What is the cause of the sensations?
Heaviness and pain in the intestines indicate improper functioning of the digestive organs. In some cases, everything is explained by functional disorders due to the pathological state of organs and tissues due to exposure to external factors. The organic nature of malfunctions of tissues and cells is possible. This is observed against the background of somatic pathological conditions.
However, most often the unpleasant sensations can be explained by the peculiarities of the diet. In order for the stomach and intestines to be normal, you need to eat correctly, following a regimen and sticking to healthy foods. Ignoring these rules and advice, a person learns very well by himself what heaviness in the intestines after eating is.
What to do if you feel heavy?
The very first thing to do when a feeling of heaviness appears is to contact a gastroenterologist to find out the cause. To relieve these symptoms, painkillers and antispasmodics are taken to alleviate the person’s condition. But it is not recommended to get carried away with them, so as not to distort the indicators that indicate the cause of the disease and make the correct diagnosis. The doctor needs to determine whether there is a pathology that requires surgical intervention.
If heaviness appears after eating, and colic is smoothed out, you can do a warm enema with a decoction of mint or lemon balm. It is not recommended to apply a warm heating pad to the stomach, so as not to aggravate the disease.
If there are no pills to relieve pain, and the heaviness and pain does not go away, you should call an ambulance.
Taking medications
There are several groups of drugs used for intestinal heaviness.
Probiotics are beneficial bacteria found in the intestines that do not harm the body. Taking similar medications helps prevent the growth of harmful bacteria that cause IBS (irritable bowel syndrome). They are sold in capsules or chewable tablets. One tablet contains the required amount of bacteria for a day.
Sedatives that combat nervous excitability and anxiety, used to treat IBS. These are tablets based on medicinal roots, soft herbal remedies: valerian, motherwort, etc. if the situation is more complex, antidepressants are prescribed, taken under the supervision of a specialist.
Drugs that relieve symptoms
If the pain persists for a long time, and visiting a doctor is not soon, you can take antispasmodic medications at home:
- “No-spa” will dilate blood vessels and relieve pain;
- “Papaverine” will reduce colic and relieve muscle spasms;
- “Spazmalgon” will eliminate pain and act as an anti-inflammatory agent;
- "Metoclopramide" normalizes peristalsis and relieves pain.
The drug "Neobutin" relieves spasms well. It temporarily reduces the active actions of neurons in the intestinal walls. Motor skills are restored, stool returns, gas formation and pain disappear. The effect extends only to the gastrointestinal tract, without affecting other organs.
Doctors do not advise treating pain with cold or warm compresses, so as not to cause pathology and inflammation.
Drugs that eliminate the cause
In order for the effect to be positive and the result to be permanent, it is recommended to provide medication relief for this condition:
- Enterosorbents used as first aid will help to quickly relieve symptoms. But, one should not draw the wrong conclusions when using only these drugs for further treatment, because the effectiveness will be insignificant.
- Treatment of intestinal diseases is carried out with enzyme preparations, such as “Mezim”, which allows you to relieve heaviness in the intestines after eating , “Creon”, “Pancreatin”. They help break down food, making it easier to digest.
- It is possible to normalize the motor-evacuation activity of the organ with the help of prokinetics (Motilium), to accelerate the removal of gases from the intestines.
- It is recommended to stabilize baocenosis (restore intestinal microflora) with multicomponent probiotics, such as Bifidumbacterin and Lactobacterin. The combined drug “Bifiform” and the monocomponent “Acilact” will also help in this case.
- Festal effectively relieves heaviness, eliminates discomfort, helps the digestion process, eliminates flatulence, and prepares the stomach, pancreas and other gastrointestinal organs for diagnosis.
Treatment with improvised means
What to do if you experience increased gas formation and bloating quite often? You can use decoctions and teas prepared at home. To do this you need:
- Prepare a decoction of fennel 1.5 tbsp. l., the same amount of calamus, 2 tbsp. l. mint leaves, 3 tbsp. l. daisies. Pour boiling water over all ingredients and cook for 15 – 20 minutes. Let it sit for 1 hour, strain. Drink 3 times after meals.
- Propolis is an excellent remedy for dysbiosis. Take 15 drops before meals 20% tincture.
- Propolis with sea buckthorn oil is an excellent remedy for treating duodenal ulcers. Heat the oil in a water bath for about half an hour, pour it into the propolis, and strain. Take 5 – 6 times a day, 1 tsp. To improve the result, take vitamin E along with this remedy.
- Chamomile tea will relieve discomfort; it has a calming effect. Drink immediately after eating.
- Dill helps with bloating. It can be added to dishes or made into dill tea. Take the seeds of the plant, pour boiling water over it, let it brew for at least 2 hours. Take 80–100 ml before meals.
