Pain in the stomach area may indicate a slight malfunction in its functioning or serious pathologies of the organ. If your stomach hurts in the upper middle, only a specialist can tell you what to do in this case after a thorough examination. A visit to the doctor is necessary, since the symptom itself is not a disease, but only indicates processes occurring in the body.
Causes of pain syndrome
In general, factors contributing to the appearance of pain in this digestive organ can be divided into 2 groups:
- pressing pain in the stomach caused by various pathologies of the digestive system;
- pain caused by pathology of other organs.
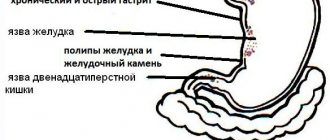
The reasons why your stomach may hurt may include the following stomach diseases:
- Polyps in which pain occurs quite infrequently. Such formations can be discovered purely by chance during the next examination. If pain does occur, it can be pressing or aching in nature.
- Inflammation of the gastric mucosa. In the chronic form of the pathology, the patient may not even notice the appearance of pain in the stomach. Such sensations may either not appear at all or be characterized by a low degree of intensity. Stomach hurts while eating. The stomach may begin to hurt immediately after eating. This especially applies to eating sour and spicy foods. In addition to pain, you may experience a feeling of fullness and heaviness, and an unpleasant taste in the mouth. The patient belches or vomits.
- Stomach ulcer, in which pain is localized in the epigastric zone. In this case, the pain can be either mild or excessively severe, which forces the patient to resort to taking painkillers. Pain occurs immediately after eating food. For such pathology there are periods of remission or exacerbation. They occur in the spring and autumn seasons.
- The greatest danger is sudden sharp pain in the stomach. It happens that a small hole is formed in the wall of the affected organ, as a result of which its contents, along with juice, flow into the abdominal cavity. If this happens, you must immediately call an ambulance. Urgent surgical intervention is required, otherwise it can be fatal.
- The causes of stomach pain may be the development of bacterial or viral infections, which contribute to the appearance of cramping pain in the stomach. In this case, against the background of pain, a person may experience vomiting and diarrhea. This disease is often called intestinal flu.
- Mild but constant pain in the stomach may be present with cancer. Moreover, their appearance has nothing to do with food intake or any other factors. Stomach cancer is the most common form of cancer. At a later stage of development, the pain intensifies, with vomiting mixed with blood, and bowel movements become black.
- Pain in the stomach can be caused by overeating, constipation, unbalanced diet, consumption of alcoholic beverages and tobacco products.
- The severity of pain in the stomach during food poisoning depends on the amount of food consumed, as well as the type of toxic substance. The first signs of poisoning become apparent after a few hours. Very rarely, the first signs appear after a few days or several weeks.
In addition to those listed above, the first group of pathologies that contribute to the appearance of stomach pain should include stress and allergic reactions of the body.
As for the second group of pathologies that cause pain in the stomach, these include diseases of the large or small intestine, convulsive diaphragm syndrome, disturbances in the functions of the heart and blood vessels, pancreatitis and appendicitis.
Pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract as a cause of pain
There are diseases in which pain bothers patients after every breakfast, lunch and dinner for a long time. In this case, consultation with a gastroenterologist is mandatory. It is important to note after what time, as well as after taking what products, they occur. This allows one to suspect damage to a specific organ of the digestive tract.
The following pain options exist:
- Occurring immediately after eating sour, spicy food or 60 minutes after eating. This symptom indicates a gastric ulcer and is especially pronounced when the defect is located in the cardiac region. This occurs due to an increase in the content of acidic gastric juice in the organ cavity and irritation of the damaged inner lining. The pain decreases with treatment with antacid drugs or independently after 60-80 minutes, after the food bolus passes further through the intestines and the pH in the stomach is normalized.
- There are also hunger pains and night pains, which most often occur 4-5 hours after a hearty dinner. They are localized in the upper abdomen or in its right half, often radiating to the lumbar region. In order to relieve pain, patients need to eat something, drink a glass of milk or mineral water (Borjomi, Essentuki). This symptom indicates a duodenal ulcer.
- Painful sensations that develop 2-3 hours after drinking alcohol, foods with excess fat, smoked meats, and marinades may indicate the presence of chronic pancreatitis. They were called "late".
- Discomfort or spasm in the liver area, radiating to the area of the right arm, which occurs and intensifies after eating fat, indicates damage to the hepatobiliary system.
Any discomfort in the body after eating may indicate a dangerous pathology. If pain occurs, it is important not to ignore it and not try to cope with home methods, but to seek advice from a gastroenterologist in order to establish a diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment.
Often the cause of pain in adolescents can be irritable stomach syndrome, which, in addition to pain, is manifested by dyspepsia, but no organic pathology is detected. In this case, it is especially important to review your diet and eliminate harmful foods that cause pain.
Treatment method
First, you should change your diet, excluding from it fresh bread, meat broths, mushrooms, puff pastry, sour berries, fruits, ice cream, chocolate, pickled and canned foods, sparkling water, smoked meats, strong coffee and tea, eggs, various sauces, radishes, cucumbers, cabbage and onions.
We should not forget that during treatment, you should not make efforts to eliminate symptoms by resorting to various medications, but rather focus all your efforts on treating the cause of such a symptom.
If a patient is diagnosed with a stomach ulcer or gastritis, then it is necessary to adhere to a more gentle diet. For these diseases, the attending physician prescribes medications that will help speed up the healing process of erosion on the digestive organs, as well as taking enzymes. In more severe forms of pathology, surgical intervention will be required.
Pain and discomfort in the stomach - causes of gastrointestinal diseases
A classic example is gastritis , a common disease of modern people who begin to forget about food hygiene. Snacks, fast food, and semi-finished products become part of life. If you do not realize their harm in time, you can face serious consequences. Inflammation of the stomach or gastritis can be accompanied by high or low acidity. In the first case, the patient will be bothered by heartburn, burning, and pain after eating. With reduced acidity, heaviness, bloating, and constant discomfort are disturbing.
