Infant vomiting is considered a fairly common situation. The causes of this condition can have a wide variety of origins. To determine them, you should take into account the child’s age and accompanying symptoms: gastric upsets, nausea without fever.
A small child, if he has a strong vomiting reflex and does not cause fever or cough, requires special attention, since such a clinic can cause a serious illness.
To help a child, it is necessary to identify the root cause of the pathological disorder, then eliminate it.
Sometimes you can do this yourself if you do a home analysis of the phenomena preceding the event:
- the appearance of pungent odors;
- intense rotation on the carousel;
- eating bad foods;
- drinking soda.
If the reason is the above problems, then it is enough for the child to provide help on his own. If the baby often vomits, or there are periodic temperature fluctuations, then he needs professional support.
By contacting the clinic, you will receive advice on what actions to take when a child vomits without fever and diarrhea periodically.
Main reasons
The specialist will determine what problems are causing the baby to feel sick and suffer from diarrhea without a rise in temperature. Three categories of provoking factors are classified when there are no deviations in temperature indicators:
- psychogenic;
- functional reasons (provoked by physiology);
- those caused by illness.
The gag reflex of the first category (psychogenic) is a common symptom in children over 6 years of age. Such vomiting in a child without fever can be caused by nervous disorders due to growing up.
A teenager is also capable of vomiting consumed foods due to dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract:
- acute gastroduodenitis;
- gastroesophageal reflux;
- gallbladder problems;
- acute spasm of the pylorus;
- nutritional gastritis;
- pyloric stenosis;
- intussusception;
- pancreatic pathology.
Having determined the cause, the doctor will prescribe appropriate treatment. It is important for parents not to delay the course of such a condition by contacting the clinic in a timely manner.
What to do
Dr. Komarovsky claims that there is nothing wrong with vomiting once. If your child continues to vomit or has a stomach ache, you should immediately call a pediatrician, because this may be a sign of illness. Before his arrival, make sure that the baby does not choke on the masses - turn his head to the side, lifting it 30 degrees. After the baby vomits, you should rinse your mouth with warm water, wipe your lips, corners of your mouth, and oral cavity with a cotton swab, after moistening it with water, a solution of boric acid, potassium permanganate or other disinfectant.
- Braiding hair for medium hair
- Crab stick cutlets: delicious recipes
- How to shave your bikini area without causing irritation
Drink
To prevent dehydration, give your child glucose-saline solutions (for example, Regidron), which can be given from a syringe in small portions or a teaspoon. Names of other rehydration solutions: Oralit, Trihydron and Hydrovit. The drugs are available without a prescription in Russian pharmacies. The release form is a powder that should be diluted in boiled water, after having cooled it. In the absence of special medications, give your baby plenty of liquid.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
For bowel movements caused by pyloric spasm and gallbladder diseases, physiotherapeutic treatment prescribed by a doctor is indicated. This method includes applications of paraffin and ozokerite, electrophoresis with novocaine on the epigastric region (administration of medicinal components using electric current), galvanization, Bernard currents.
What to give your child
If the cause of vomiting lies in allergens and toxic components in the body, or there are symptoms of intoxication of the body, then the child is given sorbents of natural origin, groups of carbon products or containing silicon, preparations with lumogel, made from aluminosilicate (Smecta). Children should not take medications intended for adults. The drugs are prescribed according to the age of the child and the presence of the disease. The baby will accept children's medications, suspensions and sweet syrups with joy - they are very tasty.
You can give children antiemetics (Motilak, Cerucal), medications with vitamins, except calciferol. Excessive intake of vitamin D causes vomiting. Homeopathy helps not only to stop vomiting, but also to eliminate the problem that caused it. Homeopathic medicines have no side effects and contain only natural ingredients. The following anti-vomiting agents are available:
- Phosphorus;
- Common Kokorysh;
- Arsenicum album;
- Ipecacuanha;
- Nux vomica;
- Pulsatilla;
- Tabakum;
- Veratrum album.