An infusion of herbs from which you can prepare yourself will help suppress pathogenic intestinal flora, as well as stop diarrhea and relieve inflammation:
- Elecampane root – 1 part, calamus root, crushed raspberry and strawberry leaves – 2 parts. Add St. John's wort, dried, crushed nettle and currant leaves - 3 parts. Medicinal letter, thyme herb, blueberry fruit, alder fruit – 4 parts. Mix everything, take 2 tbsp. l. When the collection is ready, pour liters of boiling water over the floor and leave for 10 hours. Take 150 g half an hour before meals 3 times a day.
- Eucalyptus leaves 10 g, valerian roots, calendula flowers, coltsfoot and walnut leaves 20 g each, marshmallow root, burnet, bird cherry fruits, knotweed 30 g each, oak bark 40 g. Mix everything, take 15 g of the collection, pour boiling water water (0.5 l), let it sit overnight. In the morning you can start taking it half an hour before meals three times a day.
- Blueberries – 100 g, mint leaves – 100 g, snake knotweed (roots) – 100 g, field chamomile – 200 g. Grind everything thoroughly, pour boiling water over 1 tablespoon, let cool, strain. You can take it an hour later three times a day before meals.
Healthy diet
If an incorrect diet causes heaviness in the intestines, what should you do? It is best to recommend a program for switching to a healthy diet from a doctor. Ideally, a person should eat a balanced diet, consume a moderate amount of food in small portions, quite often throughout the day. A healthy diet involves fully satisfying the body's needs for protein structures, fat molecules and carbohydrates. Food must supply adequate amounts of essential microscopic elements and vitamins. Nutrition is a source of certain amounts of energy. They are usually measured in calories. A healthy diet provides a normal amount of energy, but does not put too much strain on the gastrointestinal tract.
By neglecting the described rules for preparing a diet, you can find out for yourself how unpleasant bloating and heaviness in the intestines are. You can understand what exactly needs to be adjusted in your nutrition program by visiting a nutritionist. The most common causes of disorders are eating excess amounts of food, unbalanced foods, or low nutritional value of the food consumed.
Everything is interconnected
The causes of heaviness in the intestines listed above are closely interconnected and form a kind of vicious circle. For example, a person who eats foods with low nutritional value must constantly renew reserves of components and substances, which forces him to consume large amounts of food. This provokes overeating, while at the same time the body, quite possibly, will still suffer due to a lack of vitamins.
Even if a person can boast of good health, the digestive system is not able to process large volumes of food received in a short period of time. There is a feeling of heaviness in the intestines, because the body is unable to generate enough enzymes to break down all the products, and rapid digestion becomes impossible.
How to help your own intestines?
If a feeling of heaviness in the stomach after eating haunts the patient every day, then the first step should be to see a doctor.
Of course, you can treat yourself with various advertised drugs. But in this way a person will only fight the symptoms of the disease, and not its cause.
Such treatment may not only be ineffective, but also aggravate the existing disease. In order not to start the disease, it is important to consult a doctor as soon as possible.
After examining and studying the history of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, the doctor will prescribe the necessary examination.
This may include the following procedures:
- fibrogastroscopy of the stomach and duodenum;
- measuring the acidity of gastric juice;
- collecting bile for research;
- intestinal enteroscopy;
- X-ray examinations of the stomach and intestines;
- CT or MRI of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Ultrasound;
- blood and stool tests;
- culture for dysbacteriosis;
- tests that detect the presence of parasites in the intestines.
Fibrogastroscopy of the stomach is performed using a special device - an endoscope. It is equipped with a flexible probe with channels for the camera and the necessary instruments.
The tube is inserted into the stomach through the patient's esophagus. An enlarged image from the device's camera is sent to the computer.
Using this method, you can not only visually assess the condition of the organs, but also take particles of the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum for analysis.
The resulting fragments of biomaterial are studied under a microscope - this helps to establish the nature of the disease.
Samples of gastric juice and bile are taken using soft, thin probes inserted through the patient's esophagus.
The study of the resulting digestive fluids allows us to determine the level of acidity in the stomach and assess the functionality of the biliary tract. Depending on the results obtained, further treatment tactics are selected.
Intestinal enteroscopy is also performed using an endoscope. Only this time the probe enters the intestines through the anus. This method allows you to examine in detail the condition of the patient’s intestines.
X-ray examination is carried out using a contrast agent. During an X-ray of the stomach, the patient is given a glass of barium solution to drink, after which pictures are taken.
Barium coats the walls of the stomach, which allows you to get a clear picture. Before an X-ray of the intestine, a contrast solution is injected into the rectum using an enema.
