What is heartburn
Heartburn is a feeling of irritation and discomfort behind the breastbone that spreads upward from the epigastric region through the esophagus. The symptom occurs periodically, more often after eating, when the food is nourishing and plentiful. Sometimes an attack occurs during physical activity, when the torso is tilted, or when the person is lying down. To eliminate heartburn, you need to drink water and take antacids, i.e. substances that neutralize the effects of acids. But attacks sometimes recur frequently, causing trouble for a person and disrupting the rhythm of life.
If a person experiences heartburn more than 3 times a week, it causes discomfort. There is a dependence of the appearance of heartburn on the duration of clearance of the esophagus, various damage to the mucous membrane of this organ and other reasons. Patients diagnosed with esophagitis, an inflammation of the lining of the esophagus, may not experience heartburn.
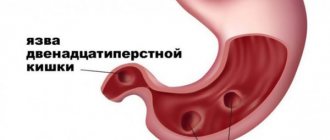
Sometimes this symptom manifests itself in gastritis with high acidity, stomach and duodenal ulcers, cholecystitis, during pregnancy, the development of a hernia, or intolerance to any foods. When heartburn occurs together with belching, this indicates possible gastritis or a stomach ulcer. If a person, when he lies down, experiences pain in the esophagus, then he may have a disease of this organ.
Patients often ask their doctor if heartburn can cause coughing? Many people have a cough along with heartburn. This happens because stomach acid is refluxed into the esophagus, which provokes an inflammatory process. Irritation also appears behind the sternum.
The following accompanying symptoms may appear:
- increased fatigue;
- belching;
- nausea;
- difficulty swallowing food.
Most people experience heartburn after overeating. This symptom occurs with chronic diseases that require therapy and lifestyle changes. Heartburn is most often characterized by a sour taste in the mouth, but if the cause is diabetes or old age, the symptoms may differ.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease
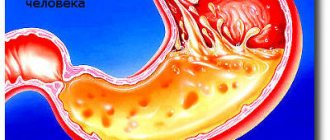
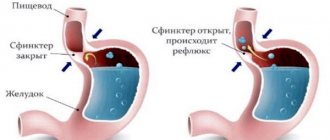
The appearance of regurgitation of gastric contents into the esophageal cavity can cause heartburn. Acid refluxate, entering the esophageal lumen, acts on the cells of its mucous membrane, causing chronic inflammation. Heartburn is a clinical syndrome that is manifested by a burning sensation in the epigastric or xiphoid process. In this case, the patient experiences an unpleasant sour taste in the mouth. This is due to the propagation of a reflex antiperistaltic wave.
Heartburn can cause an obsessive, persistent cough. It is caused by the action of the same refluxate. The contents of the stomach, and then the esophagus, can immediately enter the oral cavity with an antiperistaltic wave. It “burns” the mucous membrane of the tongue, cheeks, and oropharynx. That is, one of the pathogenetic factors is the direct effect of acidic contents. The second causal factor is reflex.
A cough is a reflex contraction of muscle fibers, which is aimed at clearing the mucous membrane of the oropharynx from dust, mucus and other irritants and substances.
Therapists and general practitioners have encountered the problem of chronic cough. When examining the bronchopulmonary system, no significant data were revealed for bronchitis, emphysema, asthma, pneumonia and other pathological conditions of the respiratory tract. Doctors are trying to use antitussives and expectorants. Obviously, their approach is unsuccessful. This makes diagnosis difficult and confuses the patient and the treating doctor. When identifying a medical history, it is very important to determine the presence of heartburn. If these symptoms exist in parallel, then one should think about the presence of reflux gastritis or esophagitis, diagnose and treat these conditions.
Cough may be one of the symptoms of reflux esophagitis
The mechanism of heartburn and cough
The mechanism of heartburn and cough is that hydrochloric acid from the stomach enters the esophagus. The acid irritates the mucous membrane, which causes heartburn. If a person experiences heartburn more than 2 times a week, this signals the development of a pathology such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). This condition can gradually lead to stomach ulcers and increases the risk of esophageal cancer. Acid reflux often causes heartburn, and coughing is also considered a sign of the disease.
Chronic cough can last more than 8 weeks, but it is not considered a typical manifestation of GERD; this disease causes a chronic symptom in 25% of patients.
The mechanism of development of this manifestation is divided into 2 types:
- In the first case, a cough appears as a reflex effect of an increase in acid in the esophagus.
