The mechanism of pain in pancreatitis
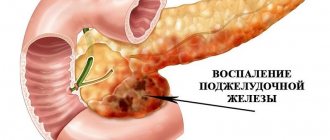
Inflammatory and degenerative processes that occur in the pancreas are called pancreatitis. The mechanism of pain is influenced by the following processes occurring in the pancreas:
- Blockage (obstruction) of the ductal system of the gland due to stagnation of pancreatic juice and bile in the ducts. Stagnation occurs as a result of a sharp spasm of the gland ducts, changes in consistency (increased viscosity due to alcohol abuse, poisoning of the body) of pancreatic juice or due to the appearance of tumors, stones, or the work of parasites (worms) in the ducts.
- Violation of tissue microcirculation. When pancreatitis occurs, there is a decrease in blood flow in the gland, the cells of which are poorly supplied with blood.
- Dystrophic changes in the pancreas. Tissues are corroded by pancreatic enzymes, which accumulate in greater quantities than necessary.
- Inflammatory processes that cause swelling of the tissues and supporting stroma (structures) of the gland. As a result, the pancreas becomes enlarged and swollen.
Provoking factors
Experts identify many reasons for the occurrence and progression of pancreatitis. According to statistics, in 30% of patients the cause of inflammation of the pancreas cannot be determined. Pancreatitis can be caused by:
- Drinking alcoholic beverages in excessive doses. Alcohol is one of the main causes of pancreatitis; with regular drinking of strong drinks, iron ceases to function normally, which has an extremely negative effect on the health of the entire body.
- Errors in nutrition. Fatty, fried and spicy foods, systematic overeating lead to excess production of gastric juice and damage to the gland.
- Abnormalities in the functioning of the gallbladder (cholelithiasis). The pancreas and gallbladder have a common excretory duct into the duodenum. If the duct is clogged with stones, stagnation of digestive secretions occurs, which causes inflammation or destruction of the gland.
- Stressful situations, nervous overstrain.
- Injuries, abdominal operations, wounds of the abdomen, abdominal cavity, in which the pancreatic gland may be damaged.
- Diabetes mellitus.
- Hormonal disorders.
- Infections (flu, mumps, colds, viral hepatitis).
- Neoplasms in the peritoneum.
- Hereditary predisposition.
- High blood pressure.
- Inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and duodenum. Gastritis, duodenitis, and ulcers can negatively affect the release of intestinal juice.
- Negative effects of medications. Many medications, antibiotics, hormones, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs have a negative effect on the pancreas and can cause inflammation.
Painkillers
To relieve pain in pancreatic colic that develops in an acute condition, drugs from the antispasmodic . These are drugs that relieve spasm of smooth muscles:
- stomach;
- intestines;
- all parts of the gastrointestinal tract.
In addition, these medications eliminate the main cause of the development of acute inflammation in the described organ - stagnation of enzymes inside.
With pancreatitis, there is also spasm and blockage
Swelling during the inflammatory process compresses, and colic provokes compression, which again worsens the course of the pathological process.
Antispasmodics, with their extensive action remove this clamp, excess enzymes come out, thus achieving several effects:
- pain relief;
- removal of stagnant enzymes;
- improved digestion.
The following drugs are mainly used.
"No-shpa" or "Drotaverine"
frequently prescribed antispasmodic in the treatment of pancreatitis. It has a gentle effect on the smooth muscles of the gastrointestinal tract, including the pancreas.
Affects the transport of ions within cell membranes and blocks contraction. The effect occurs within 20-30 minutes. It is taken in the form of tablets or given as injections (during an exacerbation, when the patient is unconscious or is tormented by incessant vomiting).
The medication should be administered into the body every 6 hours for the first few days, then the dose is reduced. Contraindications are:
- childhood;
- pregnancy;
- lactation;
- tendency to low blood pressure;
- the presence of allergic reactions to the drug.
strictly for use ; everything will depend on the degree of imminent danger to life, the threat and the decision of a specialist.
"Papaverine"
This drug is officially recognized as a children's antispasmodic . It is highly effective . The product is produced in tablets and ampoules.
Contraindicated if you are allergic to the components of the medication and have a tendency to low blood pressure.
Pregnant women are prescribed only on the recommendation of a doctor, as it can negatively affect the development of the embryo.
Painkillers are used mainly in injections up to 3 times a day.
"Motilium"
This drug is also available as an analogue "Motilak". The antispasmodic activity of the drug is based on its antiemetic effect.
Interesting fact! It affects specific parts of the brain and blocks vomiting impulses, relaxing the smooth muscles of the gastrointestinal tract.
Available in lozenges and film-coated tablets. There are forms for resorption.
In pediatrics it is used in the form of syrup (the dose is calculated per kilogram of body). The medicine is contraindicated before the age of 12 and for mothers carrying a child or breastfeeding. Analogues:
- "Motilak";
- "Passengers";
- "Motonium".
"Duspatalin"
This drug has analogues:
- "Sparex";
- "Trimedat";
- "Niaspam."
One of the most effective antispasmodics.
Acts selectively on muscle fibers of the gastrointestinal tract.
Used in the form of capsules or tablets 3 times a day, an hour after meals (or before meals).
