poor quality food, eating foods contaminated with pathogenic bacteria.
- Infections that enter the stomach with Helicobacter pylori, which causes increased acidity.
- Ingestion of toxic substances into the stomach.
- Drinking strong alcohol.
- Taking nonsteroidal medications.
- Dysbacteriosis.
- Impaired metabolism.
The causes of chronic gastritis are:
- Infections.
- Infection of the body with parasites.
- Unbalanced diet.
- Eating junk food, too spicy, fatty, hot.
- Alcoholism.
- Bad habits (smoking).
- Stress, neurosis, depression.
- Helminthic infestations.
- Uncontrolled use of medications.
- Stomach operations.
- Endocrine disorders.
- Heredity.
- Chronic diseases.
Use of the drug Trichopolum for the treatment of gastritis of the stomach
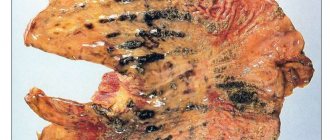
Gastritis or inflammation of the mucous membrane lining the inside of the stomach is one of the most common pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract. As studies have shown, one of the main causes of the development of the disease is a bacterium with the beautiful name Helicobacter pylori.
For this reason, antibiotics are the mainstay of treatment for the disease. Let's figure out in what cases Trichopolum is prescribed for gastritis and whether it is advisable to use this drug.
Description of the drug
Trichopolum is a popular drug with antiprotozoal and antibacterial activity. The active substance is metronidazole. Used in the treatment of certain parasitic and infectious diseases caused by microflora that are sensitive to it.
The use of Trichopolum in the treatment of gastritis makes sense provided that the bacterial nature of the disease is confirmed. If the examination does not reveal the presence of bacteria, then the use of antibiotics is not advisable.
Helicobacter pylori is highly resistant to antibacterial drugs, so two antibiotics and additional agents are prescribed simultaneously to treat the infection. Trichopolum is prescribed as one of the antibiotics as part of complex therapy. Additionally, the following drugs are used:
- Amoxicillin. A drug from the penicillin series.
- Clarithromycin. Belongs to the macrolide series.
- Erythromycin. Also a drug from the macrolide class.
- Tetracycline.
Operating principle
The active substance of the drug penetrates the cells of bacteria and protozoa, blocking the production of DNA in them, this leads to the death of microorganisms. At the same time, the substance does not have a negative effect on human tissue cells. The severity of the antimicrobial effect depends on the concentration of the active substance in the blood.
When taken orally, the drug is almost completely absorbed into the blood through the intestines. The maximum concentration develops within 1-2 hours after administration. The active substance is able to penetrate the placental and blood-brain barrier.
The active component is processed in the liver, most (up to 80%) is excreted in the urine, the rest through the intestines. With long-term use, it can accumulate in tissues.
Treatment regimen for gastritis
Treatment of gastritis with Trichopolum is advisable only in combination with an additional antibiotic and drugs to normalize the composition of gastric juice. Using Trichopolum for monotherapy does not make sense.
Advice! If metronidazole is used incorrectly, Helicobacter pylori bacteria become resistant to the antibiotic. Therefore, if therapy is ineffective, it must be replaced.
Peculiarities
Is it possible to take Trichopolum for gastritis? The peculiarities of treating the disease with this medicine are that it is antibacterial and antiprotozoal. The drug is prescribed only in combination to eradicate the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. “Trichopol” is not used without drugs that reduce stomach acidity. It should not be prescribed for the treatment of stomach and duodenal ulcers. The tablets are quickly absorbed in the intestines and reach their highest concentration within three hours after administration and are evenly distributed in the body. Completely excreted by the kidneys and liver after eight hours.
While taking Trichopolum, the patient’s urine turns dark brown due to the presence of dyes in the composition. If the drug is used simultaneously with lithium preparations, it is necessary to monitor the level of the substance in the blood. Its excess leads to intoxication of the body. Trichopolum can enhance the side effects of some medications. It is dangerous to take it simultaneously with the active substances astemizole, terfenadine, disulfiram. Side effects include nausea, vomiting, ataxia, and convulsions.