Folk remedies
For treatment with folk remedies, choose only remedies that will not harm the newborn: raisin or rice decoction, chamomile, mint or dill tea. One-year-old children can benefit from pear decoction, soaked rye crackers, and barley flour. To stop vomiting in a child over 3 years of age, in addition to the above, other folk remedies prepared from oak bark and gooseberries are suitable. An old remedy for vomiting is a weak solution of potassium permanganate.
Diet
Drinking plenty of fluids, proper nutrition, and a gentle diet that excludes foods that are difficult to digest will help improve your baby’s well-being and health after a painful condition. The weakened digestive tract will not be able to cope with it, and the condition will worsen. The child should avoid eating the following foods: raw vegetables, grapes, fish, meat dishes, sweets, fats, sausages, carbonated drinks. You can improve stomach function by adding the following foods to your baby’s daily diet:
- plain yoghurts;
- bananas;
- boiled carrots, broccoli;
- baked apples;
- kefir;
- a decoction made from dried fruits.
First aid
When a growing child vomits without diarrhea or a rise in temperature at all, then those around him do not always know what to do immediately. Let's take a closer look at how to help. When a baby has a sudden gag reflex, you need to make sure that he does not choke on waste food before the ambulance arrives. To do this, place his head with his cheek to the pillow, slightly lifting it. When the food comes out, you need to give the baby warm water so that he can rinse his mouth.
You should wipe your lips and entire oral cavity with a cotton pad. Such a swab should be moistened with plain water diluted with potassium permanganate or boric acid, or another disinfectant. Also, when deciding what to do immediately when a small child suddenly vomits in the complete absence of diarrhea or a jump in temperature, it is necessary to take into account that the body is dehydrated. Therefore, there is a need to give your child cool water (in tiny portions).
If the baby begins to vomit heavily, then adding a small amount of mint drops to the liquid consumed will help eliminate such discomfort. The drug Regidron will help relieve unpleasant urges and restore the acid-base balance. One packet of it should be diluted in slightly warm water (1 liter), and the child should be given a quarter glass of water every 30 minutes. If a one-year-old child vomits, he needs 2 tsp. medications at five-minute intervals. Children from one to 3 years old are allowed 3 tsp, children from 3 to 9 years old - 4 tsp.
If the sudden onset of vomiting without diarrhea in a child is one-time in nature, the child’s well-being does not worsen, it is permissible to delay calling an ambulance. But if severe symptoms appear, be sure to visit a doctor.
The child feels sick and vomits without fever
If the baby experiences nausea, but there is no temperature, this indicates the absence of infection. This may indicate problems with the central nervous system or the presence of appendicitis. Vomiting can also accompany diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. If a child has seasickness or Kinetosis, the baby may vomit.
Nausea and vomiting are natural responses of a child's body to vomiting. Vomiting can be a symptom of a fairly serious illness. Despite the fact that it is not accompanied by fever, it must be treated without fail. If your child has periodic vomiting, you should definitely seek help from a doctor.
When to call an ambulance
Often the child feels sick, but there is no diarrhea or fever due to a serious illness, which sometimes requires immediate surgery.
To call a doctor, the following conditions are necessary:
- the symptom occurs very often, practically does not stop;
- the child is unable to drink fluids due to frequent vomiting;
- the baby has a stomach ache, constipation, bloating;
- a semi-fainting state or excessive excitability develops;
- taking medications or chemical additives caused this symptom;
- attacks began to develop after a bruise of the skull, a fall from a height;
- convulsions, uncharacteristic lethargy, drowsiness or fever are present.
If vomiting is noticed in a child without fever, treatment against the background of the above-mentioned signs should be carried out professionally. With a single urge, when there is no discomfort, the baby plays, is able to drink water, the night passes peacefully - there is no need to call an ambulance. The main requirement is to definitely show him to the pediatrician the next day.