Contraindicated in case of allergic reactions to medication components and in children under 3 years of age (from 3-18 years of age, there are special dosages of the medicine).
During pregnancy, it is prescribed according to individual indications.
Important! You cannot adjust drug doses on your own. This should only be done by a doctor.
The nature and localization of pain in pancreatitis
Painful sensations during pancreatitis can be different, have daily recurrence and depend on the anatomical location of the lesion - the area of the pancreatic lesion (head, body, tail), and the type of inflammatory process. The nature of pain with pancreatitis varies:
- cutting;
- pricking;
- aching;
- spicy;
- blunt;
- pressing;
- burning;
- drilling;
- pulling.
In chronic pancreatitis, there is no clear localization of pain; it can vary in intensity and occur periodically (cramping type). Increased pain occurs at night. With chronic inflammation of the gland, pain is localized in:
- upper and middle abdomen;
- lumbar region, in the form of a full belt or partial - on the left side;
- back area;
- lower chest (lower ribs area).
Useful article? Share the link on VKontakte
In acute pancreatitis, patients feel a pulling, unbearable, sharp, squeezing, acute and girdling pain, which is localized in:
- left side of the abdomen;
- back;
- left hypochondrium;
- abdominal cavity.
How to recognize acute pancreatitis
During an acute attack of pancreatitis, the pancreas begins to digest not food, but itself. If you do not seek medical help in time and do not start following the rules of nutrition, swelling and inflammation of the tissue around the pancreas occurs. In advanced cases, necrosis of the gland may develop. It is simple to determine the symptoms of acute pancreatitis:
- nausea;
- bloating;
- cardiopalmus;
- significant reduction in blood pressure;
- aversion to any food and drinking water;
- dizziness;
- sharp pain under the right rib;
- flatulence;
- vomiting with bile;
- pale, yellowish skin;
- acute girdle pain during pancreatitis, which subside in a sitting or lying position if you bend your knees under you.
Treatment in hospital
Acute pancreatitis in adults is treated in a hospital using the following measures:
- First of all, it is necessary to relieve pain. For this purpose, medications such as Baralgin, Novocain, Analgin, Promedol in the form of tablets and injections are used.
- The second step is to carry out hypertension of the bile outlet channels. A drug such as No-Shpa is suitable for this.
- It is imperative to remove the load from the pancreas and ensure rest. Water fasting will help with this. In the first few days after starting treatment, you can drink regular drinking and mineral water.
- Prevention of thrombosis is often important.
How long do emergency measures last? This usually takes a few minutes, but sometimes it takes the whole day. After they are completed, a period of intensive therapy begins.
It includes taking sorbents (Smecta, Almagel) and anti-inflammatory medications (Gordox and Mannitol by drip, Contrikal). To reduce hydrolysis, diuretics (Furosemide) are prescribed.
To prevent the patient's condition from worsening, the stomach must be cleaned and drained, as well as the condition of other internal organs checked, but a full medical examination is not carried out due to its dangerous condition. To facilitate the work of the pancreas, insulin injections are given.
Thus, it usually takes about 7–10 days to eliminate an attack of acute pancreatitis or an exacerbation of its chronic form, with the first 2–3 days being the period of the most intensive therapy. After discharge from the hospital, the patient must be under the supervision of doctors for one and a half to six months.
Chronic pancreatitis should be treated with periodic examinations, adherence to the regimen and self-administration of recommended medications.
How to relieve pain in acute pancreatitis
Acute inflammation of the pancreas occurs suddenly, often the patient has to provide first aid at work or at home. Therapy for this form of pancreatitis is carried out exclusively in a hospital setting under the supervision of a physician. In case of acute girdle pain, you must call an ambulance and do the following:
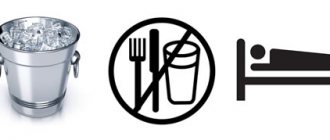
- Provide the patient with peace - both physical (sudden movements cause pain) and emotional.
- Remove or unfasten clothing that interferes with normal breathing or puts pressure on the abdomen.
- To reduce pain, you need to sit the sufferer down, tilting the torso forward, or recommend lying in the fetal position.
- The patient needs to drink a quarter glass of boiled water or mineral water without gas every half hour.
- Cold relieves pain. For 10–15 minutes, you can place a heating pad with ice, chilled gel packets, or a bottle of frozen water on your stomach (the area where the pain is located).
- Give the patient an antispasmodic - No-shpu, Papaverine or Drotaverine, if possible, make an intramuscular injection with one of these drugs.
Only doctors can determine the type of inflammation. In order not to further aggravate the situation before the doctors arrive, during an acute attack the sufferer is prohibited from:
- Taking deep breaths - they increase the pain.
- Eat food.
- Take painkillers (Spazmalgon, Analgin, Baralgin) - they dull the pain and can prevent specialists from correctly diagnosing the disease.
- Take enzyme preparations (Mezim, Creon, Festal), which can worsen the patient’s condition.
- If vomiting, do not use solutions or medications to cleanse the stomach.
- Heating the abdominal area can lead to swelling and sepsis.