Reflux esophagitis is a disease in which the contents of the stomach return to the esophagus, irritating its walls. This is due to dysfunction of the esophageal sphincter. This disease manifests itself as constant discomfort, a burning sensation in the esophagus, and pain in the epigastric region.
The absence of any manifestations other than heartburn and heaviness is characteristic of a diaphragmatic hernia . This is a pathology in which the cardia of the stomach and the abdominal part of the esophagus enter the chest through the enlarged opening of the diaphragm. There are fixed and wandering types of the disease.
A stomach ulcer is a serious disease in which the mucous and submucous membrane of the organ is severely damaged. The symptoms are extremely unpleasant. These include hunger pains, when the stomach begins to ache terribly after a certain time after eating.
Each disease can result in complications - bleeding, chronic pain, impaired peristalsis. To avoid the consequences, you will have to not only take medications, but also follow a diet, give up bad habits, and eliminate the influence of stress. Temporary conditions require a similar approach, because they appear for the same reasons as serious illnesses. The only difference is that the former can be quickly eliminated without consequences.
Traditional therapy
Folk remedies will also help in the fight against stomach pain:
- Cucumber juice can help get rid of cramping pain.
- Hot compresses can also relieve pain. To do this, you need to apply polyethylene over the compress, wrap the patient with a towel and dress him in something warm.
- St. John's wort tincture will help relieve regular stomach pain. To prepare it, take 0.5 liters of medical alcohol and pour 4 tablespoons into it. medicinal herbs and leave to infuse for 3 days.
- Plantain leaves will help relieve spasmodic pain in the stomach. To do this, simply chew them.
- A mixture of tomato juice and honey can significantly improve the digestion process and relieve stomach pain.
- Taking chamomile decoction will help eliminate stomach cramps and relieve inflammation.
- You can get rid of stomach irritation with flaxseeds. This remedy helps cure stomach ulcers, colitis and other organ pathologies that cause pain.
Everyone, without exception, knows that the digestive system requires attention and careful treatment. After all, if any pathology is allowed to develop, treatment will cause a lot of difficulties. That is why preventive measures will help maintain health for many years. It is necessary to visit your doctor regularly for preventive examinations. Early diagnosis of pathology, if present, will provide a high chance of successful treatment. And don’t neglect the process of eating. Food must be taken regularly and without haste.
The stomach is a section of the digestive tract, a temporary “storage” for food, located in the upper part of the abdominal cavity. It plays an important role in the human body; primary processing of food that enters through the esophagus occurs here. Gastralgia has a different character: dull and sharp, there may be a feeling of heaviness or pressing pain in the stomach. If discomfort spreads to other organs, accompanied by fever, nausea, diarrhea, fainting, this may indicate a serious illness, you must call an ambulance.
Sometimes heaviness occurs from excessive consumption of food or dry food. In such cases, it is worth determining the frequency of gastralgia and starting to follow a diet. If you experience any discomfort, you should consult a doctor. Early diagnosis will help avoid serious consequences.
What is the stomach and why does it hurt?
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ of the digestive system. In general, it looks like a bag, the walls of which consist of a large number of muscle fibers. The inner wall is lined with mucous membrane. The stomach is a plastic organ and is capable of stretching to large sizes when food enters it.
When food enters the stomach, gastric juice is released, which consists of pepsin, hydrochloric acid, chymosin and other enzymes. In addition, the stomach also produces the required amount of mucus, which performs a protective function. Pain in the stomach when eating food is called “gastralgia” in medical language. This is a feeling of varying degrees of discomfort in the stomach area. The patient usually points to the upper abdomen: above the navel, between the hypochondrium - this is the so-called epigastric region. Pain in it can be a manifestation of gastric pathologies, stressful situations, or as an additional sign of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Causes of pain
Gastralgia can occur due to disruption of the gastrointestinal tract, and also signal the presence of diseases of other organs. Sometimes a feeling of pressure can appear in completely healthy people, which indicates a disorder in the person’s diet, routine or lifestyle. If heaviness occurs immediately after eating and goes away quickly, the cause may be overeating. If the feeling of squeezing is not associated with eating or is constant, you should consult a doctor.
Causes of heaviness in the stomach
Compressive pain is not always a symptom of a serious illness. Sometimes the body reacts to external stimuli. If compression occurs infrequently and goes away quickly, it may be caused by:
- Allergic reaction;
- Osteochondrosis;
- Pregnancy, especially in the third trimester;
- Violation of intestinal microflora due to taking antibiotics;
- Physical activity;
- Spasm of the diaphragm.
Severe stress, depression, or driving fast can cause oppressive sensations. In these cases, epigastralgia is an additional symptom that should be paid attention to. If the severity is not associated with the listed conditions, you need to contact a gastroenterologist and conduct an examination of this organ.
Serious violations
- Diseases and infections of the respiratory tract: pneumonia, sore throat, acute respiratory infections.
- Damage to the gastric mucosa.
- Gastritis, gastroduodenitis.
- Functional disorders of internal organs.
- Poisoning.
- Polyps.
- Cancer, stomach ulcer.
- Pancreatitis.
- Pathologies of the large and small intestines.
These diseases provoke severe pain, heaviness, and discomfort.
Localization and nature of pain
Depending on where the pain occurs and what nature it is, you can understand the probable disease. The abdomen and stomach may hurt after eating, during the day or at night, on an empty stomach or after eating a large meal. An important principle is to understand what the syndrome indicates, consult a doctor in time and prevent critical consequences.
Pain after eating
The appearance of heaviness after eating may indicate serious functional disorders. After taking antibiotics, the so-called “lazy stomach” syndrome occurs; it indicates a lack of enzymes necessary for digesting food.
- Binge eating. Food entering inside puts pressure on the walls, resulting in heaviness. In the absence of illness, this sensation should go away soon after eating.
- Lactose intolerance.
- Insufficient fluid.
- Large amount of protein.
- Poor nutrition.
By the nature and location of pain symptoms, a disease or pathology can be determined. Unpleasant sensations may occur in the epigastrium after eating.