- In the second case, acid particles enter the throat, causing the patient to cough. This is how pharyngolaryngeal reflux manifests itself, which contributes to coughing as a protective reflex.
Prevention
In order to prevent the occurrence of cough in diseases of the digestive system, it is necessary to promptly diagnose and treat the underlying pathology.
Thanks to this, the risk of such a symptom occurring will be minimal. In addition, the patient will be provided with the most favorable outcome.
The appearance of cough in diseases of the stomach and lower esophagus is a rare occurrence. But it causes discomfort and inconvenience for patients. If you experience an unreasonable cough after eating, you should contact a gastroenterologist to undergo examination and begin treatment.
Overview of GERD and Pyloroduodenal Reflux
Pharyngolaryngeal reflux is similar in symptoms to GERD, but has some differences. In patients, acid enters the throat and causes an inflammatory process, which contributes to the occurrence of the following symptoms:
- cough;
- hoarseness;
- sensation of a foreign body in the throat.
A very small amount of stomach acid can cause irritation of the mucous membrane of the throat. It is difficult for doctors to diagnose chronic cough in patients who present with FHR without heartburn. 75% of people with gastroesophageal disease with cough do not develop gastrointestinal symptoms.
Doctors use pH measurements to diagnose GERD, although this test is less commonly used than examining signs and medical history. To determine the pH of the esophagus, a special probe is inserted through the patient's nose into the esophagus.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made after examining a person, studying the medical history and clinical picture, after receiving the results of laboratory tests and instrumental tests.
The most accurate ways to diagnose this disease include:
- X-rays of light;
- Ultrasound of the peritoneum;
- Ultrasound of the esophagus;
- X-ray of the intestines;
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy.
If a patient has heartburn with cough, a biochemical urine test, a stool test for the presence of blood and helminth larvae, and a blood test are prescribed. This makes it possible to exclude inflammation, make a correct diagnosis, and assess the patient’s symptoms and health status. In the differential diagnosis of diseases, it is important to distinguish gastroesophageal reflux from gastric ulcers or gastritis.
The connection between reflux diseases and cough
Patients with reflux esophagitis may cough, and this symptom can last a long period or end quickly. It depends on the irritation of the nerve endings. Chronic cough is often a symptom of GERD.
This can be seen from the following signs:
- At night and after eating, the patient experiences seizures.
- When a person lies down, he coughs more often.
If the cough continues for a long time, the possibility of reflux should be considered if the person does not smoke, does not take medications, does not suffer from asthma or colds, is not overweight, laboratory tests are normal and do not show the presence of an inflammatory process. With a symptom caused by GERD, there is no phlegm, no sore throat, and no runny nose. Sometimes the symptom is accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and fainting. Then it may be mistaken for allergic or asthmatic.
To establish an accurate diagnosis, you need to contact a gastroenterologist and undergo an examination. The relationship between cough and heartburn is observed in patients with GERD. Discomfort behind the sternum most often appears during the day. A cough combined with heartburn occurs after eating fatty foods at night, and the patient feels a sour taste in the mouth. But not all people experience such symptoms.
Some patients have no symptoms, but it progresses and can become chronic. In patients with GERD, treatment is carried out by changing diet and lifestyle. Treatment is prescribed by a gastroenterologist, and endoscopy is used for diagnosis.
Diagnostics
Diagnostic measures for a cough reflex against the background of gastric pathology are quite long, since when a cough occurs, attention is first paid to the respiratory system. Only in the absence of pathology of the lungs or bronchi, doctors pay attention to the digestive tract.
A set of diagnostic measures consists of those examination methods, the purpose of which is to identify the cause of its occurrence, as well as to exclude diseases of the respiratory system:
- General laboratory tests. Carrying out blood and urine tests almost always makes it possible to exclude respiratory pathology. The most important criterion in a general blood test is the level of leukocytes. In case of stomach diseases, the level of leukocytes will be normal, and pulmonary pathology is always accompanied by high leukocytosis.
- Biochemistry of blood. This test is performed to confirm diseases of the gallbladder and pancreas. The results of this analysis pay attention to the levels of bilirubin, amylase and alkaline phosphatase. These substances are always elevated during inflammatory processes of the gallbladder and pancreas.
- Plain radiography of the chest organs. This examination is carried out to exclude diseases of the respiratory system.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs. Thanks to ultrasound diagnostics, it is possible to identify pathologies of an inflammatory or non-inflammatory nature. Most often, ultrasound is performed if cholecystitis or pancreatitis is suspected.