Treatment in hospital
After hospitalization, to determine the symptoms of pancreatitis, the patient is prescribed a diagnosis, which includes:
- general blood analysis;
- X-ray and ultrasound of the peritoneum;
- blood chemistry;
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy (probing);
- laparoscopy;
- computed tomography.
To relieve pain, doctors may prescribe narcotic analgesics, and in severe cases, the pain relief regimen is supplemented with the prescription of neuroleptics, antispasmodics, antibiotics, tranquilizers, and antidepressants. The most common analgesics:
- Ketanov;
- Tramadol;
- Diclofenac;
- Omnopon;
- Promedol;
- Fentanyl;
- Novocaine.
Therapy for acute pancreatitis is selected individually for each patient. In addition to taking medications, the patient must adhere to a strict diet. In the first days after hospitalization, doctors prescribe:
- Bed rest. It is necessary to get out of bed and move gradually, after the doctor’s permission.
- Hunger - its duration is determined by a specialist; after the end, the food ration expands gradually.
Treatment of pancreatitis in a hospital: indications for hospitalization, length of stay, types of therapy
Hospitalization is necessary for a severe attack of acute pancreatitis, which cannot be controlled with painkillers at home. After the patient is delivered, he is transferred from the clinic’s emergency department to the intensive care ward. Treatment is carried out with the mandatory participation of an anesthesiologist and resuscitator.
Acute pancreatitis is treated as follows:
- First, doctors relieve the patient’s pain and various nervous and reflex disorders with the help of analgesics. For this, the drugs Baralgin, Promedol, Analgin, etc. are used. Novocaine blockade can be used.
- To combat hypertension in the bile ducts, doctors use No-shpu, Nitroglycerin and other drugs.
- The pancreas needs to be unloaded, so the patient is prescribed fasting. He should take alkaline drinks, such as Borjomi.
- In combination with the above measures, the prevention and treatment of blood clots in the vessels of various organs (pancreas, liver, etc.) is carried out.
To prevent the condition of a patient with pancreatitis from worsening due to intoxication, the performance of the heart and lungs is checked, and then drainage and gastric lavage are performed. This procedure is carried out with a solution of soda, Pyrroxan or Obzidan are used.
It is not always possible to cope with attacks of acute pancreatitis on your own at home.
They may be accompanied by a significant deterioration in health, acute pain, nausea, vomiting and even loss of consciousness. In such cases, hospitalization and treatment under medical supervision are necessary.
Failure to provide medical care in a timely manner at such a clinic can result in the development of complications, as well as death.
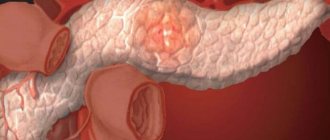
Pancreatitis is an inflammation of the pancreas, in which the digestive enzymes produced by the gland cannot enter the intestine to digest food and, as a result, begin to digest the tissue of the parenchymal organ. It turns out that the gland “eats” itself.
This is a very serious and dangerous disease that requires qualified medical care. The disease can occur in two forms: chronic and acute.
Usually, treatment of the disease takes place at home, according to the regimen prescribed by the doctor. However, the development of acute pancreatitis or exacerbation of a chronic disease may be accompanied by attacks with severe painful symptoms.
Untimely medical intervention during acute attacks of the disease can lead to the development of complications, disability and even death of the victim.
Thus, the indication for hospitalization of a patient with pancreatic inflammation is the development of an acute attack, which is accompanied by severe pain and a significant deterioration in well-being.
Nausea and profuse vomiting (especially with bile) can also be alarming symptoms. If they occur, it is recommended to consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Symptoms of an acute attack of pancreatic inflammation include:
- Severe pain in the right hypochondrium, as well as slightly above the navel;
- Vomit;
- Diarrhea;
- Temperature rise to 38 degrees or higher;
- Tachycardia.
If an acute attack of pancreatitis occurs, before the ambulance arrives, under no circumstances should you:
- Take painkillers and antiemetics.
- Bandage the subcostal area.
- Apply hot, warm or any warming compresses to the painful area.
- Drink any drinks except a small amount of water.
The patient should be placed on a sofa or bed in a reclining state, a cool cloth or heating pad should be applied to the sore spot, and fresh air should be allowed into the room.
Upon arrival, the ambulance team, after analyzing the symptoms and general condition of the patient, will provide first aid to the victim.
In order to relieve pain, the patient is usually given an injection with Papaverine diluted with saline solution.
In order for treatment to be effective, it is very important to give the patient a correct diagnosis and find out the sensitivity of his body to certain medications. For this purpose, the patient may be prescribed the following types of diagnostics:
- blood and urine tests;
- hemogram (to determine the development of the inflammatory process based on leukocyte indicators);
- CT or MRI;
- ECG;
- blood biochemistry (to determine whether there are pancreatic enzymes in the blood);
- Ultrasound (to identify the source of inflammation);
- emergency laparoscopy (for purulent pancreatitis, development of serious complications).
Based on the results of the examination, the doctor confirms or denies the presence of pancreatic disease, establishes its form, the extent of damage to the organ, whether other digestive organs are affected, whether there is a risk of complications, and also decides on the appropriate treatment methods in this case.