Contraindications
Many patients are interested in: “Trichopol” treats gastritis or not? The drug is used if the cause of the disease is the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, various infections, and the treatment regimen prescribed by the doctor does not help. You cannot take Trichopolum if the patient has blood diseases, impaired coordination of movements, is diagnosed with liver failure, or central nervous system diseases. Individual intolerance to the active substance is an absolute contraindication for use. If gastritis appears during pregnancy, the disease must be treated with Trichopolum very carefully. In the first trimester, its use is prohibited. In the second, you can take the medicine if the benefits to the woman outweigh the risks to the fetus. The medicine quickly penetrates the placenta and is excreted into milk, so it should not be used during lactation.
Reviews
Is it worth taking Trichopolum for gastritis? Reviews from patients who have undergone therapy with various drugs indicate that the medicine really helps with gastritis caused by the bacterium Helicobacter pylori and various infections. Tablets eliminate symptoms and attack the cause of the problem. You should take the medicine only as prescribed by your doctor. The advantages of Trichopolum include low price and versatility. It successfully treats sexually transmitted diseases. Disadvantages include the presence of contraindications and side effects.
Unfortunately, various microorganisms await us at every step. They are invisible, but they may well harm us. It's just the opposite. Fortunately, there are medications that suppress the activity of pathogenic microorganisms. Below we will talk about one of these drugs. In what cases are Trichopolum tablets used? How to take them?
Symptoms
Is it possible to take Trichopolum for gastritis? This is one of the drugs that is prescribed by your doctor if you have certain symptoms. You should not self-medicate if you discover the presence of a number of typical symptoms characteristic of gastritis:
- Constant nausea.
- Vomit.
- Lack of appetite.
- Pain in the upper abdomen that is sharp or burning. It goes away or gets worse when eating.
- Bloating.
- Feeling of fullness in the stomach after eating.
- Unpleasant taste in the mouth.
- General weakness, irritability.
- There is a yellow or white coating on the tongue.
- Dramatic weight loss.
- Fever.
- Heart problems, low blood pressure.
- Drowsiness or insomnia.
If gastritis is treated incorrectly or if you hesitate to see a doctor, it can cause serious complications. Among them are internal bleeding, sepsis, anemia, pancreatitis, dehydration, anorexia, ulcers, and stomach cancer. That is why many doctors recommend Trichopolum and other drugs that need to be taken in combination for gastritis.
Trichopolum for gastritis
"Trichopol" is used for gastritis quite rarely, which is due to the resistance of the Russian body to metronidazole. Just like other medications, the drug has a number of specific contraindications and side effects. In any case, you must visit a doctor before using the drug.
It is recommended by the Maastricht Treaty as one of the antibiotics for the eradication of Helicobacter pylori. But in Russia, due to the popularity of self-medication, Metronidazole is often used very widely and for other purposes, so resistance to the drug is twice as high as in Europe. This fact explains why Trichopolum for gastritis in our country is prescribed to patients less and less often. Russian doctors, when drawing up therapeutic regimens, give their preference to another drug - Nifuratel. Treatment of gastritis with Trichopolum is carried out only when the first line does not work and there is a need to correct it by making a replacement. This drug is taken for gastritis three times a day, 500 mg. The course lasts two weeks.
"Trichopol" is used for gastritis quite rarely, which is due to the resistance of the Russian body to metronidazole
Active substances, effect of the drug
The active ingredient of the drug is metronidazole, which has an antimicrobial and antiprotozoal effect. The uniqueness of this component lies in the fact that it penetrates into the very heart of bacteria, namely the DNA, influencing it in such a way that it begins to break down, which leads to the death of the microorganism.
The instructions for use indicate that the components of this product are active against a wide variety of bacteria: clostridia, lamblia, amoeba, gardnerelia, ureaplasma, trichomonas, chlamydia, gonococci, some types of cocci and bacilli, as well as Helicobacter pylori (but in this In this case, Trichopolum tablets must be combined with another drug – Amoxicillin).
So this remedy is very, very effective, although its price is not so high. But it is worth noting that the main active component of the drug is not able to have any effect on fungi and various viruses, so it is not prescribed for viral and fungal infections.
Instructions
Tradename
International nonproprietary name
Dosage form
Tablets 250 mg
Compound
One tablet contains
active substance – metronidazole 250 mg,
excipients: potato starch, gelatin, glucose solution, magnesium stearate.
Description
The tablets are white with a yellowish tint, turn yellow when exposed to light, round, flat on both sides and scored on one side.
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Antimicrobials for systemic use. Imidazole derivatives. Metronidazole.