The coprogram will help you find out how well the intestines perform their functions; in addition, in the stool analysis there is a possibility of detecting parasite eggs.
The results of blood tests may indicate inflammation, anemia, and the presence of parasites in the intestines.
Nuances and processes
If food is retained in the gastric cavity or intestinal tract, fermentation processes begin in these masses, causing bloating. A person suffers from gas formation and heaviness in the intestines. Often the sensations are accompanied by constant hunger, it is almost impossible to get enough, and every now and then you are tempted to have a snack again. Since it is easiest to get instant food, this is what people use to “dilate the worm”, without even realizing that they are only aggravating their condition.
An incorrect diet is not only an unsuccessful selection of foods, but also the culture of eating them. Currently, many people are characterized by aerophagia, that is, ingestion of air masses that enter the intestinal tract with nutritional components. To prevent this from happening, you must remain silent while eating, absorb food in small pieces, chewing carefully.
Diseases and their manifestations
Treatment of heaviness in the intestines, provoked by the factors described above, involves normalizing the diet and stabilizing everyday life, eliminating worries and stress factors. The task will be somewhat more difficult if the cause of the phenomenon is pathology, a disease affecting the organs of the digestive system. Clarification of a specific somatic disorder is the responsibility of the doctor. It makes sense to understand what diseases the symptom indicates in order to have sufficient motivation to visit the clinic.
Most often, heaviness in the intestines accompanies gastritis. This disease is extremely widespread among residents of various countries of the world. The term usually refers to the presence of foci of inflammation on the mucous membranes covering the stomach. The cause of gastritis is bacterial invasion. The pathology is expressed by slow digestion. Unpleasant sensations come immediately after a meal and bother you for some time. Gastritis is manifested by pain in the abdomen above, nausea, and weight loss. Some people have bowel movements.
Treatment of the disease
Diet and healthy lifestyle
Most often, problems with the intestines and stomach appear due to the fact that a person does not eat properly, violates the diet, or does not monitor the quality of food. Then the doctor prescribes a diet as a therapeutic therapy, in which all foods that irritate the digestive organs and have a detrimental effect on the body are excluded from the menu. These are spicy, fatty and fried foods, alcohol, cigarettes, beer, carbonated drinks, sweets, chocolate, black tea and coffee.
Instead, the patient is recommended to switch to six meals a day. Products should be steamed or boiled, with a minimum amount of fat and spices. The diet includes porridge with water, fresh and cooked vegetables and fruits, eggs, lean meat and fish, light meat and vegetarian broths. Among the drinks, mineral water without carbon, herbal infusions, decoctions and teas, compotes and jelly from dried fruits, and you can make natural juice have beneficial properties.
Medicines
If necessary, the doctor prescribes medication; it consists of taking special medications that help eliminate the cause of the discomfort. If intestinal problems are caused by stomach diseases, medications are taken to help improve the functioning of the organ. These are antacids, proton pump blockers, enzyme medications. Which medications to take is determined only by the attending physician.
What to do at the gym?
If heaviness occurs once after eating some exotic and unusual dish, then there is no need to panic.
But if heaviness becomes a constant companion of a person and not a single day goes by without it, then it’s time to sound the alarm. This may be a symptom of serious problems in the intestines.
Along with heaviness in the abdomen, the following symptoms may appear:
A feeling of heaviness in the abdomen appears due to a decrease in intestinal motility and the production of gastric juice.
This can occur with certain diseases of the gastrointestinal tract:
- intestinal infections;
- intoxication of the body;
- kidney diseases;
- chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- disruptions in the circulatory or nervous systems.
In addition, intestinal motility may decrease in women during pregnancy and in people leading a sedentary lifestyle.
In addition to physiological factors, the cause of heaviness in the abdomen may be:
- irregular meals;
- binge eating;
- eating excessively fatty foods.
Eating animal fats with a melting point higher than the temperature of the human body is especially harmful.
It’s already difficult for the body to cope with them, and they, as a rule, enter the stomach along with a large portion of indigestible protein.
As a result of this, the human intestine spends a lot of energy just to grind these products, and the person has a feeling of heaviness in the intestines.
Diagnoses and pathologies
Sometimes heaviness in the intestines indicates the presence of inflammatory processes in the gallbladder. Perhaps, in terms of prevalence, this pathology is second only to gastritis. A distinctive feature of cholecystitis is severe pain on the right under the ribs. The sensations come in fits and starts, and are especially strong if you eat something fatty, alcoholic, or salty. Often the period of exacerbation is accompanied by fever.
Colitis and enteritis are pathological conditions that also manifest themselves, among other things, as heaviness in the intestines. The terms refer to inflammatory processes localized in the large and small intestinal tract. The problem is accompanied by bloating, increased gas formation, and pain in the area suffering from pathological processes. The stool is broken.