Treatment of pancreatitis in the hospital depends on the stage of the disease at which the patient was admitted to the hospital and the presence of complications. From the emergency department the patient is sent to the intensive care unit. Ambulance specialists can also deliver the patient to the gastroenterology department.
At the same time, doctors at the stage of a person’s admission to the department have two main tasks:
- stabilize the patient’s condition, stop the attack;
- prevent the development of complications.
And only after completing these tasks, doctors begin to treat the disease.
If a person collapses with an attack of severe purulent, necrotizing pancreatitis, he is immediately sent to the intensive care unit for urgent surgical intervention under the supervision of a resuscitator or surgeon.
After providing emergency care and complete stabilization of health, the patient is immediately transferred to the gastroenterology or surgery department, where he will be under the supervision of a gastroenterologist or surgeon, respectively.
At the time of discharge, the person receives recommendations for continuing the prescribed therapy at home, and is also informed about the need for regular monitoring with a local physician. Maintenance therapy lasts another six months.
How long people stay in the hospital with pancreatitis depends on the form, stage of the disease, the nature of its course and the presence of complications.
In acute form
The acute course of the disease generally lasts from two to seven days. In this case, the first two or three days are considered the most difficult and responsible, since the patient’s condition needs to be stabilized. During this period, there remains a high risk of complications with a fatal outcome, so it is characterized by the most intensive therapy. The patient may be on a drip for the first few days.
If an acute form of pancreatic inflammation develops or an exacerbation of a chronic disease occurs, the patient may remain in the hospital for 7(10) to 14 days. The duration of treatment is also influenced by the effectiveness of the selected therapy.
If surgical intervention is necessary, after the operation the patient usually spends another week in the day ward, and after discharge he must periodically visit the doctor for one and a half to two months.
Treatment of pancreatitis in a hospital in its chronic form is carried out mainly in case of exacerbation of the disease. The duration of hospitalization may take from one to two weeks.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0ysXodb2OGw
In general, treatment for chronic pancreatic inflammation can take years. Therapy takes place at home, and during periods of acute attacks, a hospital stay under the supervision of doctors is definitely required.
The standard of treatment for pancreatitis in a hospital involves the following actions:
- Relieving pain syndrome.
- Relieving spasms of the smooth muscles of the pancreas.
- Elimination of puffiness.
- Stopping the activity of digestive enzymes of the gland.
- Therapy of the disease.
- Normalization of digestion.
- Elimination of side effects of drugs.
How is pancreatitis treated in the hospital? This question interests many patients with long-standing inflammation of the pancreas. Doctors prescribe medication therapy (including IVs, injections), diet and surgery. The use of traditional methods in hospitals is not practiced.
In most cases, pancreatitis is treated with medications. However, the first step in treating the disease will be to ensure pancreatic rest. For this, the patient is prescribed water fasting. For 3-4 days he is prohibited from eating anything except mineral still water (it is advisable to drink it slightly chilled).
In addition, a catheter can be installed in the patient’s stomach for several days, through which its contents will be released.
Treatment of the disease involves the use of the following drugs:
- Diuretics, to remove fluid and eliminate swelling.
- Painkillers (Novocaine, Promedol, Lexir, etc.).
- Antispasmodics to relieve spasms of the smooth muscles of the gland (No-shpa).
- Antienzymes that suppress the production of gland secretions to renew its tissues
- Drugs may be prescribed to prevent thrombosis in blood vessels.
- For purulent processes, antibiotics are prescribed.
- Drugs aimed at restoring normal gastrointestinal acidity.
- Vitamin therapy for general strengthening of the body, raising tone and immunity.
Medicines must be taken strictly according to the dosage prescribed by the doctor so as not to harm the body. At the same time, it is necessary to take medications that will support the functioning of the liver and kidneys, since during the treatment period they are subject to enormous stress.
To detoxify the body from medications, gastric lavage is performed with a soda solution.
Throughout the entire period of treatment, protein, electrolyte, and carbohydrate metabolism are monitored.
If necrotic processes have already begun in the gland, surgical intervention is performed. There are three ways to operate the pancreas:
- Removal of the tail and body of the gland.
- Removal of the tail, body and part of the head of the gland.
- Removing fluid formations from the pancreas and washing it.
The operation is performed under general anesthesia in the surgery department. Subject to stable health, after 1-2 weeks the patient is transferred to home treatment, lasting on average 1.5-2 months.
Emergency
First aid for exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis
In the chronic form of pancreatitis, the patient experiences similar symptoms as in acute inflammation, but they are less pronounced. At first, the pain is paroxysmal and cutting, then it becomes aching and dull. Often there are hunger pains with pancreatitis, which are relieved after eating, but do not disappear completely. In most cases, symptoms of chronic pancreatitis appear after:
- diet violations;
- nervous shocks;
- alcohol abuse;
- heavy smoking.
If acute chronic inflammation occurs, you should not self-medicate - you should immediately call a doctor. Before the ambulance arrives, you need to provide the sufferer with first aid (the same as for acute inflammation) and give the following medications:
- Painkillers (Paracetamol, Ibuprofen, Metamizole, Dicloberl, Spazmalgon, Baralgin, Ibufen). They can be taken only if the patient is sure that the pain is caused by an exacerbation of pancreatic inflammation. The dosage and type of medication depend on the recommendations of the specialist during previous attacks.