ATX code J01XD01.
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacokinetics
Metronidazole is easily absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract (min. 80%). Only small amounts are absorbed after intravaginal administration.
After taking the drug at a dose of 250 mg, 500 mg or 2 g by healthy volunteers, the maximum concentration in blood plasma in the period of 1-3 hours was, respectively, 4.6 - 6.5 mcg/ml, 11.5 - 13 mcg/ml and 30 - 45
µg/ml. The presence of food reduces the rate of absorption and reduces the maximum serum concentration of metronidazole.
Approximately 20% of metronidazole is bound to blood proteins.
Metronidazole is widely distributed in tissues and body fluids, including bile, bones, saliva, peritoneal fluid, vaginal secretions, seminal fluid, cerebrospinal fluid, brain and liver tissue. It also penetrates the placental barrier and is excreted in breast milk in concentrations comparable to the level of the drug in the blood plasma.
Approximately 30-60% of metronidazole taken orally is biotransformed in the liver by hydroxylation, oxidation and conjugation with glucuronic acid.
The main metabolite 2-hydroxymetanidazole also has antibacterial and antiprotozoal activity.
The biological half-life of metronidazole (T½) in adults with normal liver and kidney function is 6-8 hours. In patients with impaired liver function, the half-life of metronidazole may be prolonged.
Metronidazole and its metabolites are excreted mainly through the kidneys, 60-80%. Only 6-15% of metronidazole is excreted in the feces. Renal clearance is 10-10.2 ml/min. Urine may be dark or red-brown in color due to the presence of water-soluble dyes, which are products of the biotransformation of the drug.
Few studies indicate that renal excretion of metronidazole is reduced in elderly patients.
Metronidazole can be removed from the body by hemodialysis, while peritoneal dialysis is ineffective.
Pharmacodynamics
Trichopolum is a derivative of 5-nitroimidazole, which has antiprotozoal and antibacterial effects.
Trichopolum easily penetrates protozoa and bacteria. The oxidoreduction potential of Trichopolum is less than that of ferredoxin, an electron transport protein. This protein is present in anaerobic and aerobic bacteria. The potential difference leads to a reduction of the Trichopolum nitro group. Reduced form
Trichopolum inhibits DNA synthesis of microorganisms, which causes their death.
Trichopolum is active against Trichomonas vaginalis, Giardia lamblia, Entamoeba histolytica and Balantidium coli.
It also has a strong bactericidal effect against anaerobic bacteria; gram-negative rods: Bacteroides species including the Bacteroides fragilis group (B. fragilis, B. distasonis, B. ovatus, B. thetaiotaomicron, B. vulgatus), Fusobacterium species; gram-positive rods: Eubacterium, Clostridium; gram-positive cocci: Peptococcus species, Peptostreptococcus species.
Trichopolum does not have a bactericidal effect against most aerobic and partially anaerobic bacteria, fungi and viruses.
Indications for use
infections caused by anaerobic bacteria of the genus Bacteroides, Fusobacterium, Clostridium, Eubacterium, anaerobic cocci and Gardnerella vaginalis, as well as protozoa Trichomonas vaginalis, Entamoeba histolytica, Giardia lamblia and Balantidium (trichomonas infection, bacterial vaginitis, amebiasis, giardiasis, acute ulcerative gingivitis, acute periodontitis )
surgical anaerobic infections (sepsis, bacteremia, peritonitis, brain abscess, pneumonia, osteomyelitis, postpartum sepsis, abscess in the pelvic area, endometritis, inflammation of surgical wounds after surgery, trophic ulcers of the lower extremities and bedsores)
Helicobacter pylori – associated gastric diseases (as part of combination therapy, Trichopolum is used to eradicate Helicobacter pylori)
prevention of postoperative infections caused by anaerobic bacteria (mainly colon operations, gynecological operations)
Drug treatment of gastric and duodenal ulcers
The disease occurs as a result of a violation of gastric secretion and a failure in the protective mechanism. That is, it is provoked by a combination of factors:
- excessive secretion of enzymes, pancreatic juice and hydrochloric acid;
- insufficient formation of mucus on the walls of the organ, which should protect the mucous membrane from “self-digestion”;
- poor blood supply to the walls of the stomach, resulting in slow renewal or regeneration of damaged gastric mucosa;
- impaired motility of the digestive tract - food in the stomach very quickly enters the duodenum, which puts a strong burden on the digestion processes in the initial part of the small intestine;
- reflux of bile and pancreatic juice from the intestines into the stomach.