What else is possible?
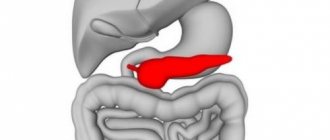
Sometimes heaviness in the intestines is explained by pancreatitis. This term refers to inflammatory processes localized in the pancreas. They lead to disruption of the functionality of the gastrointestinal tract, which is accompanied by increased gas formation, discomfort, and pain in the area. Pancreatitis is characterized by a number of nonspecific manifestations - blood pressure rises, shortness of breath bothers you, and the skin acquires an unhealthy yellowish tint.
The digestive system is formed from a large number of closely interconnected organs. If the functioning of at least one of them is disrupted, this affects the person’s condition as a whole. Localization of unpleasant sensations does not always help to immediately make an accurate diagnosis. Clarifying the condition is the responsibility of the doctor. The doctor collects the patient’s complaints, draws up a picture of the course of the disease, and refers the client to laboratory and instrumental studies. Based on the results of these measures, it is possible to determine what exactly caused the discomfort, and therefore, choose a successful course of treatment.
Diseases, symptoms, treatment of the small intestine
Various serious diseases of the small intestine and the entire gastrointestinal tract are quite common. These can be infectious and non-infectious diseases, infectious parasitic diseases and others. That is why people are interested in the question of how to check the small intestine in order to be sure that your health is in perfect order.
Gastrointestinal diseases
The most characteristic symptoms of intestinal diseases are the following:
- abdominal pain;
- heartburn and abdominal pressure;
- nausea and vomiting, accompanied by belching of air;
- elevated temperature;
- constipation or diarrhea;
- chest pain.
All of the above symptoms are the most common, but often diseases of the small intestine can manifest themselves in other factors, so only a specialist can determine this.
Signs of bowel disease
- pain in the anus;
- obstruction;
- bleeding from the anus;
- blood in stool;
- fecal incontinence;
- purulent discharge from the rectum;
- tenesmus;
- anemia.
Among the most known pathologies of the small intestine are the following:
- Inflammatory processes leading to malabsorption;
- Crohn's disease, affecting all parts of the gastrointestinal tract. This disease is especially severe in women and children;
- Intestinal hemorrhoids (varicose veins near the small intestine);
- Enteritis (inflammation of the small intestine). It can be acute or chronic;
- Whipple's disease (a rare pathology characterized by various clinical forms);
- Intestinal malabsorption;
- Diverticulosis of the small intestine;
- Dysbacteriosis;
- Polyposis;
- Giardiasis;
- Lymphoma;
- Small intestine cancer.
Symptoms and treatment of the small intestine depend on the type of disease. Let's look at some of them. But before this, it is necessary to check the small intestine in order to know which disease the patient has.
Currently, radiography, endoscopy and ultrasound
. But only in the process of a comprehensive examination will a gastroenterologist be able to make the correct diagnosis and then, based on it, prescribe effective treatment.
The small intestine consists of three parts: duodenum, ileum and jejunum.
. They are located between the stomach and large intestine. The doctor listens to the patient’s complaints and, based on this, gives a referral for radiography.
But before it is carried out, a person must follow a strict diet for 2 weeks, consume only liquid pureed porridges and soups with water. 36 hours before the x-ray, nutrition is completely stopped and the patient must undergo a cleansing enema.
Such activities will completely cleanse the intestines of food.
Immediately before the x-ray, the patient must drink barium liquid and only after three to four hours he will be examined. Since barium is not capable of transmitting X-rays, the procedure can detect abnormalities in the small intestine. This examination makes it possible to detect: enteritis, dyskinesia and intestinal obstruction
.
The endoscopy procedure also allows you to detect signs of various diseases and various inflammatory processes of the small intestine.
Using an endoscope, a special video capsule is inserted into the intestine, which will transmit to a video monitor everything that is happening on the intestinal mucous membranes.
This procedure is quite informative and effective, but, unfortunately, it is not carried out in all hospitals due to the lack of the necessary modern medical equipment.
Using an ultrasound, the doctor can see the location of all internal organs and their foreign bodies (if any). But this method does not always give 100% results, especially if a person is overweight.
Irrigoscopy involves the administration of a radiocontrast substance using an enema.
, which will help show all abnormalities in the small intestine. It is usually prescribed for the diagnosis of the duodenum.
During the fiberoscopy procedure, a specialist takes a piece of material for histology. Such an examination is prescribed only in extreme cases, if there is a suspicion of cancer.