- 2 tablets of Allochol in combination with an antispasmodic (Drotaverine, No-shpa). The drug can be taken in the absence of gallstones; it helps normalize the outflow of bile and gastric secretions from the gland.
Treatment of pain in chronic pancreatitis
Treatment of chronic inflammation is aimed at detoxifying the body, eliminating pain, relieving the inflammatory process, and normalizing digestion. After a comprehensive examination of the peritoneum and if test results are available, the gastroenterologist individually develops a treatment regimen for each patient, which includes taking medications, anti-enzyme drugs, vitamins, and following a diet. Among the medications, doctors prescribe:
- Pancreatic secretion inhibitors - used to temporarily suppress (disable) the gland. Medicines in this group include Gordox, Kontrikal, Kontriven, Aprokal. These medications:
- slow down the functioning of proteases of cellular elements and blood plasma;
- prevent pancreatic necrosis;
- reduce the functioning of the kinin-kallikrein system (KKS).
- The hormonal drug Somatostatin or its analogues (Octreotide) is used to reduce pain in chronic pancreatitis and suppress the secretion of serotonin in the gland.
- Enzyme medications (Panzinorm, Mezim, Festal, Pankurmen, Creon, Enzistal Pancreatin) - have the following effect on the health of the sufferer:
- I facilitate the process of processing food;
- reduce pain intensity;
- normalize work and reduce the load on the pancreas;
- promote proper absorption of organic substances.
- H2 histamine receptor blockers (Famotidine, Nizatidine, Cimetidine) are intended to inhibit secretion in the pancreatic gland by suppressing the production of hydrochloric acid in the intestines.
- Proton pump blockers (inhibitors) – Ezokar, Omeoprazole, Rabeprazole. The main task of these drugs is to inhibit the secretion of hydrochloric acid by blocking the proton pump in the parietal cells.
- Diuretics – Diacarb, Triampur, Furosemide.
- Antihistamines (Pipolfen, Suprastin, Peritol, Diphenhydramine) are prescribed to reduce swelling of the gland tissue.
- Antacids (Phosphalugel, Palmagel, Maalox, Altacid) are designed to neutralize hydrochloric acid, which is secreted by the stomach.
- Antispasmodics (Drotaverine, Papaverine, Eufillin, No-shpa, Riabal, Spasmolin) - prescribed to relieve pain.
- Antibacterial drugs (Amoxilav, Azithromycin, Abaktal, Sumamed) are used to eliminate bacterial microflora that may cause infection. Antibiotics completely destroy all microflora in the intestines, so they are used in combination with probiotics (Linex).
- Anticholinergics – Chlorozin, Metacin, Platyfillin, Antopit. Medicines in this group normalize digestive function.
- Antisecretory agents – Omeprazole, Lansoprazole, Omez. Medicines significantly reduce pain, suppress the secretion of hydrochloric acid, and reduce inflammation.
Methods of medical care in a hospital setting
The standard of treatment for pancreatitis in a hospital involves the following actions:
- Relieving pain syndrome.
- Relieving spasms of the smooth muscles of the pancreas.
- Elimination of puffiness.
- Stopping the activity of digestive enzymes of the gland.
- Therapy of the disease.
- Normalization of digestion.
- Elimination of side effects of drugs.
How is pancreatitis treated in the hospital? This question interests many patients with long-standing inflammation of the pancreas. Doctors prescribe medication therapy (including IVs, injections), diet and surgery. The use of traditional methods in hospitals is not practiced.
Conservative therapy
In most cases, pancreatitis is treated with medications. However, the first step in treating the disease will be to ensure pancreatic rest. For this, the patient is prescribed water fasting. For 3-4 days he is prohibited from eating anything except mineral still water (it is advisable to drink it slightly chilled).
Prevention
Preventive measures for any type of pancreatitis are simple. To prevent inflammation, you must adhere to the following rules:
- Get rid of bad habits. Minimize or completely stop drinking alcohol and smoking.
- Lead an active lifestyle, engage in light sports (for example, breathing exercises).
- Coffee lovers are allowed to drink no more than 1 cup per day. Preference should be given to natural products.
- Follow a daily routine, do not eat at night and before bedtime.
- It is worth limiting your consumption of fast food, fatty, smoked, spicy, fried foods.
- Consume sugar-containing foods in moderation.
- You need to eat fractionally, in small portions, and eat freshly prepared meals.
- Before the feast, you need to take enzyme medications (Pancreatin, Mezim, Festal).
Causes of the disease
The diagnosis of “pancreatic pancreatitis” is a fairly common occurrence these days. But why do people increasingly suffer from it? You will understand everything when you find out the reasons that stimulate the appearance of this disease.
- Too much alcoholic drinks.
- Poor nutrition, namely frequent consumption of salty, spicy and fatty foods.
- Excess weight.
- Concomitant diseases, such as: cholecystitis, hepatitis, cholelithiasis, ulcer, gastritis, tumor.
- Surgeries on the pancreas or injuries to it.
- Tobacco smoking.
- Food allergies.
- Heredity.
- Taking medications that cause the disease to appear (tetracyclines, cytostatics, sulfonamides).
