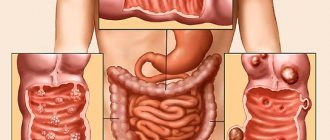
General information and classification
Most often, cancer develops in the sigmoid, cecum and ascending colon. Metastases usually spread with the bloodstream through the venous pathways, less often lymphogenously. The main directions of metastasis are the liver, lungs, and skeletal bones (lumbosacral spine).
According to the nature of tumor growth, colon cancer can be:
- Exophytic. The neoplasm is clearly demarcated from healthy areas of the mucosa and protrudes into the intestinal lumen. At the same time, the area of contact with the mucous membrane is small, the tumor is mobile and, even with a relatively large size, does not interfere with the movement of intestinal contents;
- Endophytic. The neoplasm grows in the thickness of the intestinal wall in all three directions and does not have clearly defined edges. It narrows the intestinal lumen over a relatively large area and, as it grows, disrupts the passage of contents;
- Transitional form.
In addition, experts classify colon cancer by cellular structure (the most common variant - up to 80% - is adenocarcinoma), degree of prevalence, involvement of lymph nodes in the process and the presence of distant metastases.
General symptoms
Symptoms of colon diseases increase gradually. At the initial stage they are not taken seriously, they are considered just a discomfort. Any pathology manifests itself:
- bowel dysfunction (diarrhea or constipation);
- the appearance of significant mucous secretions and blood in the stool;
- pain syndrome - the most typical are dull, aching pains in the lateral regions, in the anus, aggravated by defecation, after eating foods rich in fiber, milk, relief after completion of defecation and release of gases;
- bloating due to increased gas formation, constant rumbling;
- signs of neurasthenia, expressed in dependence of mood on stool, insomnia, irritability, tearfulness, depression.
In contrast to damage to the small intestine, patients do not experience weight loss, severe vitamin deficiencies, or signs of mineral imbalance.
Gradually, the symptoms of colon diseases become more pronounced. The discharge turns purulent, false urges (tenesmus) are added to the stool disorder, painful pressure is constantly felt in the anus, and involuntary passage of gas and feces is possible.
Adult patients experience increased fatigue and weakness, children grow poorly and do not gain weight. Often patients come to the surgeon with signs of intestinal obstruction. Diseases of the large intestine have their own characteristics. We will consider the most common pathology and functional disorders.
Causes of Colon Cancer
The exact causes leading to colon cancer have not yet been established. It is generally accepted that the main prerequisite for this disease is food preferences. A diet with a low content of plant fiber and other dietary fiber leads to a decrease in the volume of feces and a longer stay in the large intestine. Which, in turn, leads to longer contact of carcinogenic digestive products with the mucous membrane. In addition, under such conditions, the normal composition of the microbiome is disrupted in favor of bacteria, the metabolic products of which negatively affect the condition of the intestinal mucosa.
Conversely, a diet that constantly contains so-called “ballast” substances in abundance reduces the concentration of carcinogens, helps normalize the composition of microflora and regular bowel movements.
There are other predisposing factors:
- age: after 50 years of age, the likelihood of colorectal cancer doubles in each subsequent decade of life;
- excess body weight;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- adenomatous polyps of the colon: the likelihood of their malignancy is directly proportional to the size of the tumor;
- nonspecific ulcerative colitis, lasting more than 10 years;
- hereditary syndromes: diffuse familial polyposis, Lynch syndrome;
- previously suffered tumors of the breast, genitals.
How does changing the functions of the large intestine affect health?
It is believed that by the age of forty, a person’s large intestine is already heavily clogged with fecal stones. They are formed from fossilized unremoved wastes that get stuck between the folds of the mucous membrane. When surgeons remove part of the intestine, in 70% of cases they find foreign material in it, worms, stones that have accumulated over many years.
The normal width of the lumen of the ascending colon reaches 8 cm, and the sigmoid colon is 2 times narrower. The deformation causes significant stretching. In this case, compression and displacement of neighboring organs in the abdomen occurs. Accordingly, their work is disrupted. Temporary constipation occurs in everyone.