After a thorough and complete examination, the doctor will identify the disease, make the correct diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Treatment of giardiasis of the small intestine
Giardiasis is a parasitic disease
, which is caused by microscopic Giardia, which belongs to the class of protozoa flagellates. These parasites usually live in the upper part of the small intestine and come in two forms: vegetative and cystic.
Giardia can enter the body through food, drinking water, and if hygiene rules are not followed. As a result of the vital activity of these parasites, a person develops dysbiosis, abdominal pain, weight problems, biliary dyskinesia, diarrhea and other hepatobiliary, astheno-neurotic and toxic-allergic reactions.
Usually a person does not even know that he has Giardia until he has his stool analyzed for Giardia cysts.
Treatment of this disease occurs in three stages:
- A diet that worsens the reproduction of parasites (limiting carbohydrate intake and increasing fiber in the diet). To improve the flow of bile, choleretic herbs and drugs are taken: febihol, immortelle and others. To relieve toxicosis, Enterosgel, Polyphepan, activated carbon and others are prescribed. Diazolin, Loratadine, Cetrin are prescribed against allergies, and Crenon, Pancreatin, Mezim are prescribed to improve digestion.
- At the second stage, drugs that act on protozoa are prescribed, such as: Metronidazole, Ornidazole, Fazizhina, Albendazole. In addition, the patient continues to take antiallergic drugs, enzymes and sorbents.
- At the third stage, an anti-giardiasis diet, multivitamins, adaptogens, probiotics and enzyme preparations are prescribed. They are also allowed to be treated with folk remedies: drink natural birch, carrot and beet juice, as well as tincture of walnuts.
Worms in the small intestine
Worms in the small intestine cause diseases such as enterobiasis and ascariasis
. Infection with such parasites occurs through contaminated soil, unwashed fruits, vegetables and berries, from pets, unwashed hands, etc.
Signs:
- stomach ache;
- diarrhea;
- vomit;
- anal itching;
- constipation.
Also, in some advanced cases, a person develops severe skin rashes and bronchial asthma.
Drug treatment consists of taking various anthelmintic drugs. The choice of drugs depends on the specific type of worms that have been identified in the patient. These may be medications such as Decaris, Pirantel and others. Treatment is carried out at home.
Enteritis and its symptoms
Chronic enteritis is an inflammation of the small intestine, accompanied by disturbances in its functions. A person feels acute pain in the epigastrium, a feeling of heaviness after eating, and painful sensations in the epigastric region. The causative agents are:
- salmonella;
- dysentery bacillus;
- Yersinia;
- rotaviruses;
- worms, etc..
At the first signs of the disease, you need to take enterosorbent Enterodes, which will cleanse the body. You can also be treated with folk remedies: infusion of cumin, decoctions of black currant, oak bark, bird cherry. In this case, it is necessary to follow a diet.
Diverticulosis and its treatment
Diverticulitis is the presence of a diverticulum
, which is a sac-like cavity formation that communicates with the small intestine through an opening.
There are several types of localization of diverticulitis in the small intestine:
- Diverticulum 12 – duodenum;
- Meckel's diverticulum localized in the upper ileum;
With diverticulosis, bloating, diarrhea, bad breath, and pain in the abdominal area are observed.
To diagnose this disease, EGD and capsule videoscopy are used. X-rays of the small intestine, CRT and angiography are also done.
For diverticulosis, diets No. 4 and No. 3, symptomatic therapy and probiotics are prescribed. All appointments are made by a specialist gastroenterologist based on the obtained tests and research data.
Small bowel cancer
Small intestine cancer signs and symptoms can only be detected with a thorough examination. But, unfortunately, in many cases it is detected only in late stages (3 or 4), when surgical intervention is no longer effective. The reason for this is the complexity of instrumental examination of the small intestinal mucosa, as well as the absence of symptoms, which leads to late referral to specialists.
That is why the prognosis for small intestine cancer may not be encouraging. In order to identify a tumor in the early stages and eliminate oncology in a timely manner, it is necessary to conduct a number of studies.
Also today, scientists have found a way to detect small intestinal cancer at earlier stages and this is a tumor marker. Tumor markers are specific substances formed as a result of the activity of active cancer cells. They can be detected in the blood or urine of a person with suspected cancer and therapy can be started on time.
There are two types of tumor markers:
- highly specific, which appear in a specific type of tumor;
- appear in oncological diseases of various localizations.
Thanks to modern diagnostic research methods, it is possible to detect an increase in markers even with small tumors at stage 1 of the disease.
Tumor markers allow:
- determine the location of the tumor with a high percentage level;
- evaluate the effectiveness of treatment;
- anticipate the possible occurrence of relapses;
- identify individuals who are at risk.