Symptoms of acute pancreatitis
With this form of the disease, the free outflow of pancreatic juice is disrupted and it ceases to be digested by its own enzymes. A diagnosis of acute pancreatitis of the pancreas is characterized by:
- Strong pain. It occurs in the left side of the abdomen, and after a while it spreads to the entire abdomen.
- Nausea and even vomiting.
- Blood pressure becomes disorganized.
- Understanding of reality is disrupted.
- A state of shock may occur.
These symptoms are too severe to treat at home. Therefore, in case of acute pancreatitis, you should urgently call an ambulance. An experienced surgeon must examine the patient and be sure to admit him to the hospital for further treatment and observation. It is unlikely that it will be possible to avoid surgery on the pancreas in the acute form of the disease.
Chronic pancreatitis: symptoms and treatment in the initial period
The signs of this type of disease are not so scary and do not require immediate help. Now let's look at what chronic pancreatitis is, the symptoms and treatment of this type of disease.
To begin with, it is necessary to distinguish two periods in chronic inflammation:
- Elementary.
- The period of obvious damage to the pancreas.
The first period can last a long time - up to 10 years. Symptoms for this period:
- Pain syndrome. The pain can be localized in the upper and middle abdomen, in the left lumbar region and even in the heart area. Most often, such unpleasant sensations occur 15–20 minutes after eating.
- Nausea, possible vomiting.
- Bloating.
- Diarrhea.
The first point is often observed in patients, but the others may not occur. Even if some symptom appears, you can quickly alleviate the condition with the help of medications.
Antacids
Antacids are first aid for eliminating stomach pain and other dyspeptic (digestive) disorders. They are used if necessary , there is no fixed rate.
"Phosphalugel"
This drug is available in the form of a ready-made suspension for oral administration, coats the gastric mucosa, neutralizes acid and heartburn. Aluminum contains phosphate.
The maximum daily dose is 4 sachets, preferably used at regular intervals. There are no contraindications during pregnancy and childhood (even infancy) .
"Almagel"
This is a suspension that also contains aluminum salts, the effect is similar. Use 1 tablespoon up to 4 times a day.
Attention! Due to the fact that the medication contains additional substances and auxiliary components, it is prohibited during pregnancy and children.
There are types of medicine:
- " Almagel A " (with an anesthetic component);
- " Almagel Neo " (additional effect - helps against bloating).
Period of obvious damage to the pancreas
Here the signs are as follows:
- The pain becomes not as obvious as in the first case.
- In this case, dyspeptic syndrome predominates: heartburn, belching, nausea, bloating.
- Maldigestion syndrome occurs. This is when there is a disruption in the digestion of food to those particles that would be absorbed.
- Malabsorption syndrome occurs. In this case, the absorption mechanism in the small intestine is completely disrupted.
The following symptoms are typical for maldigestion and malabsorption:
- foul, profuse stool;
- weight loss;
- vision decreases in the evening;
- bleeding gums appear;
- Conjunctivitis, stomatitis, and skin itching may occur;
- anemia develops;
- due to the fact that calcium absorption is impaired, there are cramps and pain in the bones;
- neuropsychic agitation;
- the appearance of cold sweat;
- trembling in the body;
- dry skin;
- there is a feeling of constant thirst.
It is necessary to treat chronic pancreatitis to avoid surgery on the pancreas. Therapy must be adequate and reasonable. Only after passing all the necessary tests, as well as consultation with a doctor, therapy can be prescribed. Now let’s look at what kind of diagnostics a sick person should undergo in order for the picture of the disease to become clearer.
Recognition of the disease
The following types of diagnostics will give a complete picture of the disease:
- Ultrasonography. Ultrasound of the pancreas for pancreatitis is an integral analysis procedure. This type of diagnosis shows how enlarged it is in size, shows the heterogeneity of the structure, the possible presence of cysts and dilation of the ducts. The accuracy of such a study is 80–85%. This is not a very high result, so additional laboratory tests should be taken.
- Computed and magnetic resonance imaging. These types of diagnostics, as in the first case, show how enlarged the pancreas is. In addition, with the help of such studies it is possible to identify malignant formations, pseudocysts, and lesions of neighboring organs.
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. This is the most accurate procedure that shows almost 100% results. Plus, this type of diagnostics is the cheapest of the above. True, there is a minus: this method is not the most pleasant, and in some cases painful.
What tests are needed to make a diagnosis?
In addition to the above-described methods for recognizing the disease, the doctor gives directions for the following tests:
- General blood analysis. Its results show signs of inflammation and possible anemia.
- Donating blood to determine blood sugar levels. Such an analysis is necessary to find out whether the patient has diabetes.
- General urine analysis. Shows possible kidney diseases.
- Electrocardiogram and echocardiography exclude heart disease.
After passing the above tests, the picture will become clearly visible, and the diagnosis of “pancreatitis of the pancreas” will be made or not.
How and with what is pancreatitis treated in the hospital?