It has been established that fecal stones do not move for years, “stick” to their place, disrupt the nutrition of the wall, and contribute to the penetration of toxins into the bloodstream. As a result, colon diseases develop. They are caused by the main damaging factors:
- inflammatory - damage to the mucous membrane of the intestinal wall (colitis);
- varicose veins and hemorrhoids - venous congestion, compression, circulatory failure;
- proliferation of polyps and malignant transformation - long-term action of toxins on a specific site.
Fecal stones are “swept” out of the intestines when bran is added to food
All types of violations are divided into:
- functional - when there are clinical manifestations, but there are no organic changes in the intestines, they are considered reversible;
- organic - always accompanied by anatomical signs and disruption of the physiological mechanisms of digestion.
Colon Cancer Symptoms
Experts identify six sets of symptoms that characterize colorectal cancer.
Minor sign syndrome is a manifestation of tumor intoxication:
- unusual weakness;
- apathy;
- insomnia or, conversely, drowsiness;
- irritability;
- decreased appetite;
- bad breath.
Syndrome of functional signs without intestinal disorders. Usually these manifestations are regarded by doctors as signs of damage to other organs - the pancreas, stomach, bile ducts:
- abdominal pain, the location and intensity of which varies depending on the location of the tumor and its characteristics;
- nausea, belching, vomiting;
- heaviness in the stomach.
Syndrome of functional signs with intestinal disorders. These are manifestations of dysfunction of the colon itself:
- constipation, diarrhea and their alternation;
- copious, watery, foul-smelling stools;
- bloating;
- rumbling in the stomach.
Intestinal obstruction syndrome: stool and gas retention, bloating, abdominal pain and other signs of intestinal obstruction.
Pathological discharge syndrome is the appearance of mucus, pus, and blood in the stool. Usually characteristic of rectal cancer, but can also occur when the left half of the colon is affected.
Violation of the general condition of the patient. These signs usually appear at a late stage of the disease: unexplained weight loss, anemia, symptoms of damage to other organs.
Colonoscopy is the main method for diagnosing colon cancer
Colon diverticula
A diverticulum is a stretching of the intestinal wall with the formation of a “pocket” that protrudes into the abdominal cavity. The main risk factors for this pathology are chronic constipation and weak tone of the intestinal walls. The favorite localization of diverticula is the sigmoid and descending colon.
Uncomplicated diverticula may not cause any discomfort to the patient, except for the usual constipation and heaviness in the abdomen. But against the background of dysbacteriosis and stagnation of contents in the diverticulum cavity, inflammation can occur - diverticulitis.
Diverticulitis manifests itself acutely: abdominal pain, diarrhea with mucus and blood, high fever. With multiple diverticula and the inability to restore the tone of the intestinal wall, diverticulitis can become chronic. The diagnosis is made after an endoscopic examination of the colon and an x-ray.
Diverticulitis is treated with antibacterial drugs, and after the acute form is removed, beneficial microflora is introduced. Patients with uncomplicated diverticula are given proper nutrition to establish normal bowel movements and prevent constipation.
If persistent multiple diverticula have formed, long-term therapy with sulfasalicin and enzymatic agents is recommended to prevent their inflammation. If complications occur with signs of an “acute” abdomen, surgical intervention is performed.
Diagnosis of colon cancer
By palpating the abdomen, the doctor can detect a tumor-like formation, mobile or fused with surrounding tissues - this depends on the extent of the tumor.
You can indirectly assume the malignancy of a neoplasm after a stool occult blood test - any cancer of the gastrointestinal tract bleeds to one degree or another. Occult blood testing is often used as a screening method - quickly identifying patients with suspected neoplasms among large groups of people. After an in-depth examination of those who test positive for occult blood in the stool, colon cancer is detected in 5-10% of cases (glandular adenomas are found in 20-40% of cases, which are considered a precancerous condition).