Stomach pain may indicate:
- Esophageal stenosis is a narrowing of the lumen of the esophagus. Associated symptoms: nausea, vomiting, belching.
- Gastritis is inflammation of the mucous membrane.
- Ulcer. In advanced cases, surgical intervention is required.
- Obstruction is the obstruction of food between the stomach and duodenum.
- Esophageal hernia.
Abdominal pain may be a symptom of:
- Colitis.
- Esophageal ulcers.
- Urolithiasis.
- Cholecystitis.
- Pancreatitis.
- Inflammation of the esophageal mucosa.
- Irritable bowel syndrome.
Pain on an empty stomach
Pain on an empty stomach occurs due to irritation of the stomach walls. Gastric juice helps process food entering the body; in the absence of food, acidity increases and a painful sensation occurs. With a peptic ulcer, the sensation intensifies. On an empty stomach, pain manifests itself with gastritis, hypermotor dyskinesia, when a spasm occurs and the wall contracts, causing discomfort. Rarely during stress reactions.
Stomach pain radiates to the back
In some cases, after eating, and less often on an empty stomach, your back begins to hurt. Pain can be felt in the lower back with gastritis, ulcers, acute pancreatitis and hepatic colic. In this case, the localization will be different. A pulling sensation in the lower back indicates an exacerbation of the ulcer; with pancreatitis, it radiates to the lower back and scapular region. If pain radiates to your back, this is a reason to consult a doctor. In some cases, emergency assistance is required.
Relationship between epigastric pain and food intake
Early pain is usually associated with stomach pathology. They occur soon after eating (30-60 minutes), last 1-1.5 hours, and decrease as the contents are evacuated from the stomach. Characteristic for stomach diseases. Late pain – occurs 1.5-3 hours after eating. Characteristic for diseases of the duodenum. Hunger pain and night pain - relieved after eating, typical for duodenal diseases.
When abdominal pain appears, pay attention to the period of time after which it began:
- immediately after eating: possible neuro-functional disruption of the digestive tract;
- within 1 hour after eating: inflammatory processes in the stomach, acute form of gastritis or exacerbation of a chronic disease;
- 3-4 hours after eating: damage to the pancreas, gall bladder or small intestine;
- 4-6 hours after eating: chronic diseases of the large intestine.
Pain in the epigastrium after eating after 1.5-2 hours
Stomach ulcer – pain intensity can vary, from low to high. Pain may occur in the epigastrium some time after eating (1-1.5 hours) or on an empty stomach.
Unbalanced diet, consumption of low-quality products, abuse of sweets and fast food can lead to abdominal pain after eating
If stomach pain occurs immediately after eating or 1-1.5 hours after eating, this may indicate the possible presence of a peptic ulcer. The appearance of pain in the stomach 2-3 hours after eating may indicate the location of the ulcer in the duodenum. Pain in the stomach on an empty stomach and night pain may be associated with the same problem.
Also, during an exacerbation of gastritis, patients complain of a dull pain in the upper and middle abdomen, which occurs 1.5-2 hours after eating. Sometimes it is an acute, cramping or aching pain, a feeling of heaviness, a feeling of fullness in the epigastric region.
Epigastric pain after eating 4 hours
An unbalanced diet, consumption of low-quality foods, abuse of sweets and fast food can lead to abdominal pain after eating. Late pain occurs 1.5-3 hours after eating (increasing as acidic gastric contents enter the duodenum) and is regarded as a characteristic sign of duodenitis, as well as astral, pyloric and duodenal ulcers. These patients may experience “hunger” pain that appears 6-7 hours after eating and disappears after eating.
Night pains are most often observed with peptic ulcers, they occur between 11 pm and 3 am, are close in origin to “hunger” pains and also usually disappear after taking a small amount of food (crackers, sugar, milk) or even a few sips of water.
What to do for stomach pain
When the stomach hurts, a person experiences internal discomfort. Treatment depends on the disease, which can only be identified after a medical examination and consultation with a specialist. To relieve pain, take medications that reduce spasms: No-shpa, Spazmalgon. If the cause is an incorrect diet, medications that block gastric enzymes and have enveloping properties can help: Omez, Almagel.
During pregnancy, spasmodic pain in the abdomen may indicate that contractions are beginning, in which case you need to call an ambulance. If the severity is accompanied by fever, nausea, and poor health, the woman needs an urgent medical examination and consultation with a doctor.
At home, decoctions of chamomile, yarrow, mint, and flax seeds are used for calming. These substances have a calming effect and help relieve spasms.
Regardless of the cause of the discomfort, it is recommended to follow a diet to relieve symptoms and prevent the condition from getting worse. A proper diet will allow you to more accurately determine the need to see a doctor. In case of exacerbation of pain caused by poor nutrition, it is advisable to refrain from eating for at least one day, the body will “rest”. After a hunger strike, you need to gradually expand your diet, starting with soft foods: cottage cheese, yogurt, low-fat sour cream. It is advisable to exclude fried, spicy, smoked foods. Replace meat with steamed fish. Vegetables should be treated with caution; some aggressive substances contained in citrus fruits and other fruits and vegetables can be dangerous.
Diagnosis of stomach diseases
A thorough examination helps to identify a functional imbalance in the body; based on these tests, the doctor prescribes medication; in critical situations, treatment may require surgical intervention.
Procedures necessary for an accurate diagnosis:
- Ultrasound;
- Gastroscopy;
- Analysis of urine, feces, gastric juice;
- X-ray.
After medical procedures, a final diagnosis is made and treatment is prescribed.
Recommendations for the prevention of stomach diseases
Serious diseases are the result of a complex of factors affecting human health. External and internal irritants negatively affect the condition of internal organs. Much depends on a person’s lifestyle, habits, nutrition, and habitat.
To prevent serious diseases, it is recommended to follow simple rules that will help avoid problems in the future:
- The first rule is proper nutrition. Healthy food, fresh foods, and a reduction in fried, spicy, and smoked foods in the diet will help the body cope better with processing food.