Upon admission to the hospital, a sick person is treated according to the following principles of pancreatitis therapy (arranged in sequential order):
- relief of pain (with exacerbation of the disease, patients suffer intolerable pain that requires immediate relief);
- neutralization and prevention of complications (at the stage of organ suppuration, antibiotics are used in loading doses or surgical intervention (if drug correction of the condition is impossible));
- detoxification of the body (during the inflammatory process and purulent formations, a large number of toxins are released into the blood, which must be expedited and neutralized) - forced diuresis tactics are used (administration of large doses of diuretics) and abundant infusion of salt solutions (sodium chloride, potassium chloride, calcium chloride). They restore the water-salt balance, eliminating the development of dehydration, which is especially dangerous for a sick person in a similar condition;
The role of specialists in the treatment of the disease
Pancreatitis of the pancreas requires proper treatment. Therefore, the patient must undergo a consultation not with one doctor, but with several, so that an overall picture of his condition is formed, and the doctors prescribe him the correct therapy.
The patient should come for a consultation with the following specialists:
- Gastroenterologist. He prescribes treatment.
- To the surgeon. The help of this specialist is needed if the pain does not stop or any complications appear.
- Endocrinologist. Necessary if the patient has diabetes.
- Cardiologist. Consultation with this specialist is necessary to exclude possible pathologies of the cardiovascular system.
The outcome of the treatment will depend on the qualifications of the doctors. Therefore, you need to choose the best of the best in their fields. You can ask about the doctors’ experience, how many operations they performed, and whether there are any statistics. Your health is in your hands. And the speed and effectiveness of your treatment and speedy recovery will depend 80% on how experienced the specialist is.
Principles of proper nutrition for pancreatitis. Diet
With this disease, it is important to follow certain rules regarding nutrition. Since the patient’s well-being will depend on the quality and quantity of food taken. The following principles need to be known:
- You need to eat food at least 5-6 times a day. You need to eat little by little, in small portions.
- It is best to eat pureed foods. The fact is that when serving the dish this way, the gastric mucosa will not be irritated.
- Proteins should predominate in the diet (150 grams per day). The amount of fat should not exceed 80 grams per day. You also need to be careful with carbohydrates.
- There is a taboo on foods that are too hot or, conversely, cold.
- During the period of exacerbation of the condition, it is advisable to completely abstain from any food for at least one day.
Now let's look at what foods have a beneficial effect on the condition of the pancreas.
Antibiotics
A key link in the treatment of exacerbation of pancreatitis. The following medications are used.
"Tetracycline"
This is a key antimicrobial agent during exacerbation. Broad- spectrum medicine Contraindicated during pregnancy, breastfeeding, under 8 years of age, and for diseases of the liver and kidneys.
Use 1 tablet 3 times a day in courses of up to 10 days.
Attention! During pregnancy and childhood, it is prohibited for use, except in situations where there is a serious danger to the patient’s life.
"Biseptol"
Also called "Co-trimoxazole". On the first day, this broad-spectrum antimicrobial medication is taken in loading doses (up to 10 tablets), then 1-2 tablets 3-4 times a day.
The doctor will prescribe a regimen based on the patient’s age and the degree of development of complications.
is contraindicated in severe forms of liver and kidney failure, in hematopoietic pathologies, under 3 years of age, in pregnant and lactating women, and in people with allergies.
During pregnancy and childhood, Biseptol is indicated only for individual use.
"Bactrim"
This is a suspension for injection (intramuscular and intravenous) administration. Contraindicated for hematopoietic pathologies, liver and kidney failure, and for infants under 2 months.
Course of use up to 14 days. The medicine is given 1-2 times a day.
Attention! During pregnancy and childhood, only a doctor decides the advisability of using the drug.
"Sigmamycin"
Also known as "Oletetrin". Capsules or solution for injection. Contraindicated in case of hypersensitivity to the active substance.
The course of appointment is up to 10 days. The tablets are used 3 times a day before meals with a small amount of liquid.
During pregnancy and childhood, it is prescribed by a doctor according to individual indications, when the probable benefit outweighs the potential harm.
List of recommended products
The main condition for a disease such as pancreatitis of the pancreas is diet. This is the main principle of treatment. What is the essence of the diet? Use only those foods and dishes that will not irritate the mucous membrane of the pancreas. The following products can and should be used by people suffering from this type of inflammation.
- Wheat bread is stale, yesterday's bread.
- Soup made with recycled chicken or beef broth.
- Meat: chicken, veal, turkey. Method of preparation: boil, bake in the oven. The meat should not contain any seasonings.
- Fish, steamed, boiled or baked in the oven.
- Dairy products with a small percentage of fat.
- Boiled vegetables. If you want it raw, then only in grated form.
- Various types of pasta.
- Cereals (buckwheat, rice, oatmeal).
- Baked fruits (meaning apples and pears).
- Jelly.
- Compotes, jelly, weak tea.
List of foods that are contraindicated for pancreatitis
- Primary meat or fish broths. That is, fatty, high-calorie.
- Millet should not be consumed from cereals.
- Fatty meats, fish, poultry.
- Among vegetables, radishes, radishes, cabbage, sorrel and spinach are taboo.
- Fresh bread or any sweet products.
- Various types of sausages, canned food.
- Alcoholic drinks.
- Ice cream.
- Strong tea, coffee.