- Gastroscopy. Endoscopic methods are the basis for diagnosing diseases of the digestive tract. Using gastroscopy, you can visually assess the condition of the mucous membrane of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum. This examination requires special medication and psychological preparation.
Interesting! Quit smoking - heartburn appears: why does this happen?
- Duodenal sounding. Probing is carried out to assess the secretory function of the stomach, pancreas and gall bladder. The most common phenomenon that is diagnosed during such an examination is hyperfunction of the glandular cells of the stomach or insufficient amount of bile.
The duration of the examination for such symptoms can take a fairly long period of time due to the fact that cough is not a characteristic manifestation of pathology of the digestive tract.
During diagnosis, it is necessary to differentiate cough due to reflux with the following diseases:
- Asthmatic cough and bronchial asthma.
- Obstructive bronchitis.
- Damage to lung tissue.
The most important differential criterion is the absence of sputum. In addition, examination of the respiratory system does not reveal foci of inflammation in the bronchi and lungs.
How to deal with a cough due to heartburn
If a patient has a cough and heartburn, to eliminate these symptoms, the person must change his lifestyle. Only then can you get rid of cough and signs of reflux. Patients should wear loose clothing that does not put pressure on the abdomen and sternum.
It is necessary to pay attention to body weight. If the patient is overweight, then with the help of a doctor it is necessary to create a diet and increase physical activity. Do not consume foods and drinks that irritate the esophagus and stomach. After eating food, you should not go to bed for 2-3 hours. The patient needs to sleep on a high pillow.
Symptoms
Each disease has its own time of cough onset. A cough with GERD appears immediately after eating, and with diseases of the stomach or duodenum - 1-2 hours after eating.
In addition, the cough may appear at night, regardless of food intake. This is due to the fact that in some diseases, gastric juice is produced even at night. This condition is extremely dangerous, as it can lead to the formation of ulcers. If ulcers have already been diagnosed, the risk of developing gastrointestinal bleeding or perforation of the ulcer increases significantly.
Interesting! Bitterness in the mouth and nausea: causes and prevention
A cough from the stomach has the following characteristics:
- Dry. With gastrointestinal pathology, the cough will always be unproductive.
- Nasty, not bringing relief. The duration of coughing attacks can reach an hour. The longest attacks occur at night.
- The appearance of bloody sputum. During prolonged attacks, a violation of the integrity of the bronchial mucosa may occur, which will lead to the release of a small amount of blood.
Additional symptoms and the treatment needed to get rid of them depend on the underlying pathology. This may be pain in various parts of the abdomen, dyspepsia (vomiting, bowel movements, nausea), belching, deterioration in general condition, increased body temperature.
In some cases, patients develop cough and heartburn after eating, which is considered an important diagnostic criterion.
The appearance of such a symptom requires contacting a medical institution, where a comprehensive examination and selection of etiotropic treatment will be carried out.
Recommendations for treating diseases and combating symptoms
Treatment of reflux disease and elimination of symptoms such as heartburn and cough are carried out using medications. First you need to eliminate the cause that caused the disease. For this purpose, antacid medications are used, drugs that form foam, which eliminate irritation of the esophagus and suppress the action of gastric juice. Patients are prescribed H2 blockers, which reduce the production of gastric juice. If a patient has developed intestinal dysbiosis, he is recommended treatment to restore the microflora of the organ.
The drugs must be prescribed by a gastroenterologist; you cannot prescribe the medicine yourself, because this can cause various complications. Cough medications are prescribed after examination and determination of the cause of the cough. Patients are also recommended folk remedies in the form of decoctions of medicinal herbs. This helps get rid of cough, relieves inflammation and improves overall well-being. If conservative treatment does not help, then surgical intervention is resorted to.
Other causes of chronic cough
There are many other causes of chronic cough. Research shows that chronic cough has more than 20 causes. Common reasons include:
- Asthma;
- Respiratory tract infections;
- Chronical bronchitis;
- After using nasal drops;
- Tobacco use;
- Medicines such as ACE inhibitors.
If the cough persists for 3 weeks without improvement or is accompanied by chest pain, you should consult a doctor.