Share this article with your friends
articles
0
Source: https://netbolezni.net/gastroenterologiya/12-zabolevaniya-simptomy-lechenie-tonkogo-kishechnika.html
Options and reasons
Sometimes heaviness in the intestines is accompanied by a feeling of fullness in the stomach cavity. Additional symptoms usually include nausea and vomiting. A person is constantly thirsty. There is a possibility that the root cause of the manifestations is a disruption in the coordinated functioning of the muscles and nerve fibers of the gastrointestinal tract. There is a possibility of such a condition with a long, strictly limited diet, against the background of fasting. Carrying out an examination of the patient's body usually makes it possible to determine the exhaustion of the body.
A not very common, but extremely dangerous cause of heaviness in the intestines is a heart attack. Additionally, gas formation is activated in the gastrointestinal tract, the patient feels sick and vomits. When touching or examining the stomach, no pain is detected in this area. The patient's condition is rapidly progressing; dry mucous membranes of the oral cavity and tongue are bothersome.
If heaviness in the intestines is accompanied by fever and increased gas production, the likely cause is the presence of foci of inflammation. Sometimes symptoms accompany severe poisoning. Clarification of the condition in some cases helps to identify a combination of liver, kidney, and pancreas diseases. If the heaviness in the intestines is chronic, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Digestive disorder
Gastritis
Diarrhea
19464 November 10
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Digestive disorder: causes of occurrence, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract that cause indigestion are among the most common in the population. Signs of digestive disorders to one degree or another are observed in almost a quarter of the world's population, but the majority do not seek help from doctors and treat themselves, which in some cases threatens to develop complications.
Diseases of the digestive system can occur in childhood or adolescence and become chronic.
Types of digestive disorders
Digestive disorders can be divided into two large groups.
The first includes diseases caused by a lack of pancreatic enzymes and substances necessary for digesting food - gastric juice, bile. In these cases, characteristic symptoms are heartburn, belching, bloating, colic, and pain in the iliac region.
The second group includes disorders caused by impaired absorption processes in the intestine. These disorders are characterized by spastic pain, increased peristalsis (rumbling) in the abdomen, a feeling of fullness, unstable bowel movements (constipation or diarrhea), exhaustion, and muscle weakness.
Possible causes of indigestion
Doctors call dysmotility of the esophagus
. Pathologies of motor activity of the esophagus lead to difficulty in moving food into the stomach and, conversely, easy entry (reflux) of concentrated gastric juice onto the walls of the esophagus.
Another significant cause is functional dyspepsia
, which combines conditions caused by temporary (no more than 3 months) disruption of the stomach, duodenum and pancreas. Patients complain of pain or discomfort in the iliac region, heaviness, a feeling of fullness in the stomach after eating the usual amount of food, bloating, nausea, vomiting, belching, heartburn. The pain is characterized by frequency (on an empty stomach or at night) and rapid cessation after eating or taking medications that reduce stomach acidity.
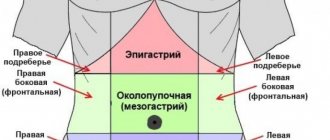
If the pain is localized in the left hypochondrium or is girdling in nature, then problems with the pancreas can be suspected; if in the right hypochondrium, dysfunction of the liver and gall bladder can be suspected.
When examining such patients, it is often not possible to identify “organic” diseases (ulcers, tumors, pancreatitis).
Digestive problems may result from functional disorders of the biliary tract
(biliary system). They are based on a violation of synchronicity in the functioning of the gallbladder and the sphincter of Oddi, through which bile enters the duodenum. With sphincter spasm, not only stagnation of bile in the gallbladder occurs, but also disruption of the pancreas, which together leads to acute pain, which is often localized in the right hypochondrium and can radiate to the back. Attacks are triggered by eating fatty and spicy foods, cold drinks, and stressful situations. Pain in the right hypochondrium can be combined with a feeling of fullness. Characteristic symptoms also include nausea, bitterness in the mouth, bloating, and constipation.
Another cause of indigestion is irritable bowel syndrome.
- painful conditions in which pain or discomfort in the abdomen goes away after a bowel movement. In this case, stool is characterized by irregularity with a predominance of diarrhea (diarrhea) or constipation.
The causes of irritable bowel syndrome include infectious diseases, nervous stress, poor quality nutrition, consumption of large amounts of gas-forming foods, and overeating.
The main symptoms of this disease are bloating, cramping pain in the abdomen, which usually intensifies after eating and subsides after bowel movements. It is noteworthy that at night the pain stops.
With diarrhea, the number of bowel movements can reach 5 times a day, and the urge to defecate may occur after every meal. There is often a feeling of incomplete bowel movement. With constipation, the character of feces resembles “sheep’s”, consisting of small dense pellets. So-called constipative diarrhea may occur - loose stools after several days of delay.