- The second rule is diet. Overeating at night, large amounts of food increase the load on the stomach, leading to heaviness and unpleasant sensations. The last meal should be a few hours before bedtime, this will help digest food while the digestive organs are in the active phase.
- Proper consumption of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, balanced dosage.
- When taking antibiotics, take supplements that help improve intestinal microflora.
The stomach is a sensitive organ of the human body, acutely reacting to external and internal changes. Malnutrition, stress, diseases of adjacent internal organs affect his condition. If gastralgia is periodic, you should consult a specialist. Preventing diseases in the early stages will help prevent serious consequences and maintain health.
If your stomach constantly hurts after eating, you should seek help from a doctor. Treatment is prescribed after determining the cause of this condition. Pain syndrome can appear immediately after eating or 2-3 hours after eating.
Medical indications
Stomach pain after eating can be strong, intense, weak or moderate. At the same time, the patient may experience the following symptoms:
- belching;
- bloating;
- bubbling;
- nausea;
- poor appetite;
- After eating, your stomach hurts and diarrhea or constipation appears.
Severe and acute pain can occur after eating expired food, food poisoning, or appendicitis. Treatment is prescribed after determining the cause of abdominal pain after eating.
Burning pain syndrome is caused by eating spicy and salty foods. A similar symptom occurs during exacerbation of gastritis and pancreatitis. Treatment of the disease consists of taking antispasmodics and following a diet.
If you experience persistent abdominal pain after eating, you will need immediate medical attention. This symptom manifests itself against the background of various gastrointestinal diseases. If the syndrome in question is permanent, then it is recommended to follow a special diet. If necessary, complex treatment is carried out. Real pain in the stomach after eating is localized in the hypochondrium and iliac region. Often she can give it to the back. Treatment of the disease is prescribed taking into account the location and cause of the pain syndrome.
If there is pain in the stomach after eating and around the navel, then you will need to examine the duodenal mucosa. With cholelithiasis, pain in the stomach after eating spreads to the right hypochondrium. A similar symptom appears after eating fatty, fried and sweet foods.
Feeling of a lump in the stomach
Gastritis
33297 August 21
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Feeling of a lump in the stomach: causes of occurrence, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods.
The feeling of a coma in the stomach is described when one experiences a feeling of heaviness, discomfort and fullness in the stomach, even when it is only slightly filled. Sometimes patients find it difficult to determine the exact location of the coma and point to the lower third of the sternum or solar plexus. In some cases, a feeling of a lump and cramps in the stomach may occur on an empty stomach.
Types of feeling of a coma in the stomach
A feeling of heaviness or coma in the stomach can be an independent symptom, but may be accompanied by other unpleasant sensations. Sometimes it is heartburn, sour belching, bloating, constipation.
In some cases, a feeling of a lump appears when swallowing
, making it difficult for chewed food to pass through.
In addition, patients may complain that food did not enter the stomach, but stopped in the esophagus.
In such patients, vomiting of unchanged food is possible. When describing symptoms, you should pay attention to the time of onset of discomfort - before
or
after eating
.
The patient may feel heaviness in the stomach with pain or heartburn, on an empty stomach or after eating, and night pain also occurs.
Sometimes the sensation of a lump in the stomach occurs
regardless of food intake
.
In such cases, they complain of stomach spasms
, sometimes accompanied by a feeling of a lump in the throat.
What diseases cause a sensation of a lump in the stomach?
Eating more than your usual amount of food
, accompanied by a feeling of fullness and heaviness in the stomach. This condition is not a manifestation of the disease and goes away on its own after some time.
It should be noted that stomach capacity varies depending on eating habits.
People who are small or
have undergone gastric resection
can eat a small portion, otherwise they will not only experience a feeling of heaviness or fullness in the stomach, but also vomiting.
A sensation of coma may occur when consuming foods that cause excess gas.
, as well as
food that is difficult to digest
(salads with mayonnaise, fatty, fried and smoked dishes) and
highly carbonated drinks
.
When eating dry and hastily,
an unpleasant sensation in the epigastric region is caused by poor processing of the food bolus with saliva and insufficient secretion of gastric juice.
However, a feeling of coma or discomfort in the stomach, or more precisely, in the epigastric region, may appear after eating even a small amount of food
.
This condition can be caused by diseases of the gastrointestinal tract or other reasons.
First of all, they assume indigestion, or functional dyspepsia. Its symptoms most often include pain and discomfort immediately after eating, a feeling of heaviness and fullness in the stomach, heartburn, belching, nausea, sometimes vomiting, reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus, bloating and bowel dysfunction.
Dyspepsia can be a symptom of both functional disorders of the gastrointestinal tract and organic diseases.
Functional causes of dyspepsia are often caused by errors in diet and medications.
Iron ions have an irritating effect on the gastric mucosa, which is most pronounced when taking medications based on ferrous iron. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, which are systematically taken for rheumatic and non-rheumatic diseases of the musculoskeletal system, also cause undesirable effects: heaviness and discomfort in the stomach, nausea, vomiting, and dyspeptic disorders.
Neurological disorders
(neuroses, depression), psychological trauma almost always affects the state of the gastrointestinal tract, leading to impaired motility.
Functional dyspepsia is not accompanied by erosive or ulcerative lesions of the stomach; its symptoms disappear when the general state of health is normalized.
One of the common causes of discomfort in the stomach immediately after eating is
gastritis
. It is accompanied by functional and inflammatory processes that have a negative effect on the gastric mucosa. Symptoms of gastritis include heaviness and pain in the stomach, indigestion, nausea, heartburn, sour belching and bloating when eating any food. The inflammatory process leads to atrophy of the mucous membrane and disruption of the glands that secrete gastric juice.
Insufficient gastric juice and weak peristalsis of the stomach and intestines make it difficult to digest food.
Gastritis is often accompanied by dyspepsia. In addition to a feeling of heaviness and aching pain in the epigastric region after eating, poor appetite, weakness, fatigue, and irritability are noted. When pressing on the abdomen, a dull pain appears in the projection of the stomach.