Consumption of the above products will lead to a negative outcome, which is called “inflammation of the pancreas” (pancreatitis, simply put). In order not to play roulette with your health, remember the foods that you should not eat if you have this disease. After all, following a diet is already 60% of the positive outcome of the disease.
Treatment of chronic pancreatitis
Therapy for this disease is aimed at reducing the amount of bile. Pancreatitis of the pancreas, the treatment of which is limited to the use of special tablets, will give a temporary result. And if, in addition to this, the patient eats properly and follows a diet, then this will be an almost 100% guarantee of successful recovery.
But let us now dwell on the drugs that help fight this disease.
So, medications that help relieve muscle spasm:
- These are pancreatic pills. Pancreatitis is treated with the following antispasmodics: “No-shpa”, “Spazmoverin”, “Spazmol”.
- Substance for the preparation of dosage forms "Papaverine".
The following drugs reduce the secretion of gastric juice:
- Omeprazole capsules.
- Tablets "Ranitidine", "Famotidine".
The following drugs normalize the digestion process and regulate the functions of the pancreas. “Allohol”, “Pancreatin”, “Phenipentol” are tablets for the pancreas. Pancreatitis is not a death sentence.
Also, for the treatment of pancreatitis, drugs are prescribed that inhibit the production of pancreatic enzymes. Among such drugs, Aprotinin solution is often used.
If there is severe pain or a person loses weight, then hospitalization and further therapy are possible strictly under the supervision of specialists. Surgical intervention is prescribed if the pancreas is no longer subject to treatment. Treatment and diet will not help with severe damage. Only removing one part of it will save it from further destruction.
It cannot be said that after drug treatment there is a complete recovery. It’s sad to say, but pancreatitis cannot be completely cured. But in order to prevent the pancreas from further destruction, it is important to undergo treatment, as well as follow a strict diet, which was described above.
Treatment of pancreatitis in a hospital: indications for hospitalization, length of stay, types of therapy
The operation is prescribed if the patient has developed complications, signs of jaundice, pain that cannot be relieved with medications, despite long-term treatment.
Indirect types of surgery on the bile ducts or stomach and intestines can be used. If necessary, surgery is performed to drain the cysts, remove stones, and sometimes pancreatic resection may be necessary.
Many patients want to know how many days it takes to treat acute pancreatitis. Typically, hospital treatment lasts from 7 to 10 days, and then he is discharged, but the person undergoes maintenance therapy for another 6 months.
If the disease has taken severe forms, then after 2-3 days of intensive treatment the patient should remain under the supervision of doctors for about 1.5-2 months.
For chronic types of pancreatitis, the patient (if he does not need surgery or is in remission) stays in a medical institution for 1 day for examination.
How many days patients remain in bed after surgery depends on the type of surgical intervention and the recovery ability of the patient’s body. Usually this period does not exceed 7 days. After this, the person is transferred to home treatment, which lasts 1.5-2 months. He takes medications, follows a diet, and exercises.
Treatment of acute pancreatitis
This type of disease requires hospitalization. In the hospital, the patient is prescribed the following therapy:
- Intravenous infusion of drugs that will help cleanse the blood of toxins and pancreatic enzymes.
- Painkillers.
- Tablets that will destroy gland enzymes. For example, Kordox tablets.
- Anti-vomiting medications.
- Antibiotics.
- Antispasmodics.
In addition, therapy includes:
- Complete interruption of oral nutrition for up to 6 days. This is necessary so that the activity of the pancreas is temporarily suspended.
- Intravenous nutrition.
- Artificial activation of urination so that toxic substances leave the body in the urine more quickly.
- Colon lavage.
Diuretics
They are used to instantly remove toxins from the body during the first two days of an exacerbation.
The tactics used are forced diuresis , taking large doses of diuretic medications, and then restoring the original volume of fluid in the body by administering copious amounts of injectable solutions.
Furosemide or Lasix
highly effective diuretic . Can be used in the form of tablets or injections up to 2-3 times a day. Duration of administration does not exceed 3-5 days (sometimes administered once in a large dose).
The danger of excessive intake lies in the leaching of microelements from the body - potassium and magnesium, which directly affect cardiac activity. During pregnancy and childhood, it is prescribed for threatening .
"Diakarb"
mild
diuretic , the effect is cumulative and develops over several days.
Used for mild intoxication or as a continuation of the main therapy with Furosemide.
The advantages of the medicine will be the preservation of the microelement composition of the blood and its mild action (the body has time to restore fluid loss). The course lasts up to 5 days, use 1-2 tablets per day.
When carrying a baby, you should careful when taking the drug and do not overestimate the doses prescribed by your doctor. Children are prescribed if necessary .
Prevention of pancreatitis
To avoid a relapse and to prevent the disease from hitting you again, it is important to follow the following rules:
- Eat properly. Following a diet is the most important condition for maintaining the health of the pancreas.
- A strict ban on any type of alcoholic beverages.
- Stop smoking.
- Reduce physical activity. Running, jumping, visiting baths and saunas have a bad effect on the pancreas. The ideal option is breathing exercises and massage.
From the article you learned what a disease called “pancreatitis of the pancreas” is. We determined what methods to treat this disease, as well as how to recognize the disease. We learned that a strict diet is the key to a speedy recovery for the patient.