Possible complications
In addition to general stress for the body, there are 3 main complications: dehydration, weight loss, and airway obstruction. With diarrhea and profuse vomiting, rapid loss of body weight occurs due to lack of appetite, which is dangerous for low-birth-weight, premature babies. Obstruction of the respiratory tract occurs due to the entry of vomit into it. To avoid this, you need to keep the baby's head upright. Against the background of a violation of the water-salt balance, loss of mineral salts and fluids, dehydration occurs, the symptoms of which are:
- lethargy;
- dry diaper within 4 hours;
- tight, dry skin;
- there are no tears when crying;
- fast weight loss.
Diseases accompanied by no increase in temperature, vomiting
If a seemingly healthy child has vomiting or diarrhea, not accompanied by a rise in temperature, it is advisable for the child’s parents to know what to do. It is better to immediately visit a pediatrician, since such a symptom sometimes indicates the presence of a serious disease.
Similar manifestations are characteristic of the following pathologies:
- Intestinal infections: a common enterovirus, sometimes dangerous typhoid fever or other pathologies. These problems are accompanied by temperature fluctuations, but the attacks are not triggered by food. This symptom becomes an isolated case. Often diarrhea is more pronounced, the stool is of an extremely liquid consistency with mucus, foam, and an unpleasant odor. The child experiences irritability, is exhausted, and is constantly lethargic. He has no appetite and the baby rarely pees. There are signs of dehydration. Therapy is carried out in a hospital for newborns. At an older age, you can be treated at home. The patient is prescribed to take absorbent, antibacterial agents, antiviral and rehydrating drugs, and probiotics. If necessary, antipyretics are prescribed simultaneously with painkillers.
- Food poisoning. Eating spoiled or low-quality foods provokes vomiting, which occurs after meals with characteristic frequency. The stool is liquid, often streaked with blood. There is a paroxysmal pain in the peritoneum. The general condition worsens significantly. If the baby has such vomiting, he needs to be taken to the clinic. Older children can be treated at home. Gastric lavage is performed, it is recommended to take absorbent, rehydrating agents and prebiotics, drugs that relieve the inflammatory reaction and spasms. To prevent severe dehydration, a glucose-salt fluid is given. It is better to administer the products with a syringe or using a teaspoon in small portions. Powders should be diluted in cool boiled water. In a situation where there are absolutely no medications at home, you need to give the child significant amounts of water. It is not advisable to feed babies in the described situation.
- Allergies to prescribed medications, certain foods. The symptom begins immediately after a meal or therapy. Vomit contains food that has not been completely digested. Against this background, swelling, skin rashes, breathing problems, and snot appear. Health activities can be carried out at home, but it is better in a hospital, under the supervision of a doctor. The basis of therapy is antiallergic medications. Absorbents and hormones are also prescribed. When allergens become a provocateur of vomiting, and signs of intoxication are noted, the child is recommended sorbents of natural origin, medications with lumogel, a group of carbon medications, and aluminosilicate products. Therapy is prescribed according to the age of the baby and the specific diagnosis. Children accept children's medicines, sweet syrups or suspensions with joy, since they are quite tasty.
- A child can get sick with similar manifestations if there is dysbacteriosis. In this condition, the gag reflex appears extremely rarely - once a month, the stool is foamy, constipation, flatulence are also noted, a whitish coating forms on the tongue, a rash appears, and itchy skin. The therapy is allowed to be performed at home; its essence is to correct nutrition and normalize the natural microflora. Probiotics are prescribed for this purpose.
- Intussusception. This diagnosis may be accompanied by a lack of temperature rise and bilious vomiting. The pain syndrome is cramping in nature and is noted in the epigastrium. Since the child cannot help himself, he cries. The stool is jelly-like and may contain blood particles. Treatment is carried out surgically.
- Gastritis occurring in the acute phase or duodenitis. The pathologies are characterized by nausea, which is often followed by bilious vomiting. It is accompanied by bloating of the peritoneum, painful contractions and a complete lack of appetite. Wellness activities are aimed at following a diet, drinking frequently and taking prebiotics.