Irrigography - an X-ray examination of the colon (with contrast) or colonoscopy - endoscopy of the large intestine will help to visualize the tumor. Colonoscopy allows not only to assess the condition of the mucous membrane of the large intestine, but also to take samples of tumor tissue for subsequent examination under a microscope (oncological diagnosis should always be confirmed histologically - after studying the structure of the cells).
Ultrasound examination allows you to assess the condition of other abdominal organs and lymph nodes in this area. Computed tomography is used to detect distant metastases.
To assess the patient’s general condition, clinical and biochemical blood tests, urine tests and other studies are prescribed.
On the role of microflora and dysbiosis
The important role of the large intestine in heat production (warming human blood) is rarely mentioned. Heat is generated by microflora. The intestinal loops are covered with a fat layer to preserve the energy of the “stove”. The produced beneficial substances help stimulate the immune system. Only E. coli produces 9 vitamins (including B1).
It has been proven that by eating 1000 kcal each from fruits, nuts, and vegetables, a person becomes much more resilient than by consuming 3000 kcal of boiled “dead” meat food. On the contrary, it takes energy and overloads the digestive tract.
People get tired quickly and feel cold. The problem of dysbiosis affects not only the functioning of the intestines, but also the general condition of the body. Poor nutrition affects it much more often than colon diseases.
Microflora for their own nutrition must receive “live” food, which includes mainly plant products
Inflammatory pathology
Inflammatory diseases of the large intestine (colitis) occur both when pathogenic microorganisms enter (Shigella in dysentery) and when their own opportunistic flora is activated (Clostridium in pseudomembranous colitis). It has been established that E. coli can transform into pathogenic strains.
Pseudomembranous colitis
The disease is a serious complication of antibiotic therapy (less often occurs under the influence of treatment with cytostatics, immunomodulators, laxatives) and dysbacteriosis. Caused by overgrowth of clostridia in the large intestine. Considered to be a nosocomial infection.
Bacteria in normal numbers are not considered pathogenic. Having received the “majority”, they cause inflammation of the wall with the released toxin.
In places covered with films (membranes), all layers of the intestinal wall are destroyed up to the release of feces into the abdominal cavity
The disease is accompanied by severe intoxication, high fever, diarrhea, severe abdominal pain, vomiting, headaches, dehydration, severe electrolyte and protein disturbances, and depression of the cardiovascular system.
It is especially difficult to tolerate in old age, in the presence of other diseases. In the initial stage, symptoms disappear when medications are discontinued. In severe cases, hyperkalemia and death from cardiac arrest develop. Let's consider two diseases not associated with infection.
Ulcerative colitis
The disease refers to chronic lesions. Inflammation begins in the rectum and spreads upward to other parts of the large intestine. The mucous membrane is a surface covered with ulcers and bleeds easily. Usually the process does not go deeper than the submucosal layer.
This significantly increases the risk of transformation of ulcerative epithelium into polyps or intestinal cancer. The causes of the disease have not yet been established. The most likely hereditary predisposition, genetic and immune changes in the family.
Symptoms:
- frequent diarrhea, less often stool retention;
- pain of a constant nature, located in the left iliac region and above, decreases after defecation;
- at times, bloody discharge from the intestines;
- weakness, decreased performance, constant feeling of fatigue;
- weight loss
In the treatment of the disease, a strict diet is used with the exclusion of irritating foods and milk. Sulfasalazine is prescribed for long courses. If there is no effect, corticosteroids are added. Local therapy includes rectal suppositories with anesthesin for pain relief, with methyluracil, microenemas with herbal decoctions (chamomile, calendula).
Variants of the prevalence of ulcerative colitis
In severe cases, the bottom of the ulcer deepens and corrodes a nearby vessel. If there is intestinal bleeding, patients are operated on, resection (removal) of the affected area is performed, and the anus is removed to the abdominal wall. Surgery is vital for bleeding, but it does not stop the inflammatory process.
Crohn's disease
A disease of unknown origin that can affect the entire digestive tract. Teenage boys and young men are more often affected; the next “peak” of prevalence occurs after the age of 60 years. In 75% of cases, inflammation is localized in the area of the terminal ileum and the beginning of the large intestine (ileocolitis).