Causes of disorders leading to the development of the disease
- hereditary predisposition - in such patients an increased number of cells responsible for the synthesis of hydrochloric acid was found; this leads to its production in large quantities when exposed to provoking factors;
- the microorganism Helicobacter pylori, which infects goblet cells responsible for mucus secretion and causes inflammation;
- long-term use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and glucocorticoids (both simultaneously and separately), which leads to a decrease in mucus production; as a result, the walls of the organ become vulnerable to the effects of enzymes, hydrochloric acid and pancreatic juice;
- smoking and alcohol - nicotine stimulates the formation of hydrochloric acid and impairs blood circulation, and alcohol destroys the gastric mucosa;
- frequent stress – this increases motor skills and increases the production of hydrochloric acid;
- Among the rare causes are diseases in which the development of an ulcerative process in the gastrointestinal tract is possible: hyperthyroidism, Zollinger-Elisson syndrome.
Symptoms of the disease
- nausea, belching and sour vomiting, heartburn;
- pain in the pancreas, in the right hypochondrium, which begins after eating and goes away with the use of acid-reducing drugs;
- “hunger” pain that appears on an empty stomach; they go away as soon as a person eats.
Treatment of stomach and duodenal ulcers
Currently, an effective scheme has been developed to combat peptic ulcer disease with medications, which solves several goals at once:
- eradication (destruction) of the microorganism Helicobacter pylori;
- rapid elimination of symptoms, especially pain;
- acceleration of ulcer healing;
- prevention of exacerbations and complications.
Several groups of drugs are used in the treatment of the disease.
- Antibiotics (Amoxicillin, Clatrimycin). The primary task is the destruction of microorganisms. After a course of treatment with drugs, the regeneration of the mucous membrane is significantly accelerated and the secretion of hydrochloric acid is reduced. Without antibiotic therapy, the risk of re-exacerbation of the disease increases sharply.
- Proton pump inhibitors (Omeprazole and its analogues). Antisecretory drugs that block the formation of hydrochloric acid enhance the effect of antibiotics.
- Enveloping preparations containing bismuth (Ventrisol, Sucralfate, De-Nol). For 6 hours, protect the surface of the gastric mucosa and ulcers with a film. Take the medication on an empty stomach half an hour before meals. In addition to mechanical protection, the drugs increase mucus production and also prevent the absorption of various substances.
- H2-histamine receptor blockers (Ranitidine, Roxatadine, Famotidine, Cimetidine). They belong to the group of antisecretory agents that reduce the formation of pepsin and hydrochloric acid, and also improve cell regeneration and increase blood supply to the walls of the organ.
- M-anticholinergic agents (Scopolamine hydrobromide, Atropine sulfate). Drugs that suppress intestinal motility and reduce the secretion of glands by blocking the transmission of impulses by the vagus nerve. Thus, they reduce pain and eliminate dyspepsia. Due to pronounced side effects on the visual organs, they are rarely used.
- Antacids (Phosphalugel, Gastal, Almagel). By neutralizing hydrochloric acid and pepsin, they reduce the acid level of gastric juice and stimulate the production of mucin, which serves as protection for the mucous membrane. Consume an hour after meals.
- Adsorbents. Preparations that have the ability to absorb and remove toxins, gases, allergens, heavy metal salts and microorganisms from the body.
Fighting the microorganism Helicobacter pylori
First-line therapy is based on a combination of three drugs that are prescribed during an exacerbation of the disease:
- proton pump inhibitors (Rabeprozole, Omeprazole, Panteprozole or Lanzoprozole);
- medicine Bismuth tripotassium dicitrate;
- antibiotics (Clarithromycin 500 mg and Amoxicillin 1000 mg).
The duration of the treatment course is 1 – 2 weeks. If the disease proceeds without complications, then therapy aimed at reducing secretion can be stopped immediately after eradication. If there are complications or concomitant severe pathologies, it is necessary to continue treatment with antibiotics together with one of the proton pump inhibitor drugs or H2-histamine receptor blockers until the ulcerative process heals for approximately 2 to 5 weeks.