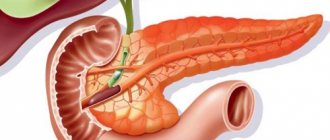
- Pathologies of the liver or pancreas. Vomiting spasms occur immediately after meals from one to several times daily. Vomit contains bile and undigested food. Associated symptoms also include: severe pain in the epigastrium, flatulence and belching. Inpatient measures are recommended using hepatoprotectors, enzyme medications, a course of painkillers, and a therapeutic diet. Drinking plenty of fluids and special, gentle nutrition can slightly improve the condition. A weakened food system is unable to cope with heavy foods, which can lead to worsening of the condition. The following foods should absolutely not be given to your baby: sweets, raw vegetables, soda, grapes, sausage, fish or meat dishes. The following will help improve the functioning of the digestive organs: baked apples, natural yoghurts, bananas, well-boiled carrots, compote with dried fruits, low-fat kefir. Physiotherapy is recommended for medical treatment. With intestinal emptying, which is associated with spasms in the pylorus, problems with the gallbladder, ozokerite applications, paraffin application, novocaine electrophoresis on the epigastrium, and galvanization help significantly.
- Diseases of the central nervous system, which include ischemia, childhood tumors, hydrocephalus, changes in intracranial pressure, are also often accompanied by vomiting. Children's behavior changes dramatically, and lethargy occurs. In newborns, bulging of the fontanelle is also observed. Recovery depends on the illness and can be carried out both at home and in a hospital setting. Therapy is based on taking medications that improve cellular nutrition. In case of tumor processes and hydrocephalus, only surgical measures are performed.
- Swallowing a foreign object into the esophagus. After this, vomiting occurs with food particles with mucus, often with blood impurities. The child is very restless and has difficulty breathing. There are two types of help: surgical intervention or observation, which involves waiting for the swallowed object to come out during bowel movement.
When a child suddenly starts vomiting, and without any rise in temperature or signs of diarrhea, then what should parents do immediately? You can offer antiemetic medications (Motilak, Cerucal), various vitamins, excluding calciferol. Abuse of vitamin D contributes to the development of vomiting attacks. It is allowed to use homeopathic remedies, since they are characterized by the absence of adverse reactions. The following substances are recommended: Nux vomica, Phosphorus, Ipecacuanha or Tabacum.
If done incorrectly, complications may occur. The child loses weight sharply, and there is a risk of damage to the digestive system. This can cause blood segments to appear in the vomit.
Causes of vomiting in babies
Doctors identify a number of reasons why a child may vomit without fever:
- Pyloric stenosis is a congenital anomaly of the development of the pylorus of the stomach. In infants, it manifests itself during the newborn period, namely at the age of 2-4 weeks. Its main symptom is vomiting, which is also described as “fountain” vomiting. The contents of the vomit are curdled milk; they do not contain any admixture of bile. The smell of vomit is sour, with an acidic reaction.
- Pylorospasm. In young children, pylorospasm is manifested by persistent regurgitation of more than 2 tablespoons, even 1-2 hours after feeding, poor weight gain, attacks of colic, and insomnia. Female representatives are more susceptible to this pathology. With pyloric spasm, children are restless, but diarrhea is extremely rare.
- Gastroesophageal reflux. The main symptom of the disease is frequent regurgitation. With reflux, anxiety, weakness, hypersalivation, hiccups, morning cough, and sometimes sudden attacks of suffocation are also observed.
- Cardiospasm. With this pathology, when food enters the esophagus, it expands, but the lower esophageal sphincter remains narrowed. In this regard, vomiting occurs. Sometimes cardiospasm is accompanied by pain in the heart area.
- Intussusception. It is observed in 80% of infants. Most often diagnosed at the age of 5-7 months. This anomaly is more often recorded in boys. The vomit contains bile impurities. Children often cry and press their legs to their tummy. In addition, anemia of the skin and mucous membranes is observed. One-year-old children may completely refuse to eat.