Which doctors should I consult for indigestion?
It is important to remember that the initial symptoms of spasm and impaired motility of the esophagus most often occur in childhood (regurgitation, sudden vomiting of unchanged food immediately after eating, pain when swallowing) and require consultation with a pediatrician.
If such symptoms appear for a long time (more than a month) in an adult, you should visit a general practitioner to receive a referral for examination of the gastrointestinal tract and make an appointment with a gastroenterologist.
The treatment of functional digestive disorders, including irritable bowel syndrome, is carried out by internists, gastroenterologists and psychotherapists.
Diagnosis and examinations for digestive disorders
If a disease of the esophagus is suspected, fluoroscopy is prescribed, which can reveal a violation of the passage of barium suspension into the stomach and dilation of the esophagus. To exclude organic lesions of the esophagus, esophageal manometry and esophagoscopy are performed.
Diagnosis of functional dyspepsia usually involves a clinical blood test; blood chemistry; stool occult blood test; C-urease test for diagnosing Helicobacter pylori infection; gastroduodenoscopy for the purpose of visually assessing the condition of the stomach wall and excluding its ulcerative lesions and tumors; Ultrasound of the liver, gallbladder and pancreas to clarify their condition.
Approach to therapy
Currently, etiotropic treatment is practiced - first, the causes that provoked the pathology are established and corrected, while the symptoms are considered secondary. In some cases, it is not possible to eliminate the root cause, and for some diseases there are no cures. In this case, relief of the patient's condition is achieved by relieving symptoms.
It so happens that many people do not perceive heaviness in the intestines as a serious problem, and pharmacies have many products to improve their general condition. It is worth remembering: constant use of such drugs has a negative effect on the liver, gastrointestinal tract, and kidneys. In addition, the root cause, the original pathology, whose symptoms are suppressed, gradually develops and becomes more complicated.
Heaviness in the intestines after eating
A constant problem with the intestines, lower pain and gas formation after a meal can occur in any person. If this uncomfortable sensation appeared once, for example, a person had overate the day before, then this should not cause concern; after the stomach and intestines are unloaded, the illness will go away on its own, and nothing special needs to be done. But when heaviness of the intestines, pain, nausea after eating are constantly bothering you, then this is a cause for concern, as it may indicate a serious disease in the body. Most often, intestinal problems after a meal appear for the following reasons:
- When a person overeats, it is harmful to the digestive organs, since they are constantly under excessive stress, they work at full capacity, and this is bad. When a person regularly fills his stomach, he experiences constipation or diarrhea, flatulence, and stomach pain.
- Aerophagia also causes discomfort in the digestive organs, since excess air swallowed during meals has an irritating effect on the walls of the stomach, and this is the root cause of discomfort.
- Alcohol abuse, smoking and other bad habits have a detrimental effect not only on the digestive organs, but on the entire body.
- An eating disorder can cause stomach and digestive problems. During this disease, the entire gastrointestinal tract suffers and the patient runs the risk of many complications.
Frequent stress contributes to the destruction of intestinal microflora.
Nervous strain and frequent stress affect the stomach and intestines, destroy beneficial microflora, disrupt the functions of these organs, which leads to difficulty digesting food, pain in the lower part, regardless of the quantity and quality of food, constipation, and a person is constantly in a bad mood.- The use of certain medications negatively affects the functioning of the stomach and intestines, destroying beneficial microflora, causing pain and heaviness in the abdomen. It is better if drug treatment is prescribed by a qualified specialist; independent treatment and use of drugs is dangerous.
First aid: how to relieve the condition
If it is not possible to visit a doctor, and the condition is extremely unpleasant, to relieve discomfort, you can take any of the drugs available in modern pharmacies - they have a fairly large selection of over-the-counter products for the stomach and intestines. In addition, such drugs are irreplaceable if the severity in the gastrointestinal tract is due to excess food consumption and poor diet. They will help if you have eaten low-quality products.
As a rule, the product present in the first aid kit of any of our citizens is activated carbon. This drug belongs to the category of enterosorbents. The slightly more expensive Polysorb, Enterosgel, and Polyphepan have similar properties.
In some cases, enzyme medications available in pharmacies under the names “Creon” and “Mezim” help alleviate the condition. Festal has proven itself well. To activate the movement of food through the gastrointestinal tract, you can take Itoprav, Ganaton. If you have problems with gas formation, Simikol and Espumisan come to the rescue.
How to help your own intestines?
If a feeling of heaviness in the stomach after eating haunts the patient every day, then the first step should be to see a doctor.
Of course, you can treat yourself with various advertised drugs. But in this way a person will only fight the symptoms of the disease, and not its cause.