Impaired motor-evacuation functions
upper digestive tract is always accompanied by a feeling of coma or a feeling of heaviness in the stomach. Disorders of esophageal motility are usually caused by incoordination of the esophageal sphincters. Uncoordinated work of the esophageal muscles can lead to a delay in the bolus of food on the way to the stomach, the reflux of food particles into the respiratory tract, and reflux (return of stomach contents into the esophagus). Impaired gastric motility leads to slow emptying, which is accompanied by a feeling of heaviness and fullness even with a small amount of food consumed, pain in the epigastric region, heartburn, nausea and vomiting.
Motility disorders of the esophagus and stomach may be associated with gastroesophageal reflux disease, gastritis, tumors and stenoses (narrowings), metabolic disorders (hyperkalemia, hypercalcemia), postoperative complications of gastrectomy, taking certain medications (opiates, antidepressants, hormones), alcohol and nicotine .
Peristalsis worsens with a sedentary lifestyle and with age.
Stomach cancer can also cause symptoms such as a feeling of heaviness or a lump in the stomach. Moreover, depending on the location of the tumor, its manifestations vary. If the tumor is located closer to the esophagus, problems with swallowing food occur. This is accompanied by increased salivation, nausea, vomiting, and pain in the epigastric region. When the tumor is localized in the lower parts of the stomach, closer to the duodenum, a prolonged feeling of heaviness after eating and bloating is characteristic. When burping, a putrid odor may be felt.
Which doctors should you contact if you feel a lump in your stomach?
If there is a constant feeling of a lump in the stomach or a feeling of heaviness, it is necessary to contact or to make a preliminary diagnosis. The gastroenterologist may also refer the patient to an oncologist. A consultation may also be required.
Diagnosis and examination if you feel a lump in the stomach
First of all, clinical blood and stool tests are necessary for differential diagnosis.
Establishing diagnosis
Why your stomach hurts after eating needs to be found out before taking medication. You cannot self-medicate. A similar symptom manifests itself as a result of increased secretion of gastric juice or spasm of the stomach walls. Doctors identify the following causes of pain:
- Binge eating. Eating a large amount of food helps to stretch the walls of the stomach, which leads to pain. At the same time, the patient feels nauseous. To eliminate abdominal pain after eating, it is recommended to adjust your diet and take enzymes (Mezim, Pancreatin);
- Diaphragmatic hernia. As a result of the enlargement of the hole located in the front part of the body, prolapse and strangulation of the upper part of the stomach is observed. Hernia is treated surgically.
The stomach may hurt after eating due to pyloric spasm. The cause of this condition is pathology and dysfunction of the nervous system. Abdominal pain after eating appears within 15-20 minutes. The above-described symptoms cease after complete elimination of its contents from the stomach. Treatment of the disease consists of taking antispasmodics and drugs that affect the functioning of the nervous system.
Stomach pain after eating can occur due to esophageal stenosis. This condition occurs as a result of injury, tumor, or the presence of a foreign body in a given organ. The patient may experience nausea and vomiting. The patient must follow a liquid diet. Pain in the stomach after eating can occur as a result of severe spasm of the walls of this organ. Doctors include exhaustion of the body as the consequences of obstruction.
How does abdominal discomfort occur after eating?
Many associate discomfort after eating with the stomach. But if you look at it, it turns out that the main processes of food digestion take place in the intestines. Of course, it is important what we eat, how we chew food, but in the end the “conductor of digestion” is the pancreas. It is she who produces special digestive enzymes, which in the intestines break down food (proteins, fats and carbohydrates) into simpler elements, helping the body digest and absorb it.
If for some reason there are not enough enzymes, then after eating you may experience discomfort, heaviness, bloating, and flatulence.
Symptoms of the disease
After eating, the stomach enlarges, squeezing the inflamed gallbladder. This leads to pain. Treatment of the gallbladder should be prescribed by a qualified specialist. Abdominal pain can occur due to food intolerance. A similar reaction occurs to dairy and fish products. The patient is advised to follow a diet and take special enzymes that stimulate the processing of intolerant components.
If abdominal pain occurs 2-3 hours after eating, then you need to remember your diet. To speed up the process of removing toxins from the body, sorbents such as activated carbon and Enterosgel are taken. To relieve symptoms, Smecta and other drugs that improve digestion are prescribed. The gastric gland, located near the stomach, can become inflamed. In this case, the patient exhibits the following symptoms:
- cutting pain 20-40 minutes after eating;
- pain in the middle and right hypochondrium.
In severe cases of pancreatitis, a girdling pain syndrome occurs. Doctors include infectious process, trauma, and problems with the duodenum as the reasons for the development of the disease. Treatment of pancreatitis consists of following a gentle diet and taking anti-inflammatory drugs.
Abdominal pain can be caused by gastroduodenitis. The disease develops against the background of poor nutrition. Treatment of gastroduodenitis involves following a diet, taking antacids, sedatives and drugs that reduce the acidity of gastric juice. The drugs must be prescribed by a doctor.
The causes of abdominal pain may be associated with a stomach or duodenal ulcer. The wound surface can form on the stomach or duodenum. Aggressive food and acidic gastric juice, getting into problem areas, provoke pain. Treatment of ulcers is carried out by following a gentle diet and taking special medications.
Preventive measures
The mucous membrane of the stomach can become inflamed due to the bacteria Helicobacter pylori. Rarely, the disease develops due to poor nutrition. If your stomach hurts, treatment for gastritis involves taking antibacterial drugs and following a diet. Doctors advise excluding spicy, fatty, sour, flour and smoked foods from the menu.
With overeating and poor nutrition (dry food), abdominal pain appears rarely and is short-term. To eliminate symptoms, it is recommended to normalize your food intake:
- fractional meals in small portions;
- dinner no later than 3 hours before bedtime;
- exclude heavy foods from intake;
- The liquid is consumed before meals or in between meals.
If the pain syndrome is constant or acute, then the patient’s body temperature may increase and digestion may be impaired. In this case, it is recommended to immediately seek help from a doctor. The disease is life-threatening for the patient, so self-medication is not recommended. In acute cases of pain, doctors advise refusing food and drinking clean water. The patient should urgently make an appointment with a gastroenterologist.