- Acute gastroduodenitis. The disease causes severe headaches and abdominal pain, insomnia, nausea and vomiting. Basal temperature, as a rule, remains within the physiological norm.
- Gastritis of nutritional origin. Inflammation of the stomach is accompanied by nausea, severe pain, vomiting and dry mouth, hypersalivation, belching and hiccups appear. A child often vomits without fever precisely due to alimentary gastritis. This condition is often diagnosed in children with poor nutrition, that is, they eat a lot of spicy, fried or fatty foods.
- Pancreatitis is the most common disease of the pancreatic gland in childhood. Against the background of this pathology, vomiting without diarrhea and fever may be observed. Children complain of lack of appetite and pain in the abdomen. Bile impurities may be found in the vomit.
- Cholecystitis. The presented pathology can also cause the child to vomit without diarrhea. When the disease worsens, body temperature sometimes rises to 38-39 °C. The etiology of cholecystitis may be associated with infections as well as infestations.
- Food intoxication. Vomiting due to food poisoning in children under one year of age is a fairly common occurrence, while hyperthermia, as a rule, is not observed.
- An acetonemic crisis is characterized by a violation of metabolic reactions in the body. Symptoms of the disease appear due to an increase in the number of ketone bodies (acetone, β-hydroxybutyric acid) in the baby’s body. Vomiting during a crisis is indomitable and repeated. Along with vomiting, signs of dehydration and intoxication are also observed.
Regurgitation in infants is a physiological process
Note. If a baby refuses to eat in the morning and complains of headache and nausea, this may indicate increased intracranial pressure. If you have such a problem, you should consult a neurologist. He will tell you how to treat this pathology.
Diseases that provoke vomiting without temperature changes in infants
Among infants, the described symptom can cause certain pathologies:
- Gastroesophageal reflux. This pathology is characterized by the fact that there is little vomiting. They have a sour smell. Release is observed immediately after feeding, the baby is worried and has hiccups. Hypersalvation is noted. Health activities are allowed to be carried out at home. Medicines that suppress the production of hydrochloric acid by the stomach, as well as antacids, are recommended. The frequency and dose of milk should also be adjusted.
- Pyloric stenosis. With this diagnosis, vomiting is abundant and uniform, occurring in a stream half an hour after feeding the newborn. The symptom appears on the 2nd–3rd day of the baby’s birth. The baby quickly loses weight and has seizures due to dehydration. Treatment is urgent and surgical only.
- Pylorospasm. Infants do not experience very abundant emissions. Conservative treatment can be carried out at home. The newborn is prescribed fractional feeding in small portions and warm compresses on the abdominal area. If there is no result, urgent surgery is required.
- Sometimes a congenital pathology is observed - esophageal diverticulum. Then the baby experiences scanty vomiting of mixture or digested milk. The pathology is dangerous due to complications such as weight loss. Requires hospitalization and surgery.
The child has nausea and diarrhea
The simultaneous presence of nausea and diarrhea in a child may indicate the presence of various ailments. If a child is nauseous and has diarrhea at the age of two or seven years, this may indicate that his body is reacting to teething. Also, if these symptoms are present, parents need to remember what foods they consumed. This is explained by the fact that nausea in a child may be accompanied by diarrhea in the presence of food poisoning.
It is important to know! Nausea, which is accompanied by diarrhea, indicates that the baby has problems with the gastrointestinal tract. In this case, these symptoms can appear in a child separately from each other or collectively.
Before providing first aid to the baby, parents need to determine what factors caused the disease. If vomiting and diarrhea in a child is accompanied by fever, nausea, and pain in the abdominal area, this may indicate the presence of intestinal infections. Treatment of this disease requires drinking large amounts of water. This process also requires replenishing electrolytes and salts that have been lost by the body.
During the treatment period, the child must be put on a special diet. The intake and types of products are determined by the doctor depending on the course of the disease and the individual characteristics of the patient. If there are intestinal infections, the baby will experience dehydration. If the amount of fluid lost is not managed in a timely manner, it can lead to death. That is why in this case the child is not treated independently.