Traditional methods
There are a large number of folk remedies that can reduce or completely eliminate discomfort and heartburn. Many of them are based on the use of baking soda, chalk or honey. However, there are other ways to treat this condition at home. As with any self-administered treatment, it is recommended that you consult with your physician to evaluate whether the treatment will be safe and effective.
Along with the use of folk remedies, it is recommended to use activated carbon in a dosage of 1 tablet per 10 kg of body weight. You need to drink it once a day for 30 days.
Aloe has beneficial properties . It needs to be frozen for 7-10 days, then taken out of the freezer, ground and mixed with honey in equal proportions. Take the resulting remedy for 10 days, one teaspoon before meals. This will help reduce the burning and sore throat.
Potato juice , which has long established itself as one of the most effective herbal remedies for diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, also reduces the manifestations of the disease For heartburn, it is taken mixed with honey.
Development mechanism
When a cough occurs, the first thing that comes to mind is a cold, but there are no symptoms, no runny nose, no red throat, but there is heartburn, and this indicates poor functioning of the stomach. Reflux esophagitis is considered a fairly common cause of persistent cough. It is provoked by acid located in the stomach and constantly leaving its limits, irritating the esophagus. In addition to heartburn, other symptoms are present: belching, difficulty swallowing food, weakness of the body and extreme fatigue.
Reflux often occurs due to frequent overeating of fatty and spicy foods shortly before bedtime. Then it becomes chronic and urgent therapy and changing bad habits are required to maintain health. Reflux attacks are accompanied by a sour taste in the mouth and heartburn. But this does not happen to everyone - in older people and those suffering from diabetes, this attack passes without symptoms. They only feel a sore throat and difficulty swallowing, hoarseness and a long, debilitating cough.
Treatment of the problem
How to treat cough symptoms in the presence of heartburn with medications, the doctor will answer exactly after a comprehensive examination. It is important to exclude serious pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as stomach cancer.
Medications are predominantly used to treat reflux. First of all, the causes that caused the pathology are eliminated. What are they used for:
- Antacids.
- Preparations with a foaming effect that suppress irritation of the mucous membrane with hydrochloric acid.
- H2 blockers, which reduce acid secretion.
If intestinal dysbiosis occurs, drugs that restore the microflora are prescribed.
Cough during the treatment of reflux is treated after all diagnostic tests, and only if the doctor considers it appropriate. Treatment of this condition lasts quite a long time, in other cases up to six months.
Folk remedies also help well in eliminating symptoms. But they can be treated after a full examination and with the permission of the attending physician. Traditional recipes are aimed at reducing stomach acidity, improving sphincter function, and relieving inflammation of the lining of the esophagus and stomach.
Traditional recipes are used for heartburn, the treatment of which is also aimed at eliminating cough. The most effective recipes are presented:
- Herbal infusion. Take a mixture of herbs and other components in equal quantities: pineapple fruits, snake knotweed root, lemon balm herb, calendula flowers, oregano herbs, white jasmine and angustifolia fireweed. Chop all the herbs and place 2 tablespoons of the mixture in a thermos, adding 500 ml of boiling water. Leave for at least three hours, then strain. Every 1.5 hours, drink 50 ml of infusion and do this all day.
- Infusion of chamomile and other herbs. Take a spoonful of chamomile flowers and two wormwood and mint each, pour a liter of boiling water into the bowl with the raw materials, then leave for 2 hours. After this, strain and drink half a glass half an hour before your meal.
- Raw potatoes. Reflux can be successfully treated with raw potatoes. Before each meal, you need to drink a little potato juice, just prepared, and eat a slice of raw potato sprinkled with granulated sugar.
In difficult cases, when treatment with medications and folk remedies does not bring a positive result, surgery is performed.
Now you know for sure whether heartburn can occur at the same time as a cough. It turns out that this also happens if a person suffers from reflux disease. To avoid complications, it is necessary to ask for help from specialists at the first symptoms.
GERD in children
Unfortunately, stomach cough can occur even in the youngest age group of children. Then the characteristic signs are frequent regurgitation or a gag reflex, which bother the child throughout the first year of life.
Additional symptoms of GERD in children may include:
- wheezing;
- gag reflex, which has periodic repetitions;
- laryngitis;
- burning sensation behind the sternum;
- asthma condition.
You can also recognize gastroesophageal reflux disease in the pediatric population by child behavior:
- constant refusal to eat;
- increased irritability;
- restless behavior, similar to that when pain occurs with colic;
- poor weight gain;
- arching of the back during or after feeding.