Prevention of abdominal pain involves following the following recommendations:
- you can’t overeat;
- you need to eat often and in small portions;
- it is necessary to consume only fresh and high-quality products;
- fatty, spicy, smoked, pickled and salty foods are excluded from the diet;
- It is recommended to give up fast food and processed foods;
- Do not abuse alcohol or smoke.
Regular visits to a gastroenterologist will allow you to promptly identify the disease and prescribe effective treatment.
Pain in the stomach can be of different types, depending on the causes of its occurrence. Drawing, paroxysmal, sharp, sharp pains bring discomfort. In any case, pain is an unpleasant condition and should not be tolerated.
Stomach hurts very badly, first aid
Stomach pain can be of various types.
The stomach can be susceptible to diseases and pain in two cases:
- consumption of a lot of fatty, spicy, sweet foods, rapid chewing and swallowing;
- the influence of negative emotions, stress, fear, anger.
Often there is pain in the stomach after eating, neuroses, due to some diseases. Before you begin measures to relieve pain, you need to find out the cause of its occurrence.
Pain in the stomach, first aid for pain in the stomach, you need to wait, listen to the sensations. There is nothing to eat. Lie in bed with your feet higher than your head. Relax, drink ice water or warm mint tea.
Mint relaxes the stomach muscles and helps relieve muscle spasms. Chew fresh dandelion leaves. Drink chicken broth, do not eat dairy products. If pain persists for several hours, you should consult a doctor. There may be several reasons for stomach pain:
- Alcohol, nicotine, stress. These factors increase the production of gastric juice, which, in turn, corrodes the gastric mucosa.
- Fatty food. Food enzymes cannot cope with the breakdown of such food, resulting in bloating, heaviness, and pain.
- Consumption of caffeine, which is found in coffee, tea, and cocoa. It also irritates the stomach and stimulates the production of gastric juice.
Taking aspirin tablets can affect the inner surface of the stomach, even causing bleeding. What diseases cause stomach pain? Diseases that affect the occurrence of pain in the stomach are as follows:
- peptic ulcer;
- obstruction in the intestines;
- attack of appendicitis;
- duodenitis;
- internal hernia that impinges on organs;
- gastritis;
- Kalitis of chronic form;
- enteritis of a chronic nature;
- pancreatitis, cholecystitis in acute form;
- irritable bowel syndrome;
- hunger;
- dyspepsia.
Stomach pain can occur in pregnant women. The growing uterus puts pressure on neighboring organs and causes pain. You can drink a decoction of a mixture of yarrow herb, St. John's wort and chamomile. First put it in boiling water and let it brew for about three hours.
If a woman in labor has low acidity or gastritis, then they drink mineral water - “Borjomi”, “Essentuki”. To eliminate nervous disorders and stomach pain after them, take sedatives - motherwort, valerian.
Stomach hurts very badly, pain after eating. The pain occurs during the day and at night. Night pain syndrome is associated with gastritis. Since during the day the pain subsides when eating, but at night the gastric mucosa becomes very irritated. This causes unbearable pain.
Short-term use of painkillers: Almagel, phosphalugel, Maalox, only relieves the attack, but its causes remain. You need to see a doctor to find out.
How to help digestion?
To compensate for the lack of digestive enzymes of the pancreas, pancreatin enzyme preparations can be used. They help improve food digestion. Helping with fat digestion is especially important. The required enzyme for this is lipase, which is produced only by the pancreas. At other stages of digestion, except for the intestines, it is simply not there2. Therefore, when choosing an enzyme preparation, its quantity is so important. How to figure it out?
The most common and familiar drug for improving digestion is pancreatin in tablet form3. Pancreatin is the active ingredient of an enzyme preparation to improve digestion, but this does not mean that pancreatin preparations are all the same.
Since we started with the lipase content in the drug, it is worth noting that tablet forms of pancreatin can contain from 25 units (IU) of lipase. There are a number of drugs in which this amount may be higher: 3500–4500 IU of lipase. The optimal amount of lipase that should be contained in an enzyme preparation in case of dietary errors is recognized to be 10,000 units4.
But the most important thing in choosing a drug is not even the amount of lipase. The defining property is the release form5,6.
Studying the necessary conditions for the effective operation of the enzyme preparation, scientists came to the conclusion: the preparation must have small particles of the active substance. And the size of these particles should not exceed 2 mm5,6.
The tablet form is recognized as the least effective for an enzyme preparation, since it does not allow the drug to work physiologically6,7, which means to precisely integrate into an already working system and get to where the enzymes work in natural conditions.
Pain after eating
Stomach pain after eating can be very sharp and severe.
Painful sensations that appear after eating can be strong, sharp, sharp. They are accompanied by the following accompanying symptoms:
- bitter taste in the mouth and sour belching;
- feeling of fullness, bloating;
- sounds of rumbling and seething;
- feeling of nausea and gag reflex;
- decreased appetite;
- digestive disorders: diarrhea, constipation, diarrhea, gas formation.
The reasons for stomach pain are as follows:
- Binge eating. This has a bad effect on the gastrointestinal tract. The digestive organ cannot digest such an amount of food and becomes stretched. Normally, you need to eat in small portions and often so that the stomach can digest the food.
- Irritable bowel syndrome. A condition when, after eating spicy, salty, very fatty foods and smoked foods, a burning sensation and discomfort are felt. To normalize this condition, it is enough to observe moderation in food and eat healthy food. Eat on time, without snacking on the run.
- Diaphragmatic hernia. This is when part of the stomach becomes strangulated or prolapses into the abdominal or chest cavity. It is treated surgically.
- Pyloraspasm is a spasmodic condition of the gastric region at the junction with the intestine. Appears when there is a malfunction of the nervous system. The spasms end with a feeling of nausea and a gag reflex.
- Gastric stenosis. Often there are organ injuries as a result of a foreign object or the growth of cancerous tumors. Drink liquid food during attacks.