Such treatment may not only be ineffective, but also aggravate the existing disease. In order not to start the disease, it is important to consult a doctor as soon as possible.
After examining and studying the history of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, the doctor will prescribe the necessary examination.
This may include the following procedures:
- fibrogastroscopy of the stomach and duodenum;
- measuring the acidity of gastric juice;
- collecting bile for research;
- intestinal enteroscopy;
- X-ray examinations of the stomach and intestines;
- CT or MRI of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Ultrasound;
- blood and stool tests;
- culture for dysbacteriosis;
- tests that detect the presence of parasites in the intestines.
Fibrogastroscopy of the stomach is performed using a special device - an endoscope. It is equipped with a flexible probe with channels for the camera and the necessary instruments.
The tube is inserted into the stomach through the patient's esophagus. An enlarged image from the device's camera is sent to the computer.
Using this method, you can not only visually assess the condition of the organs, but also take particles of the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum for analysis.
The resulting fragments of biomaterial are studied under a microscope - this helps to establish the nature of the disease.
Samples of gastric juice and bile are taken using soft, thin probes inserted through the patient's esophagus.
The study of the resulting digestive fluids allows us to determine the level of acidity in the stomach and assess the functionality of the biliary tract. Depending on the results obtained, further treatment tactics are selected.
Intestinal enteroscopy is also performed using an endoscope. Only this time the probe enters the intestines through the anus. This method allows you to examine in detail the condition of the patient’s intestines.
X-ray examination is carried out using a contrast agent. During an X-ray of the stomach, the patient is given a glass of barium solution to drink, after which pictures are taken.
Barium coats the walls of the stomach, which allows you to get a clear picture. Before an X-ray of the intestine, a contrast solution is injected into the rectum using an enema.
The coprogram will help you find out how well the intestines perform their functions; in addition, in the stool analysis there is a possibility of detecting parasite eggs.
The results of blood tests may indicate inflammation, anemia, and the presence of parasites in the intestines.
There are many options - how to decide?
The choice in favor of a specific name is made based on the characteristics of the case and which symptom dominates over the others. If it is possible to accurately determine the cause of the discomfort, it is also taken into account when choosing a remedy to alleviate the condition. For example, after absorbing large volumes of food, it is necessary to use enzymatic active compounds - they stimulate the digestive process and help get rid of unpleasant heaviness. When eating harmful, unhealthy foods, simple carbohydrates, it is wise to use sorbents and drugs that stimulate the release of gases in case of heaviness and bloating.
If you experience frequent, disturbing heaviness in your intestines, you should consult a doctor. Constantly taking pills to relieve symptoms will only do harm. Having found out the exact cause of poor health, you can choose a good treatment program with minimal negative consequences for the body.
Nutrition rules and diet changes
To get rid of heaviness in the intestines, as a rule, it is enough to adjust the meal plan and menu. The main idea of the diet is to unload the gastrointestinal tract and minimize the entry of harmful, heavy foods into the body. It is necessary to eat in small portions, taking breaks between meals of no more than four hours. During meals, you should eat a reasonable amount of food (small portion).
You should review your diet and balance your diet. About half of the foods entering the body are normally complex carbohydrates. Approximately a quarter of the nutrition is protein structures, the same amount is fatty. It is reasonable to use a medical diet recommended by doctors as a basic menu. It is adapted to the characteristics of a specific lifestyle, realities, taking into account your tastes.
Symptoms
Heaviness and bloating in the intestines may be the first, but not the only clinical manifestations. The malaise has the following characteristics:
- Time of occurrence: immediately after a meal or a short period of time after a meal. It is often expressed under other conditions - stress and excessive physical activity. In some cases it occurs for no apparent reason.
- Duration of the attack. The severity can be short-term (lasts no more than 10 minutes) and long-term (the attack lasts from several hours to a couple of days).
- Frequency. Most often the condition is one-time in nature, but it can be periodic, frequent and permanent.
- Localization. The source of discomfort can be observed only in a certain area of the abdomen or spread to the entire peritoneum.
Persons suffering from heaviness in the intestines should seek qualified help as soon as possible if they experience additional symptoms:
- nausea ending with profuse vomiting;
- heartburn and belching;
- rumbling and seething in the stomach;
- pain of varying severity and localization;
- violation of the act of defecation;
- decreased or complete lack of appetite;
- flatulence or increased gas production;
- bad breath;
- signs of intoxication;
- bloating;
- increase in temperature indicators;
- problems swallowing saliva, food, or liquid;
- fluctuations in blood pressure and heart rate;
- decreased performance;
- weakness and lethargy;
- weight loss.
In addition to the main manifestations, the clinical picture will include symptoms characteristic of the underlying disease.