A study of Crohn's disease showed the importance of three factors:
Symptoms and treatment of Crohn's disease in adults
- heredity - confirmed by the distribution among twin brothers, the connection of gene mutations with ankylosing spondylitis (ankylosing spondylitis), and the isolation of a special mutant gene.
- infections - suspicions fall on the paratuberculosis bacterium, studies are being conducted on connections with viral and bacterial pathogens;
- immune disorders - evidenced by the detection of an increase in T-lymphocytes and antibodies to E. coli in the body of patients, but specific antigens have not yet been discovered.
The inflammatory process, unlike ulcerative colitis, spreads deeper, involving the entire intestinal wall and lymphatic vessels. Areas of lymphocyte accumulation have clear boundaries and alternate with normal tissue. Due to the compaction of the wall, the lumen narrows.
Ulcers on the mucous membrane look like slits and cracks. The formation of characteristic granulomas (tubercles) makes it look like a “cobblestone street”. This sign is used in differential diagnosis. The muscle layer is destroyed over time, abscesses and fistula tracts are formed, going into the peritoneum or neighboring organs, onto the skin of the abdomen.
Symptoms of the disease are usually divided into intestinal and extraintestinal. Intestinal manifestations include: prolonged diarrhea, pain most often in the right iliac region (masked as appendicitis), intensified after eating, radiating to the navel, throughout the abdomen, nausea and vomiting, bloating, weight loss (more often when the small intestine is involved).
How other organs are involved in the inflammatory process is unknown. Extraintestinal signs include:
- loss of appetite;
- constant fatigue;
- wave-like increase in temperature;
- in the mouth - aphthous stomatitis with very painful ulcers, bleeding;
- from the eyes - inflammation of the membranes (conjunctivitis, uveitis, keratitis);
- spinal spondylitis, inflammation of the joints of the arms and legs, development of stiffness;
- skin rashes in the form of erythema nodosum, pustules, vascular angiitis.
Characterized by fatty degeneration and cirrhosis of the liver, the formation of stones in the bile ducts, sclerosis of the ducts (the formation of a malignant tumor is possible). At the same time, cystitis, urolithiasis, pyelonephritis, amyloidosis occur in the urinary system, the kidney enlarges and forms hydronephrosis.
Fistulas are manifested by anal fissures, connections to the bladder, rectum, and in women with a uterus
Treatment is conservative and differs little from ulcerative colitis. The following are used as symptomatic help: enzymes, enterosorbents, probiotics, iron supplements for anemia, vitamins.
Alternative techniques include:
- a method of saturating the body with oxygen in a special chamber (hyperbaric oxygenation);
- plasmasorption and plasmapheresis;
- use of stem cells.
Functional diseases
Functional diseases of the large intestine are also called dyskinesias, neurogenic colitis. A special place in modern gastroenterology is given to irritable bowel syndrome. The main unifying feature is the absence of any organic disorders in the intestinal wall.
Much less often, the following risk factors are added: previous acute intestinal infections, insufficient physical activity, overeating heavy meat foods. Similar symptoms are possible in pregnant women. The consequences are divided into 2 types:
- hypotension - expressed in dysfunction of fecal evacuation, stagnation, atonic constipation, constant heaviness and dull pain in the abdomen;
- hypertonicity - motility accelerates, water and mucus are released in a significant volume, at the same time beneficial microflora is excreted, the patient feels cramping pain in the abdomen, frequent diarrhea, dry mouth.
The main cause of dyskinesia is considered to be a breakdown of nervous regulation due to frequent stress.
During the examination, no changes were found in the tests, except for dysbacteriosis. Examination of the intestines does not show any disruption of the wall structure. Doctors try to treat such cases with:
- proper daily routine;
- normalization of emotional stress;
- physical therapy;
- balneological procedures (baths, showers);
- physiotherapy methods;
- herbal decoctions and tinctures.