- Obstruction of the stomach. This is a blockage of the stomach lumen due to a cancerous tumor or overgrown internal polyps. Food does not travel through a certain area that is blocked, causing severe pain.
- Inflammation of the gallbladder or cholelithiasis. After a portion of food, the stomach stretches and puts pressure on the inflamed gallbladder, causing pain.
- Allergic reaction to certain foods. The stomach refuses to accept these foods and digest them. For example, milk, fish.
- Poisoning. After taking low-quality products, pain occurs within several hours. You need to take activated carbon tablets.
What recommendations should you follow to avoid stomach pain:
- do not eat a lot of food at one time;
- eat food often and in small portions;
- Products must be checked for quality and freshness before cooking;
- exclude smoked, salted, pickled, spicy, and fatty foods;
- do not abuse alcohol and smoking;
- exclude dry snacks, do not eat on the go and cook from semi-finished products.
Pain due to gastritis, ulcers
Gastritis can cause pain in the abdominal area.
With gastritis, pain occurs immediately after eating food. The patient regurgitates and the taste in the mouth becomes unpleasant. Heartburn and a burning sensation appear. A person feels tired, tired, weakened.
The functioning of the cardiovascular system is often disrupted. There are pains in the heart. Pressure drops are observed. State of drowsiness, pale skin, sweating, which increases after eating. There is a burning sensation in the mouth.
With a peptic ulcer, the pain syndrome is intense. It appears two hours after eating. Seasonal exacerbations of the disease may occur - in spring and autumn. Sour belching occurs, after eating there is nausea and possibly vomiting.
The patient may lose weight. Acute pain is life-threatening. This indicates that undigested enzymes are thrown from the stomach into the abdominal cavity.
This video will tell you about the causes of pain and rumbling in the stomach:
Epigastric pain after taking
Most often, pain in the epigastrium is caused by diseases of the intestines, stomach, pancreas, problems with the gallbladder, as well as hernias.
The most common disease in which epigastric pain occurs after eating food is pancreatitis . When the pancreas is inflamed, a person feels severe discomfort in the epigastric region (upper abdomen), and it becomes difficult for the body to digest proteins and fats.
Some of the most common diseases that affect people of all ages are accompanied by pain in the epigastrium - these are pathologies of the stomach, especially its mucous membrane. The leaders are gastritis, ulcers, gastroesophageal reflux disease. Often epigastric pain is caused by peritoneal hernias. Also, epigastric pain can be associated with diseases of the gallbladder and bile ducts.
Intense pain in the epigastrium (upper abdomen), which subsides after a couple of days but remains constant, is a fairly characteristic symptom of pathologies of the large intestine, in particular colitis.
Polyps and other causes
If there are polyps in the stomach, the pain is dull, aching, intensifies during palpation of the area of the diseased organ, there is a feeling of nausea and the urge to vomit.
Pain appears due to cancerous tumors. If the tumor is the first stage, the patient loses weight, as the feeling of hunger decreases, he quickly fills up. Loss of appetite, aversion to food, and anemia may develop. In the later stages of cancer, there may be bleeding, vomiting blood, and the stool turns dark.
Poisoning with substances or products also causes pain in the stomach, it is acute, the patient feels sick and vomits. Signs of poisoning appear several hours after eating and depend on the substance with which the person was poisoned.
Dizziness and loss of consciousness appear. The feeling of pain in the stomach occurs after physical exertion and nervous shock. In constant stressful situations, gastritis and ulcers may develop. If pain is localized in the upper abdomen, then this is an attack of pancreatitis.
Girdle pain radiates to the back. The abdomen is tense and painful, a rise in temperature and increased heart rate are possible. When duodenitis occurs, the small intestine is affected, which also causes dull and aching pain, and the stomach is bursting with a feeling of heaviness.
When the diaphragm spasms, blood circulation is disrupted. The pain is sharp and acute when changing body position or deep breathing. Pain may occur due to chronic colitis.
It manifests itself due to heredity, chronic stress or allergies. Children may experience pain associated with fear and fear of school and teachers.
Causes
Unpleasant sensations in the stomach appear as a result of digestive disorders, which is caused by a deterioration in the depository, motor, secretory, evacuation, excretory, absorption, endocrine or protective functions.
Secretion disorder
With secretory dysfunction, a qualitative or quantitative change in gastric juice occurs, which disrupts its ability to digest food. If the amount of gastric juice secreted differs from normal, then they speak of hyposecretion or hypersecretion.
These disorders are not always a consequence of a stomach disease; in some cases, the cause is a deterioration in the functioning of the nervous, urinary or endocrine systems. Qualitative changes are manifested in the concentration of hydrochloric acid (probably a decrease, increase and absence of hydrochloric acid).
With hypersecretion, a lot of hydrochloric acid and pepsinogens are released, which leads to an increase in the digestive ability of the juice. The pathology develops against the background of the use of certain medications (glucocorticoids, salicylates) and gastrointestinal pathologies (peptic ulcer, hypertrophic and erosive gastritis).
With hypersecretion, acid is present in the stomach even in the morning on an empty stomach, although normally only traces of it should be detected. The disorder manifests itself as pain in the upper abdomen, heartburn, sour belching, a feeling of pressure and fullness, vomiting, nausea, worsening evacuation of chyme into the intestines (after eating, discomfort in the stomach lasts a long time).
With hyposecretion, the production of gastric juice and pepsinogen is reduced or absent, so food is digested slowly or not at all. Pathology develops with anorexia, chronic infectious-toxic processes, tumors in the stomach, atrophic gastritis, lack of vitamins (C, E, B), as well as electrolytes, water or complete proteins.
Hyposecretion is clinically manifested by dyspeptic symptoms, decreased digestion speed and deterioration of gastric motility, increased fermentation and putrefaction, dysbacteriosis, and diarrhea.
Motor dysfunction
When gastric motility is impaired, peristalsis and muscle tone of the organ changes, the evacuation of chyme is disrupted, which is why heartburn, vomiting, belching, and pylorospasm occur. With hypertonicity, pain appears in the epigastric region, increased peristalsis of the stomach, the contents of the organ move more slowly into the small intestine, which leads to frequent sour belches and vomiting.