If the baby has nausea and diarrhea, parents need to call an ambulance, whose doctor can adjust his treatment.
What are the best ways to quickly remove lice from a child? What to do if your child’s stool turns white? Read in this article.
A child has a runny nose - how to quickly cure it? Read the link https://klubmama.ru/zdorove/detskie-bolezni/nasmork-u-rebenka.html
Causes of vomiting when treatment is not required
Among infants, food expulsion is a common occurrence. Even healthy babies may experience regurgitation, more than once during the day. Parents need to watch what their newborn vomits.
By water
As soon as the child has vomited, it is necessary to drink him, giving small portions of water, since a large volume of liquid will cause a new release. Then the vomiting attack will happen again. The release of particles of absorbed food along with a watery mass is evidence that the symptom is caused by taking medications that are not suitable for the baby.
Their ingredients have a negative effect on the gastric mucosa, severely irritating it. Also, vomiting water can be caused by rotavirus infection, which at the same time provokes stomach upset.
Slime
If the vomit contains mucus, there is likely an infection of the intestines or a pathology of the nerve system. Sometimes this condition is caused by surgery. If there is repeated release of gastric contents with mucus, and there are no other signs of intoxication, be sure to visit the clinic to get tested.
For newborns, this condition is typical when overfed. When mucus penetrates the bronchi, the baby begins to become very worried due to breathing problems.
Night release
A single release of gastric contents at night provokes a poor microclimate, accumulation of air in the stomach, a lot of food eaten, an uncomfortable position, and fear. This situation does not require therapy. It is worse when gagging causes suffocation. To prevent dangerous pathologies, hygiene rules must be observed.
Often, children's vomiting occurs completely without a jump in temperature and does not require any treatment.
It is only necessary to eliminate the provoking factor:
- Teething. This event causes mild vomiting, which does not impair appetite or cause weight loss. Its cause is swallowing air, feeding sessions at the time of pain. To eliminate this symptom, you need to use pain-relieving gels, teethers, and massage the gums.
- Lure. When introducing complementary foods, one-time vomiting is caused by a lack of enzymes and the body’s rejection of the product. You should temporarily stop feeding such food.
- Psychogenic factor. It can develop during strong experiences, stress, and become a reaction to reluctance to eat certain foods. You need to eliminate any stressful situation, and when this does not help, visit a psychologist.
- Climate change. When the baby adapts to new realities, the following symptom becomes a reaction.
- Indigestion. The problem causes frustration and vomiting. It is necessary to review the diet and offer the baby to drink more.
Prohibited events
Often unexpectedly detected by parents, vomiting in a child without fever or diarrhea baffles them.
It is prohibited to carry out the following procedures yourself:
- rinse the stomach when the baby is unconscious;
- give the child any antiemetic or antispasmodic drugs;
- use antiseptics to cleanse the stomach;
- introduce antibacterial agents into treatment;
- ignore visiting the pediatrician again after you feel better and symptoms disappear.
What to give when vomiting without fever
Before using medications to eliminate vomiting, the etiology of this condition must be established. This will require consultation with a doctor.
Rash and fever in a child
The most popular medications for vomiting are sorbents. They adsorb toxic substances on their surface, so they are most often used for poisoning and intestinal infections. These medications can be used to treat children of all ages.
To eliminate vomiting, the following medications are usually used:
- Activated carbon;
- Dramamine;
- Smecta;
- Cerucal;
- White coal;
- Zofran;
- Motilium;
- Metoclopramide;
- Enterosgel;
- Polyphepan;
- Polysorb;
- Riabal;
- Atoxyl;
- Filtrum;
- Bromopride;
- Enterodesis.
Note. There is a wide selection of antiemetics available on the pharmaceutical market. Each of them has its own contraindications, so in order not to harm your child, you should not self-medicate, it is better to trust your pediatrician.
There is no need to force feed your baby after vomiting.