If the first-line treatment regimen is ineffective, proceed to the next treatment option - second-line (quadruple therapy) using four drugs:
- proton pump inhibitors;
- Bismuth tripotassium dicitrate;
- Tetracycline;
- Metronidazole.
If Helicobacter pylori is not detected during diagnosis, doctors prescribe basic treatment using proton pump inhibitors. To relieve pain attacks and dyspeptic disorders, antacids and M-anticholinergic blockers are used as additional therapy. This course lasts 3 to 8 weeks until the symptoms disappear completely and the ulcer scars.
With drug therapy for ulcers, hospitalization in a hospital is not necessary. Outpatient treatment or day hospital treatment is indicated for exacerbation of uncomplicated forms of the disease. Immediate hospitalization is only necessary in a few cases:
- with frequent relapses of peptic ulcer;
- with severe concomitant pathologies;
- in patients with a weakened body;
- in case of complications of the disease - perforation or perforation of an ulcer, gastric or intestinal bleeding;
- with newly diagnosed ulcers.
Effect
Trichopolum tablets have a fairly quick effect. So, once they enter the digestive tract, they almost immediately begin to be absorbed into the blood. At the same time, approximately 80-85% of all substances are available (the rest can be excreted without reaching the goal), which is not so little.
The maximum content of the substances of this drug in the blood is observed approximately 1-3 hours after administration. But it is worth noting that eating food can reduce the rate of absorption.
The active substance can penetrate almost all tissues of the body and many organs. Thus, metronidazole enters the lungs, skin, liver, cerebrospinal fluid, kidneys, brain, saliva, bile, seminal fluid in men and vaginal discharge in women. And this property explains such a wide range of applications and effects.
Substances are excreted by the kidneys (about 70-80%) and through the intestines along with excreted feces (about 7-15%). And some of the components decompose in the liver.
Indications
The price of the drug is not so high, but, nevertheless, Trichopolum tablets are effective for a wide variety of diseases, as the instructions for use prove this. Here are some of these diseases:
- stomach ulcer and gastritis (prescribed along with other medications);
- peritonitis (inflammation resulting from perforation of the abdominal organs with subsequent entry of the contents of the affected organ into the cavity);
various sexually transmitted diseases, such as gonorrhea, gardnerellosis, trichomoniasis, ureaplasmosis and others;
- inflammatory processes of the female genital organs associated with the activity of microorganisms (vaginitis, endometritis);
- parasitic infections (giardiasis);
- meningitis;
- abscesses;
- osteomyelitis;
- cystitis caused by bacterial infection;
- sepsis;
Description of the drug
Doctors sometimes prescribe Trichopolum for gastritis if the disease is bacterial. The drug is not modern, but is still used. "Trichopol" is a synthetic antibacterial agent that is included in the complex therapy of gastritis. It is appropriate to use together with tablets that reduce stomach acidity. If gastritis is not caused by bacteria, these tablets are not prescribed. The active substance in the composition is metronidazole. It acts as an antibiotic. Nifuratel has become an analogue of the drug in modern medicine. The medicine "Trichopol" not only destroys bacteria, but also relieves inflammation.
The drug is considered universal, as it is used for bacterial infections, vaginitis, urethritis, peritonitis, abdominal abscess, after surgery, to prevent complications. "Trichopol" destroys the cellular structure of Giardia, dangerous bacteria that affect the human liver and intestines. The product inhibits the activity of anaerobic bacteria, trichomoniasis pathogens and other harmful microorganisms. "Trichopol" is not recommended for use by children under 18 years of age. If it is prescribed, the course of treatment is carried out under the supervision of a doctor.
Contraindications
Instructions for use should be studied, because there are some contraindications. Here are the cases in which Trichopolum tablets cannot be used:
- problems in the liver (in this case, the substances will not be eliminated completely, which can lead to intoxication, but it may be advisable to reduce doses);
- renal failure (in this situation, the doctor may also prescribe reduced doses);
- leukopenia (and in the anamnesis too, that is, already suffered once);
- children's age (namely up to 3 years);
- sensitivity to metronidazole, intolerance to this substance;
- period of breastfeeding (the active substances of the drug penetrate into the mammary glands and are excreted along with milk);
- pregnancy, especially the 1st trimester (metronidazole enters the amniotic fluid, the placenta and then to the fetus);
- taking the drug in the second and third trimesters is also undesirable (unless the effectiveness exceeds the risks to the fetus);
- some diseases of the nervous system.