Hypotonia develops against the background of stress, infections, neuroses, hypoacidity or pain. It manifests itself as heaviness and a feeling of fullness in the area of the xiphoid process, nausea, since rotting and fermentation in the stomach is increased due to the weak evacuation ability.
Hyperkinesis (excessive physical activity), among other things, is provoked by rough, plentiful food rich in cellulose and proteins, and alcohol. On the contrary, hypokinesis (lack of motor activity) of the stomach occurs if a person eats delicate foods for a long time, poor in fiber, vitamins and proteins, but rich in carbohydrates and fats, and also if he drinks a lot of water before and after meals.
Hypertonicity and hyperkinesis of the stomach often causes pylorospasm, vomiting and nausea. Hypotonicity of the esophageal sphincter leads to belching; if the activity of the stomach muscles is increased, then severe heartburn appears.
Enzyme deficiency
Enzyme deficiency occurs due to limited secretion or insufficient activity of pancreatic enzymes, which leads to impaired breakdown and absorption of nutrients.
The pathology can be primary (the pancreas is affected, causing its exocrine function to be impaired) and secondary (enzymes are synthesized, but are inactivated or not activated in the small intestine). The disease is manifested by increased gas formation, anemia, steatorrhea, diarrhea, lack of vitamins, and progressive weight loss.
Against the background of impaired gastric motility, nausea, heartburn, vomiting, and a feeling of fullness of the organ occur.
Due to a lack of lactase, lactase deficiency develops. During the disease, milk sugar (lactose) is not broken down, that is, milk and products made from it are not digested. Lactose must be broken down in the small intestine and converted into glucose and galactose, which can enter the bloodstream.
With lactase deficiency, milk sugar cannot be broken down, which means it penetrates into the large intestine, where it begins to ferment, which causes increased acidity, excessive gas formation and water secretion. In addition to abdominal discomfort, after drinking milk, patients complain of diarrhea or constipation, flatulence, and sleep disturbance.
With a deficiency of the enzyme that breaks down gluten, celiac disease develops, which is characterized by chronic inflammation of the small intestinal mucosa and impaired absorption function. Gluten contains a substance that is toxic to the intestinal mucosa and causes its atrophy. Celiac disease provokes the occurrence of diarrhea, steatorrhea, and polyhypovitaminosis.
Discomfort in the stomach appears after eating foods containing gluten (bread made from wheat, barley, oat, rye flour, pasta, semolina, beer, kvass; traces of gluten are found in chocolate, ice cream, cocoa, instant coffee, sausages, sausages, canned food ).
Enzyme deficiency can be diagnosed in childhood, but can also manifest itself in an adult. For example, a decrease in lactase levels begins as early as 3-5 years, so some people already in adulthood find that after drinking milk, which they previously tolerated well, abdominal discomfort begins.
Poor nutrition
Often the cause of stomach discomfort is the lack of a meal schedule, overeating and eating unhealthy foods. If you skip meals for a long time or even periodically, and then eat your fill, if you give preference to fatty, fried, spicy foods, if you combine incompatible foods, then it is difficult for the stomach to digest food due to the inability to synthesize the required amount of gastric juice and enzymes.
As a result, food does not leave the stomach for a long time and begins to ferment, causing bloating, belching, and nausea.
If gas formation in the stomach is increased, the air causes the walls of the organ to expand, and this causes discomfort.
When creating a menu, it is also necessary to take into account the compatibility of products, since different products require different enzymes and different amounts of gastric juice. Nutritionists identify six groups of substances (proteins, fats, carbohydrates, acids, sugars, starches), which behave differently when digested.
For example, an acidic environment is required for the breakdown of proteins, and an alkaline environment is required for carbohydrates, and if they simultaneously enter the stomach, the digestion of food slows down and discomfort in the stomach occurs. Long-term adherence to diets that limit the consumption of protein, fat or carbohydrates also has a negative impact on digestion.
For the normal functioning of the entire body, all these substances are required in a certain ratio. If you eat a lot of protein foods, rotting processes begin to actively occur in the stomach and intestines, putrefactive bacteria multiply, which are the cause of dysbiosis. When you eat predominantly carbohydrate foods, fermentation begins in the intestines. Fatty foods contribute to obesity.
Homemade recipes for stomach pain
Fresh cucumber juice is a folk remedy for stomach pain.
If the causes of a painful condition are known, you know all your chronic diseases, then during an exacerbation you can alleviate the condition with the help of folk remedies. There are time-tested recipes:
- You can relieve an attack of pain with fresh cucumber juice.
- Various compresses and a hot heating pad will help calm the stomach.
- St. John's wort tincture helps eliminate painful sensations. For 0.5 liters of alcohol, take four tablespoons and leave for three days.
- Severe pain is relieved by infusion of meadowsweet herb.
- The best pain reliever is considered to be an infusion of honeysuckle leaves and stems, which is made by steeping a tablespoon in a glass of boiling water for one hour.
- Cramps can be relieved by chewing plantain leaves.
- The composition of heated olive oil and honey has a good effect.
- Use elecampane and Cahors root. Take two tablespoons of the ingredients, mix and boil for ten minutes. The product is used for low acidity.
- If you have high acidity, you can relieve stomach pain with potato juice and honey. Add a tablespoon of honey to a glass of juice. Drink on an empty stomach. It also helps with heartburn and belching.
- Cabbage juice with honey helps relieve pain from stomach ulcers.
- Tomato juice with honey will help relieve pain and improve digestion.
- A decoction of calamus roots helps with pain and has antibacterial, tonic, and anti-inflammatory properties.
- Chamomile decoction reduces pain in the stomach.
- Stomach irritation is relieved by flaxseed decoction. The product helps with colitis and enteritis. There are many reasons for attacks of stomach pain. It is necessary to establish the correct diagnosis and the factors that provoked the attacks of pain with the help of a doctor. He will prescribe the correct, qualified treatment.